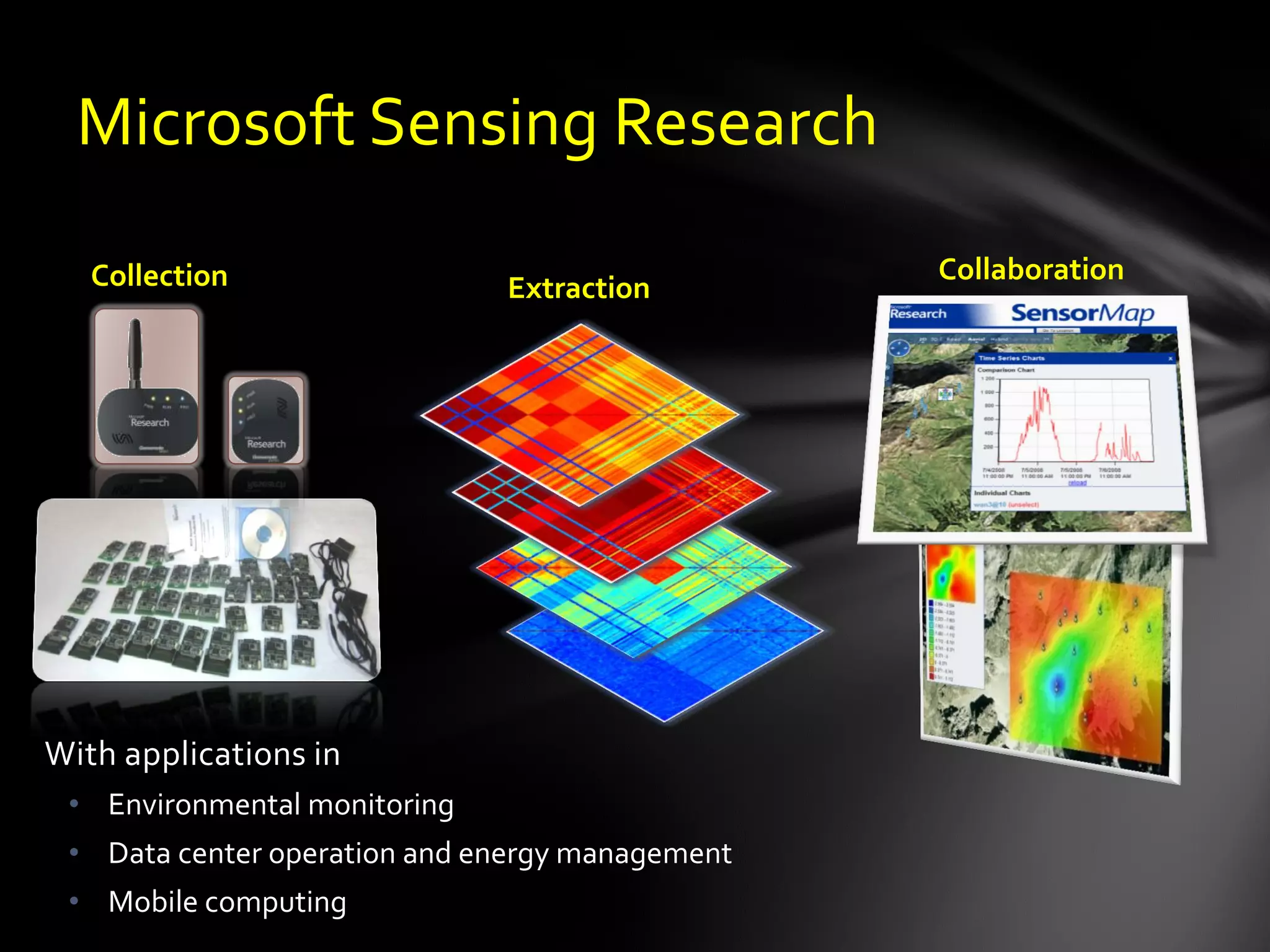
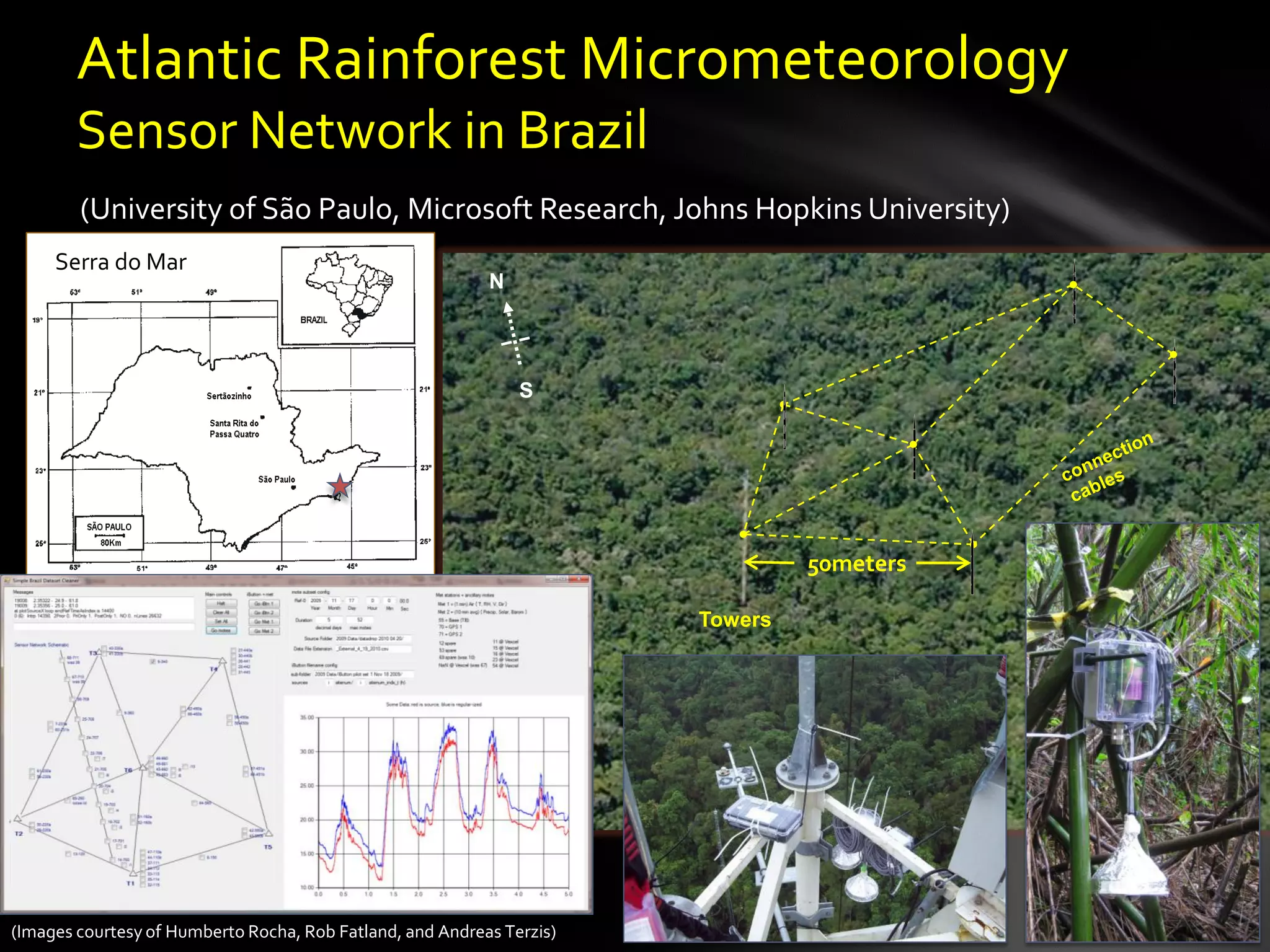
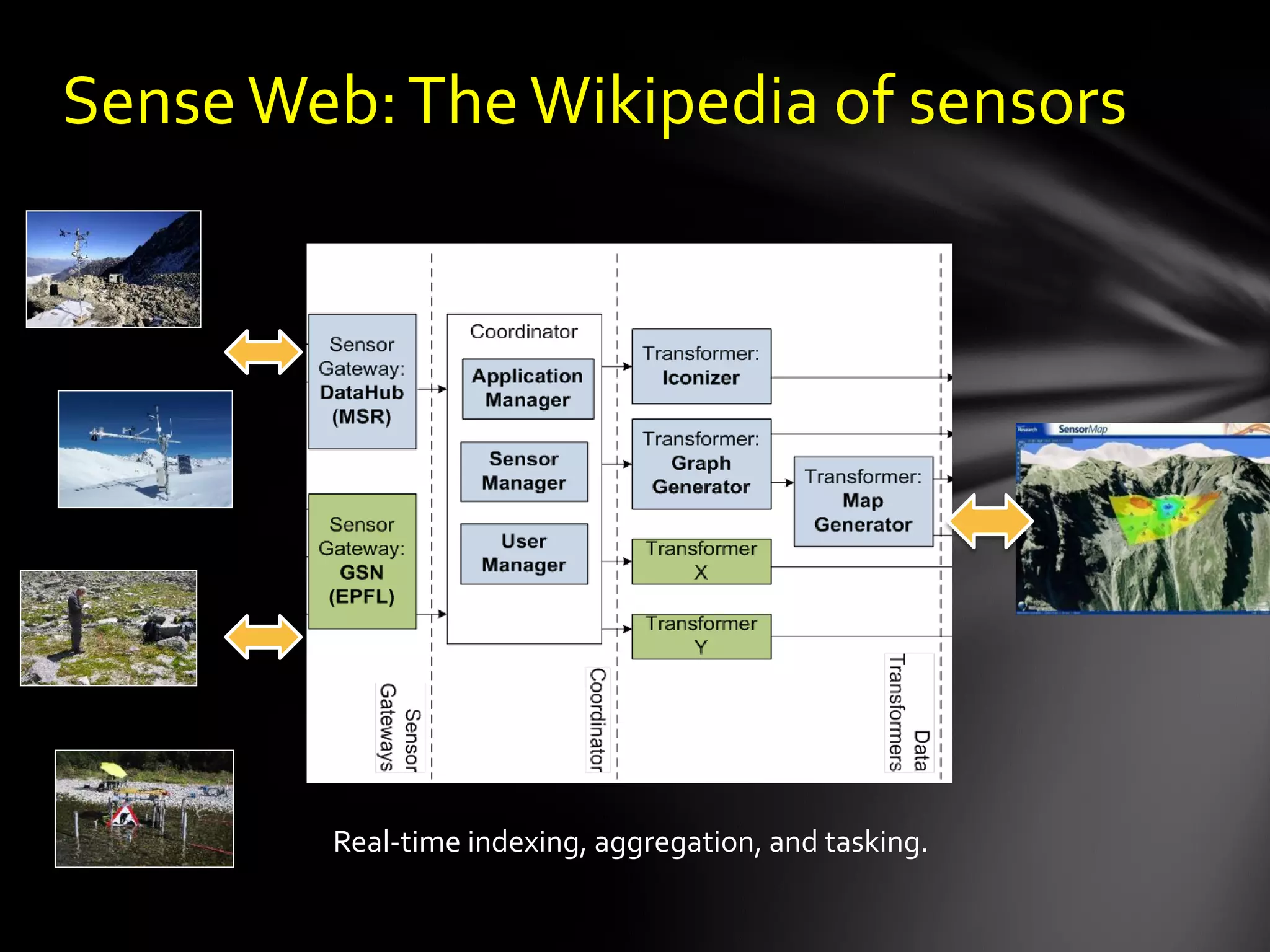
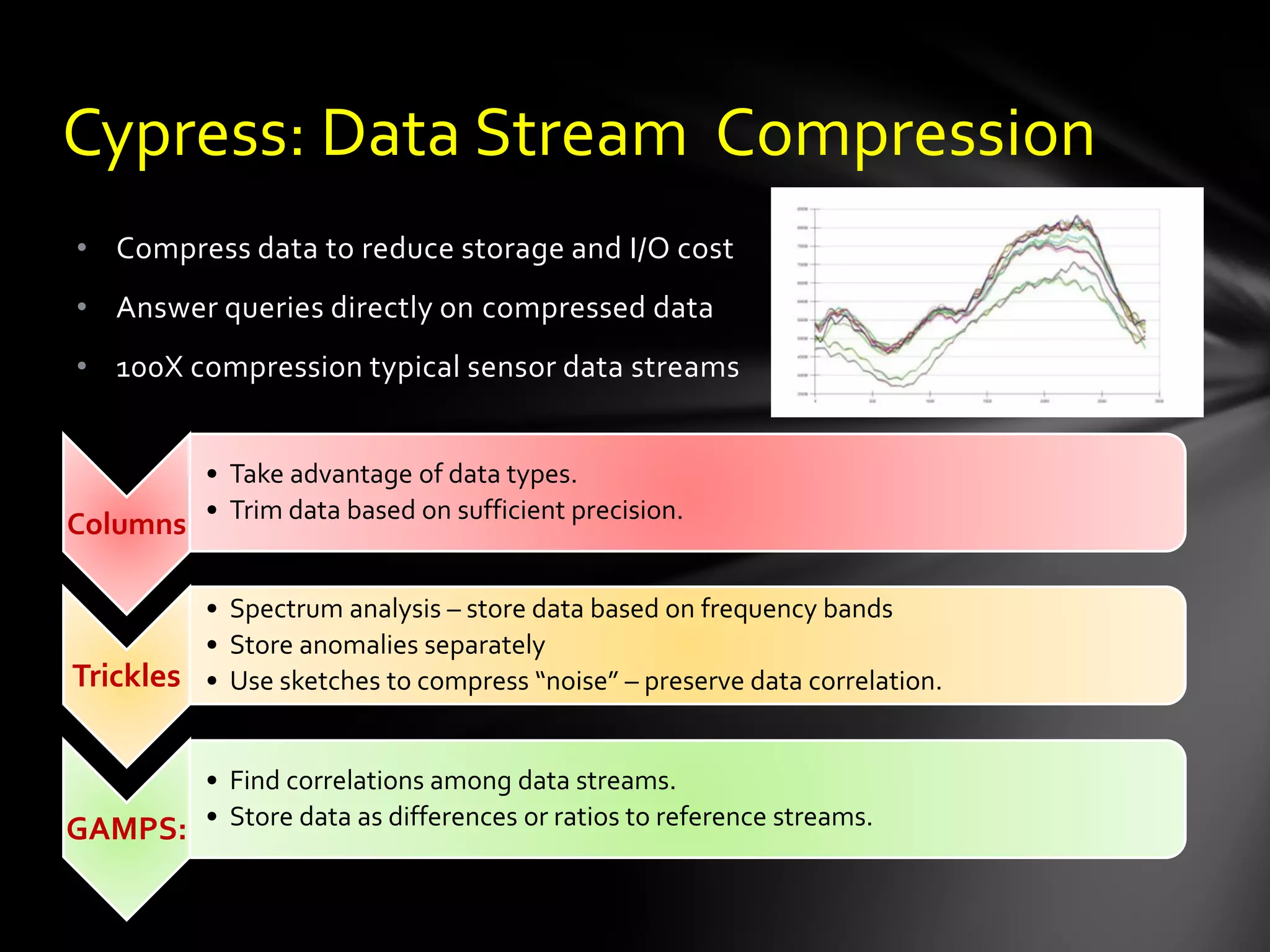
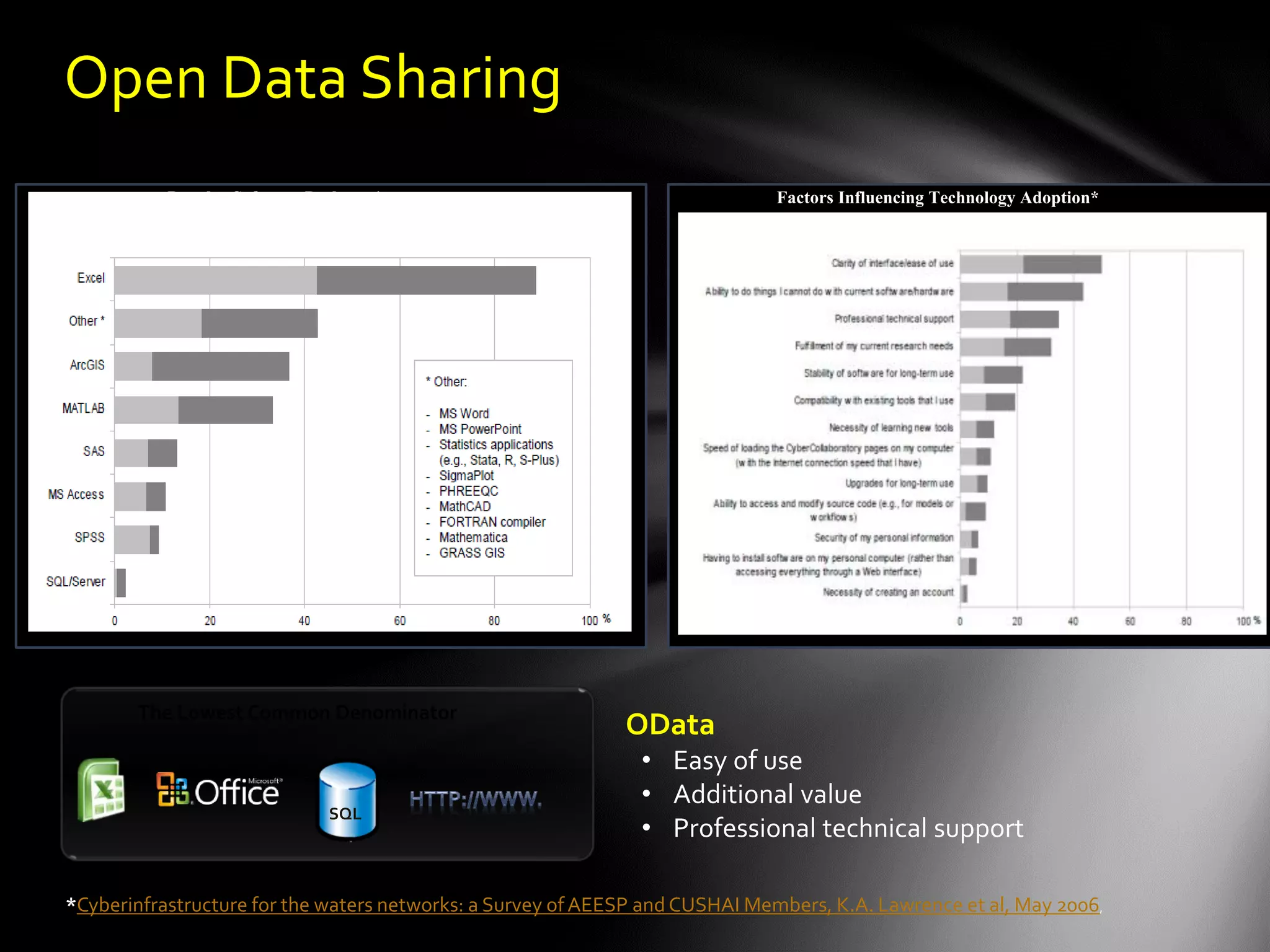
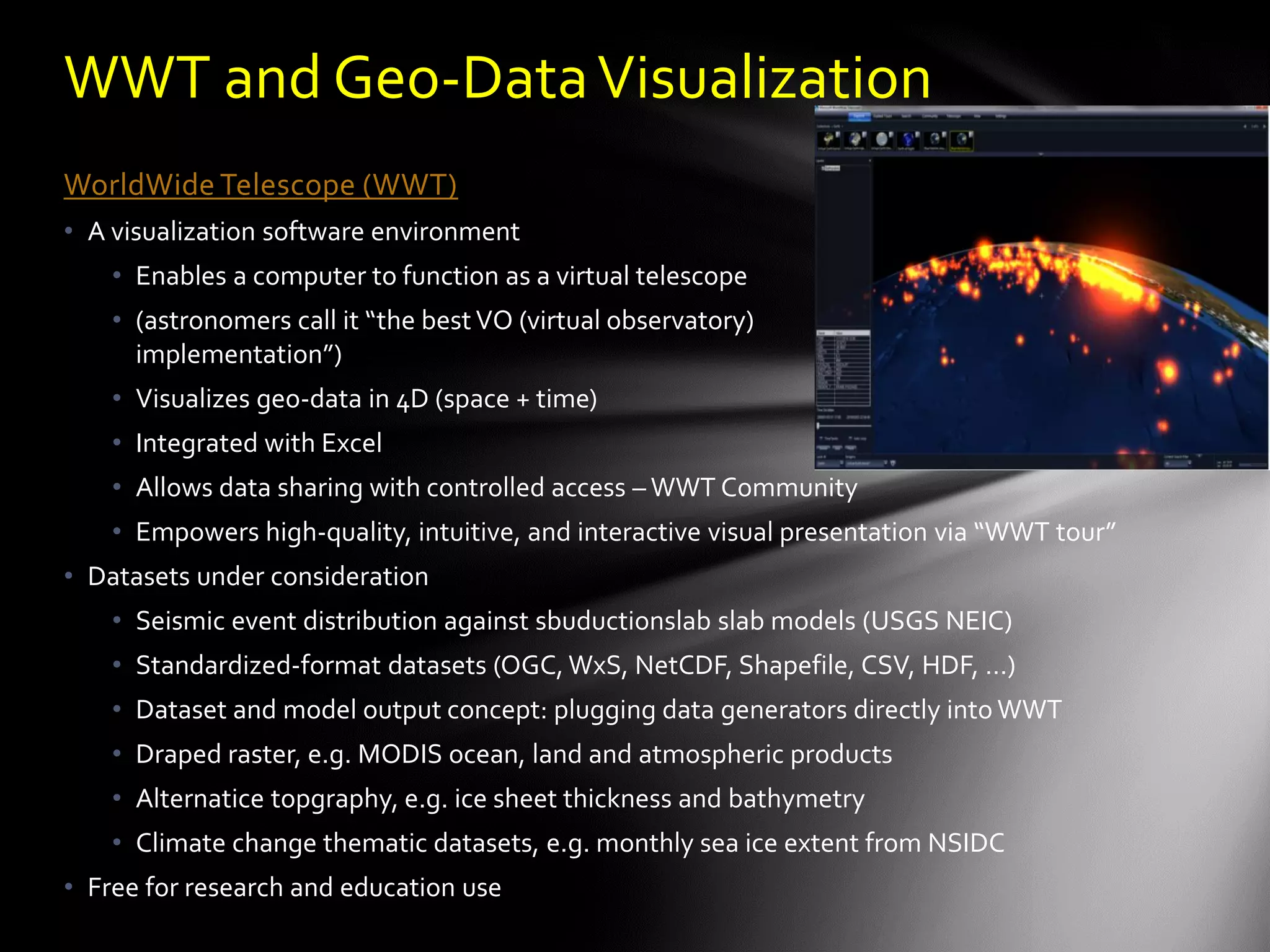
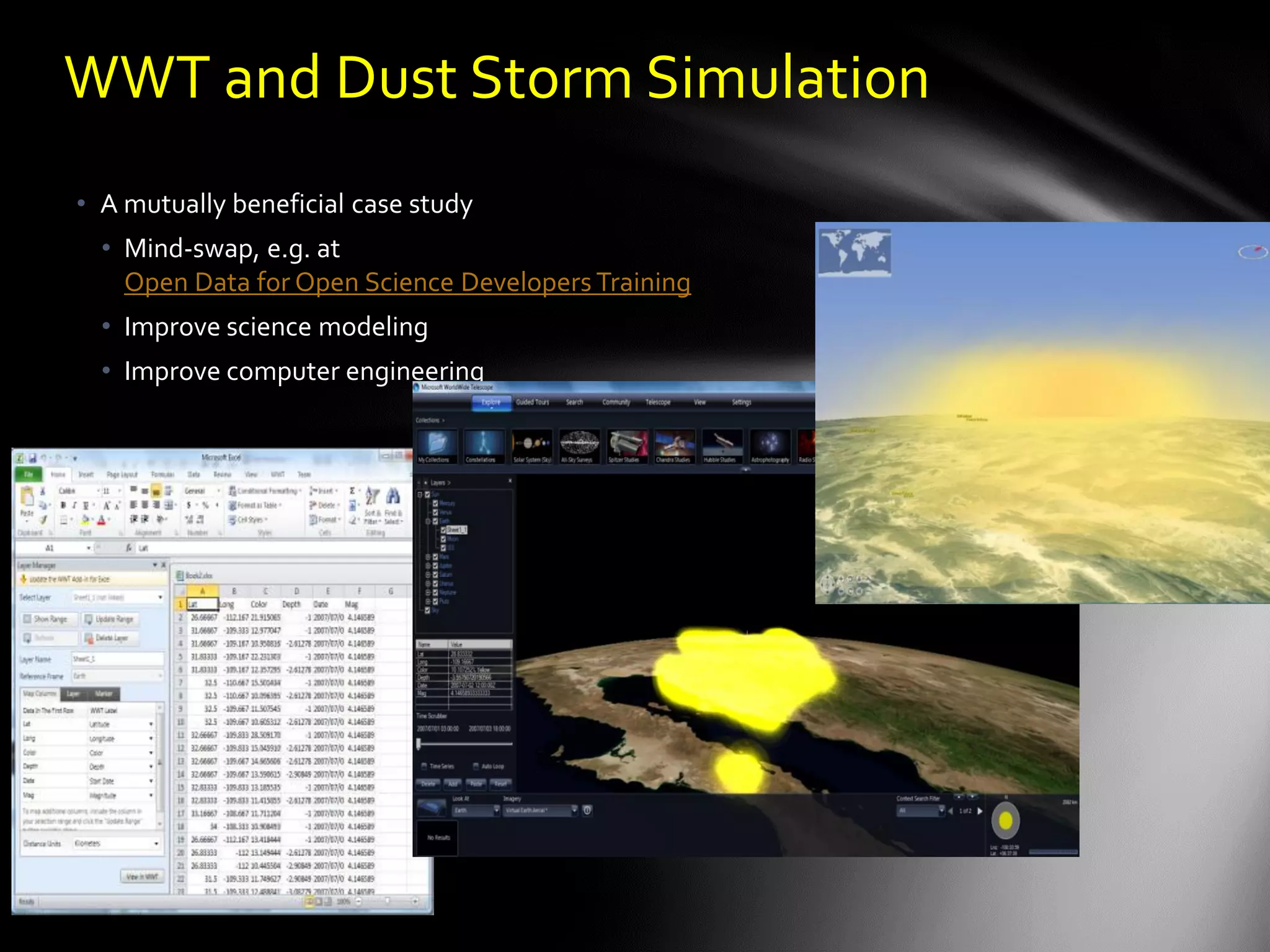
The document discusses the vision of creating a 'Wikipedia of Sensors' for environmental monitoring that includes a toolkit for participatory monitoring and data sharing using Microsoft technologies. It outlines key challenges and necessary technologies for sensor data management and emphasizes the importance of making environmental data discoverable and accessible for research and citizen science. The initiative focuses on fostering collaboration among various disciplines to enhance environmental research and improve data interoperability.