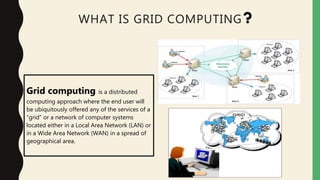
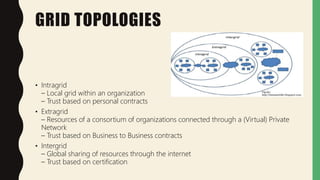
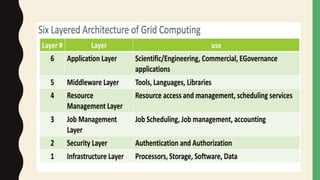
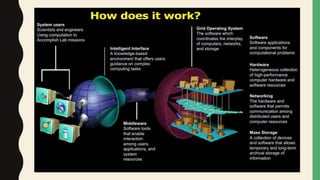
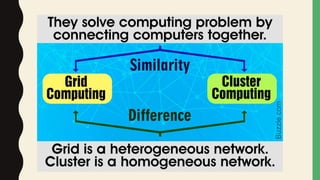
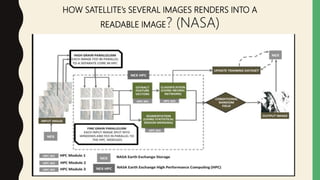
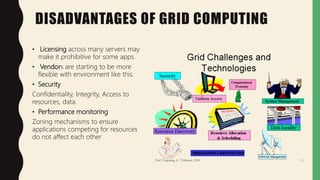
Grid computing is a distributed computing approach that allows users to access networked computer systems and resources located across different areas. It provides computing resources like processors, storage, and applications to users regardless of where those resources are located, similar to how the electrical power grid provides electricity to users without knowledge of its source. Key benefits of grid computing include solving large-scale problems through parallel processing and optimally utilizing idle computing resources. Security, licensing, and performance monitoring present challenges to grid computing's adoption.