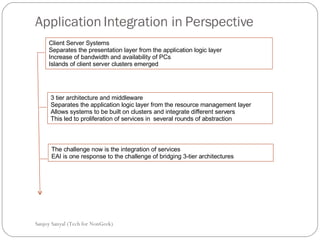
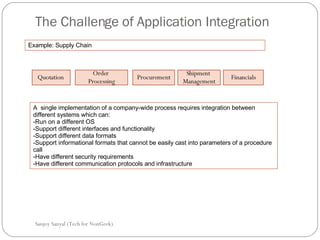
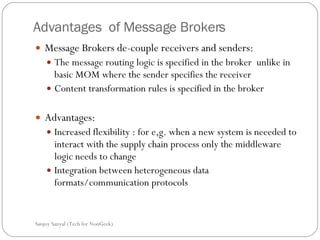
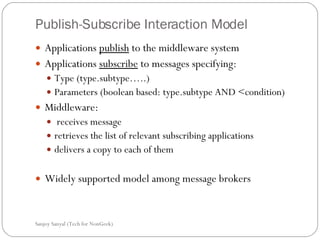
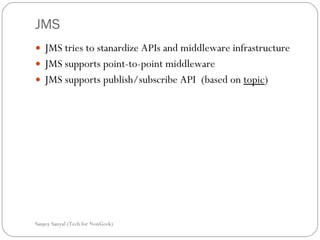
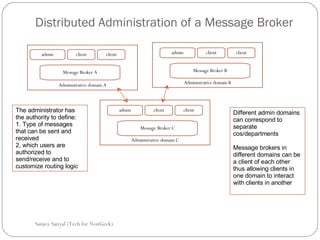
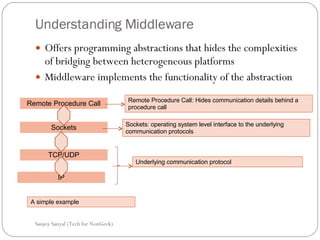
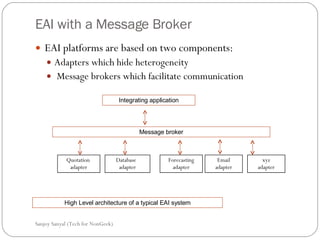
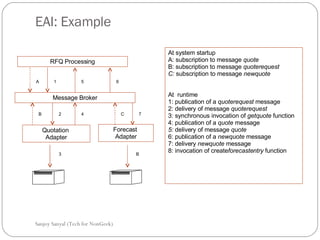
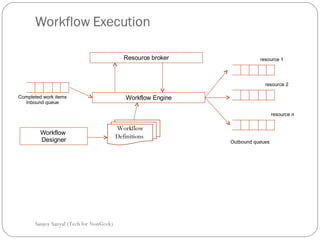
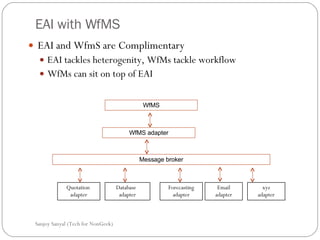
This document discusses enterprise application integration (EAI) and the role of message brokers. It notes that EAI is needed to integrate coarse-grained, heterogeneous applications and platforms. Message brokers provide adapters to access different systems and filter/route messages between applications. They allow for loose coupling and flexibility when new systems need to be integrated. While EAI platforms can be expensive to implement, message brokers play an important role in enabling integration between disparate enterprise applications and systems.