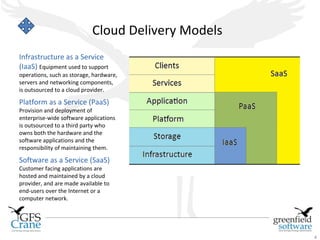
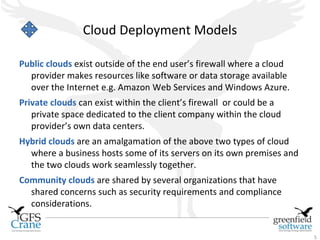
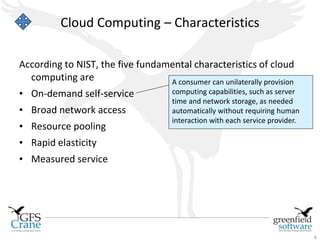
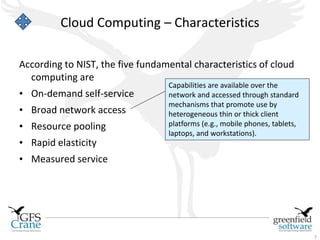
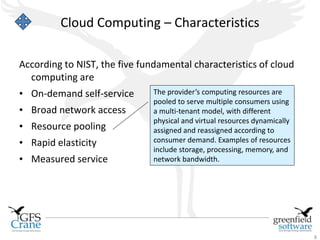
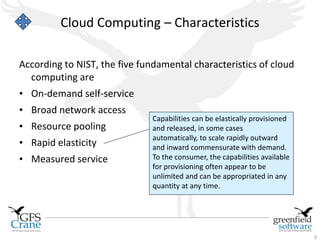
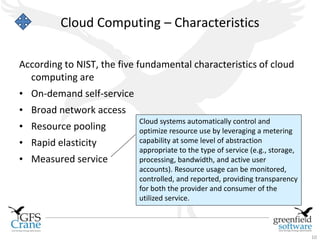
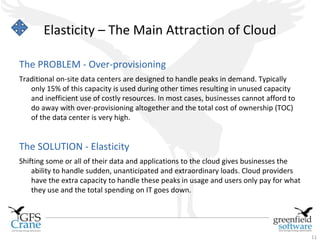
The document discusses cloud computing and Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM), defining cloud computing as scalable and elastic IT-enabled capabilities delivered via internet technologies. It outlines the advantages of cloud computing, including cost savings and manageability, and describes various cloud delivery and deployment models such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of DCIM in optimizing data center performance and resource management while enabling businesses to provision resources flexibly across multiple platforms.