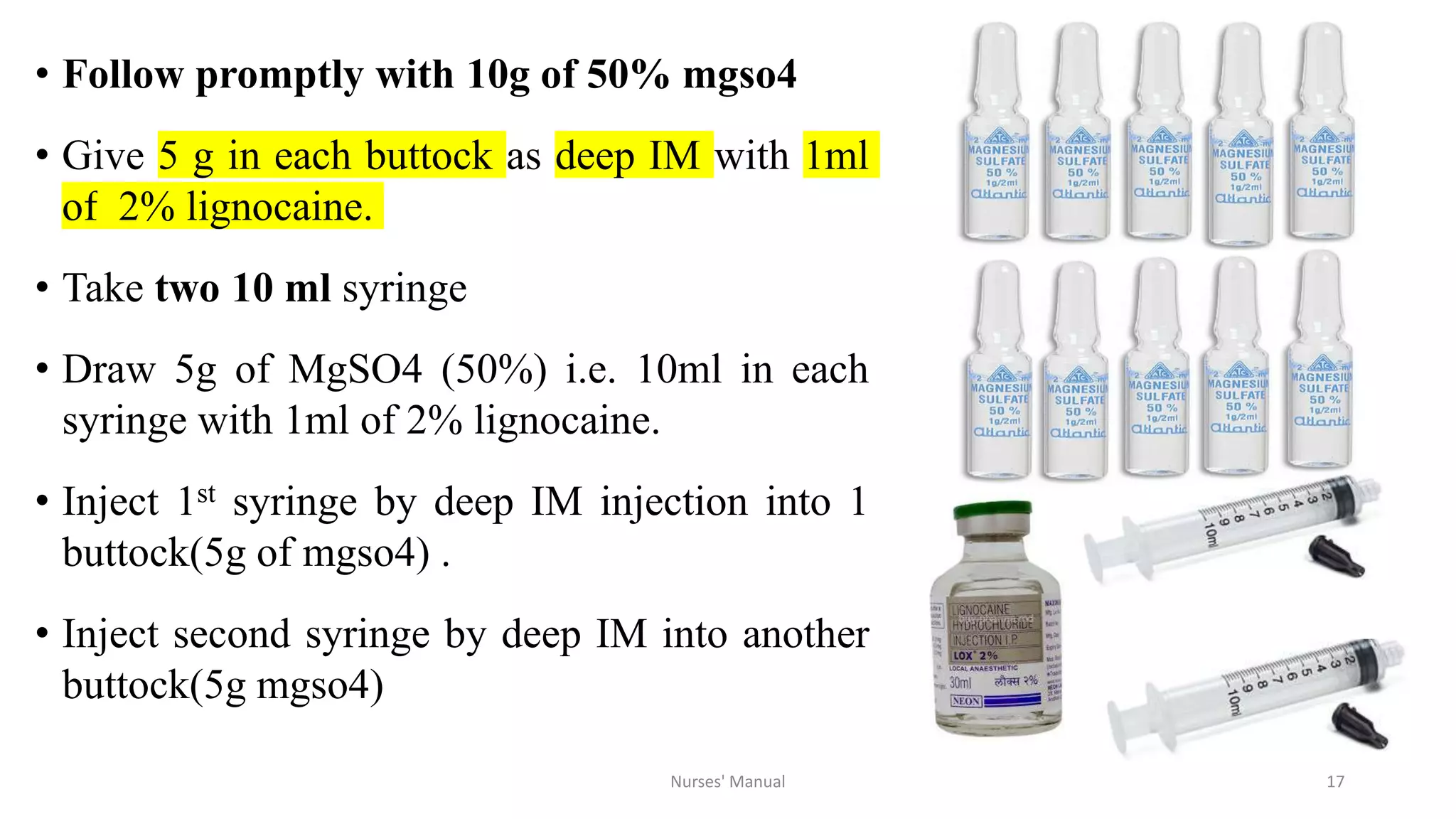
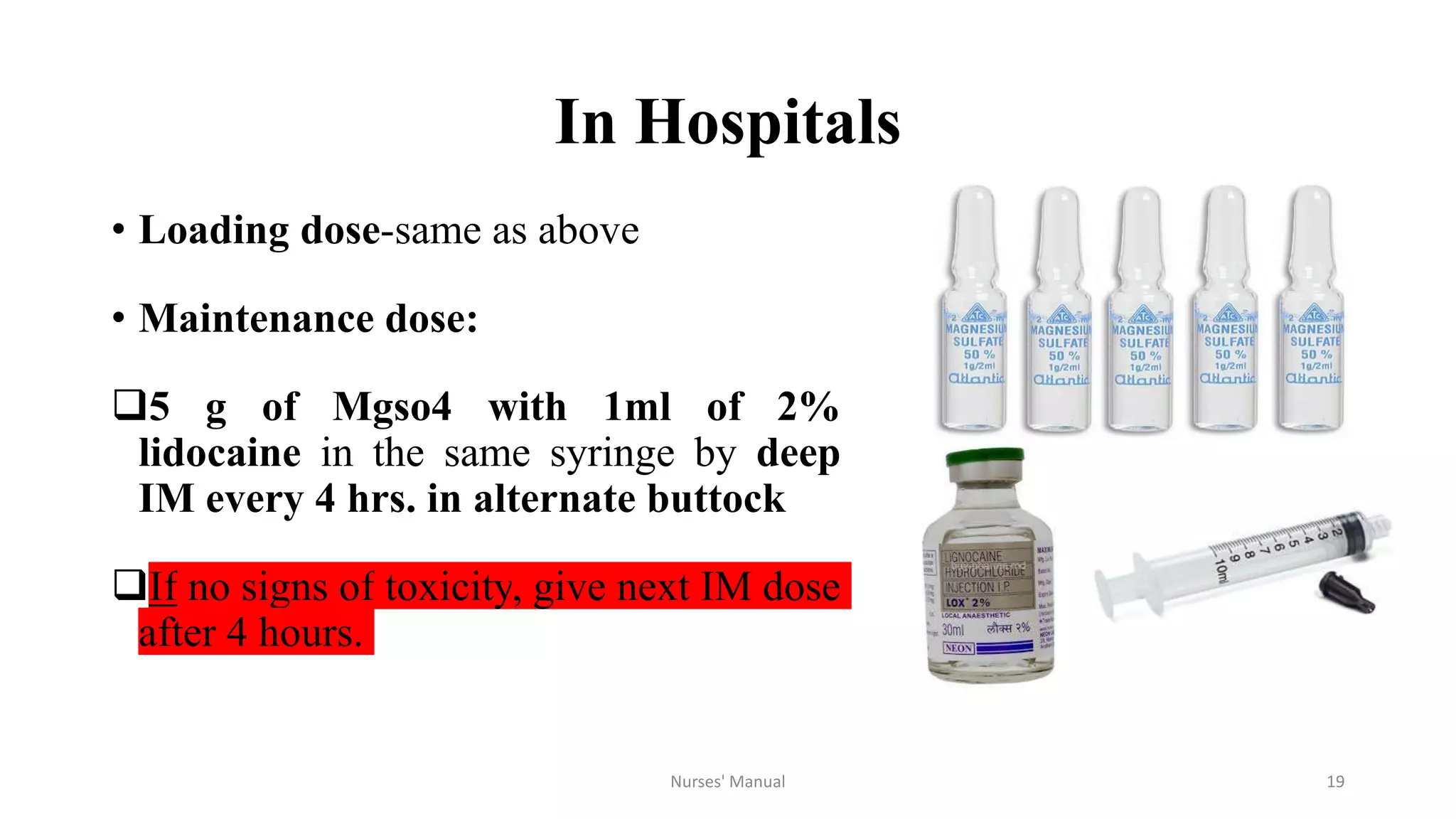
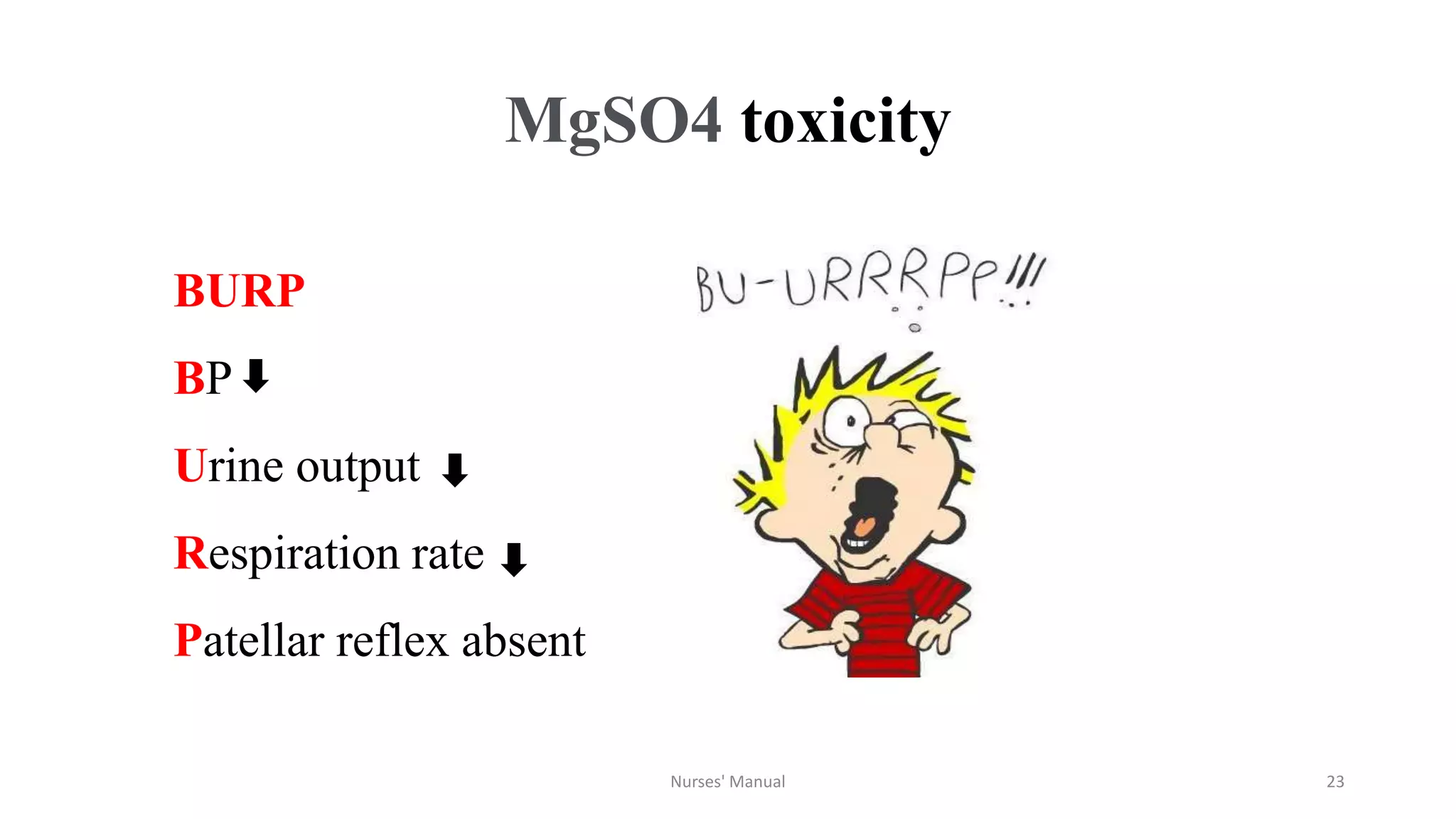
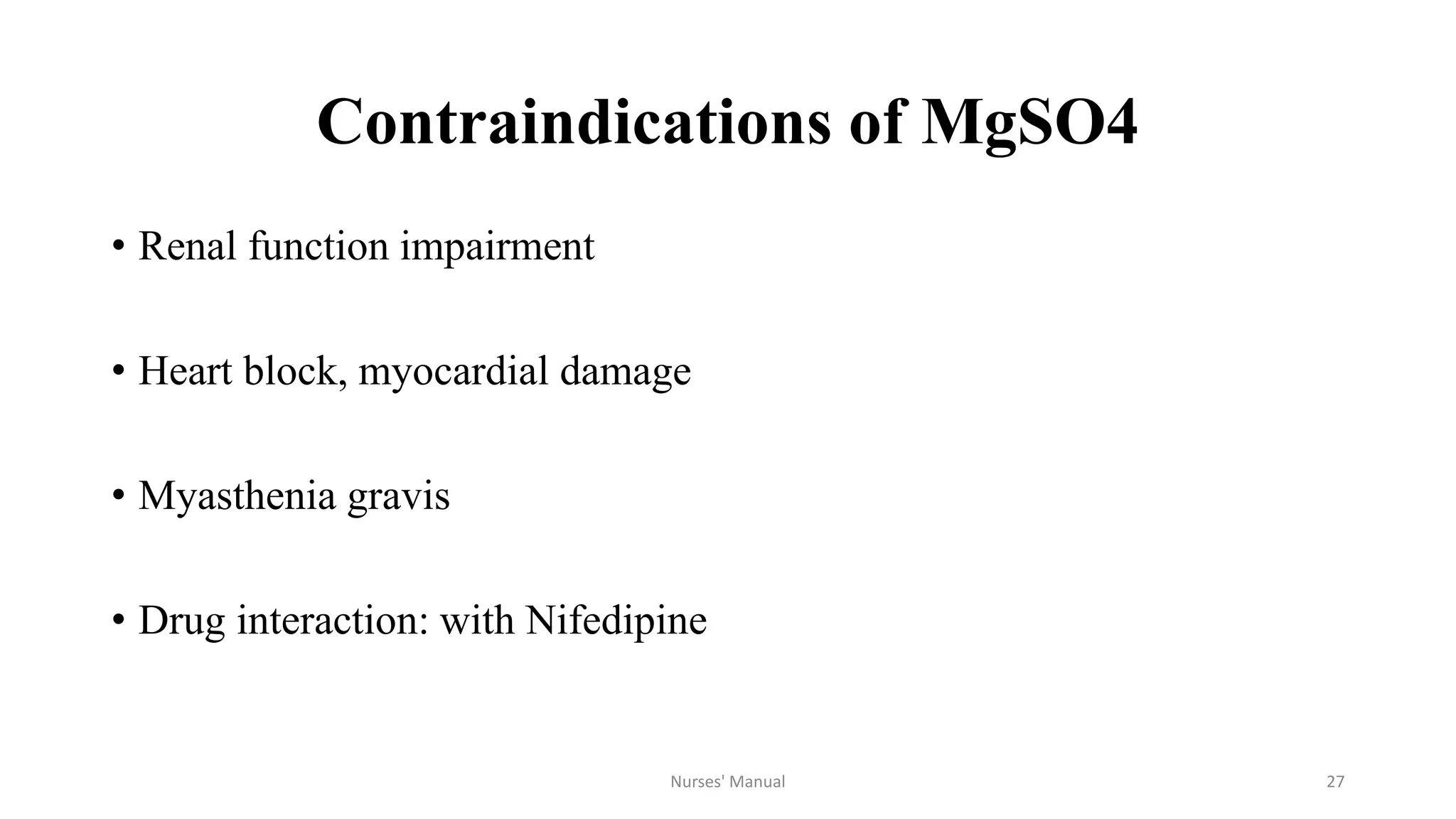
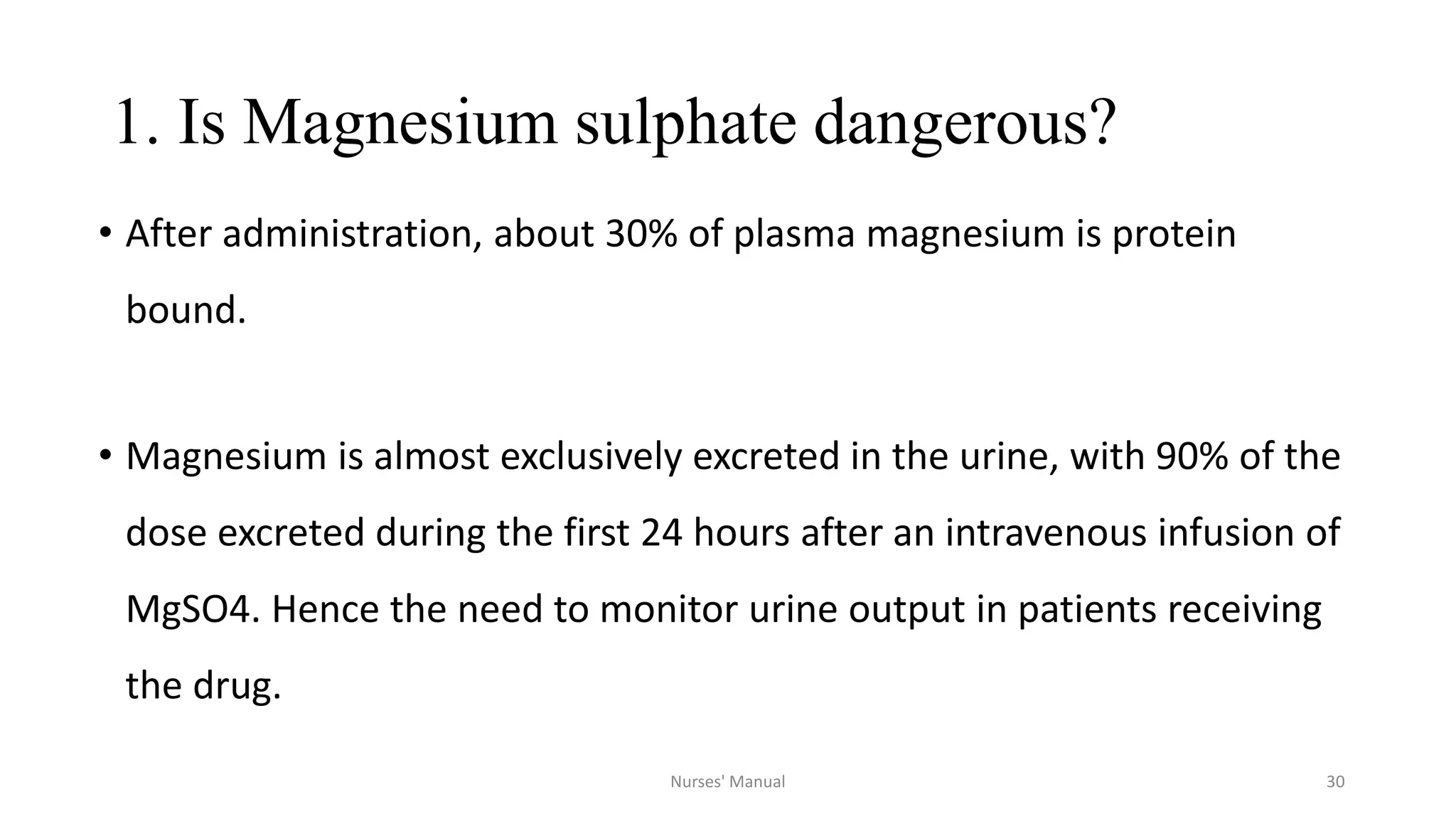
Magnesium sulfate is the drug of choice for preventing and treating convulsions in severe pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. It acts as an anticonvulsant by blocking calcium channels in the nervous system. For treatment, it is administered intravenously as a loading dose followed by intramuscular maintenance doses every four hours. Nurses must monitor patients for signs of toxicity such as decreased respiratory rate and absent patellar reflexes. While magnesium sulfate can be dangerous if not properly monitored, studies show the benefits outweigh the risks for both mother and baby when administered and monitored correctly. However, eclampsia remains a major cause of maternal deaths in Nepal possibly due to lack of availability, proper administration