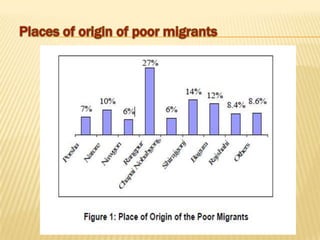
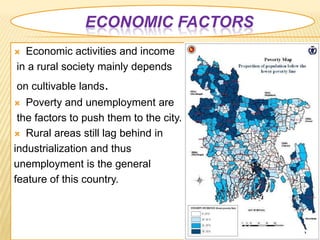
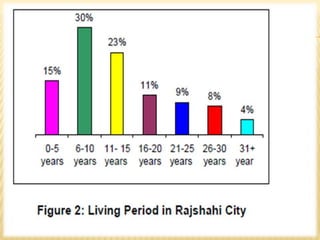
The document discusses population migration from rural to urban areas in Bangladesh. It identifies several factors that contribute to migration, including natural factors like monsoon flooding and riverbank erosion, as well as economic factors such as poverty, unemployment, and seasonal food insecurity in rural areas. It also examines the social structure and social stratification in Bangladesh, noting traditional class distinctions had little importance and identifying key social classes based on employment status.