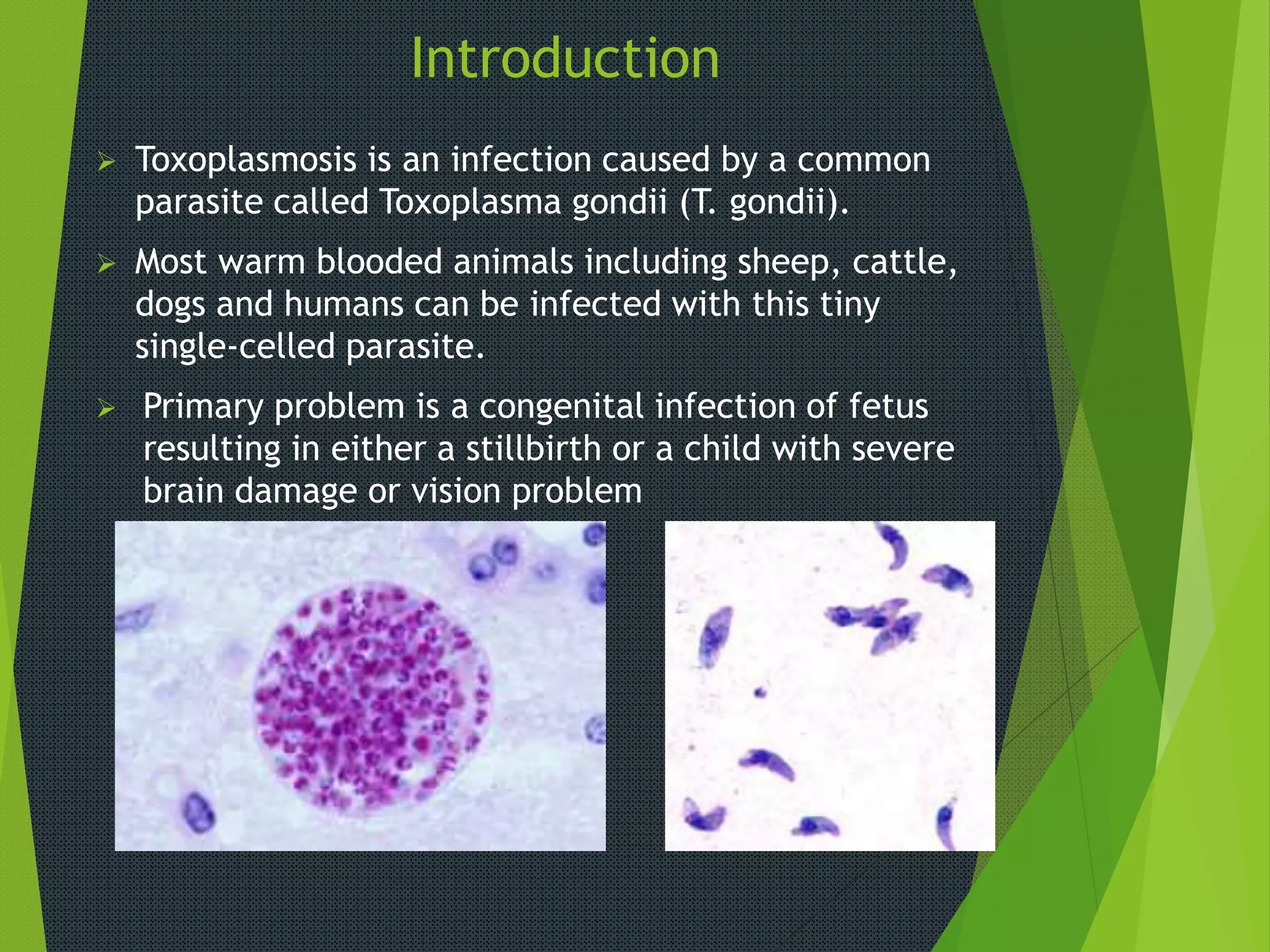
Toxoplasmosis is caused by the parasite Toxoplasma gondii, which can infect humans and warm-blooded animals. Primary risks are congenital infection of fetuses, which can cause stillbirth or brain/vision damage in children. Symptoms may include flu-like symptoms or organ problems in those with weak immune systems. Transmission occurs through undercooked meat, cat feces, and mother-to-child. Treatment focuses on medications for those with weak immune systems.