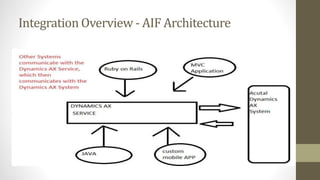
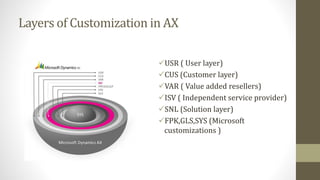
The document outlines the Application Integration Framework (AIF) in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012, explaining its architecture, document exchange methods (synchronous and asynchronous), and types of services (document, custom, and system services). AIF facilitates data integration between AX 2012 and other systems using XML documents and includes capabilities for managing integration ports. The document also includes instructions for lab sessions on creating and consuming services within AX 2012.