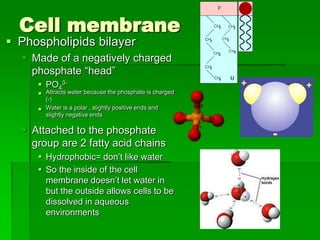
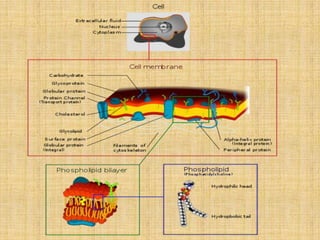
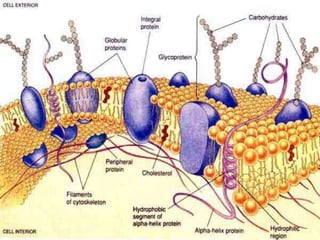
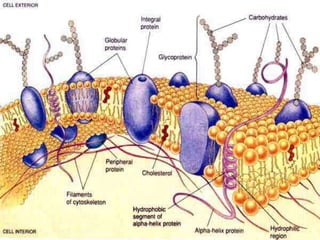
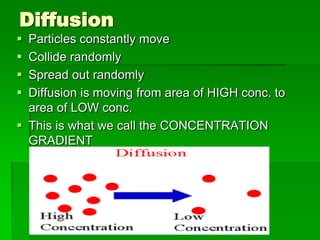
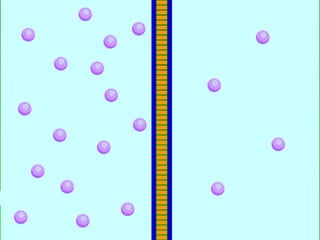
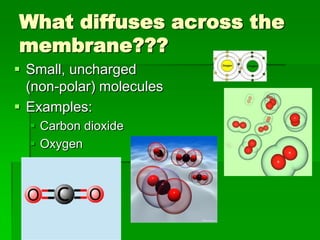
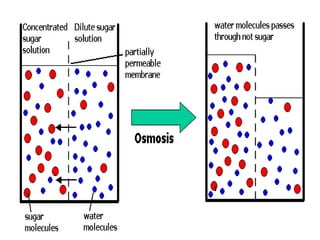
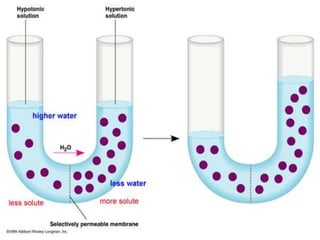
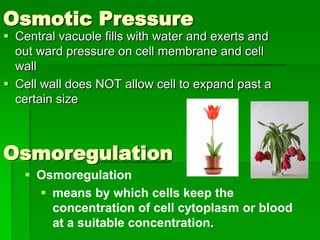
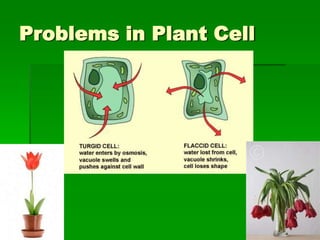
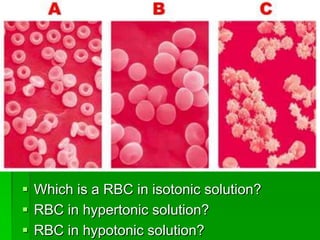
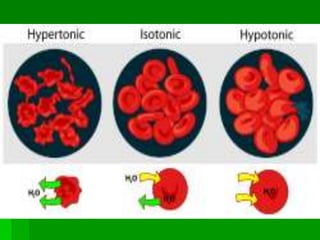
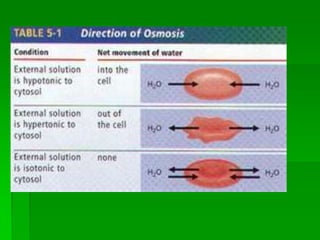
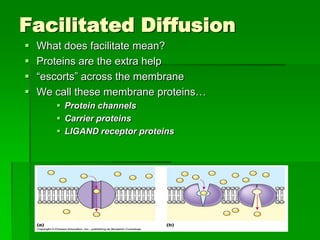
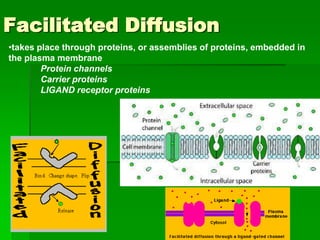
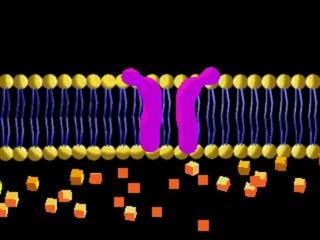
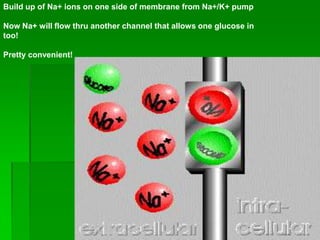
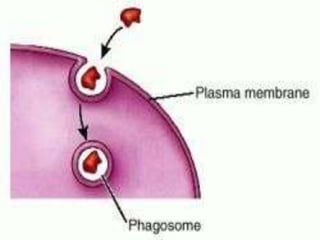
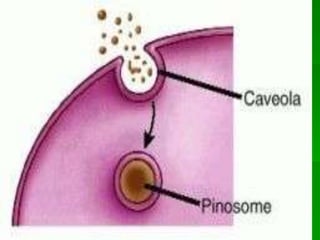
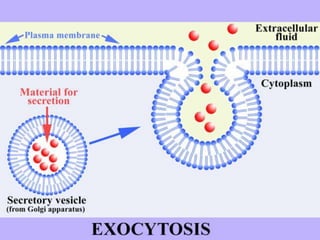
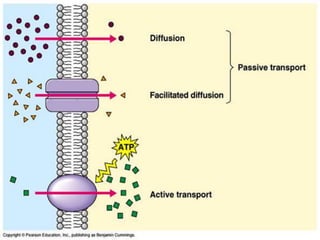
This document discusses cell boundaries and membrane transport. It begins by defining cell boundaries as the cell membrane and cell wall. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that regulates what moves in and out of the cell through passive and active transport. The cell wall provides additional structure and protection for some cell types. The cell membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Materials move across the membrane through diffusion, osmosis, and protein-mediated transport processes. Osmosis allows water to move across the membrane down its concentration gradient. Active transport requires energy and pumps molecules against their concentration gradient with protein transporters. Cells maintain equilibrium through these passive and active transport mechanisms.