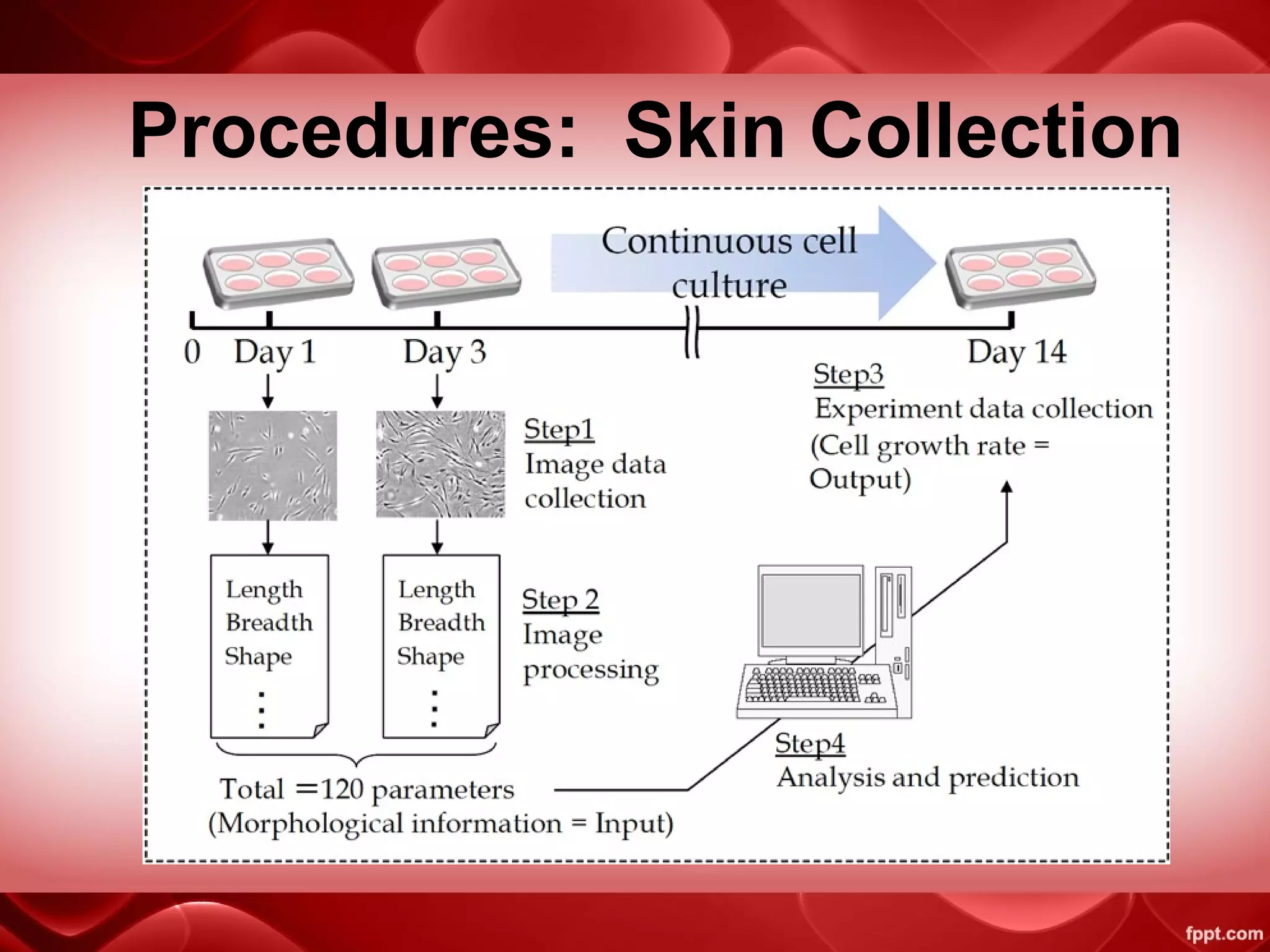
This document discusses the history and status of tissue banking in Bangladesh. It begins by defining a tissue bank as an establishment that collects and stores human cadaver tissue for medical research and education. It notes that tissue banking activities in Bangladesh were initiated in 1985 in cooperation with the IAEA. Standards and procedures for tissue banking are then outlined, including donor screening, infectious disease testing, ABO and HLA typing where relevant, and collection procedures for different tissue types like bone, skin, and heart valves. Finally, current and potential applications of tissue allografts in Bangladesh are mentioned, such as for burn patients, orthopedic and spinal surgeries, and eye and oral/maxillofacial procedures.