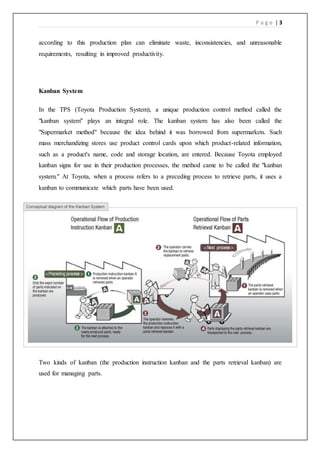
The document discusses the Toyota Production System (TPS), a lean manufacturing framework focused on efficiency, waste reduction, and high-quality vehicle production. It highlights key pillars such as just-in-time manufacturing, standardization, and kaizen, while also addressing the system's advantages and disadvantages, including implementation challenges and potential supply chain risks. Ultimately, TPS is crucial to Toyota's success and is recognized for its innovative approach to production and workforce engagement.