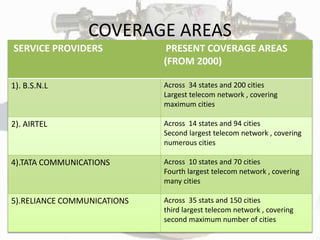
The document discusses landline telephones, covering their history, technology, advantages, and disadvantages compared to cell phones. It details the evolution from early telephony by Alexander Graham Bell to the decline of landlines with the rise of digital and cellular networks. Additionally, it provides insights into major service providers, comparison of tariff plans, and value-added services in the telecommunications industry.