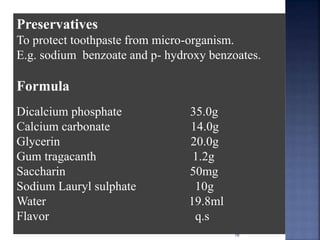
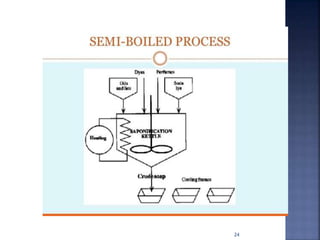
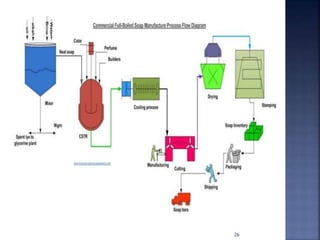
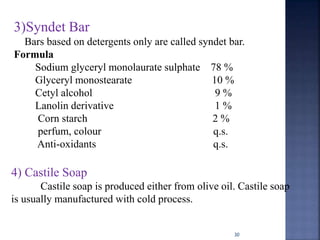
This document discusses the formulation and manufacturing of toothpaste and soap. It provides details on the ingredients and purposes of toothpaste such as cleansing, polishing, stain removal and reducing tooth decay. It also discusses the requirements of gelling agents and bleaches in toothpaste formulations. For soap manufacturing, it describes the raw materials of fats, oils and alkalis used. The different types of soaps and their formulations are outlined, including transparent soap, bathing bars and liquid soaps. Finally, it provides a reference for further information.