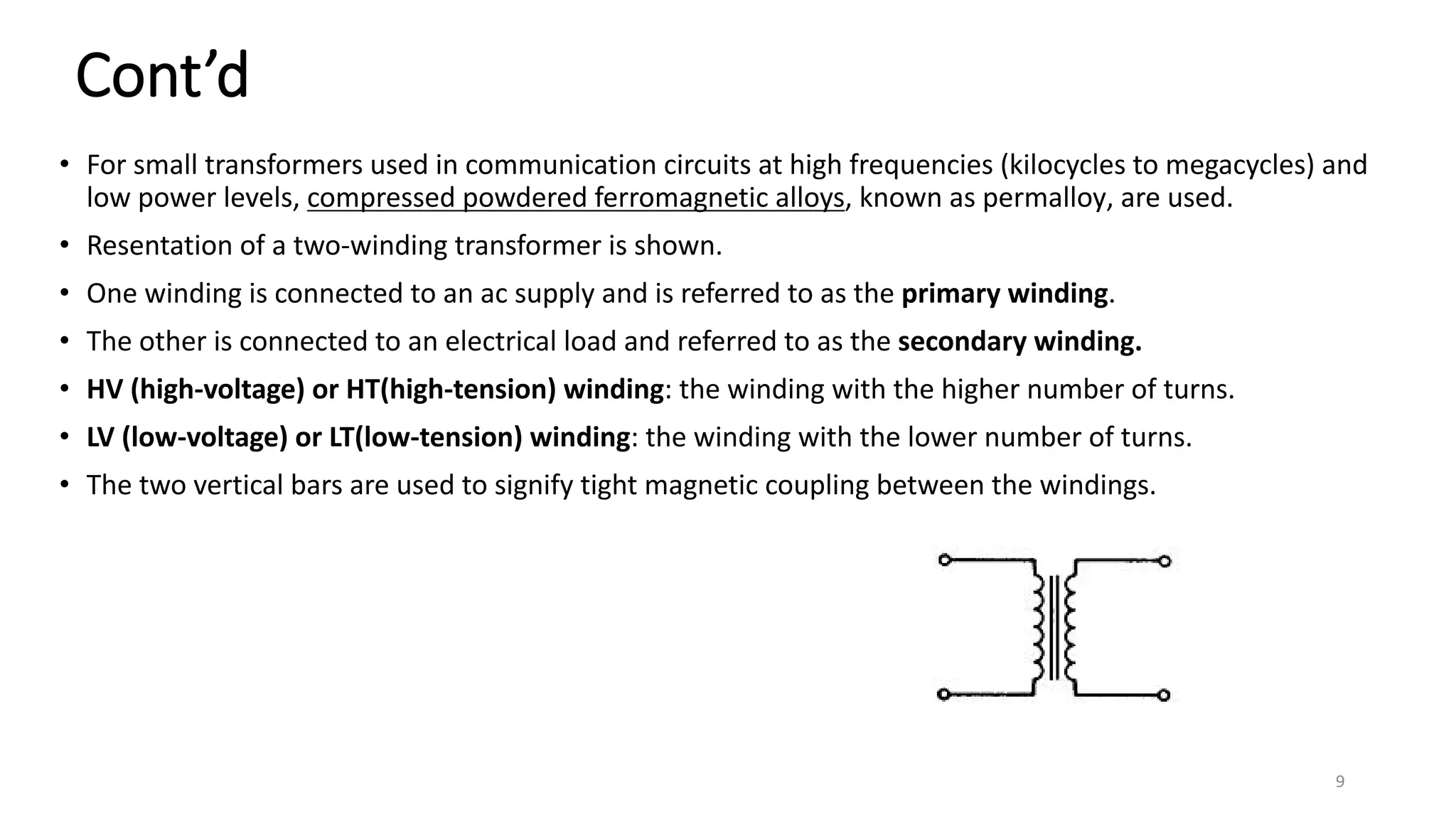
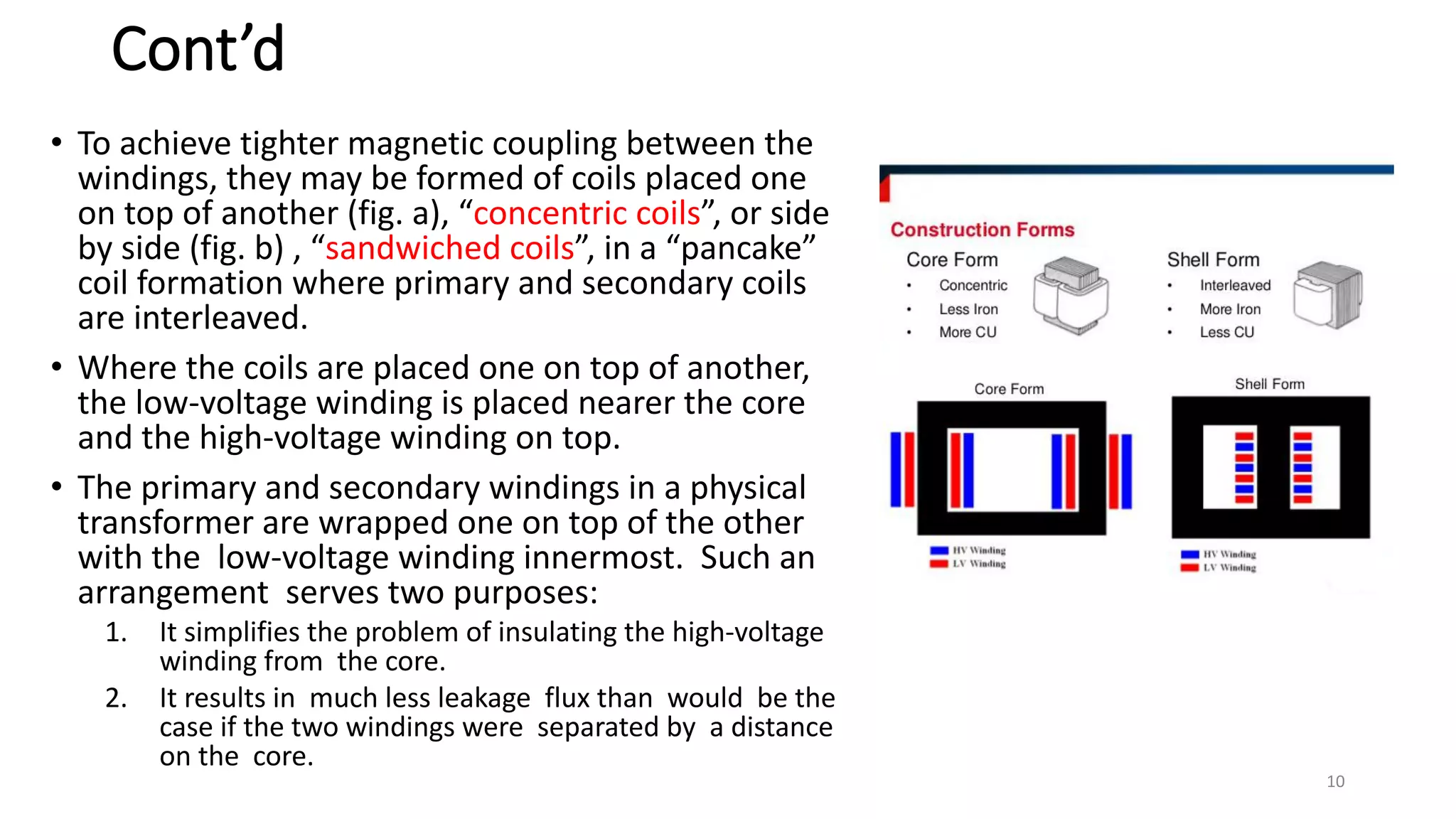
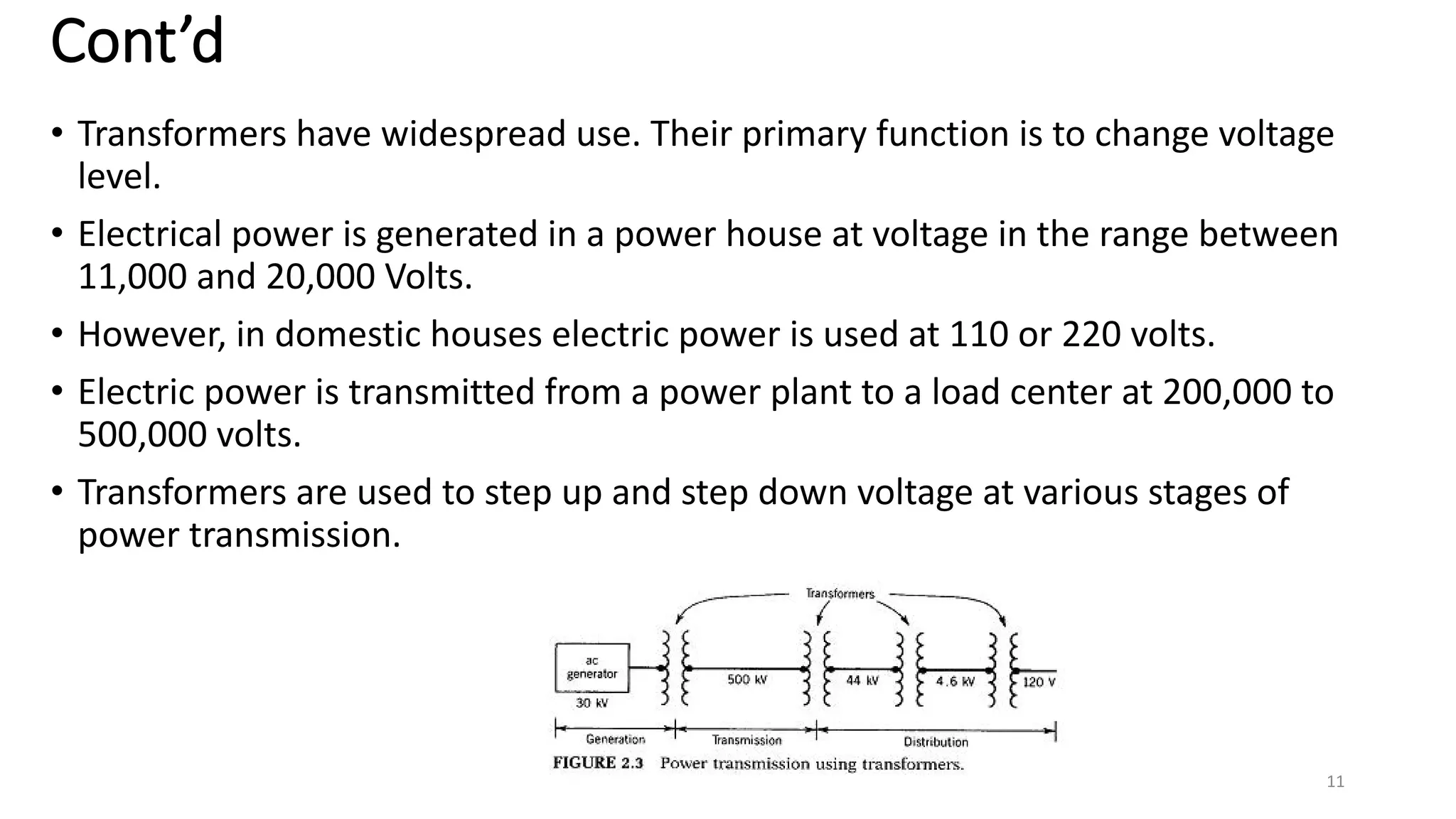
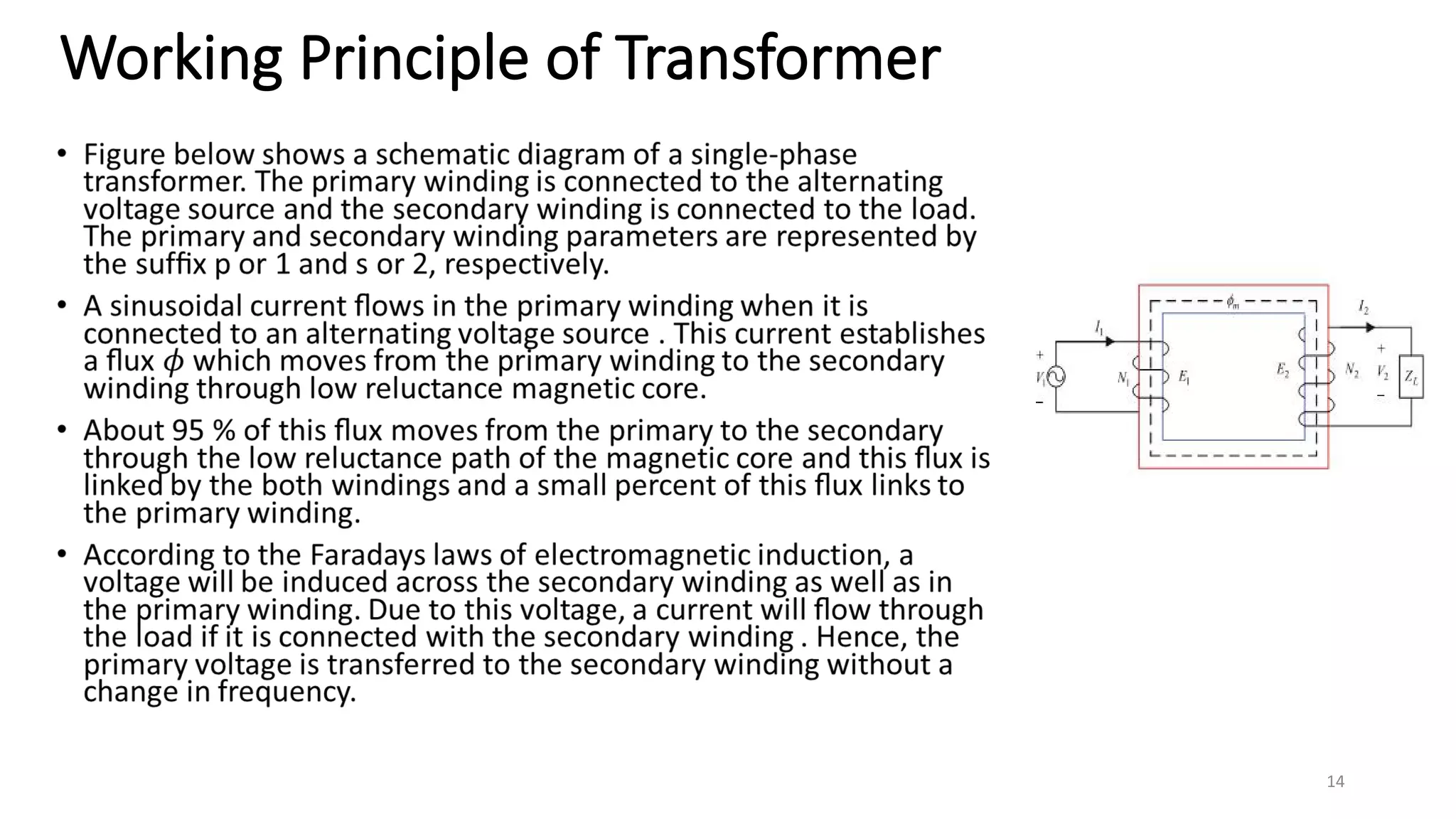
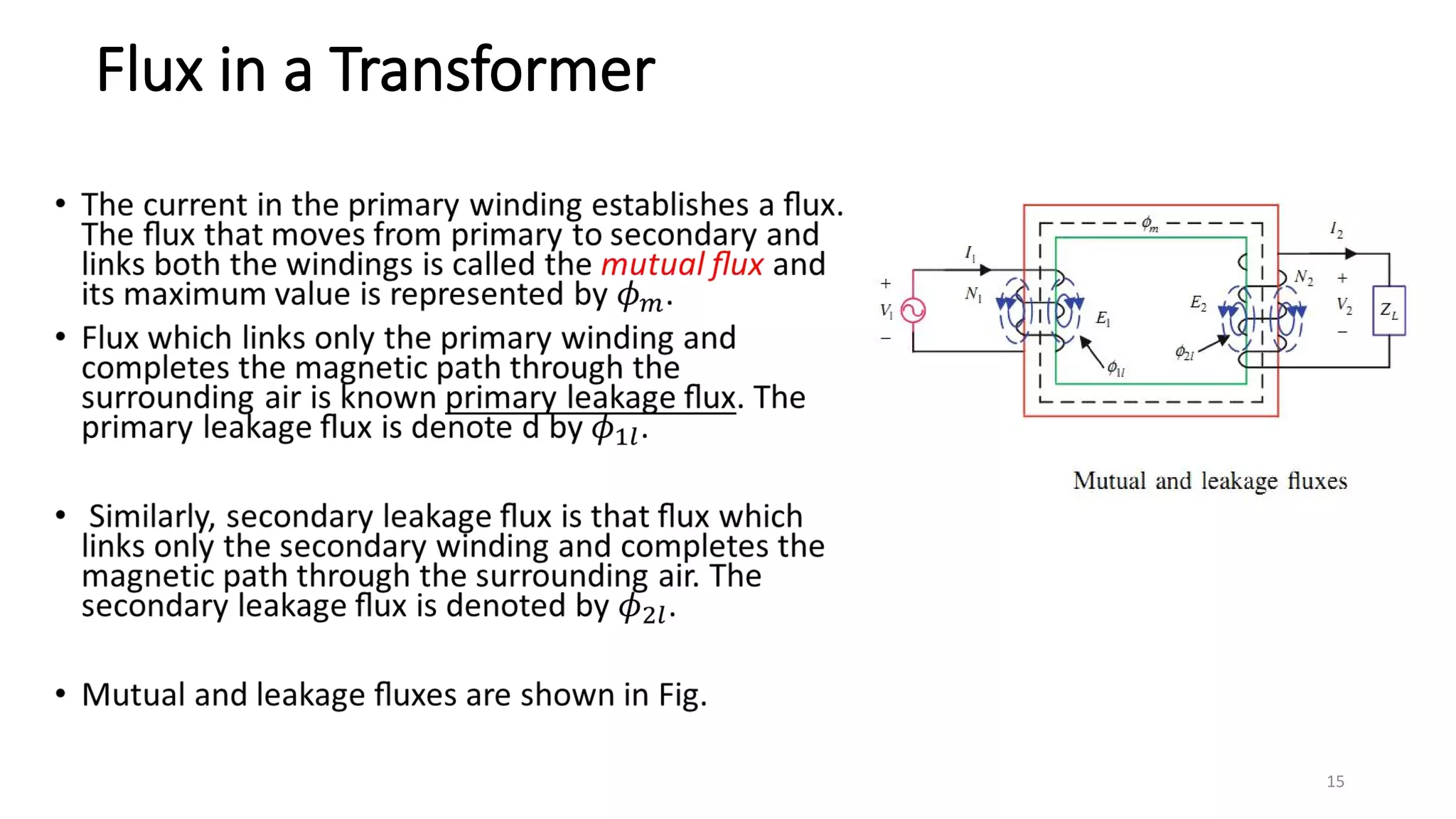
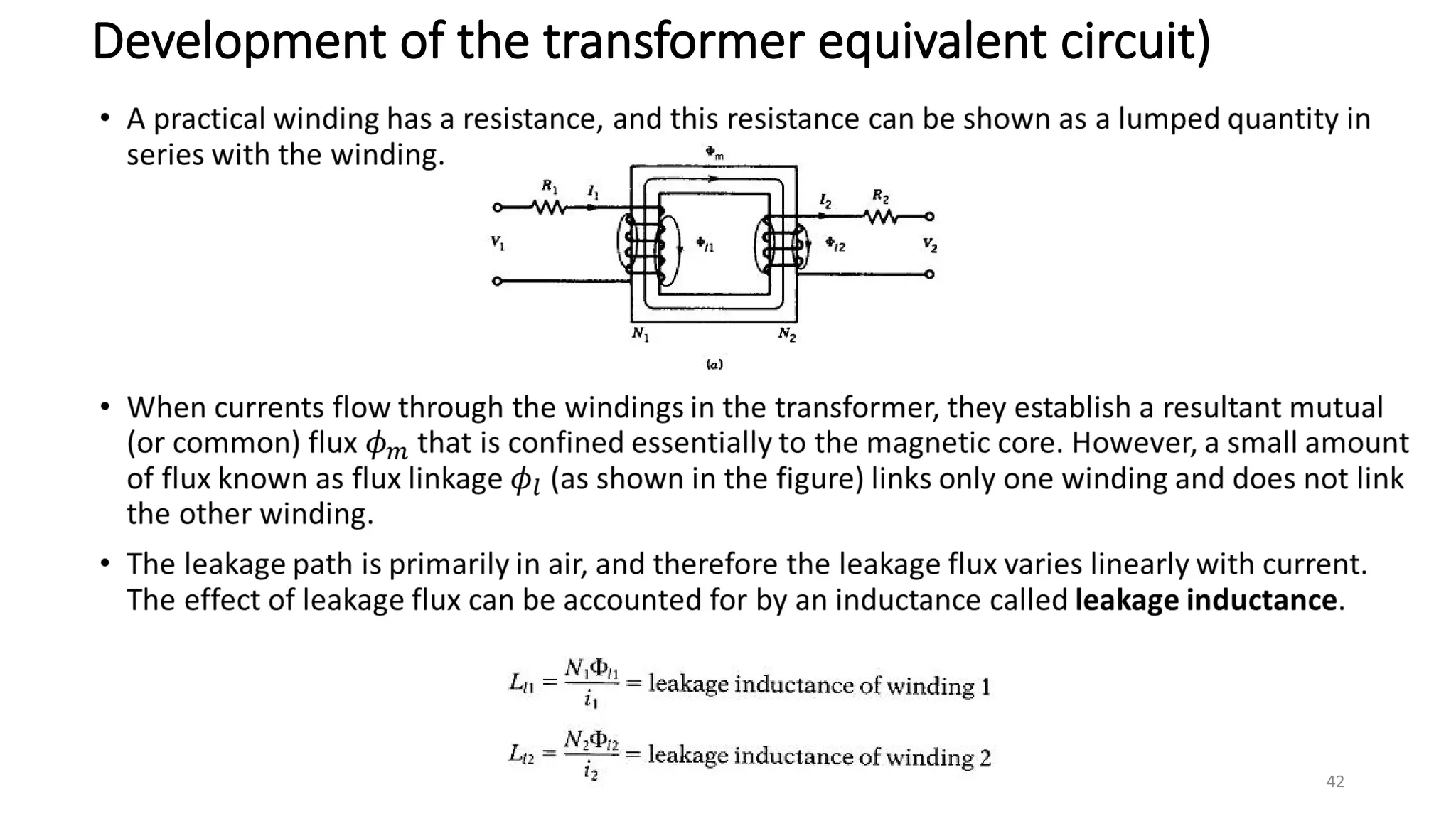
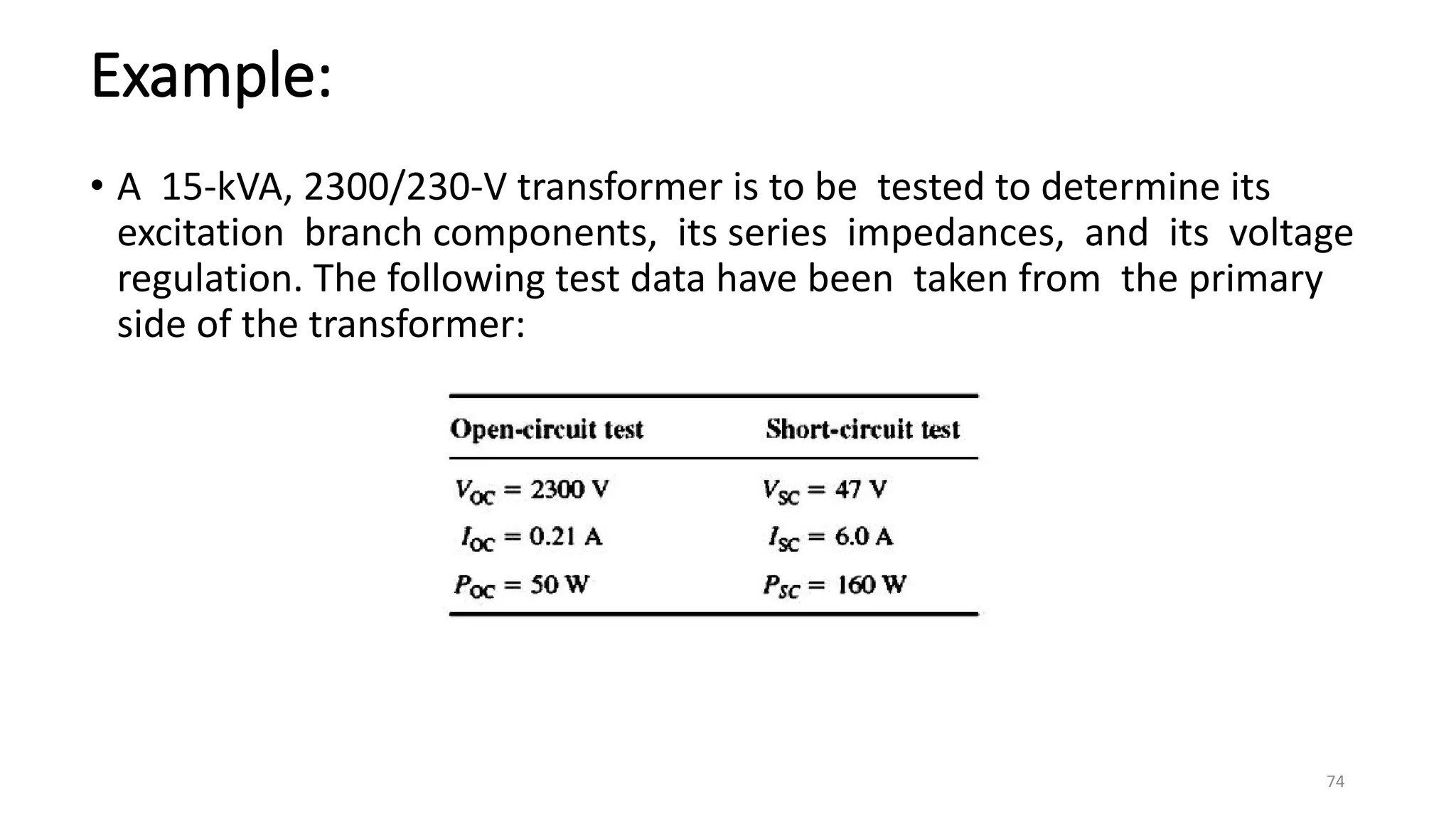
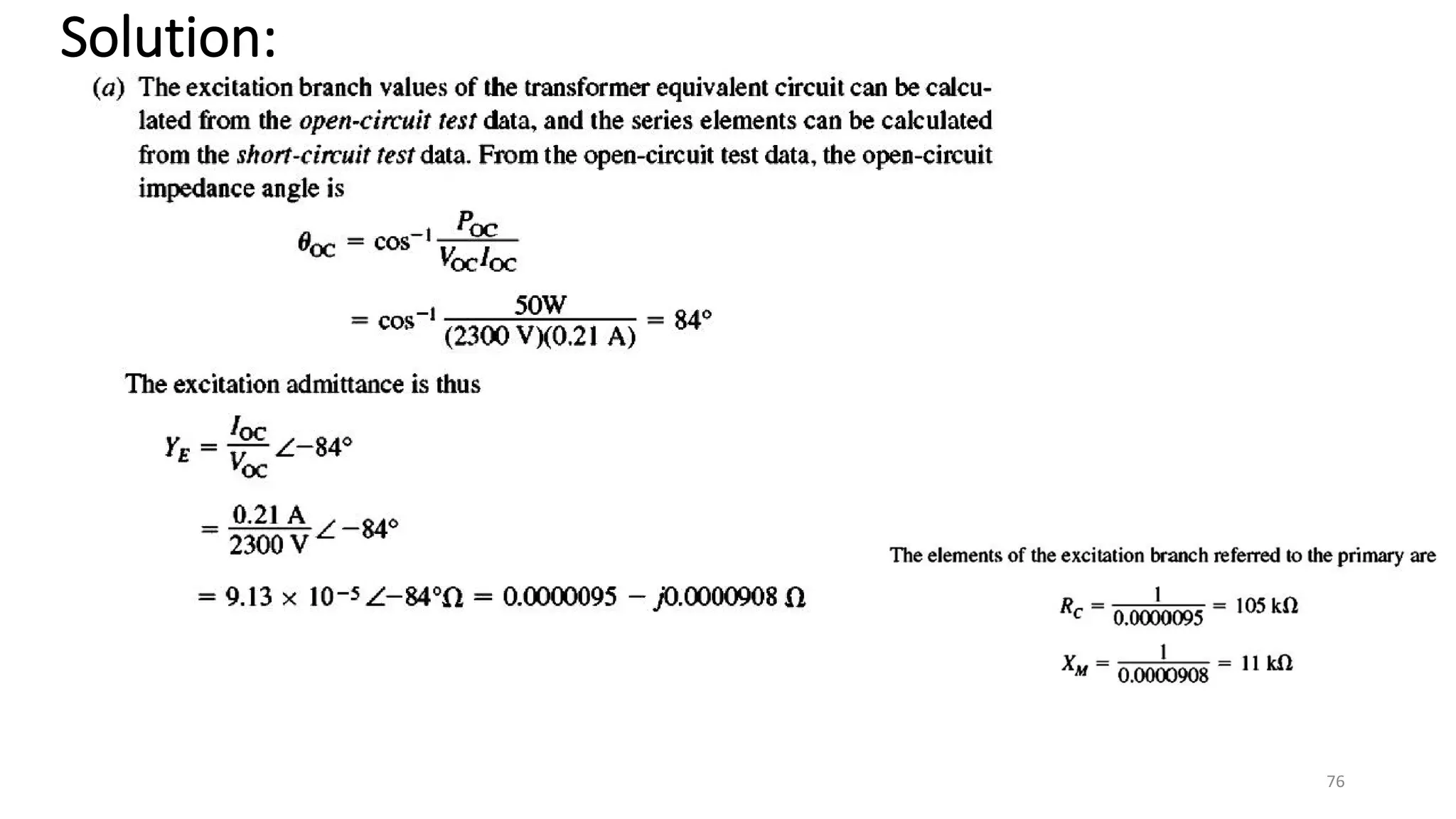
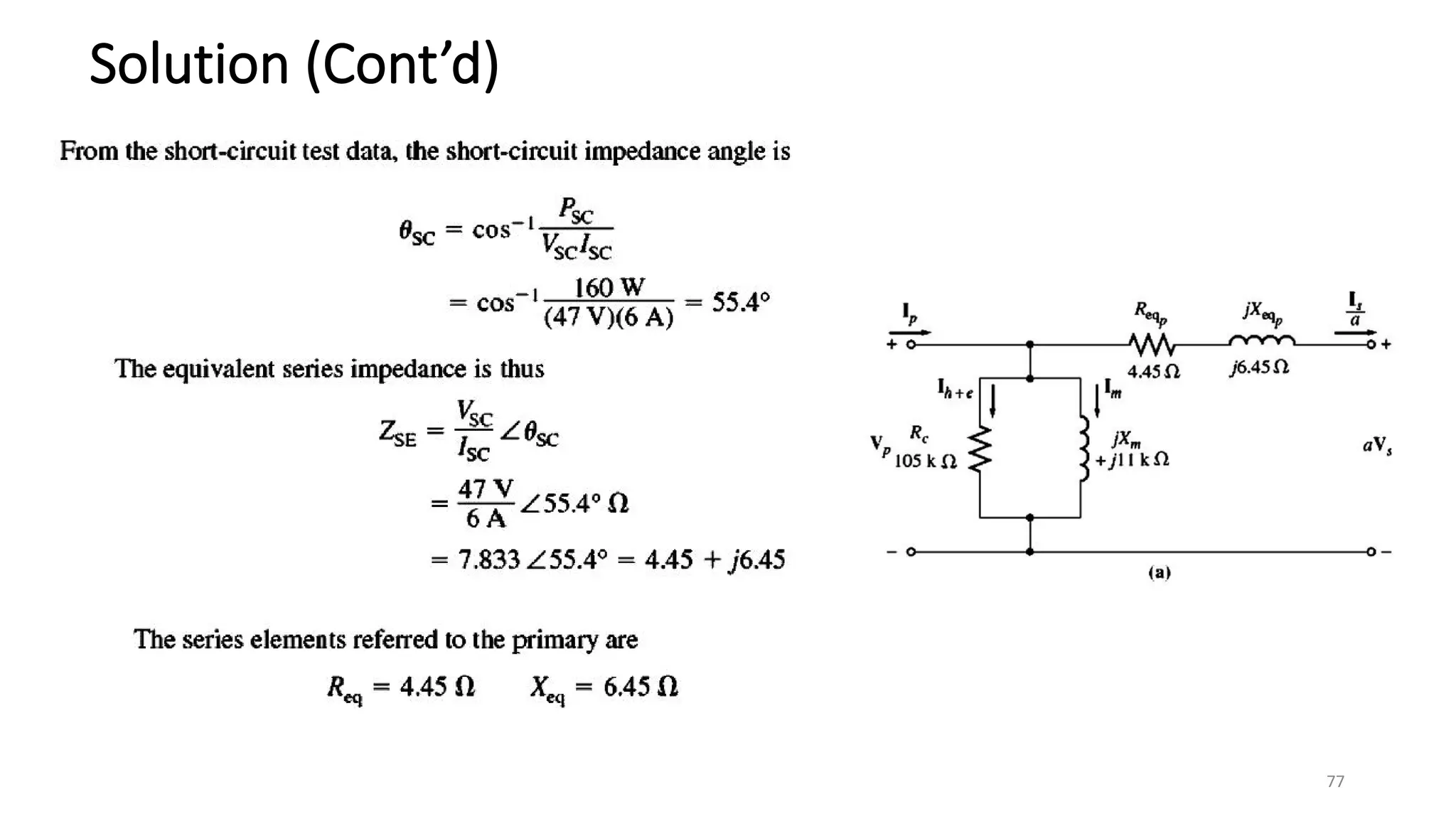
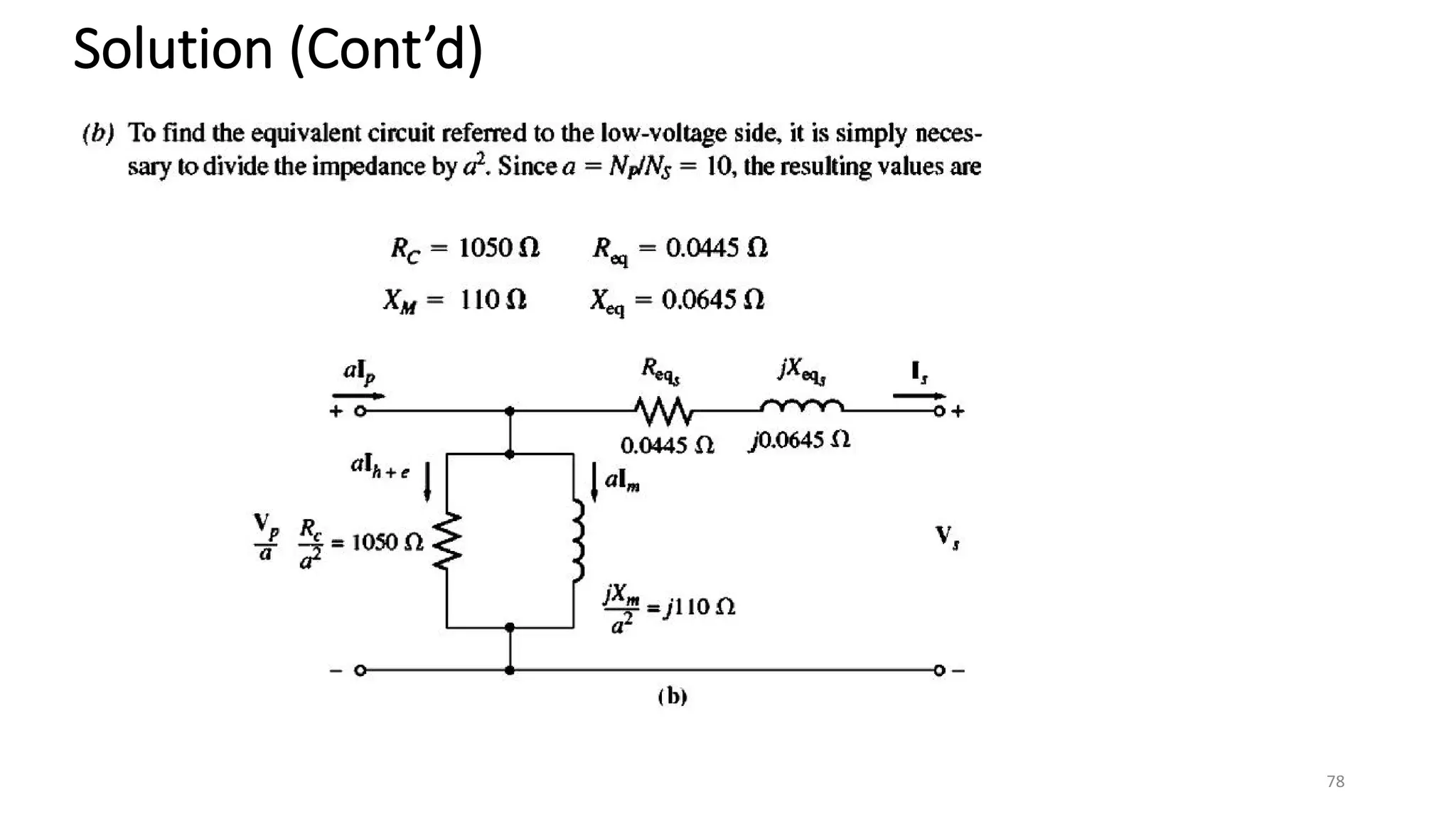
i. A transformer is a static electrical device that transfers energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. It consists of two or more coils wound around a core.
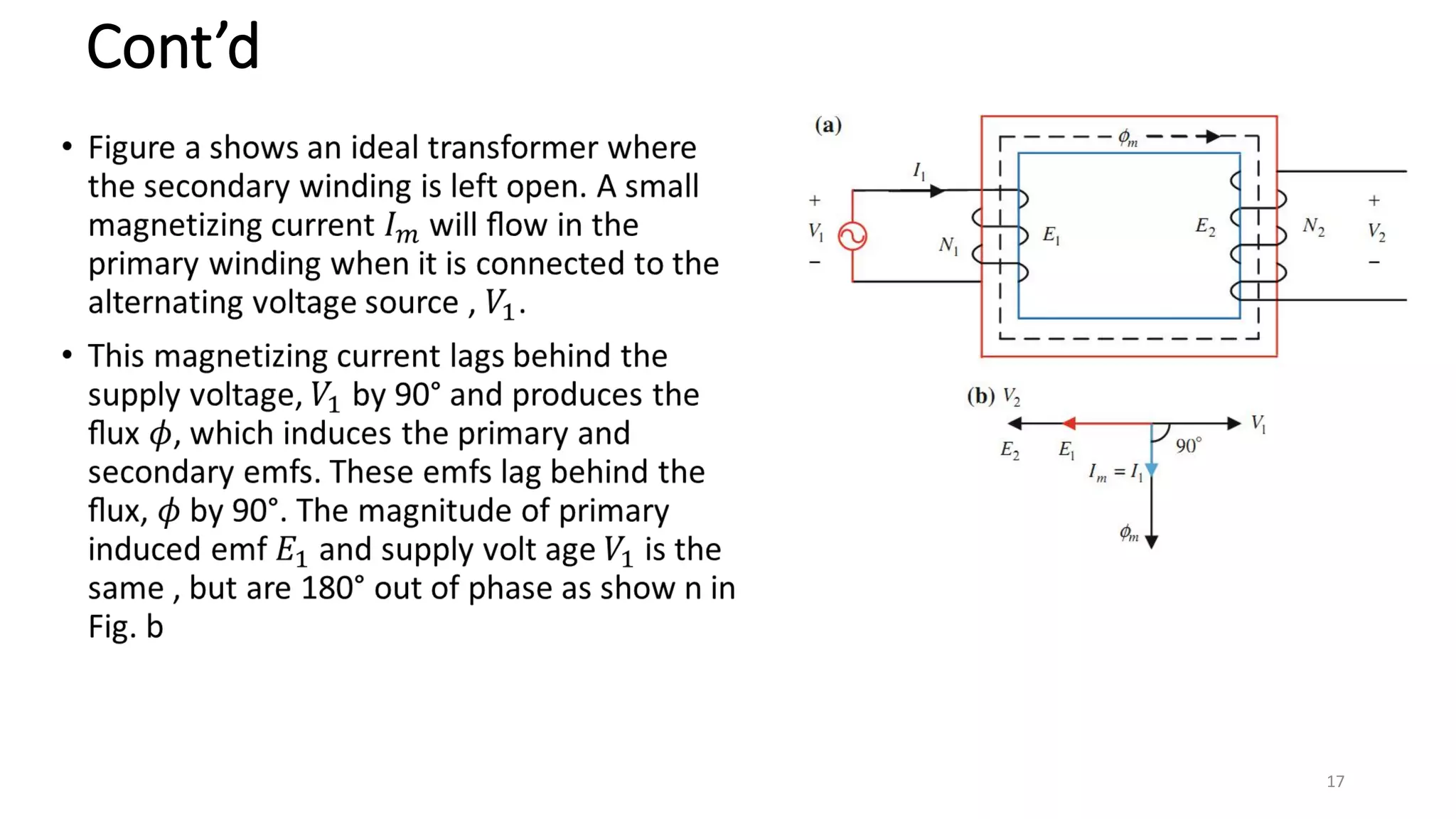
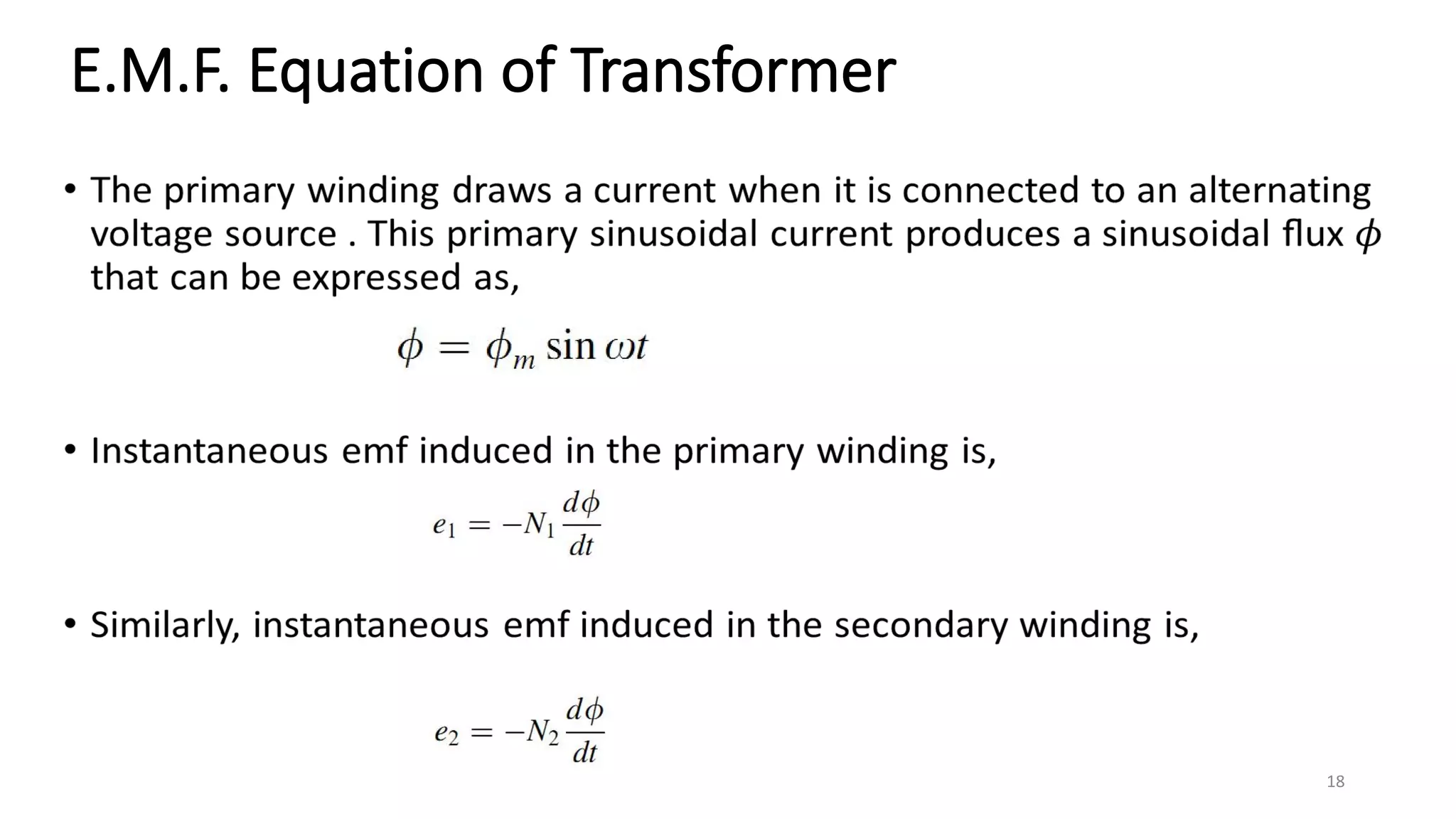
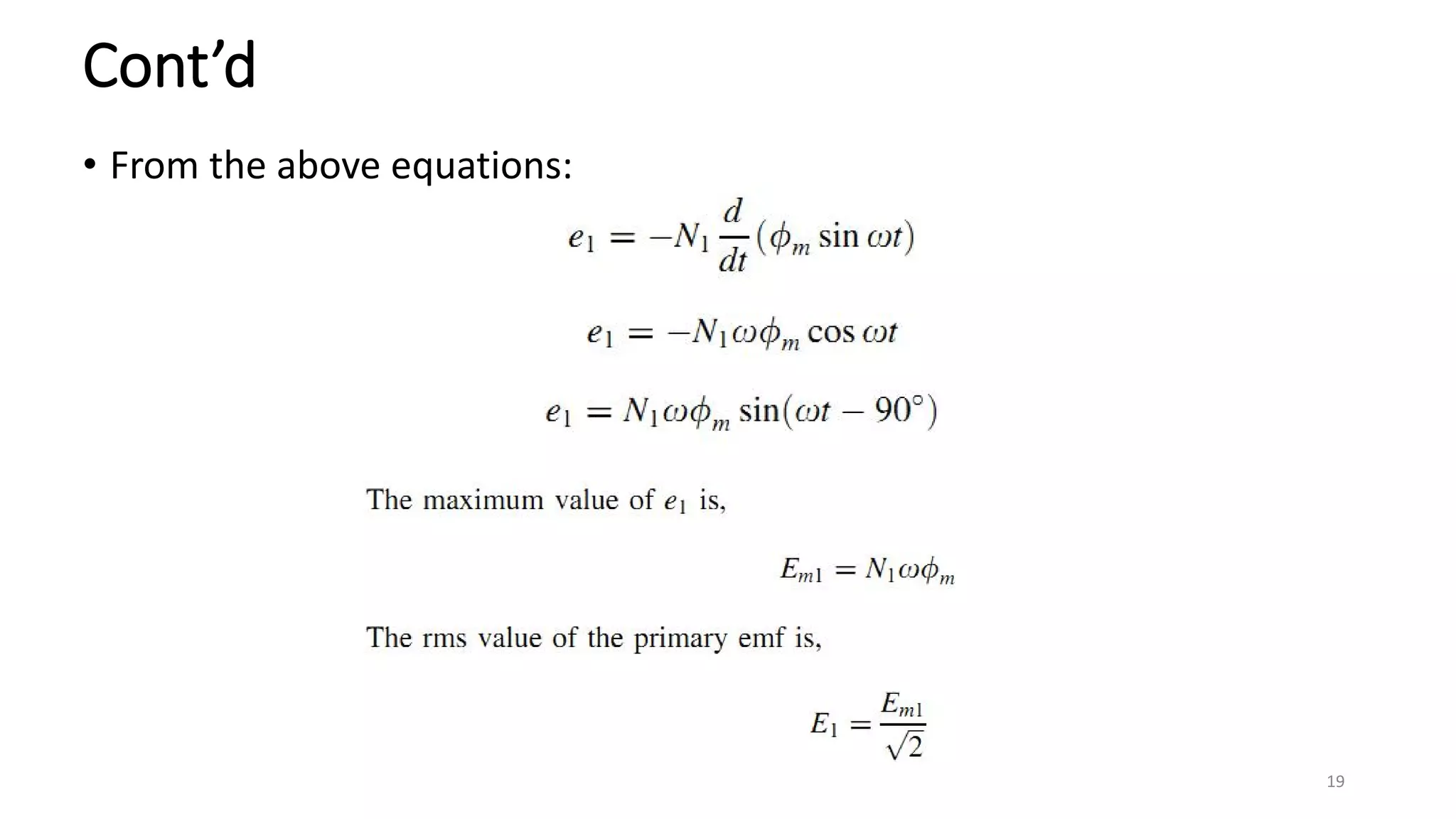
ii. Transformers operate based on mutual induction between the coils - a changing current in one coil produces a magnetic flux that induces a voltage in the other coil. This allows transformers to increase or decrease voltage levels while isolating the input and output circuits.
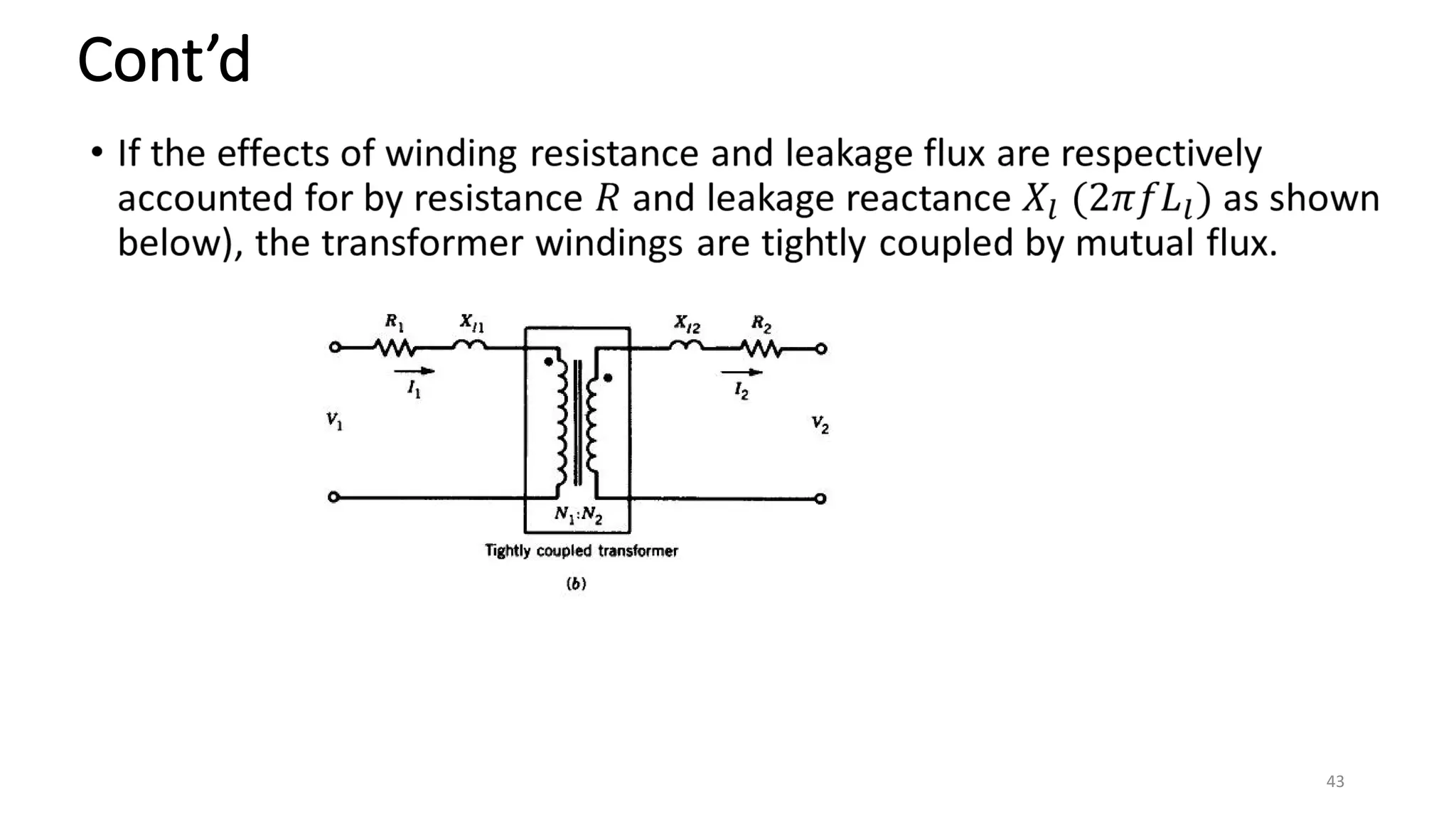
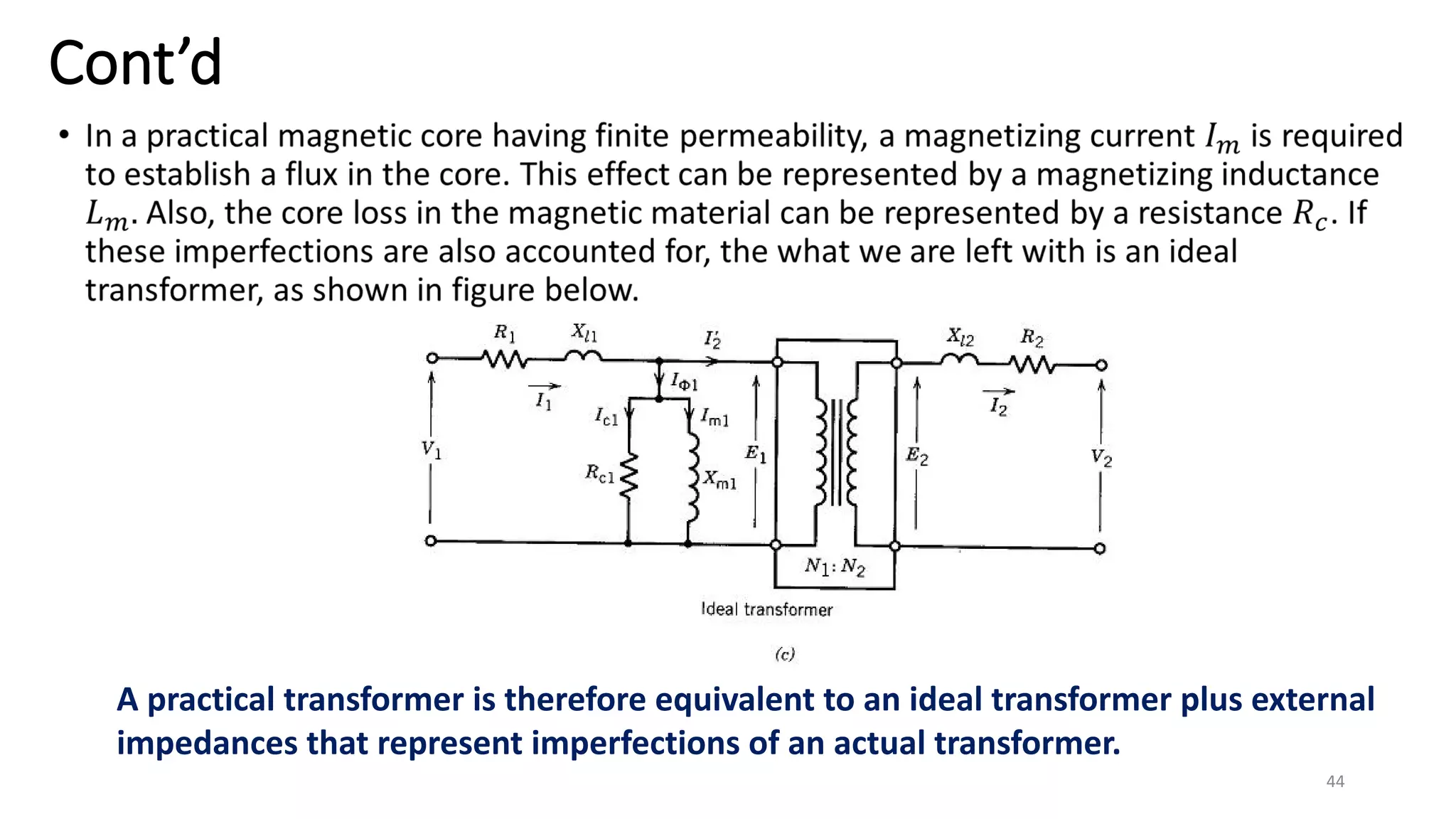
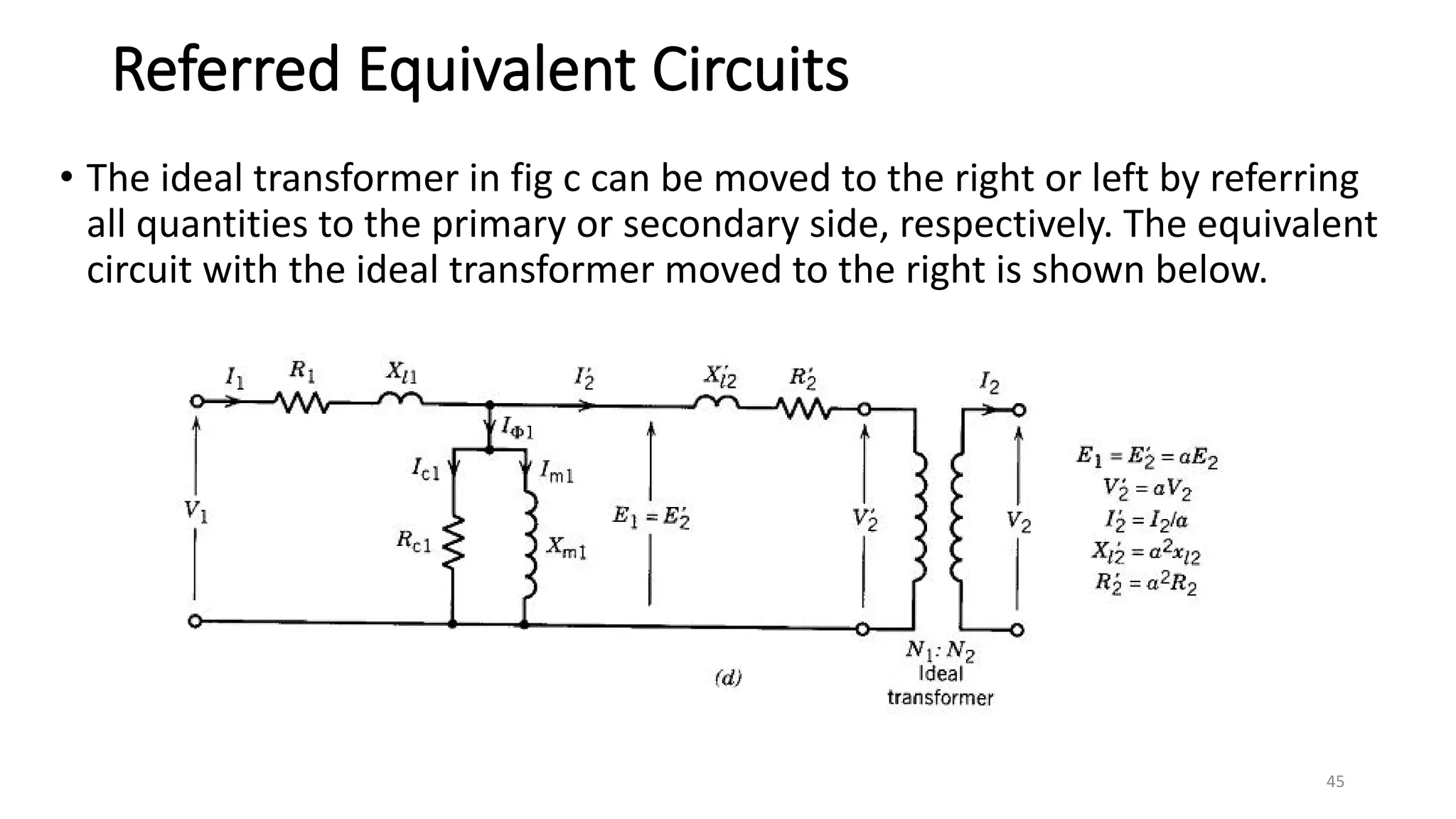
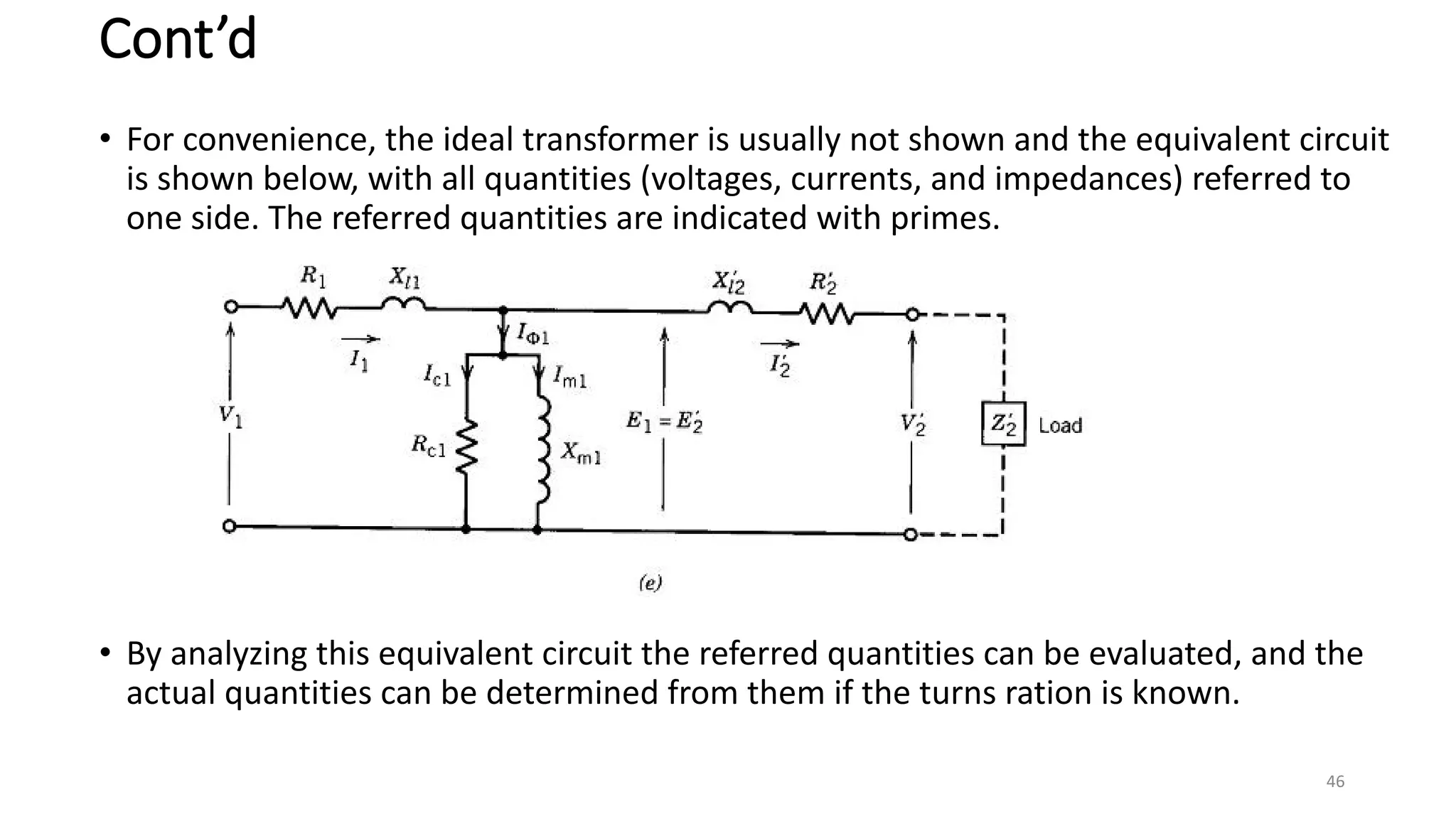
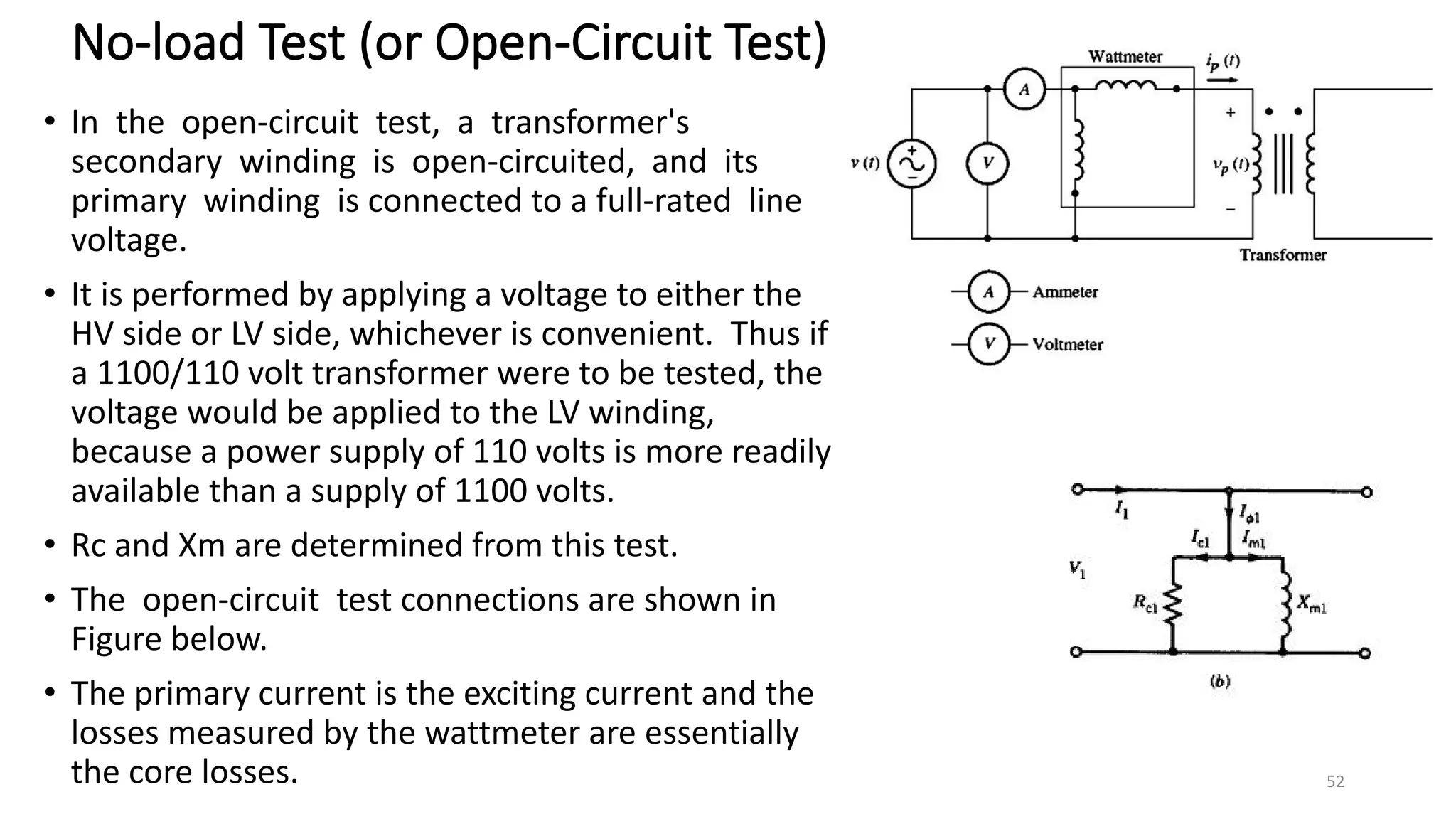
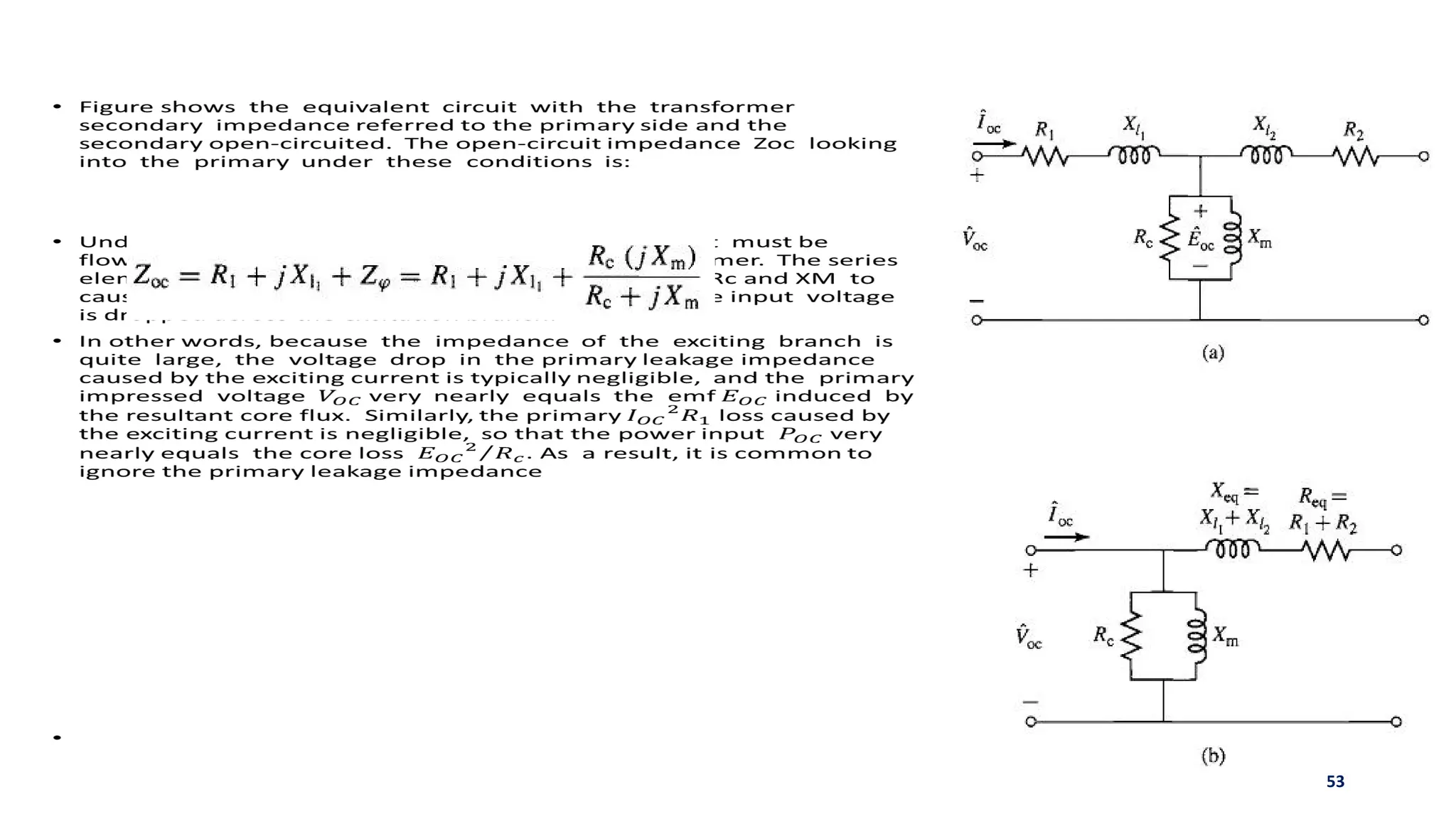
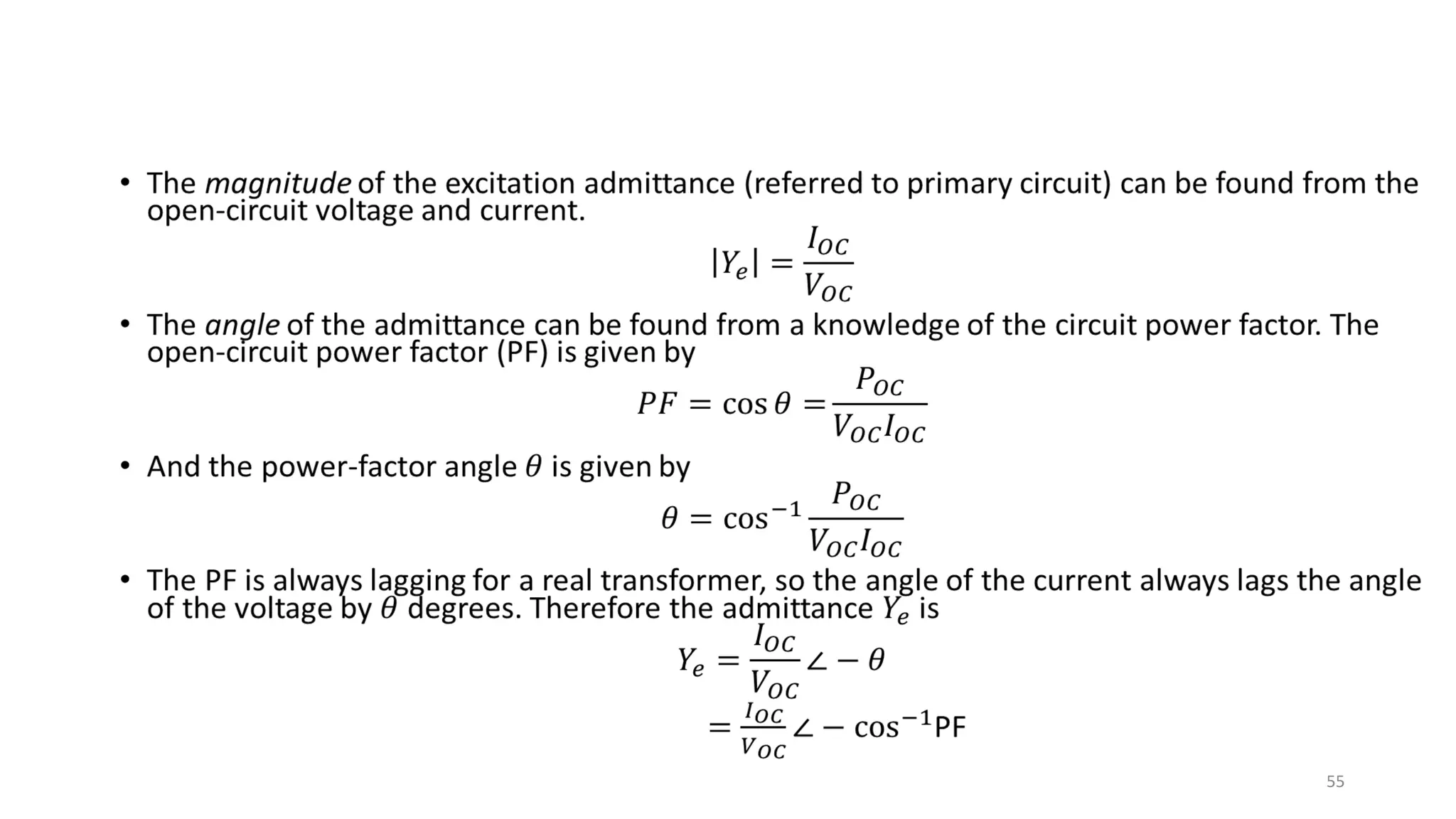
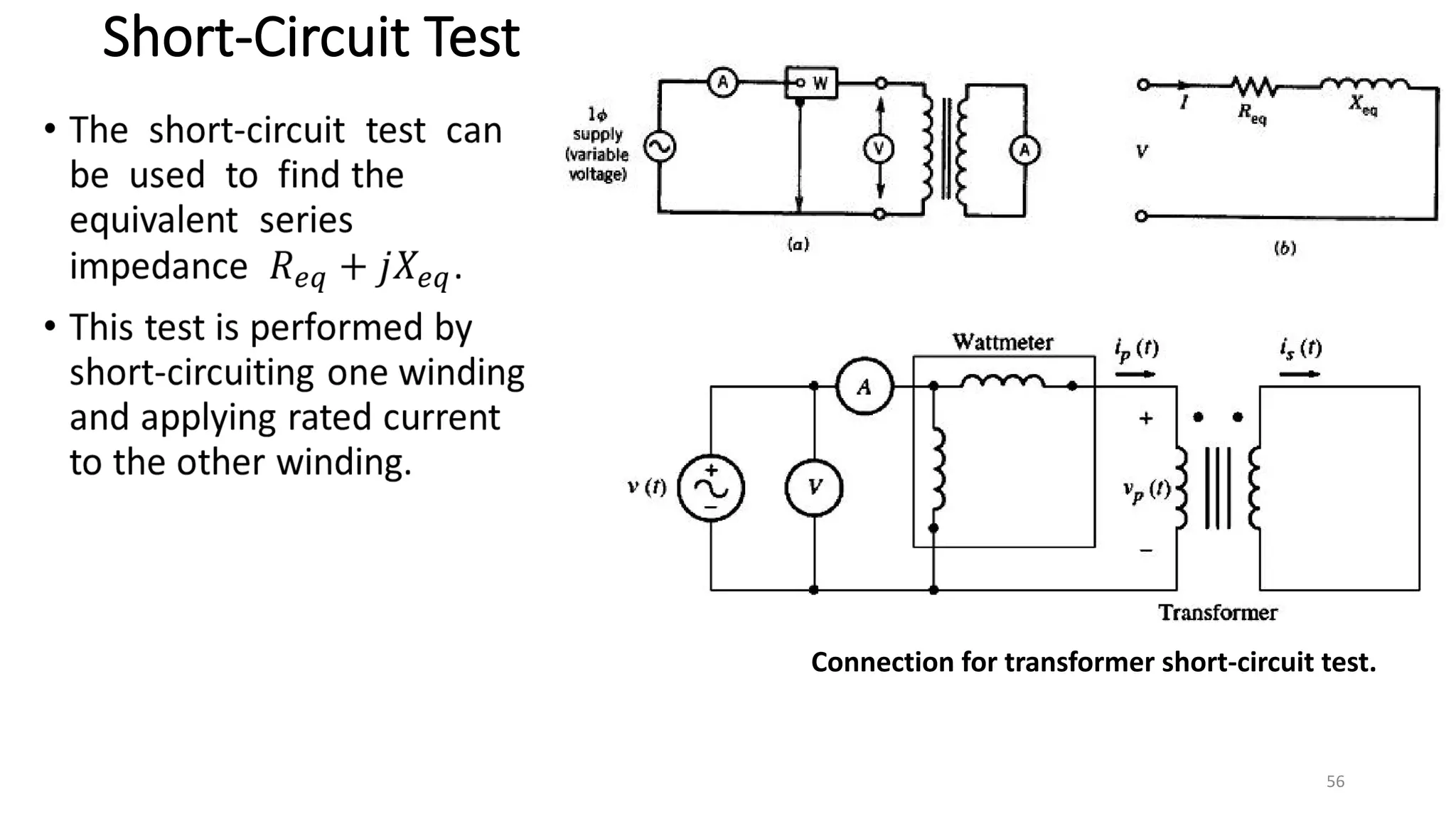
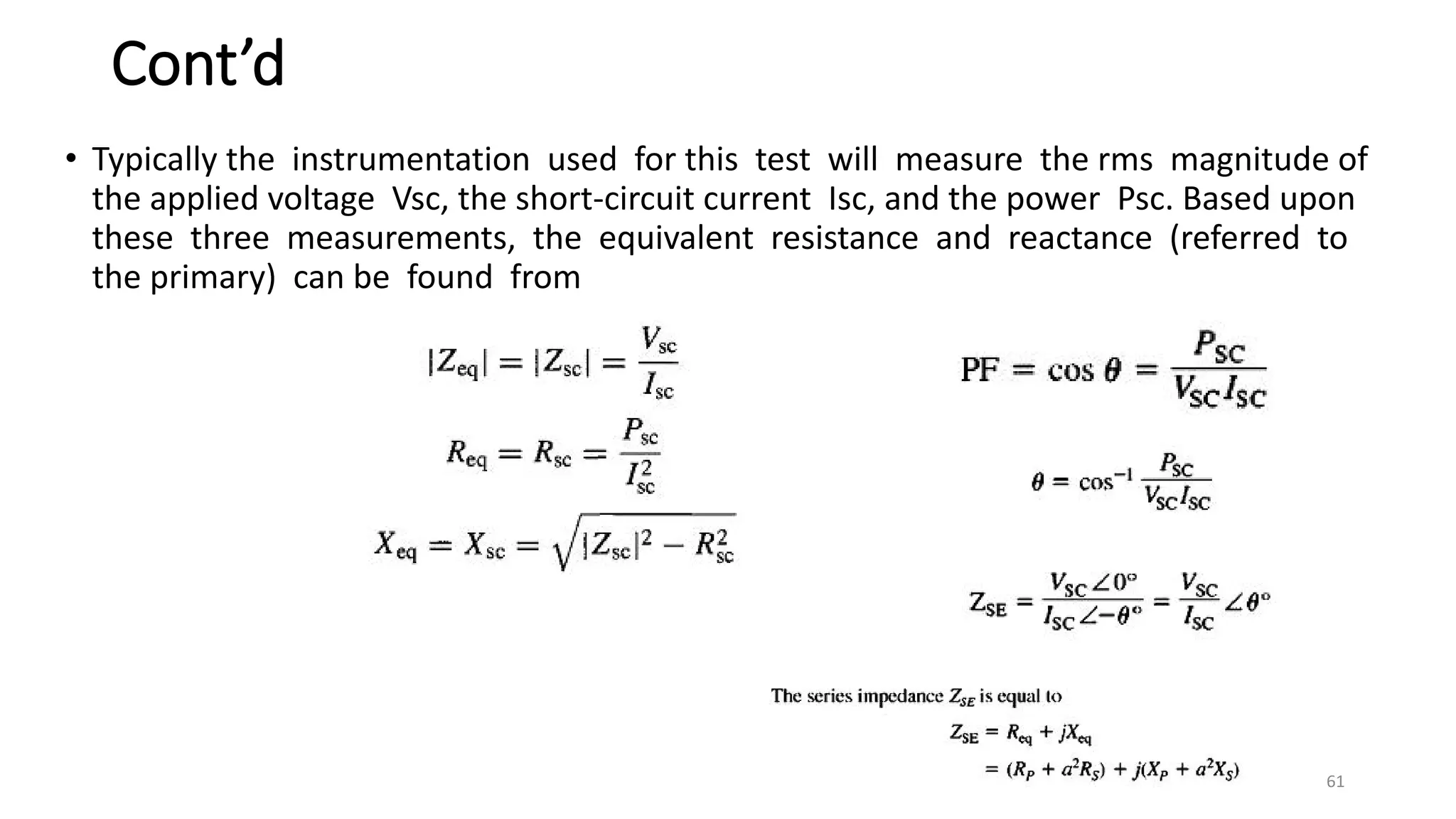
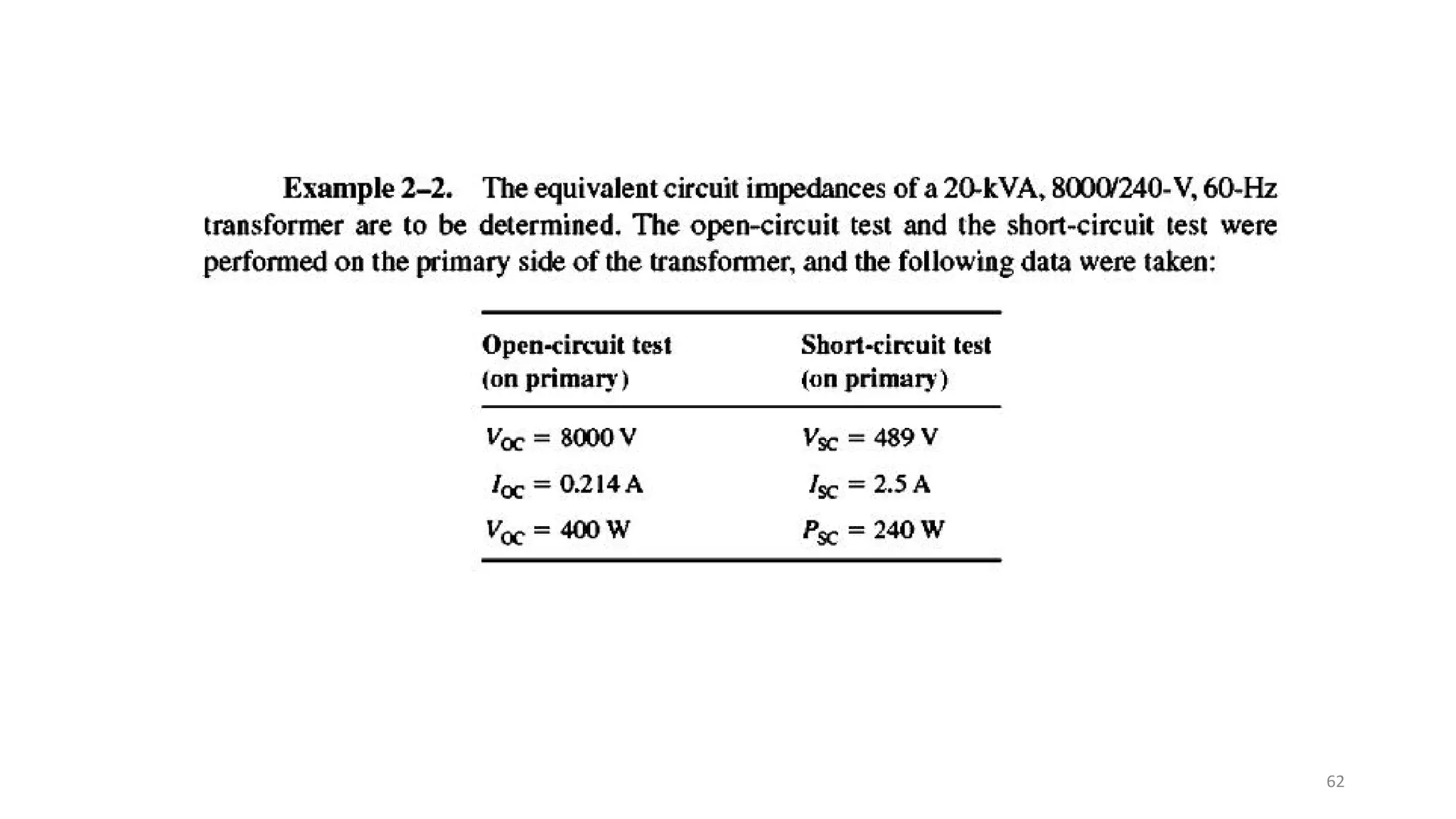
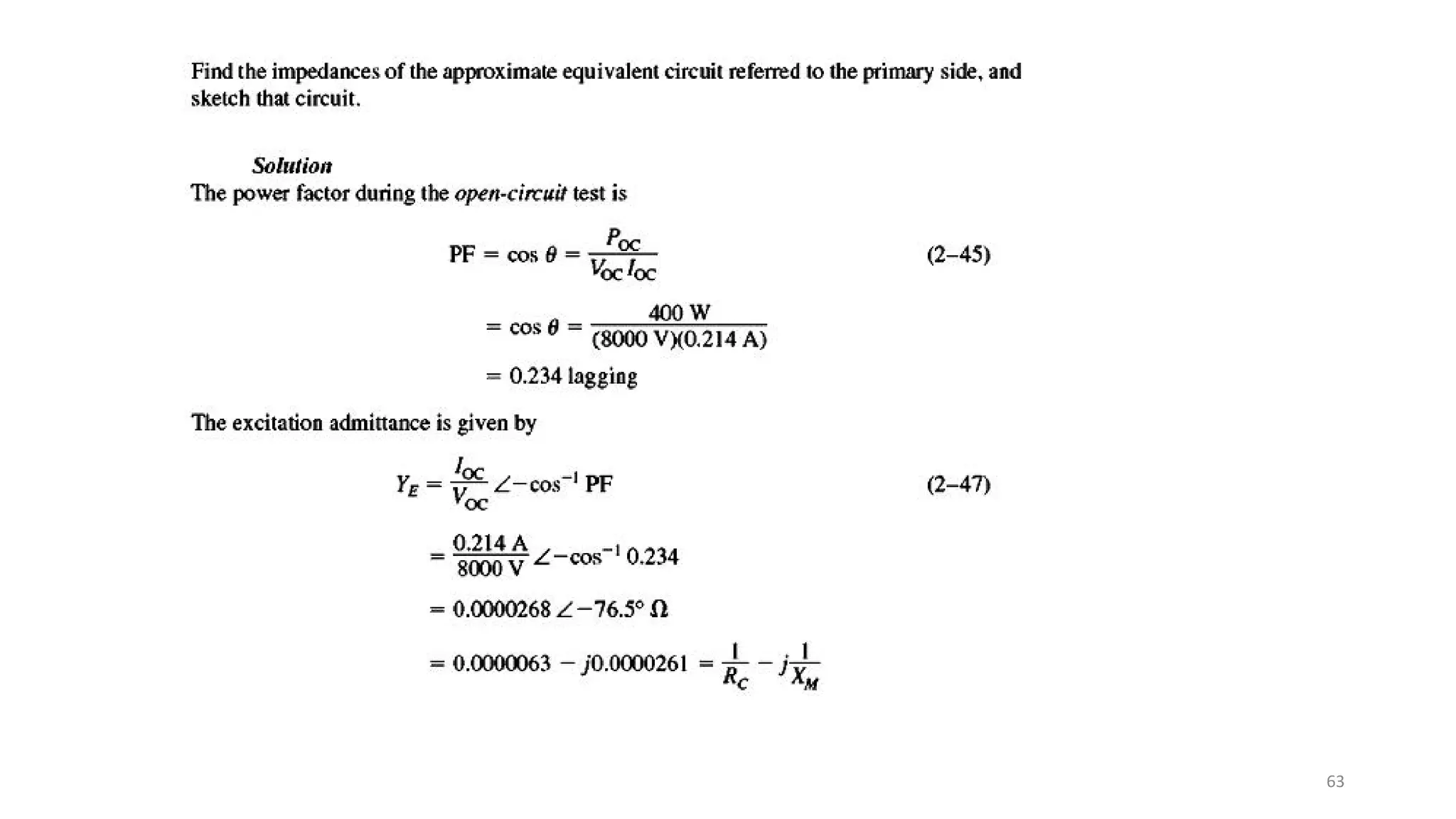
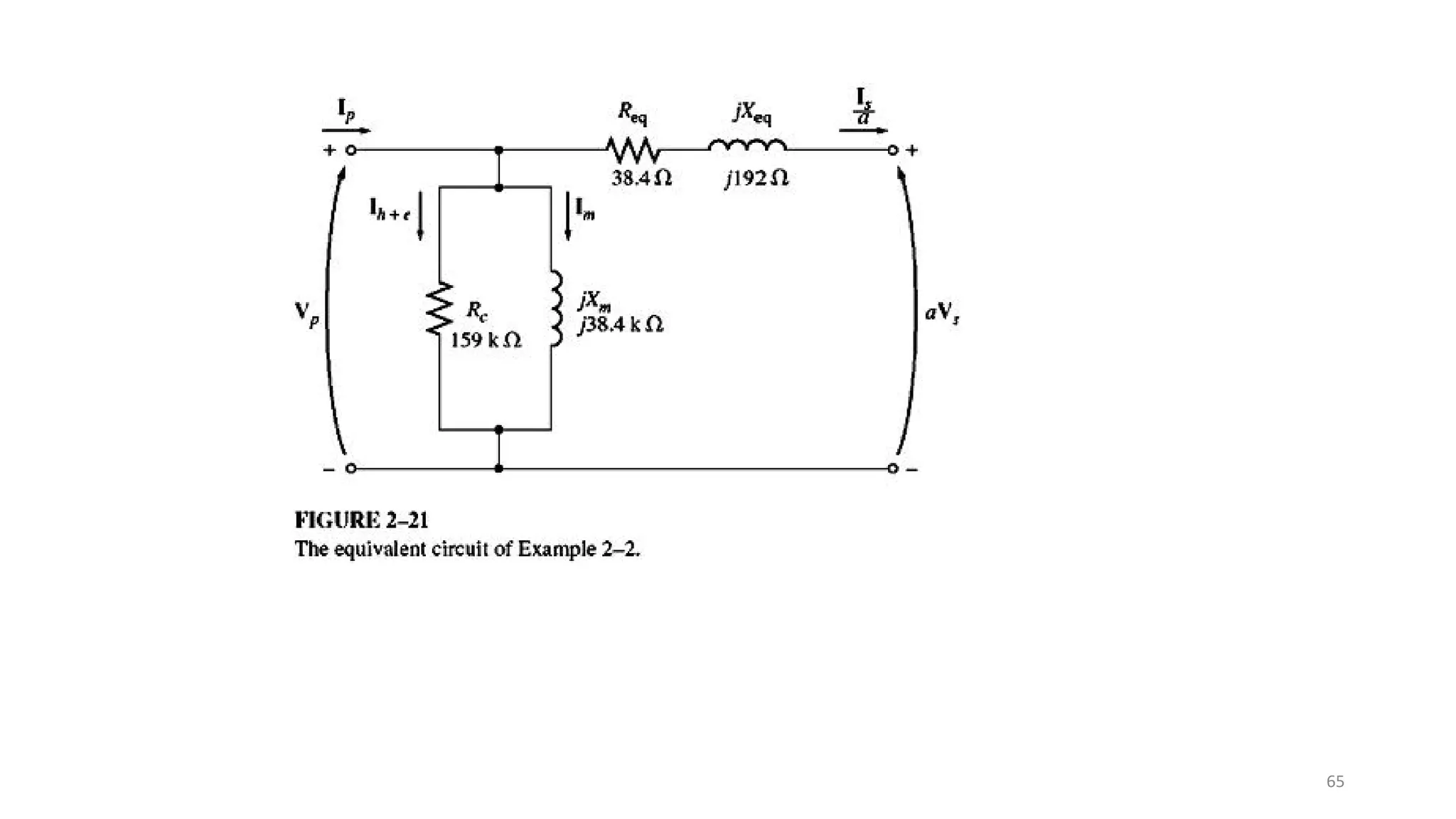
iii. The ideal transformer has no losses, but practical transformers have resistances that cause heating losses. Short-circuit and no-load tests are used to determine a transformer's equivalent circuit parameters and efficiency.