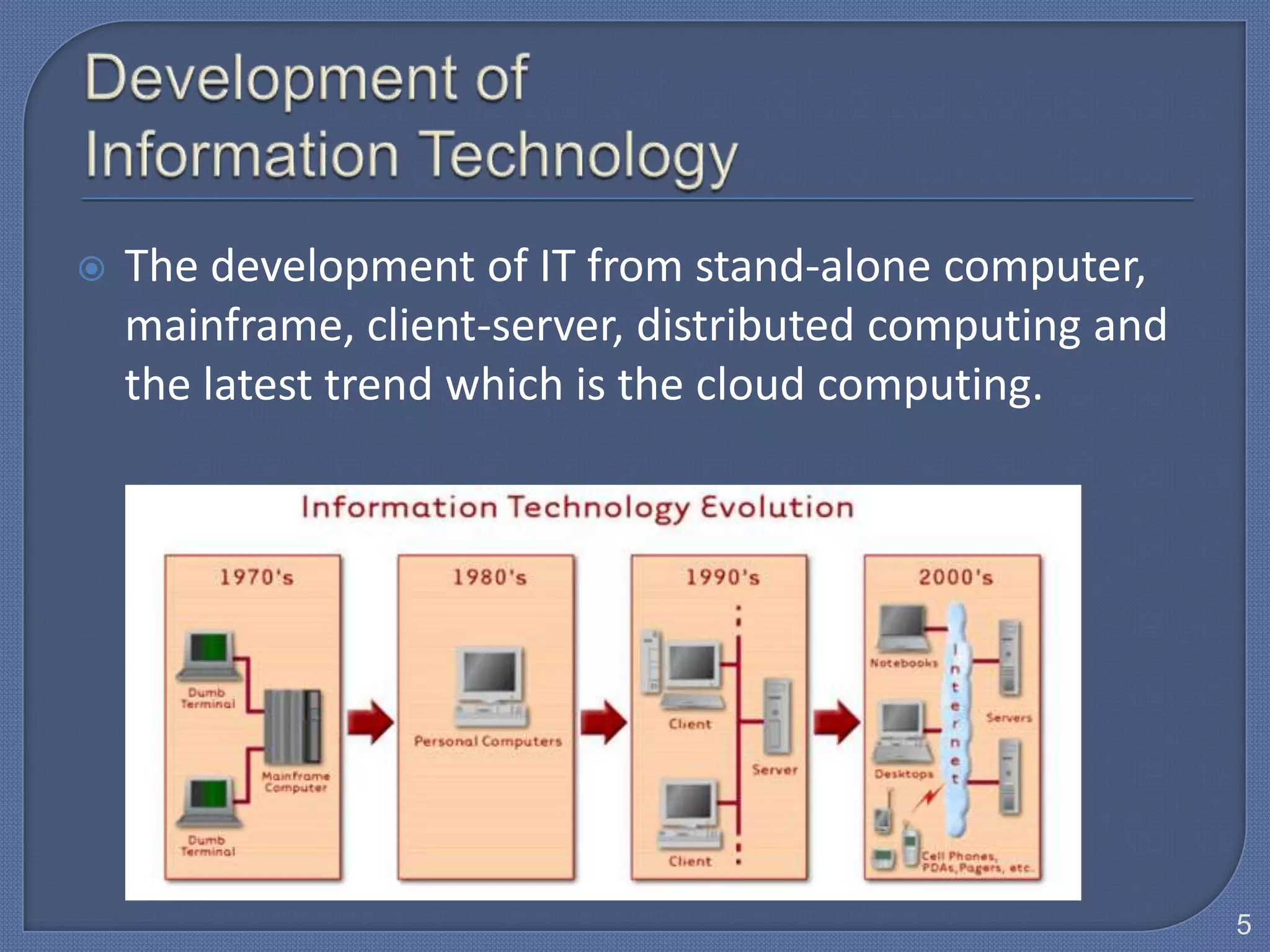
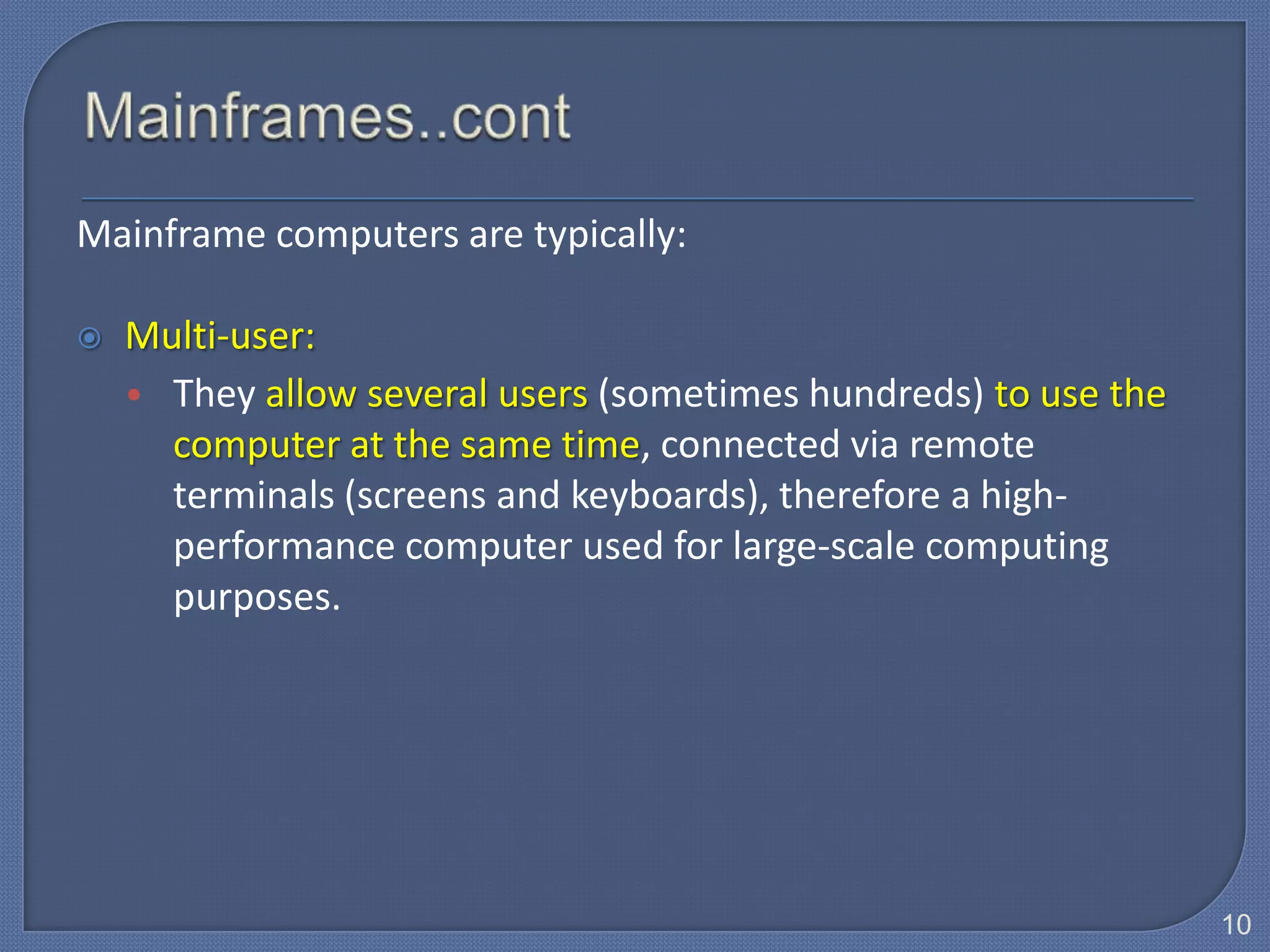
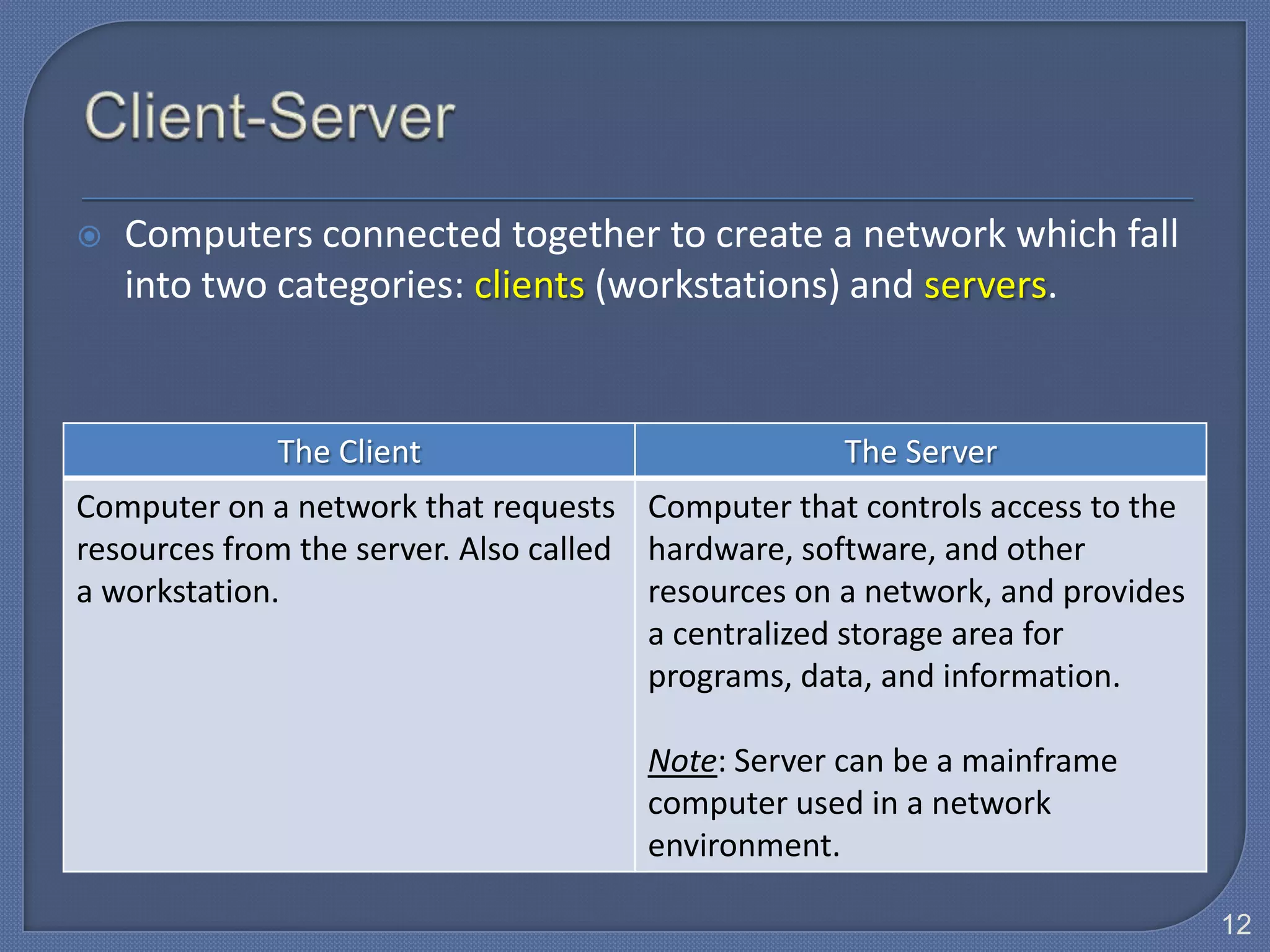
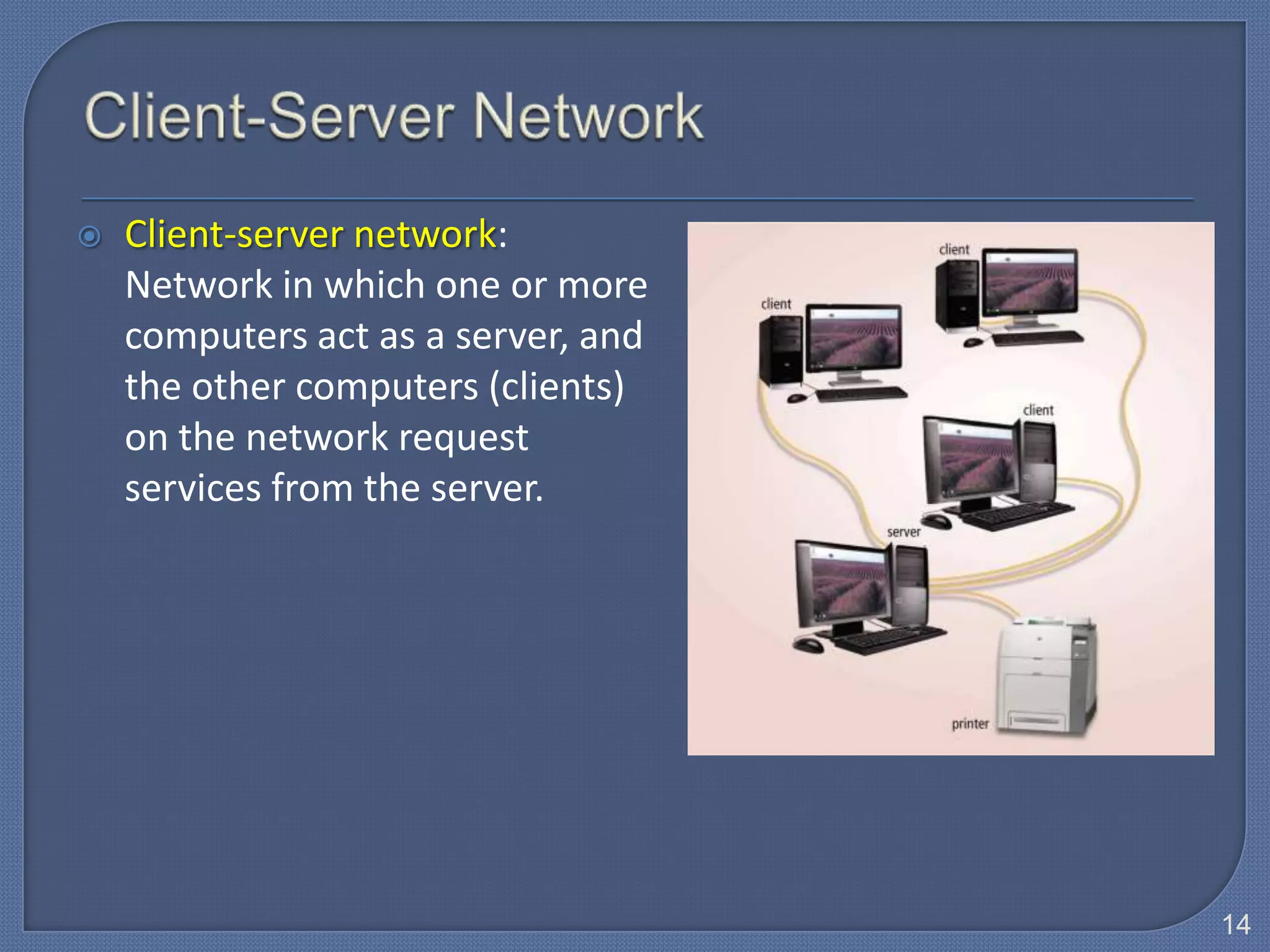
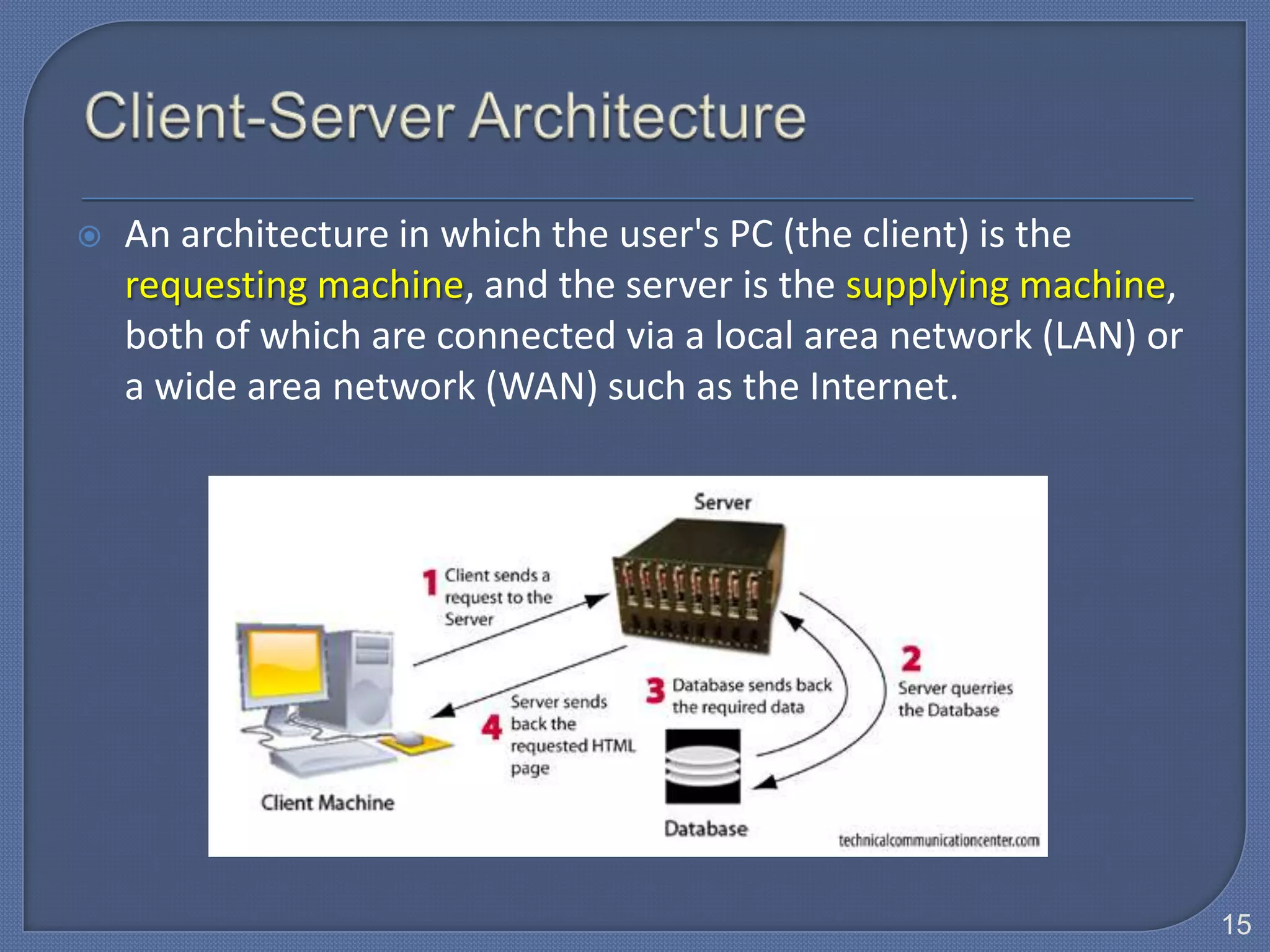
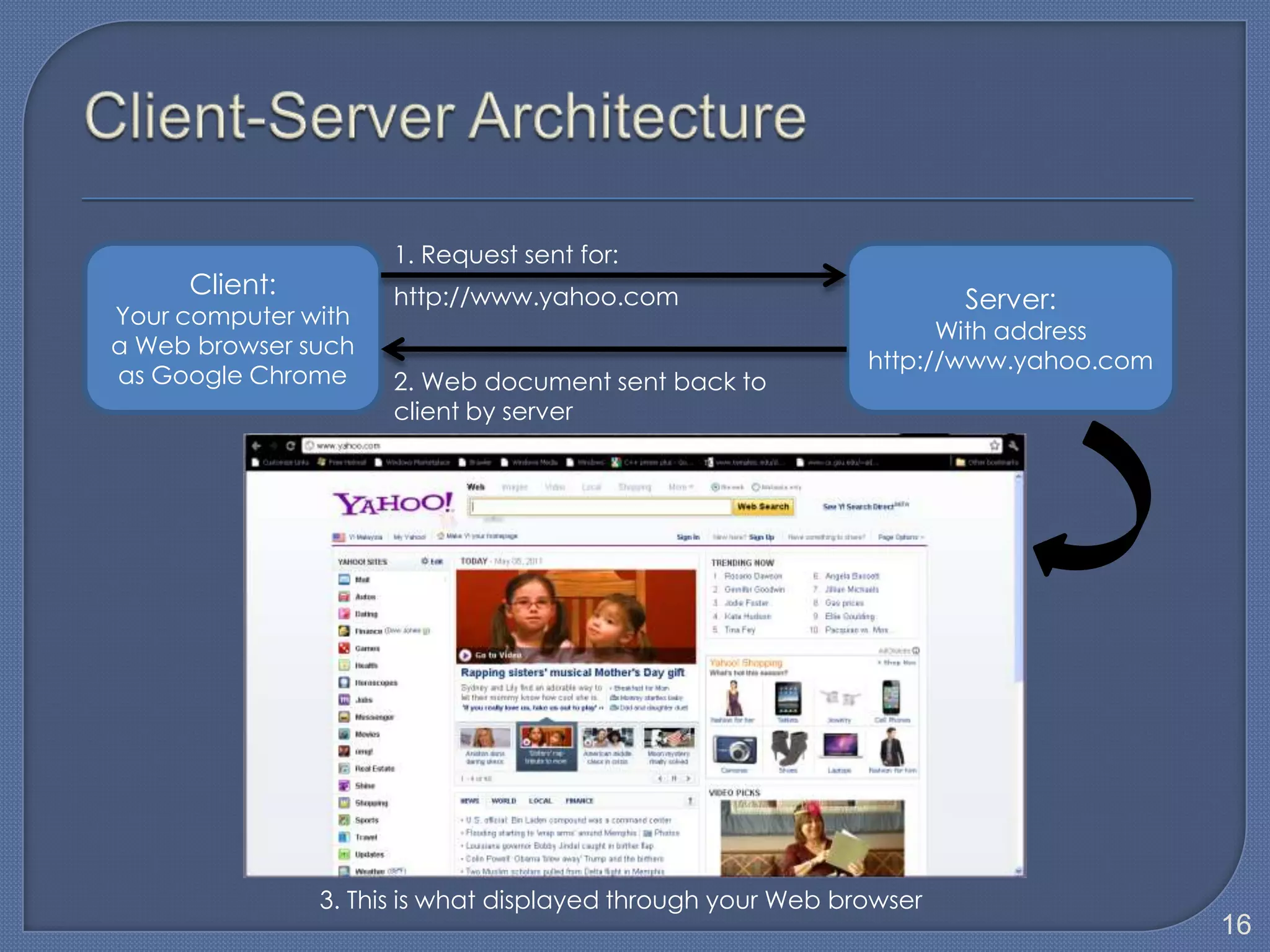
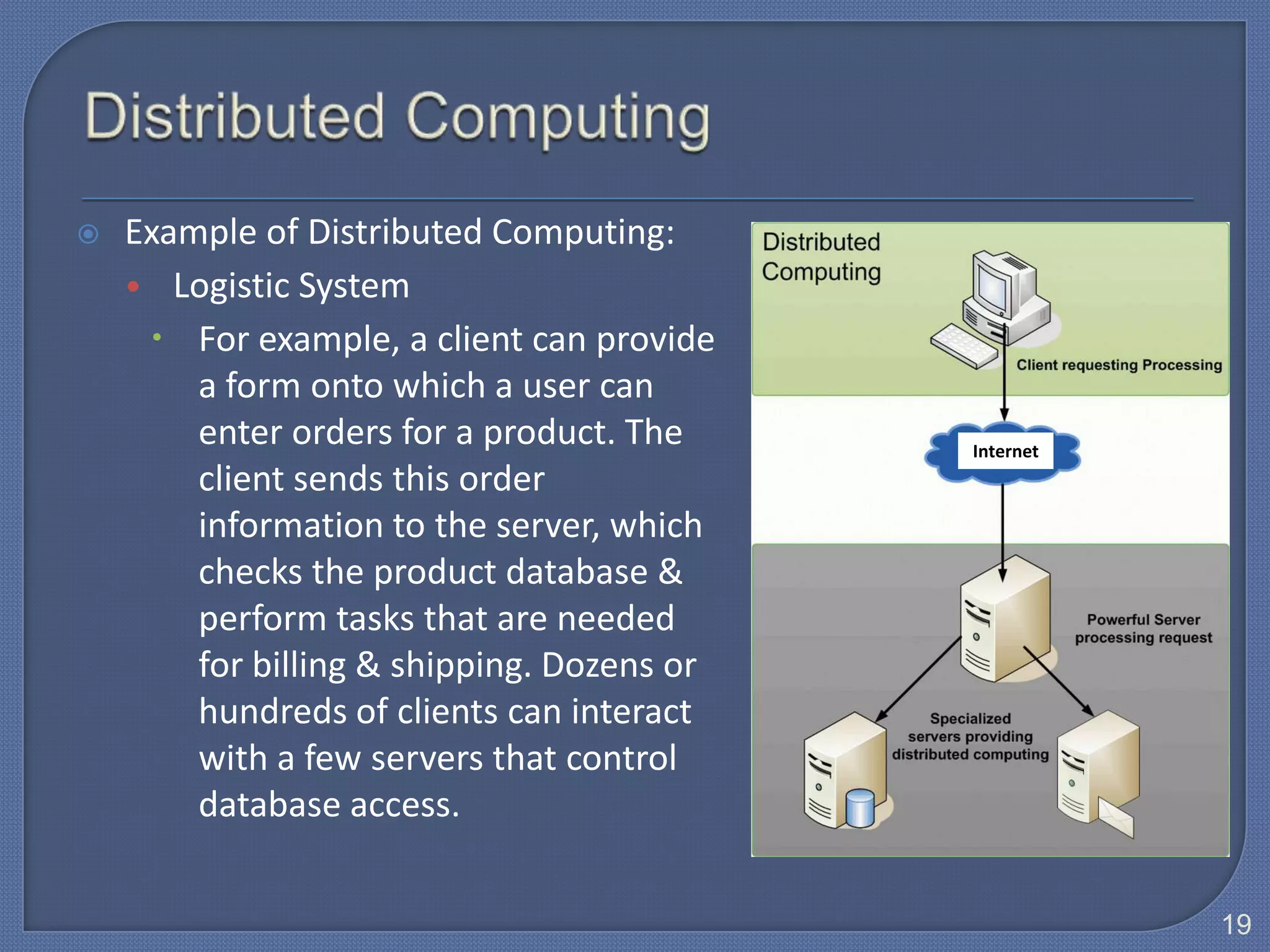
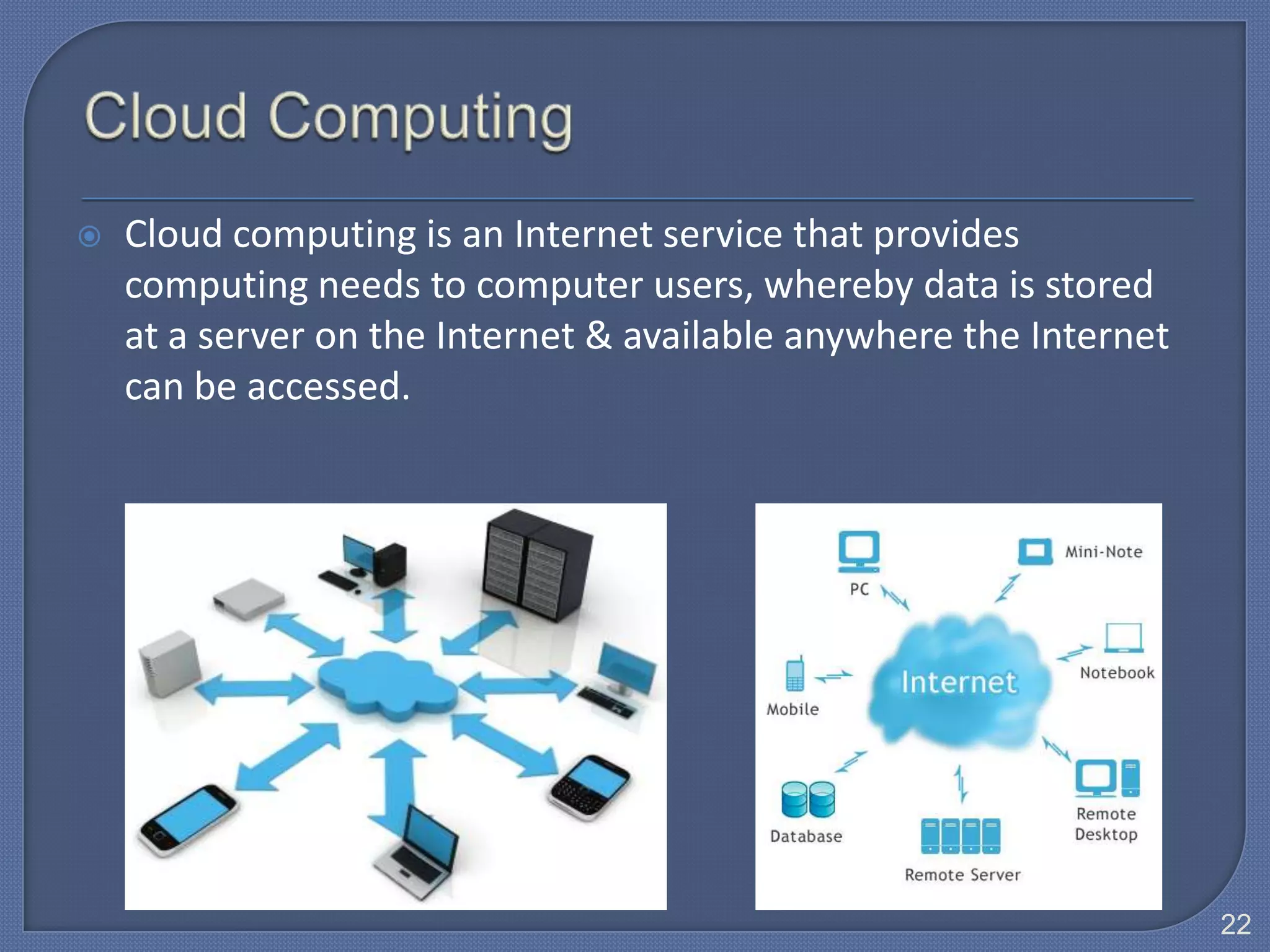
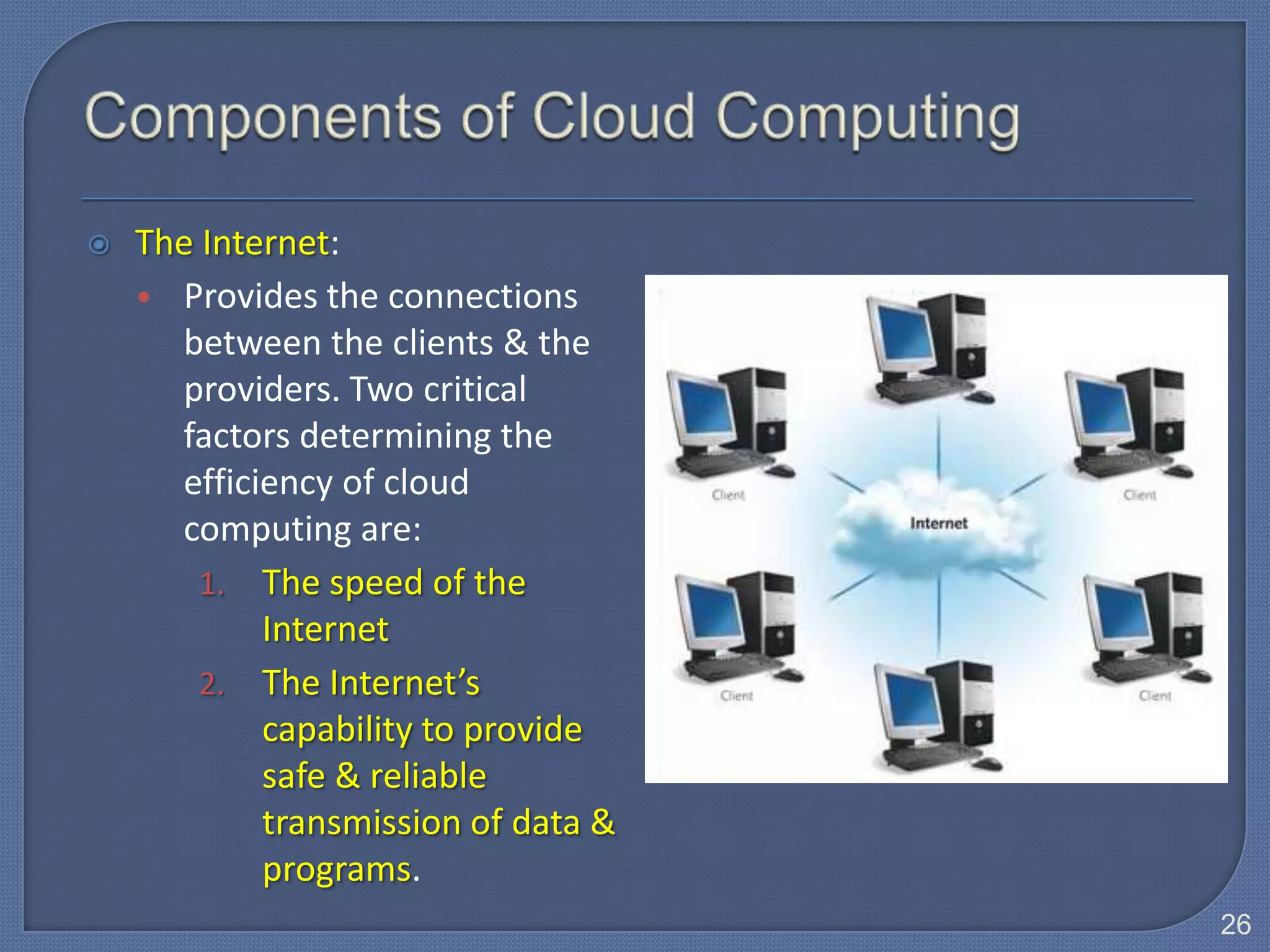
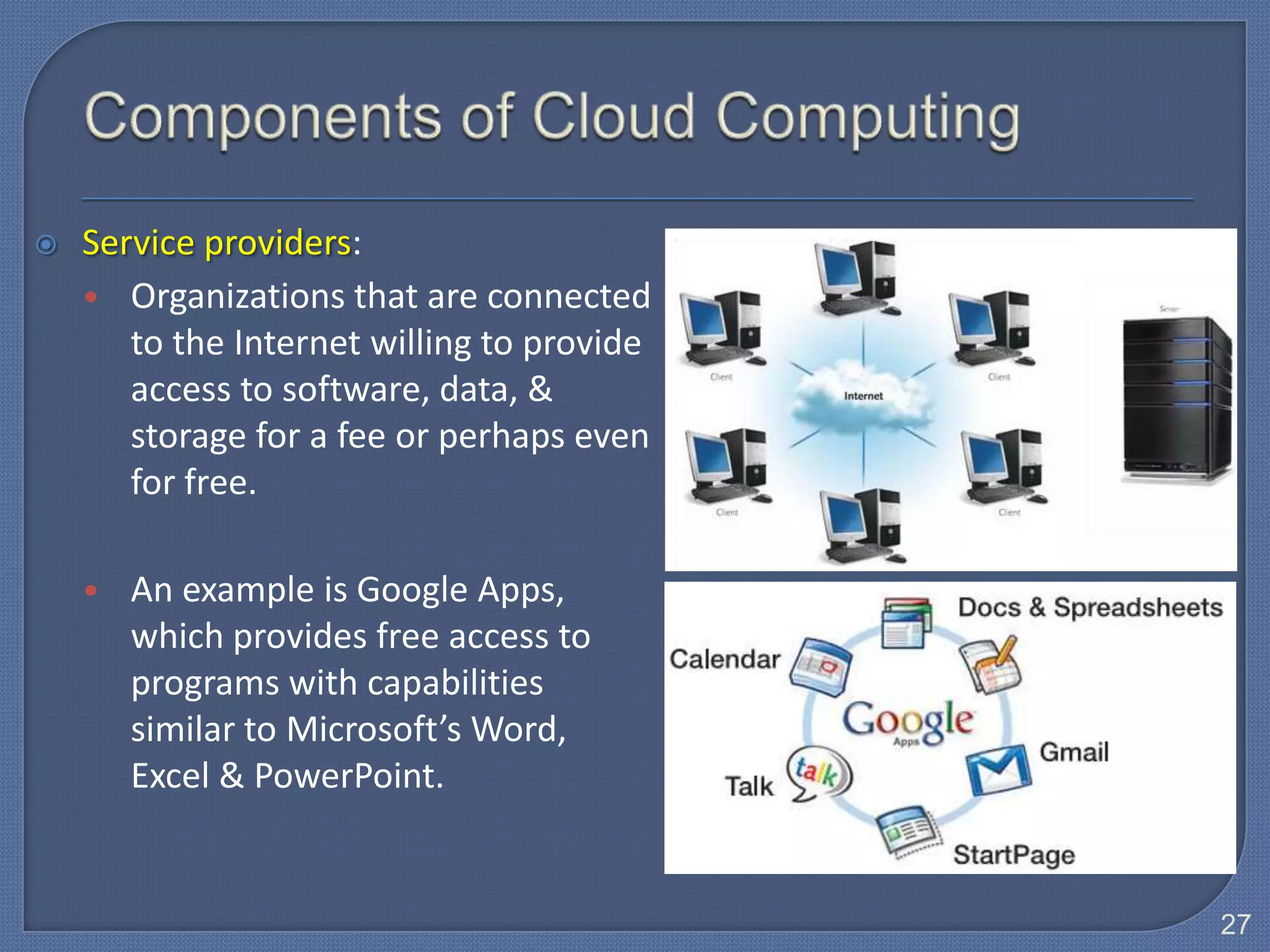
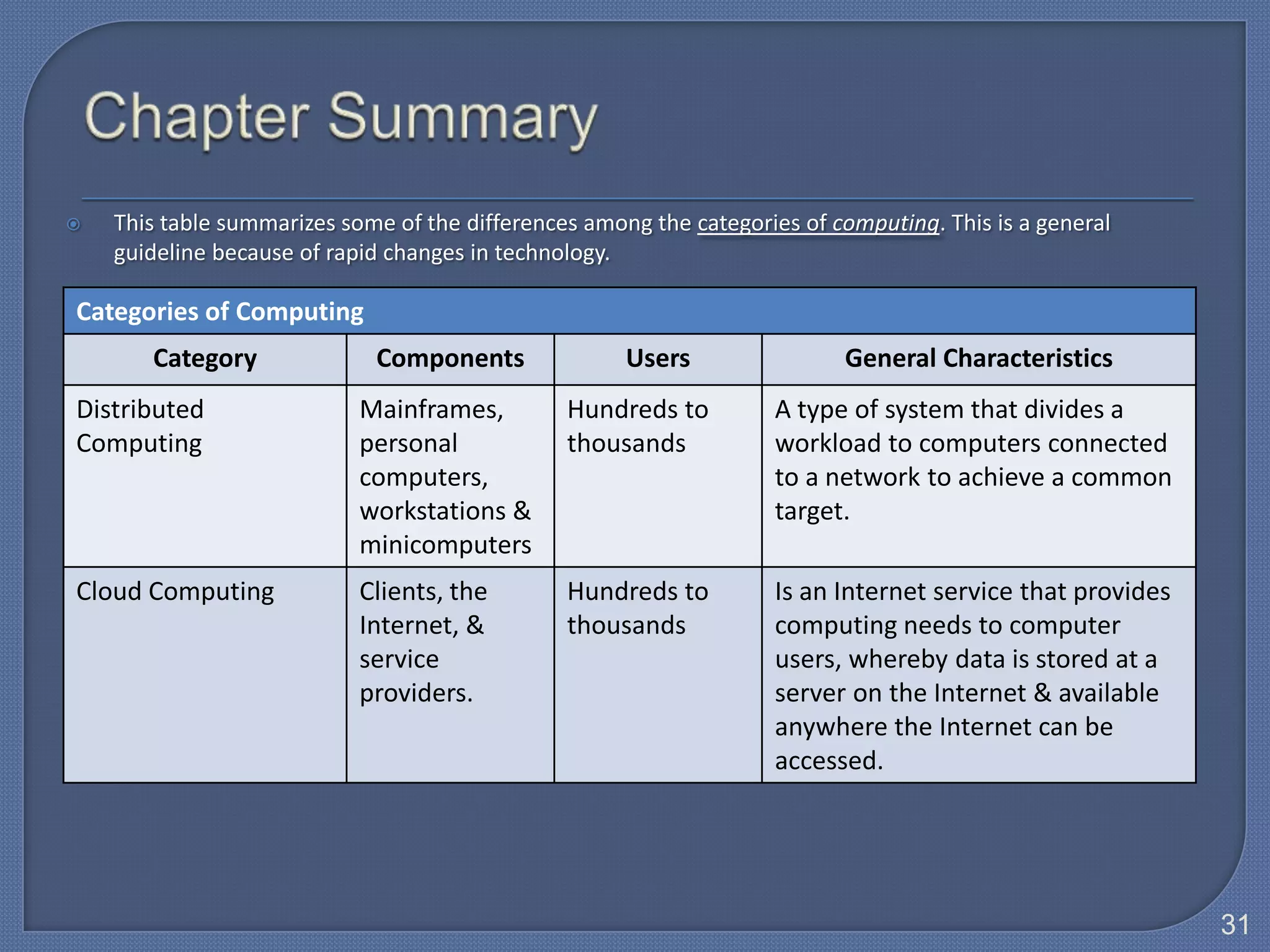
The document defines Information Technology (IT) and summarizes the development of IT from stand-alone computers to the current trend of cloud computing. It discusses stand-alone computers, mainframes, client-server networks, distributed computing, and cloud computing. The development progressed from individual stand-alone computers to networks of connected computers and servers, and now to cloud-based computing where resources are accessed over the Internet.