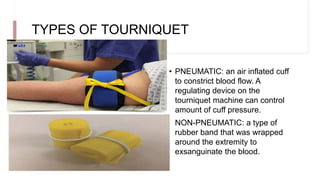
Tourniquets are devices used to control blood flow to an extremity during surgery. They promote optimal surgical conditions by creating a bloodless field. There are pneumatic tourniquets, which use an inflatable cuff, and non-pneumatic types that use rubber bands. Proper tourniquet use includes exsanguinating the limb, applying the appropriate pressure for the patient and limb size, and limiting the duration of inflation to under 3 hours. Complications can include nerve injury, muscle damage, and post-tourniquet syndrome if not used correctly. Antibiotics are recommended after inflation to prevent surgical site infections.