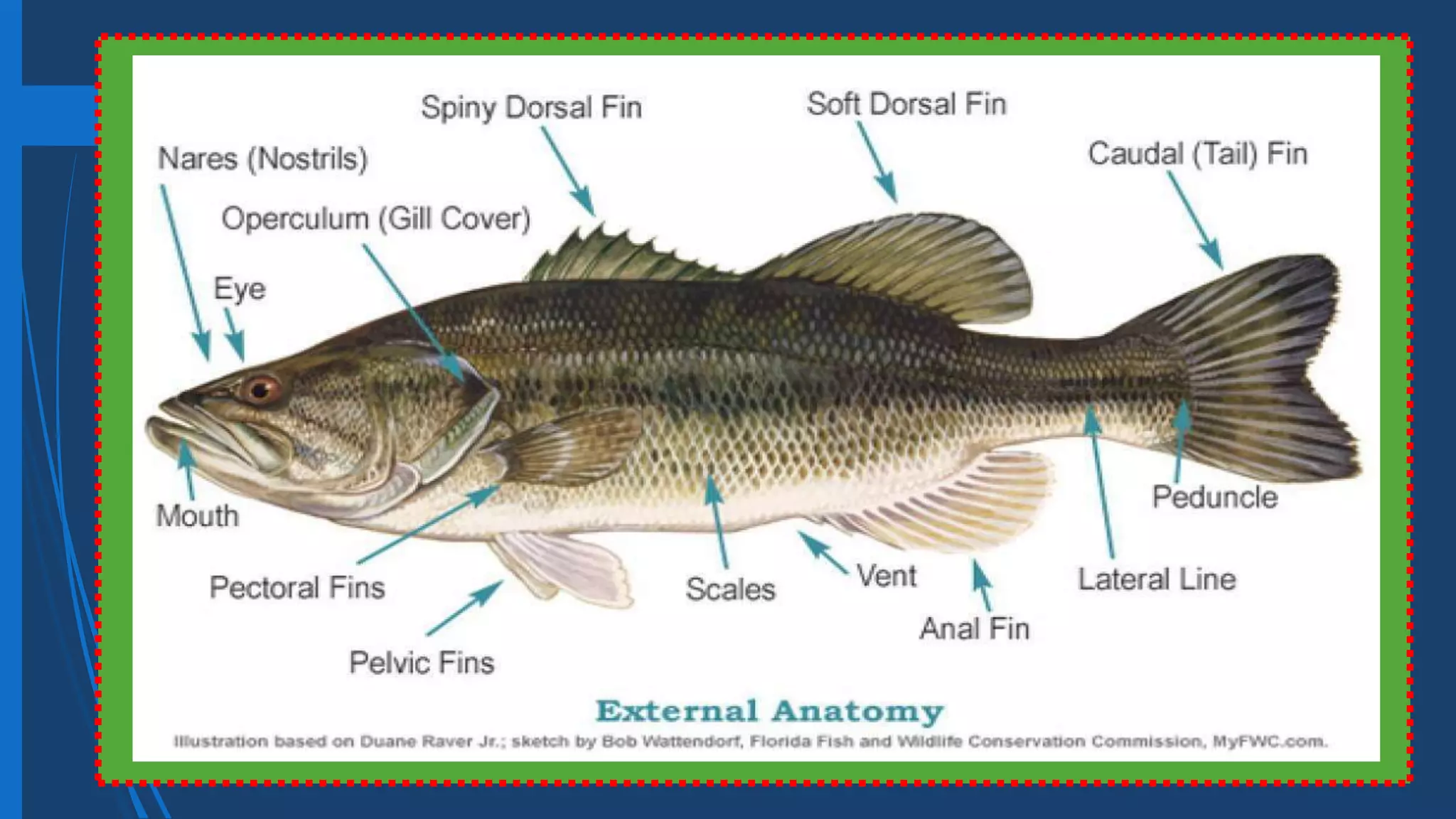
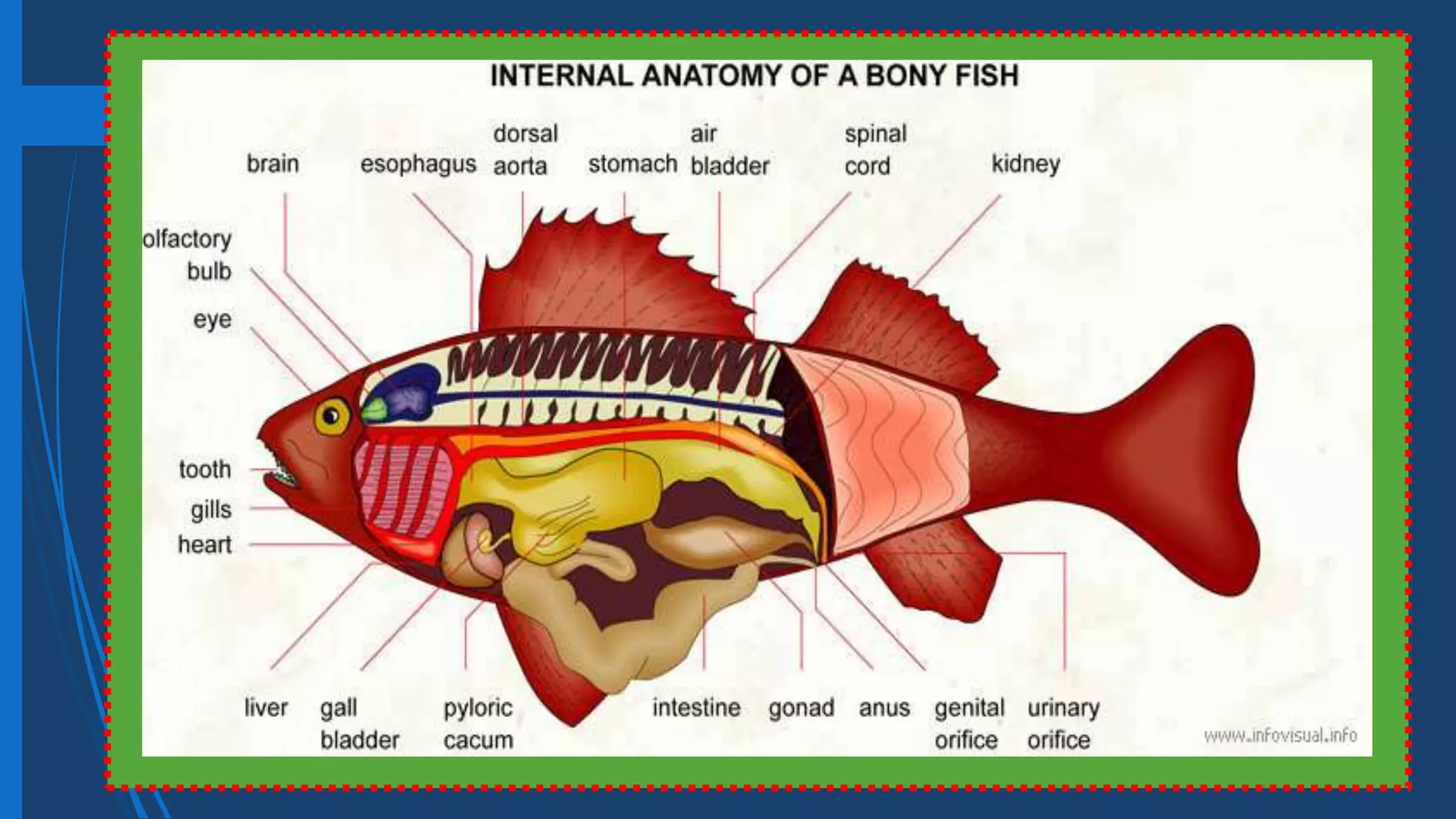
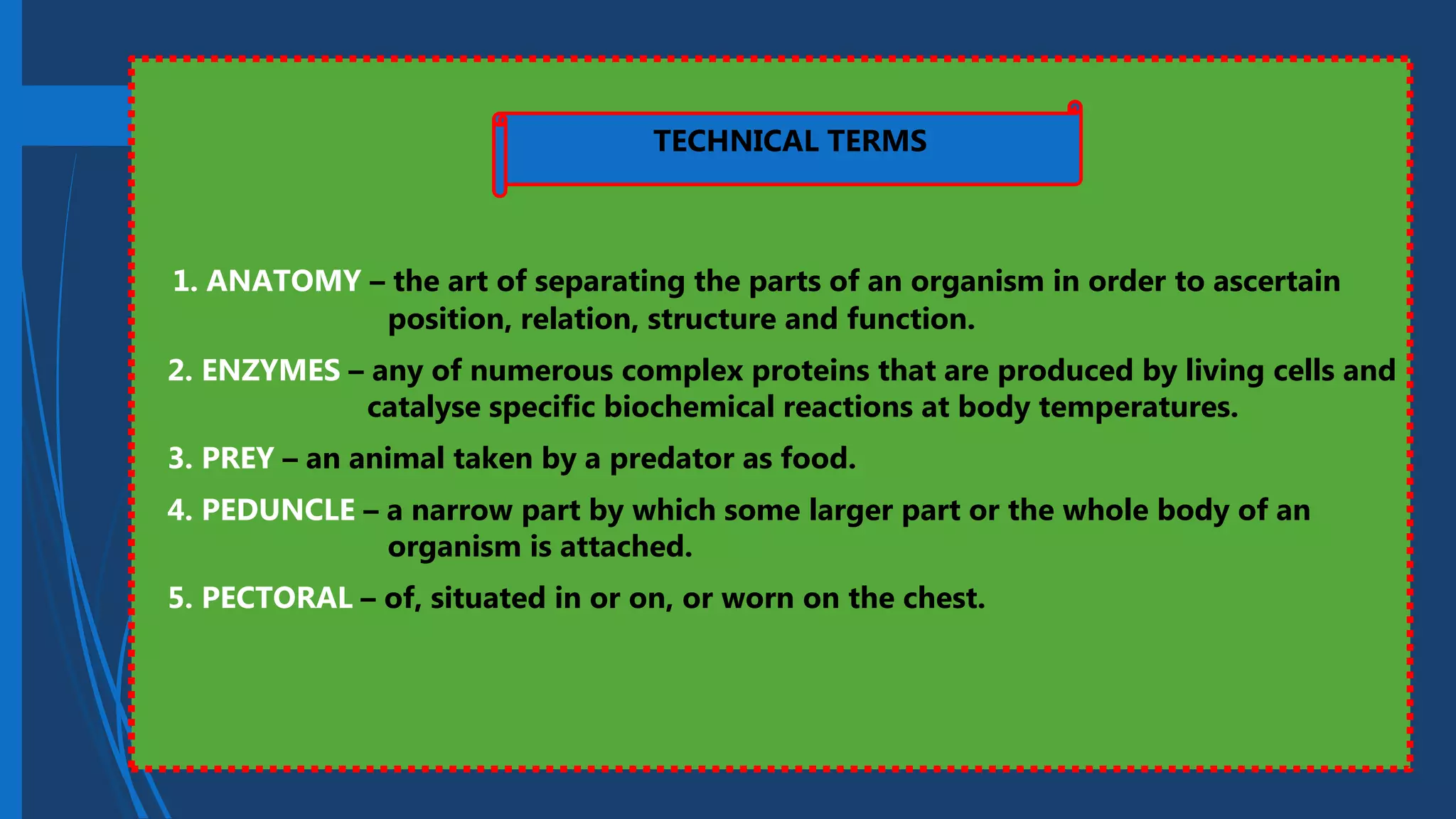
This document provides information on fishery arts and the anatomy of fish. It discusses fishery as the business of catching, handling, and presenting fish and aquatic products. It notes there are three main branches: fish culture which is raising aquatic products under controlled environments, fish capture using fishing methods from vessels, and fish preservation which extends the shelf life of fish using science. It also outlines the external and internal parts of fish like fins, scales, eyes, mouth, swim bladder, and organs like the brain, heart and gonads. Finally, it defines some technical terms used in fishery arts.