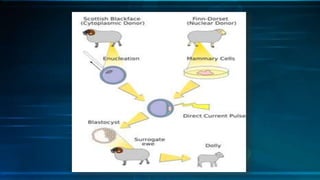
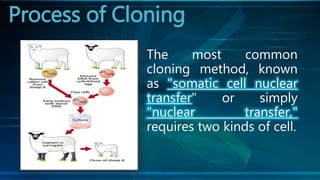
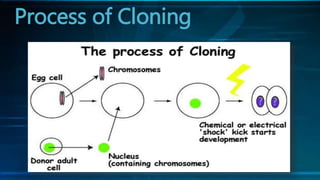
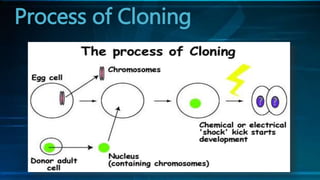
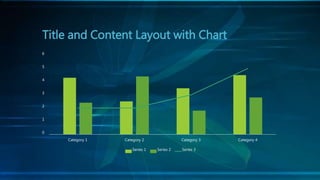
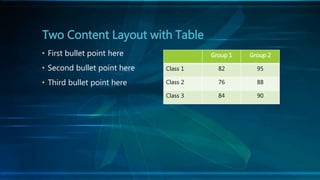
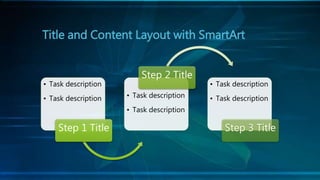
The document discusses cloning and the cloning process. It defines cloning as processes used to produce genetically identical copies. It describes Dolly the sheep, the first mammal cloned from an adult cell. The process of cloning involves transferring the nucleus of a donor adult cell into an egg cell that has had its nucleus removed. The egg is then placed in a surrogate womb to mature. Cloning has produced genetically identical animals like cows, sheep, and mice. However, clones do not always look identical as environment also affects development.