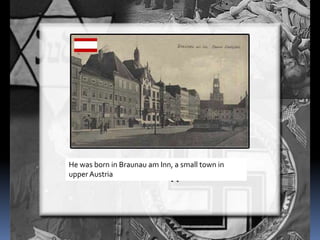
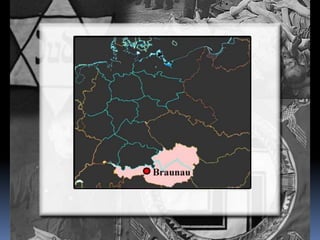
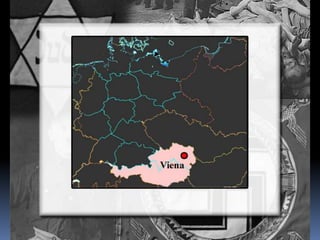
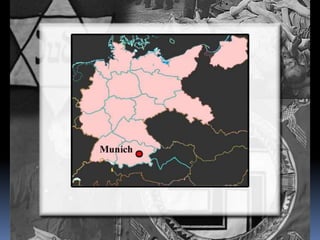
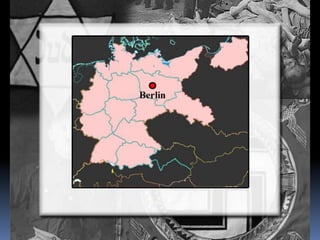
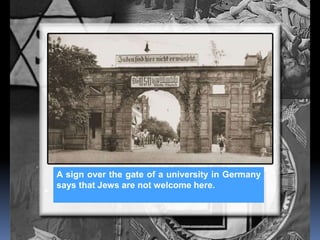
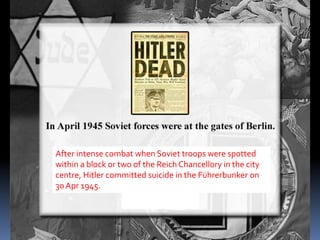
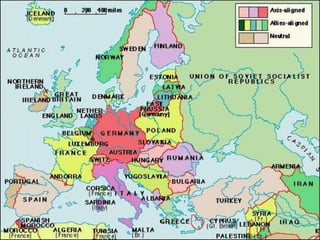
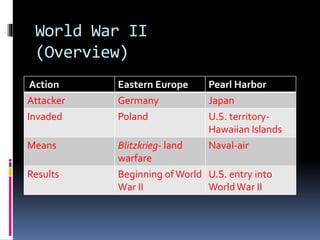
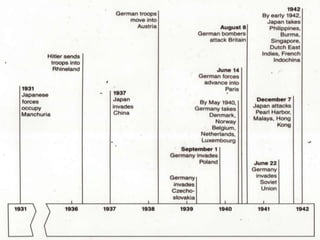
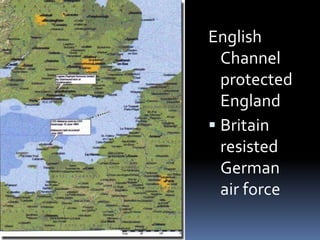
Hitler began rearming Germany in violation of the Treaty of Versailles, and the European democracies pursued a policy of appeasement by allowing Germany to remilitarize and annex Austria and the Sudetenland region of Czechoslovakia without resistance in hopes of avoiding war. The Munich Agreement of 1938 saw Britain and France agree to Hitler's demands for the Sudetenland despite Czechoslovakia being a democratic ally, setting the stage for Germany's further expansion.











![Treaty of Versailles – end of WWI
The main points of
the Treaty [BRAT]
1. Germany had
to accept the
Blame for
starting the war
2. Germany paid
extremely high
Reparations for
the damage done
during the war.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation13-150128065718-conversion-gate02/85/Presentation13-15-320.jpg)