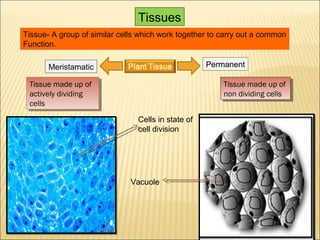
This document summarizes different types of plant and animal tissues. It describes tissue as a group of cells that work together to perform a common function. It then discusses the two main types of plant tissues - meristematic and permanent tissues. It provides details on various simple and complex permanent tissues in plants. The document also summarizes the four primary types of animal tissues - epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissues - and includes descriptions of their structures and functions.