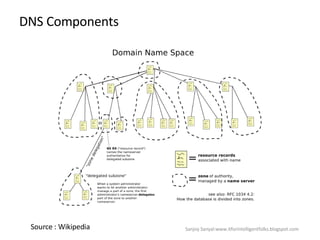
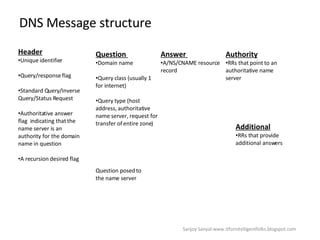
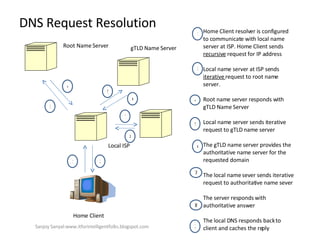
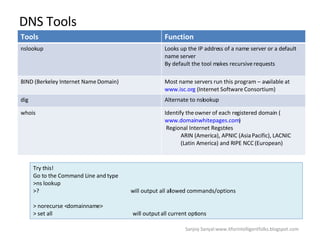
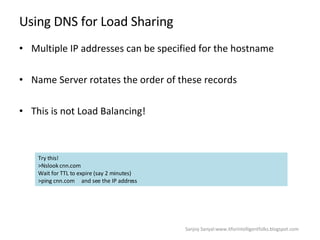
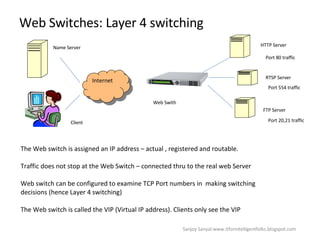
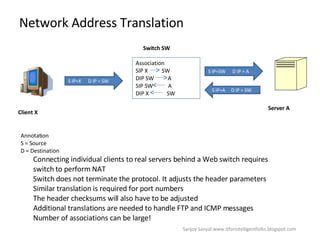
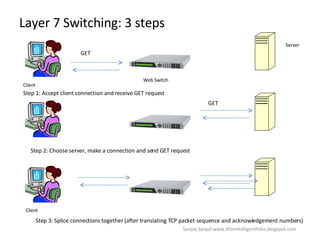
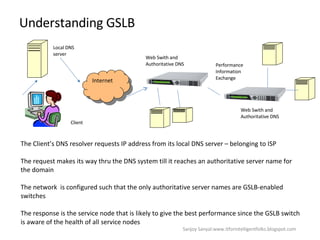
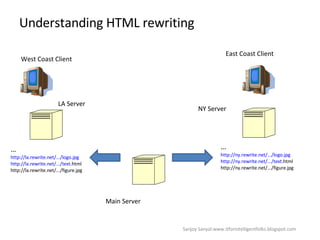
The document discusses content network navigation and DNS. It defines navigation, switching, routing and explains how DNS translates hostnames to IP addresses. It describes the components of DNS including the domain name space, name servers, resource records, and resolvers. It explains DNS requests, resolution process and tools like nslookup. It also summarizes load balancing techniques for switches including policies for best available server, persistence and differentiated services.