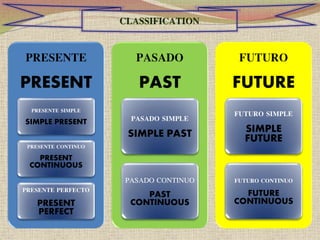
The document provides a comprehensive overview of English verb tenses, including present, past, and future forms, along with their affirmative, negative, and interrogative structures. It offers examples for each tense to illustrate their usages in everyday language. Additionally, the content covers auxiliary verbs and their roles in forming different verb tenses.