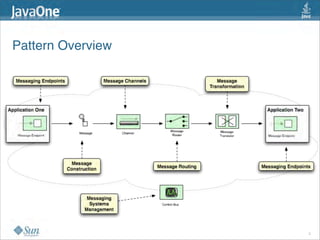
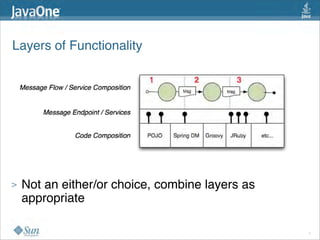
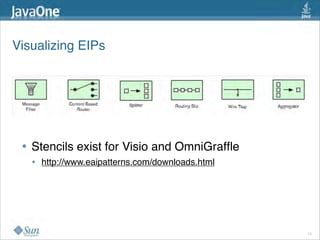
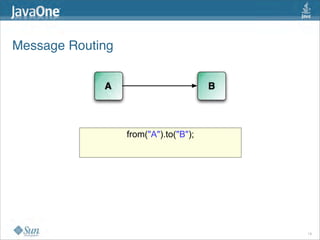
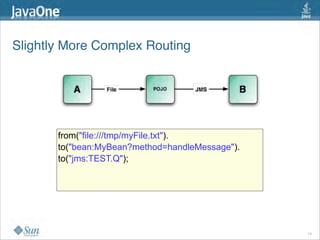
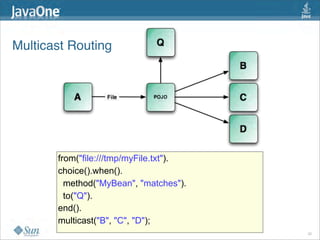
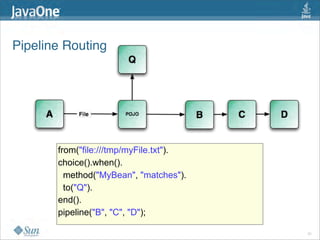
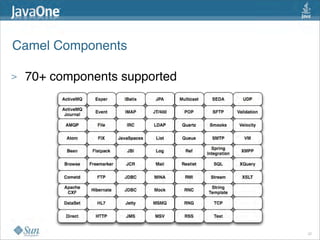
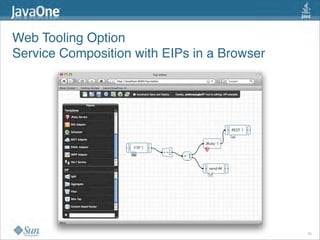
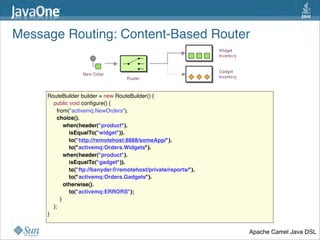
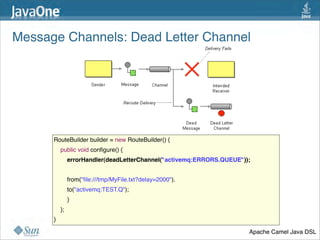
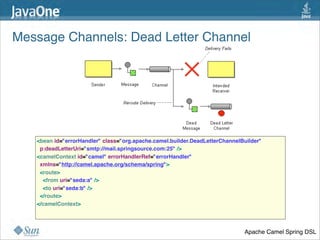
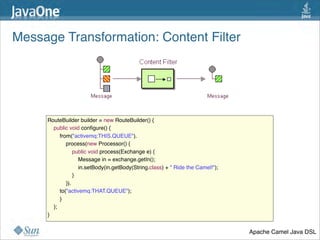
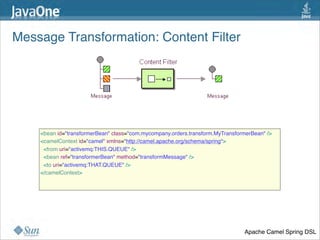
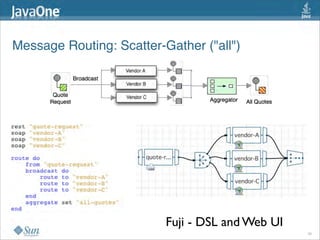
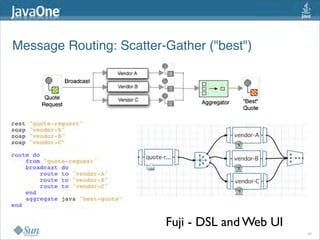
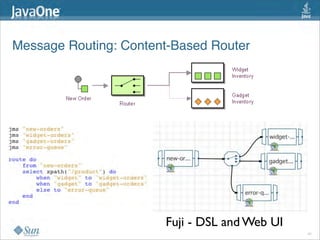
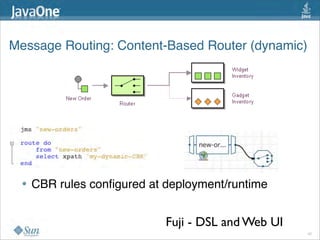
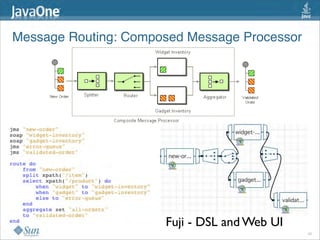
The document discusses design patterns in the context of enterprise integration patterns (EIP), emphasizing core principles, strengths, and challenges of using asynchronous messaging in integration. It highlights frameworks like Apache Camel and Project Fuji for simplifying integration, including examples of message routing and service composition. Additionally, it explores various components, tooling options, and the importance of both flexibility and productivity in implementing these patterns.