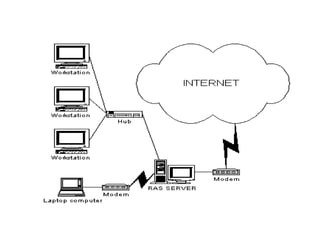
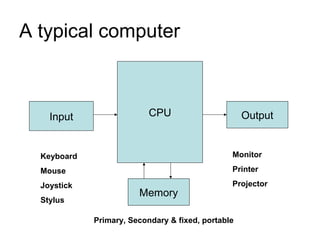
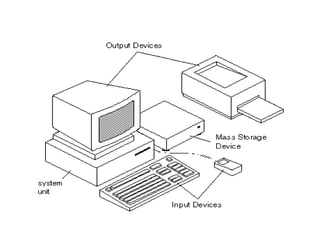
This document provides a classification of different types of digital computers and their applications. It classifies computers as personal computers, laptops, network computers, mini/microcomputers, PDAs, workstations, servers, mainframes, and supercomputers. It then describes each type and provides some key applications for personal computers, education, science, industry, entertainment, business, and government. These include uses like documentation, gaming, education, research, software development, e-commerce, banking, weather forecasting, and more. It also outlines the basic components of a computer including input, output, CPU and memory.