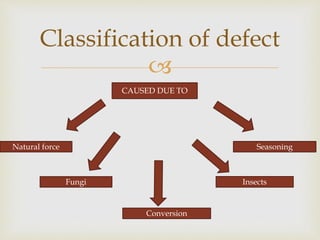
Timber is wood that is used for construction purposes and is generally obtained from tree trunks. Timber can be in various forms such as standing timber from living trees, green timber freshly cut, or rough timber from felled trees. Timber is classified based on how it is processed, whether it is from coniferous or deciduous trees, and other characteristics. Good timber is durable, resistant to decay and insects, strong, and uniform in color and grain. While timber has advantages such as strength and workability, disadvantages include combustibility, susceptibility to decay and insects, and dimensional changes with moisture. Defects in timber like knots, shakes, and rot reduce its strength, durability, and utility.