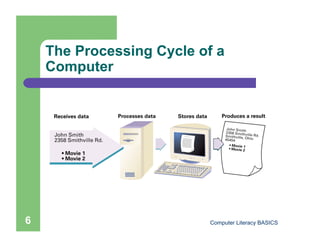
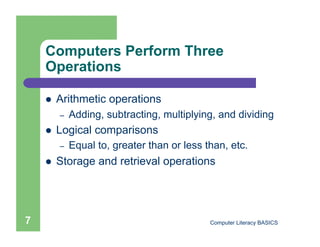
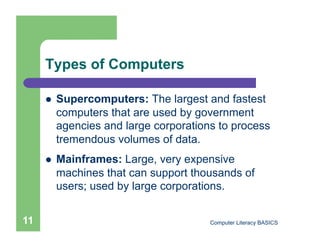
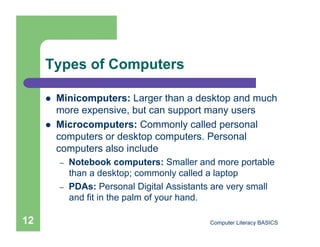
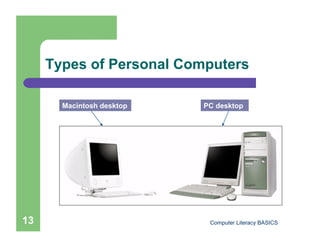
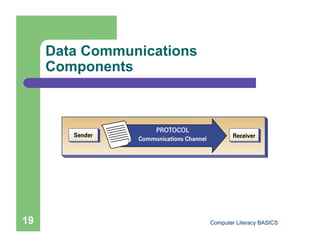
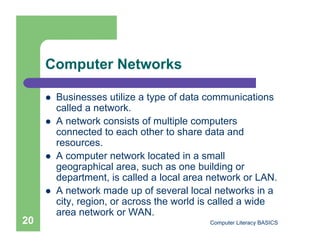
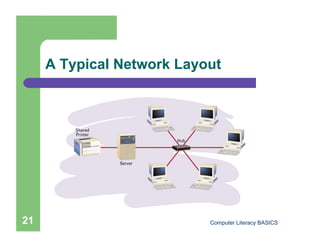
This document introduces computers and their uses. It defines a computer, describes how they are used in daily life, and classifies different types from supercomputers to microcomputers. The document also outlines computer systems and their basic hardware components, how data is communicated through networks, and how computers have become integrated into most aspects of modern society.