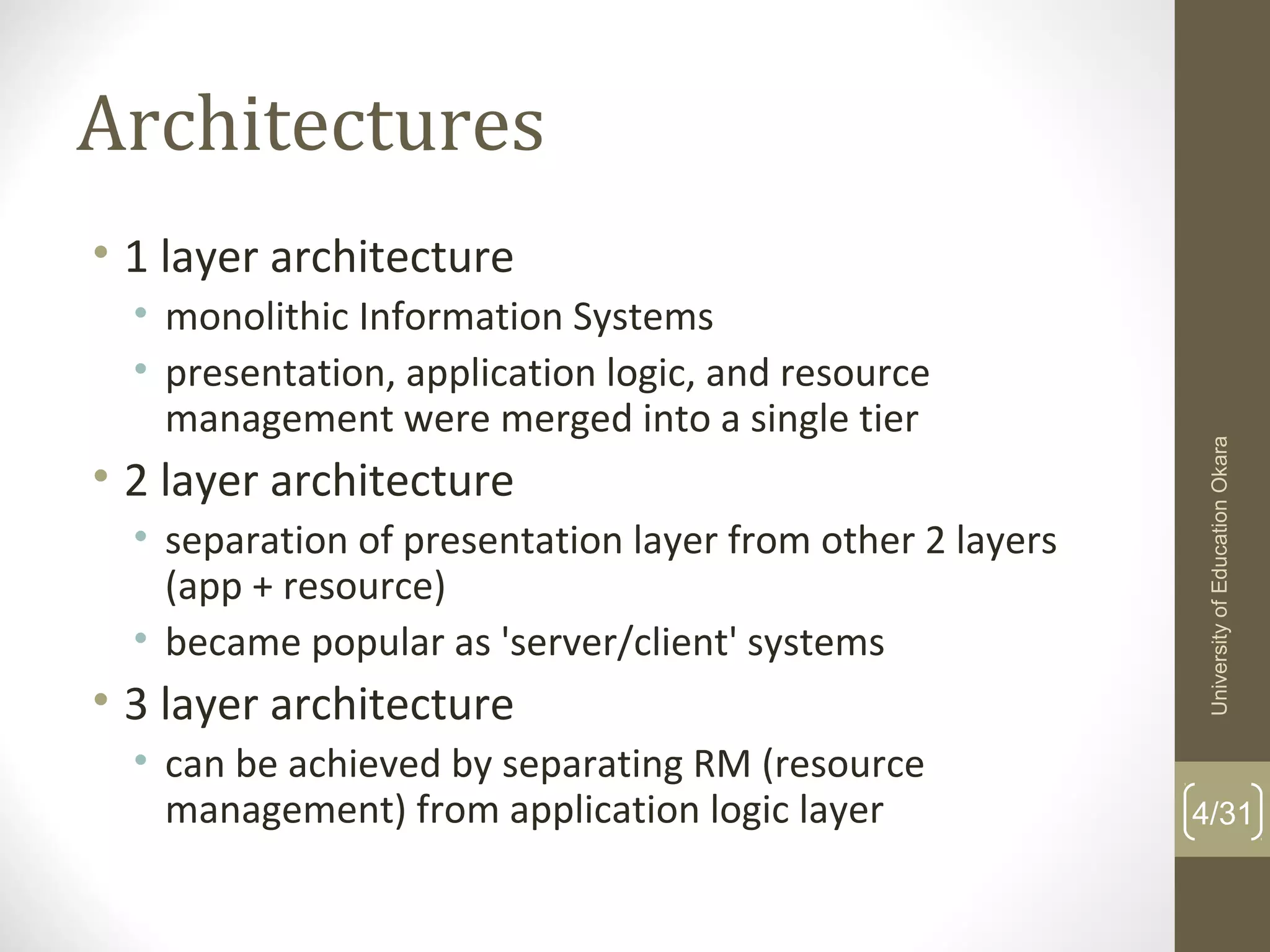
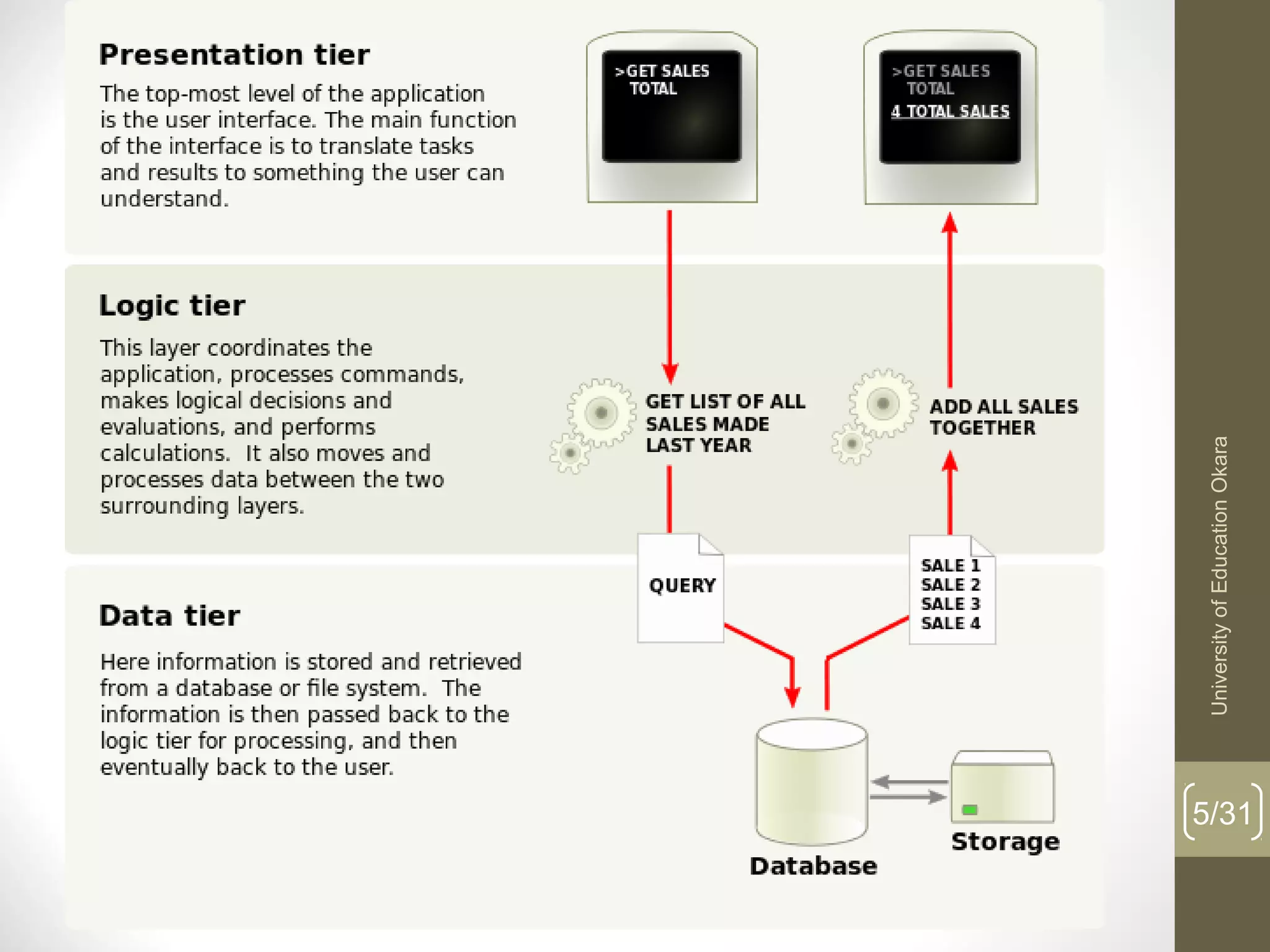
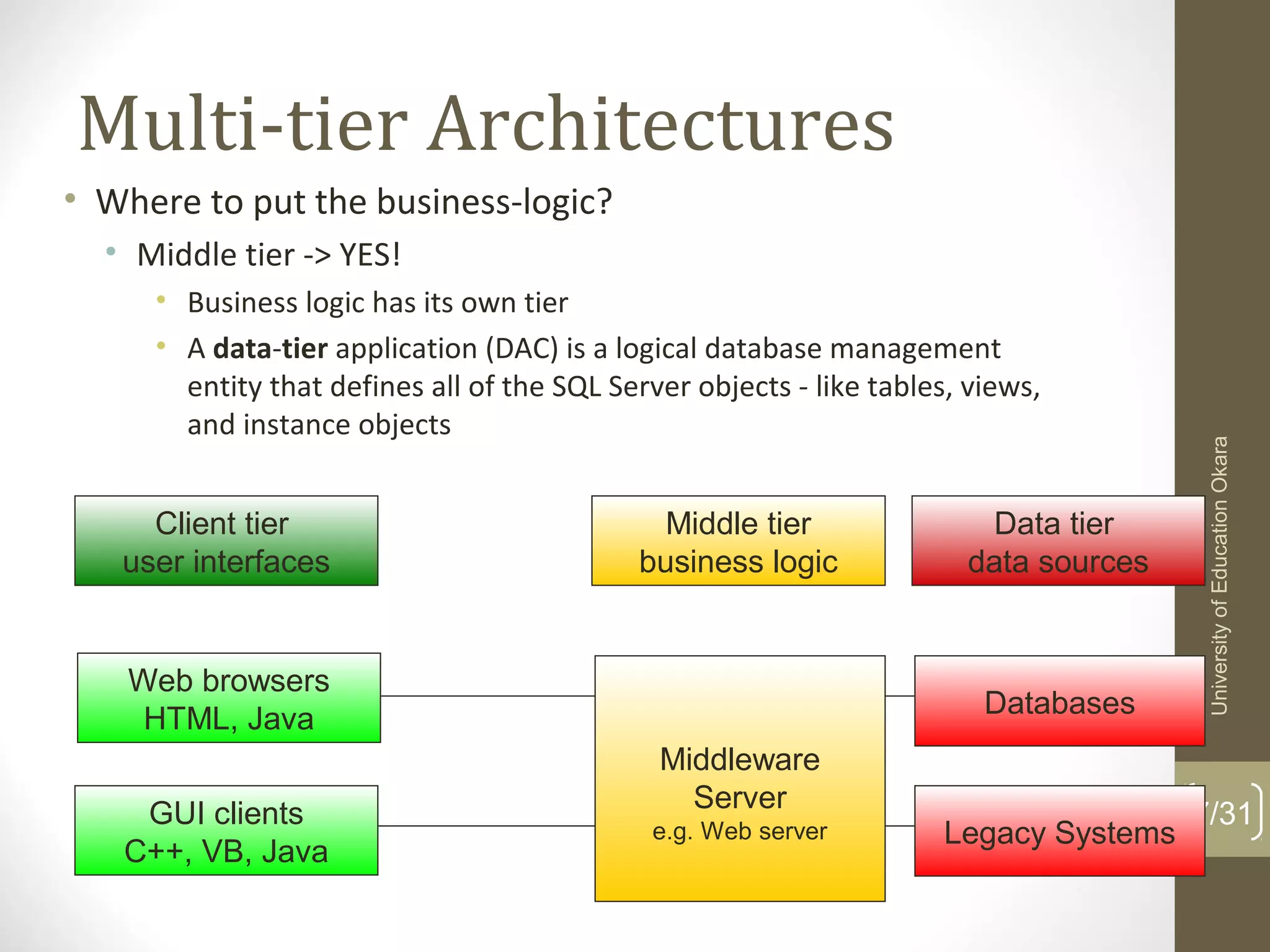
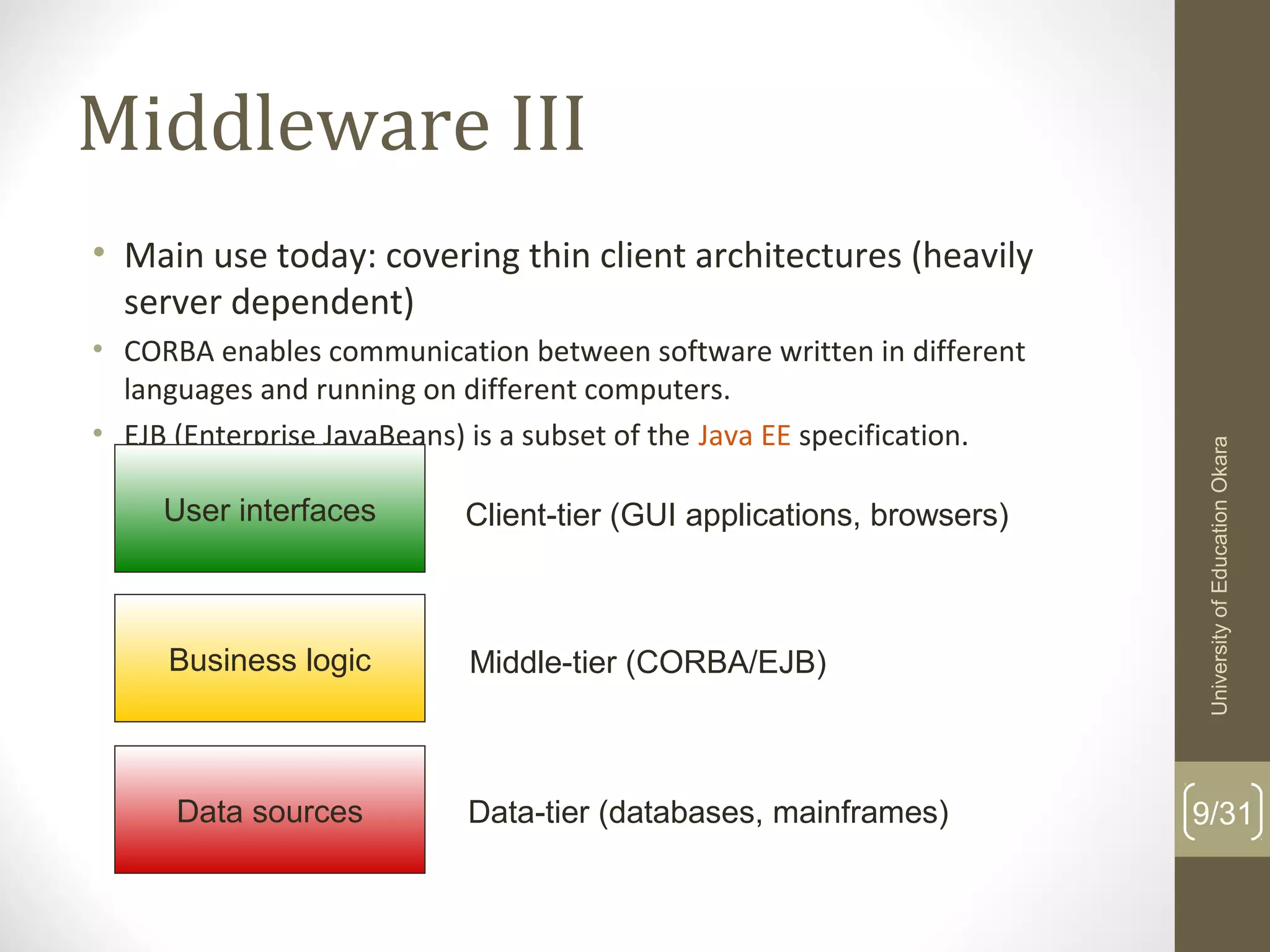
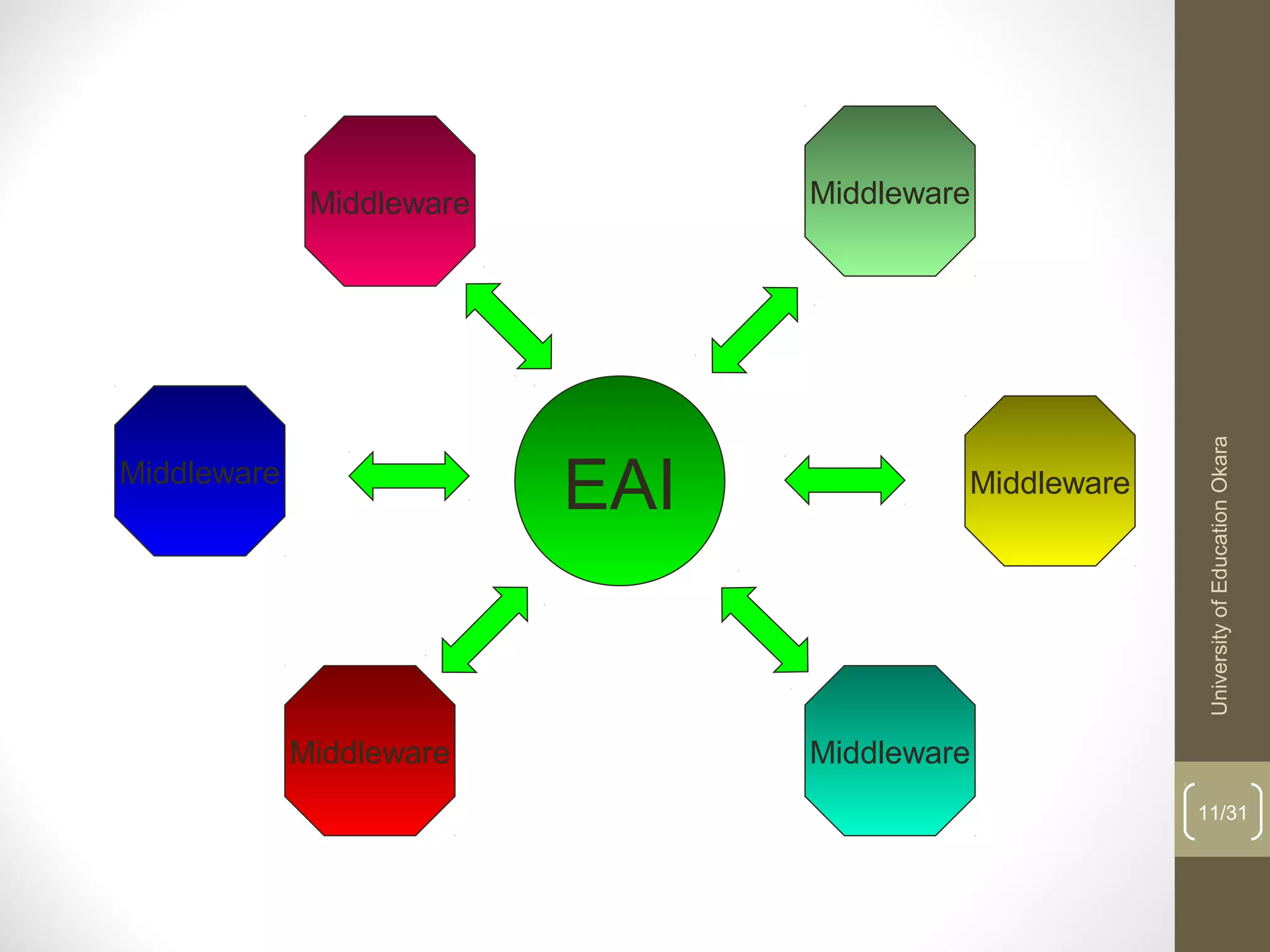
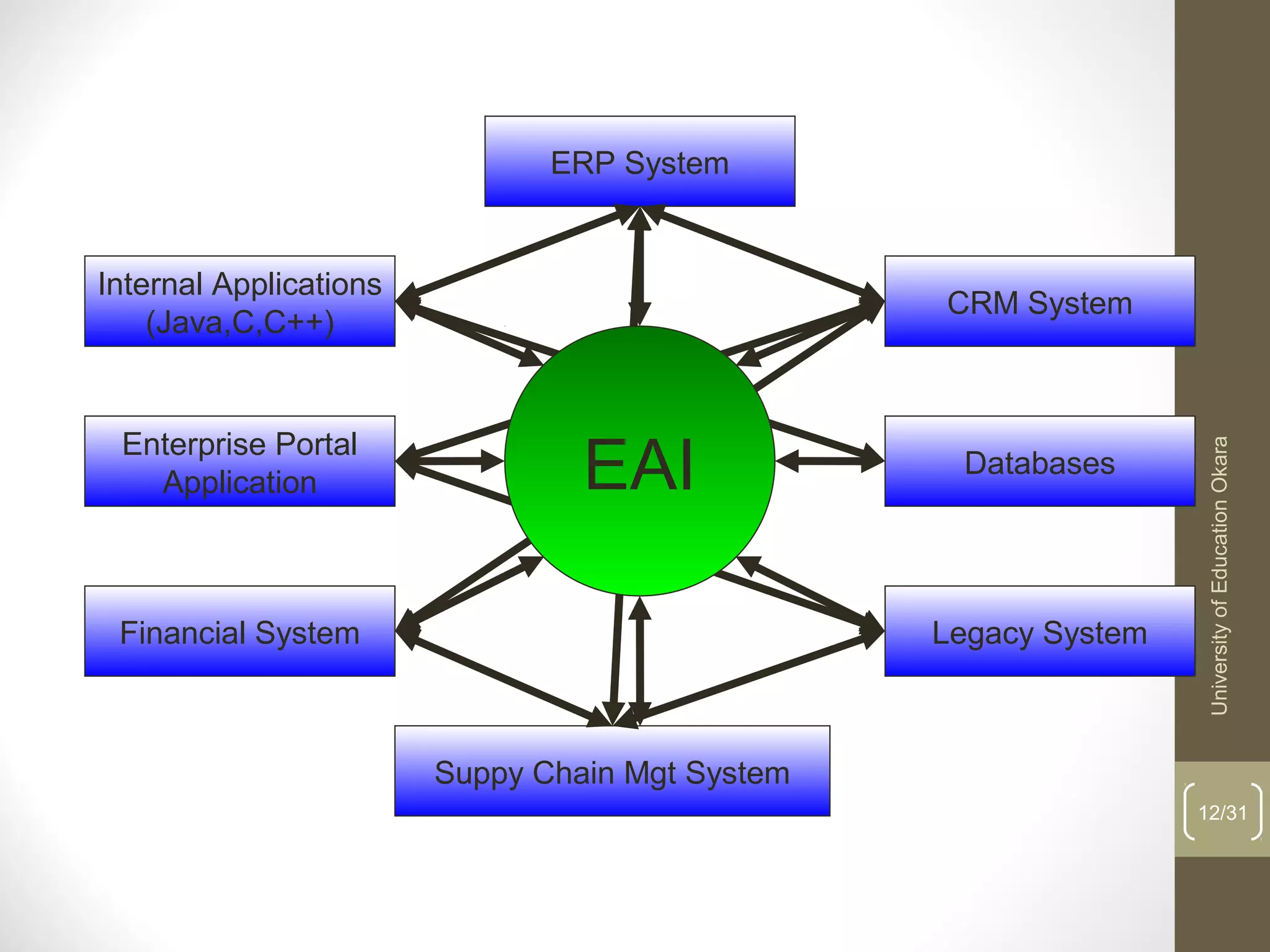
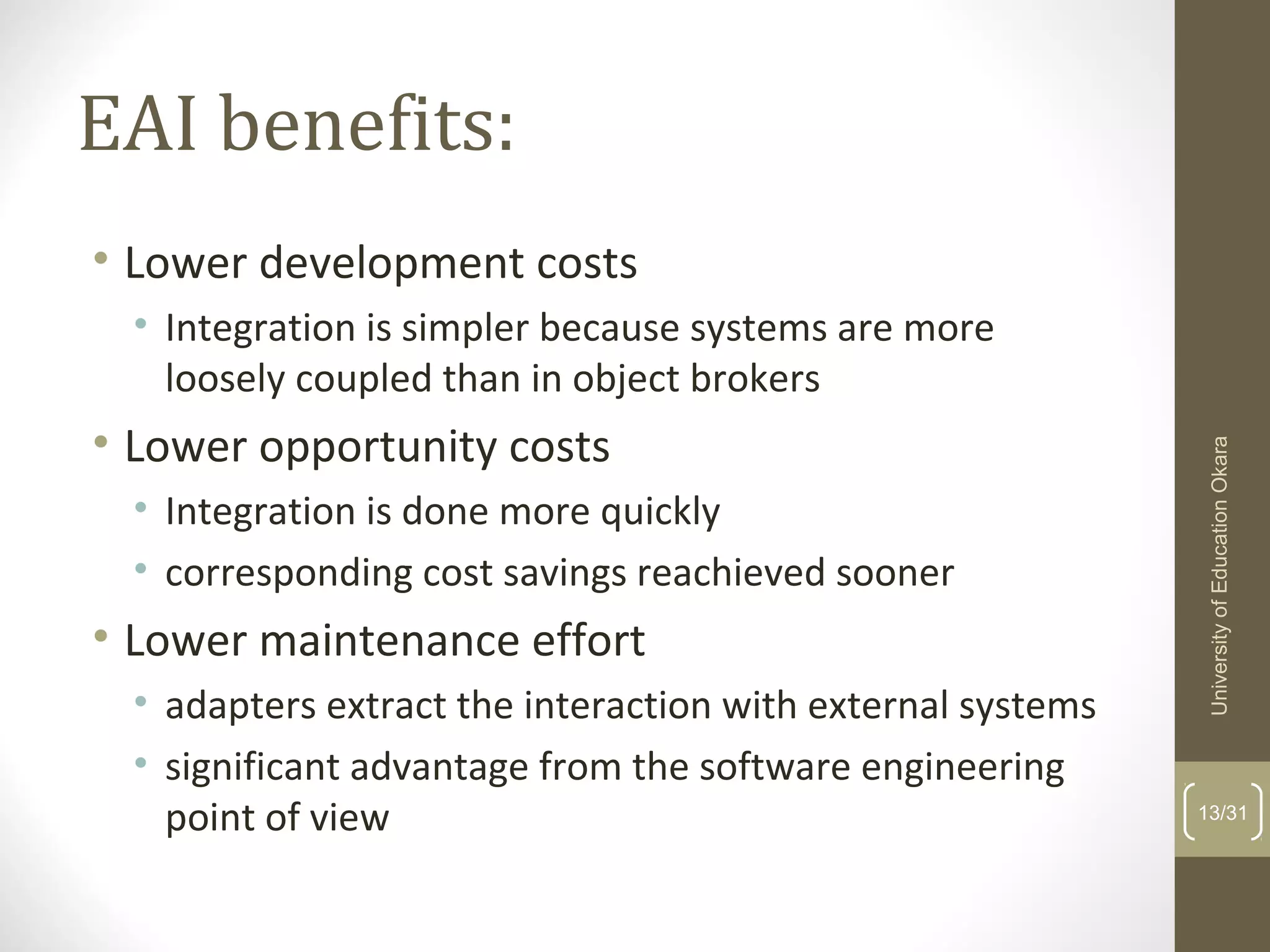
This document discusses enterprise application integration (EAI). It defines EAI as the unrestricted sharing of data and business processes among any connected applications and data sources in the enterprise. The document outlines EAI architectures including 1 layer, 2 layer, 3 layer and multi-tier architectures. It describes middleware and how it allows communication across different platforms. Benefits of EAI include lower development costs, integration and opportunity costs as well as lower maintenance efforts.