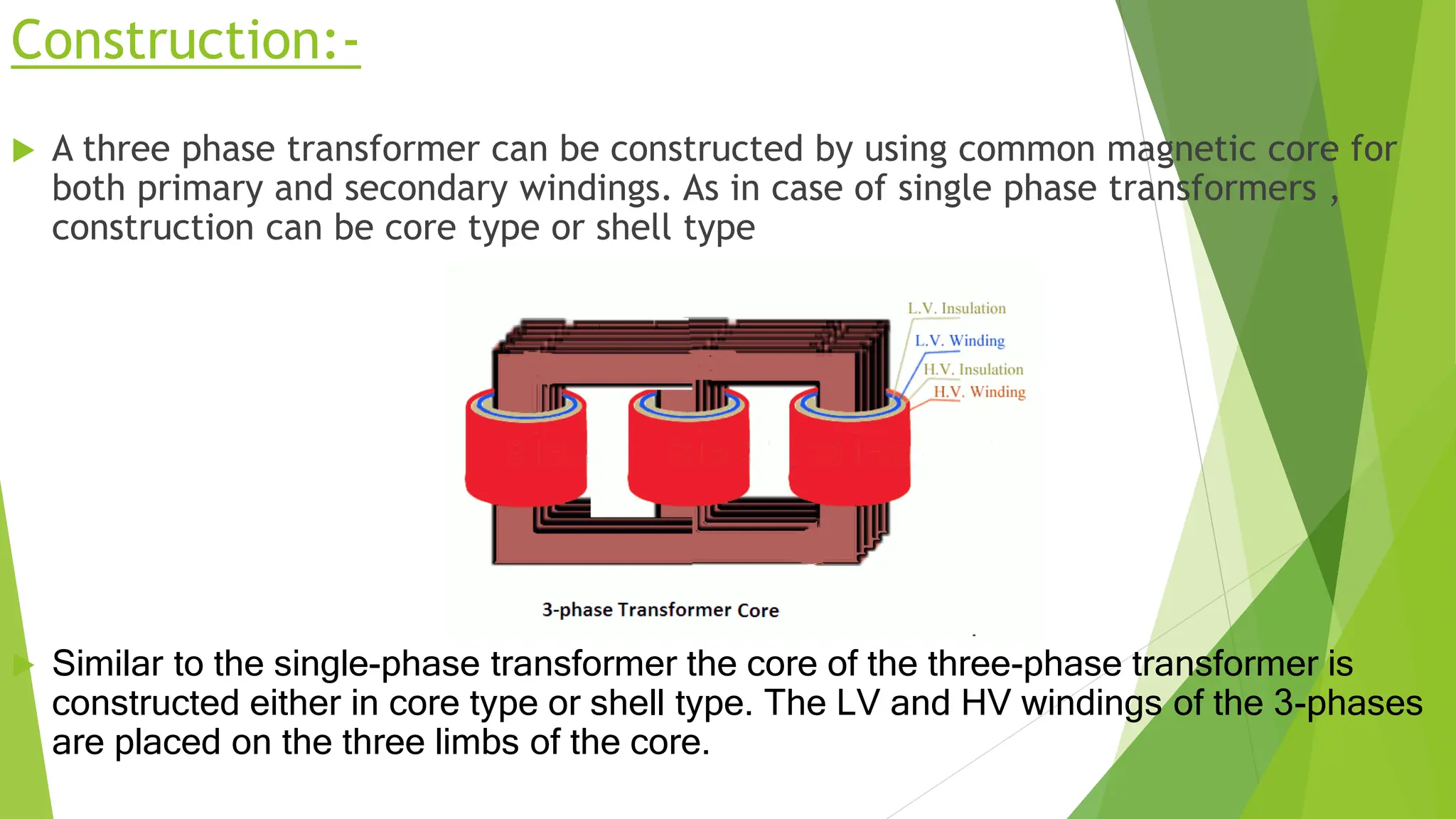
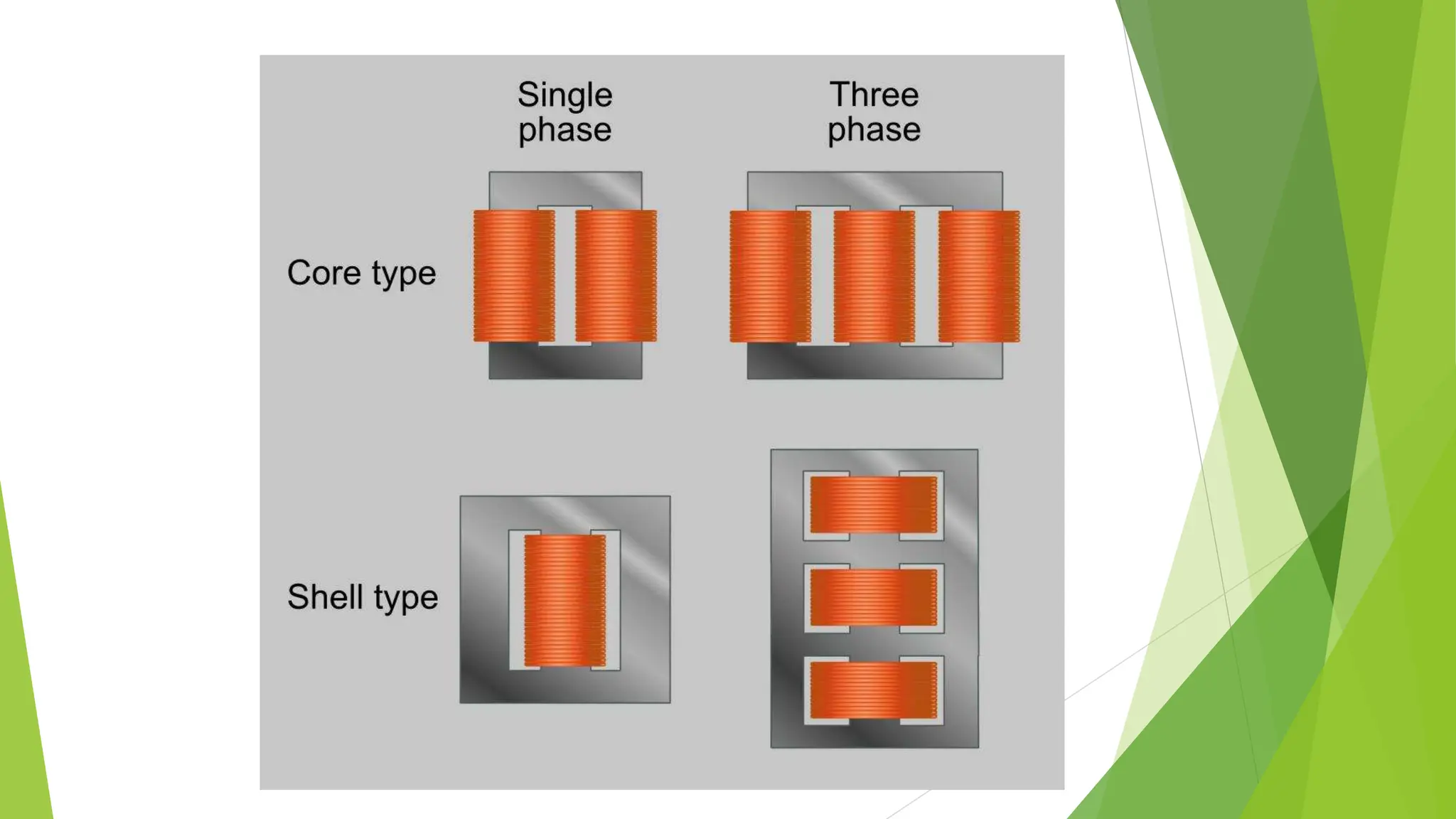
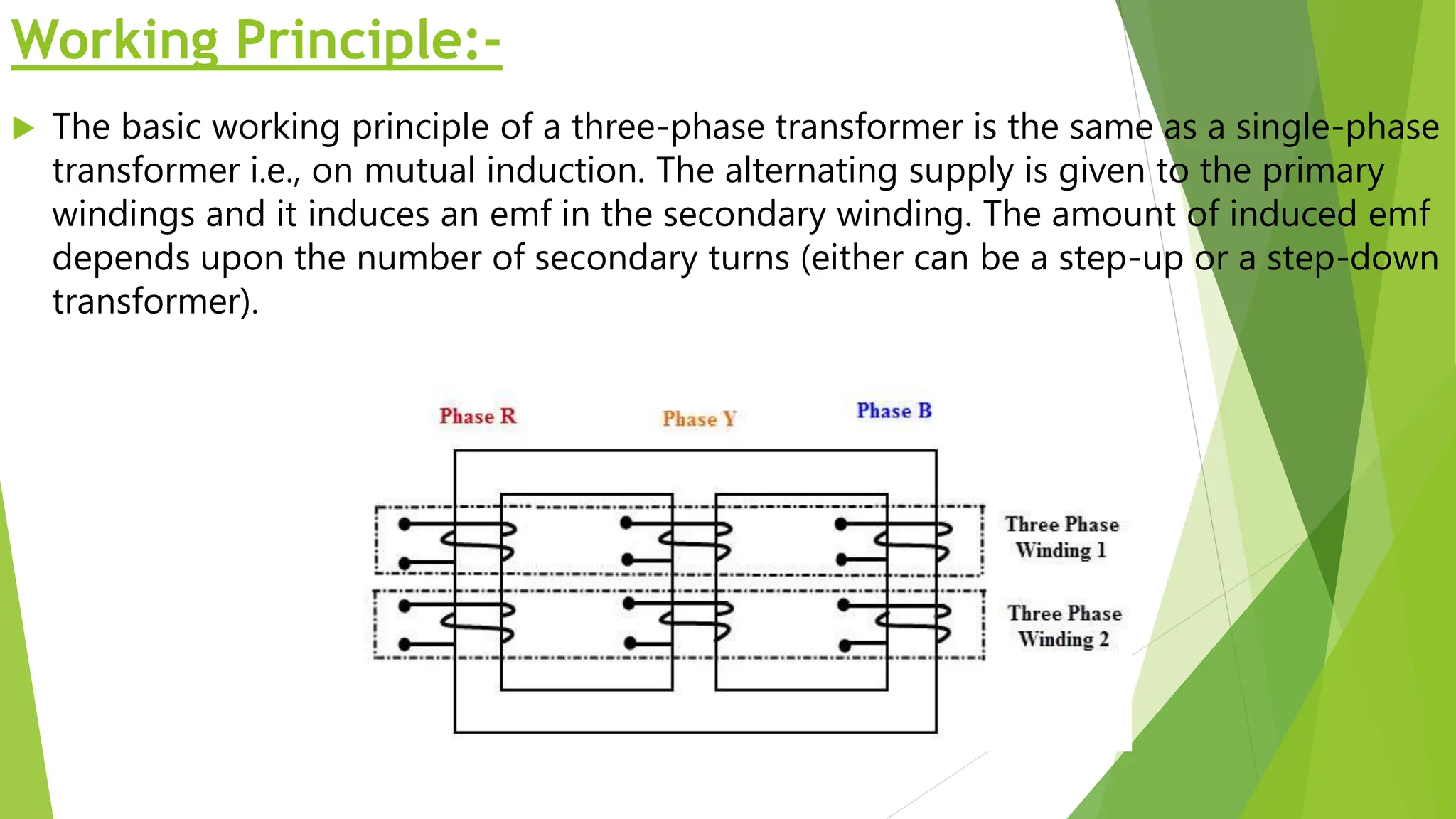
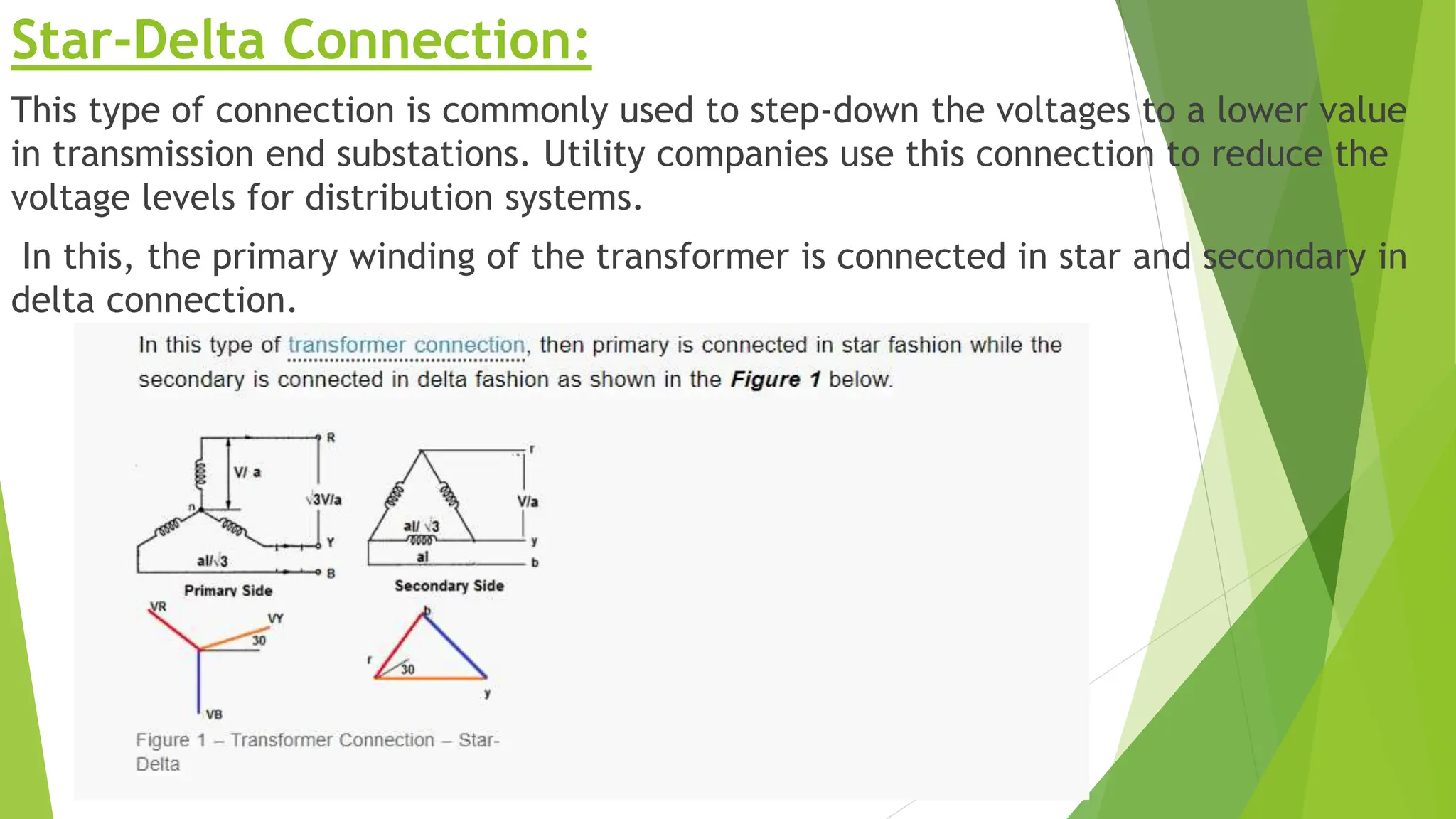
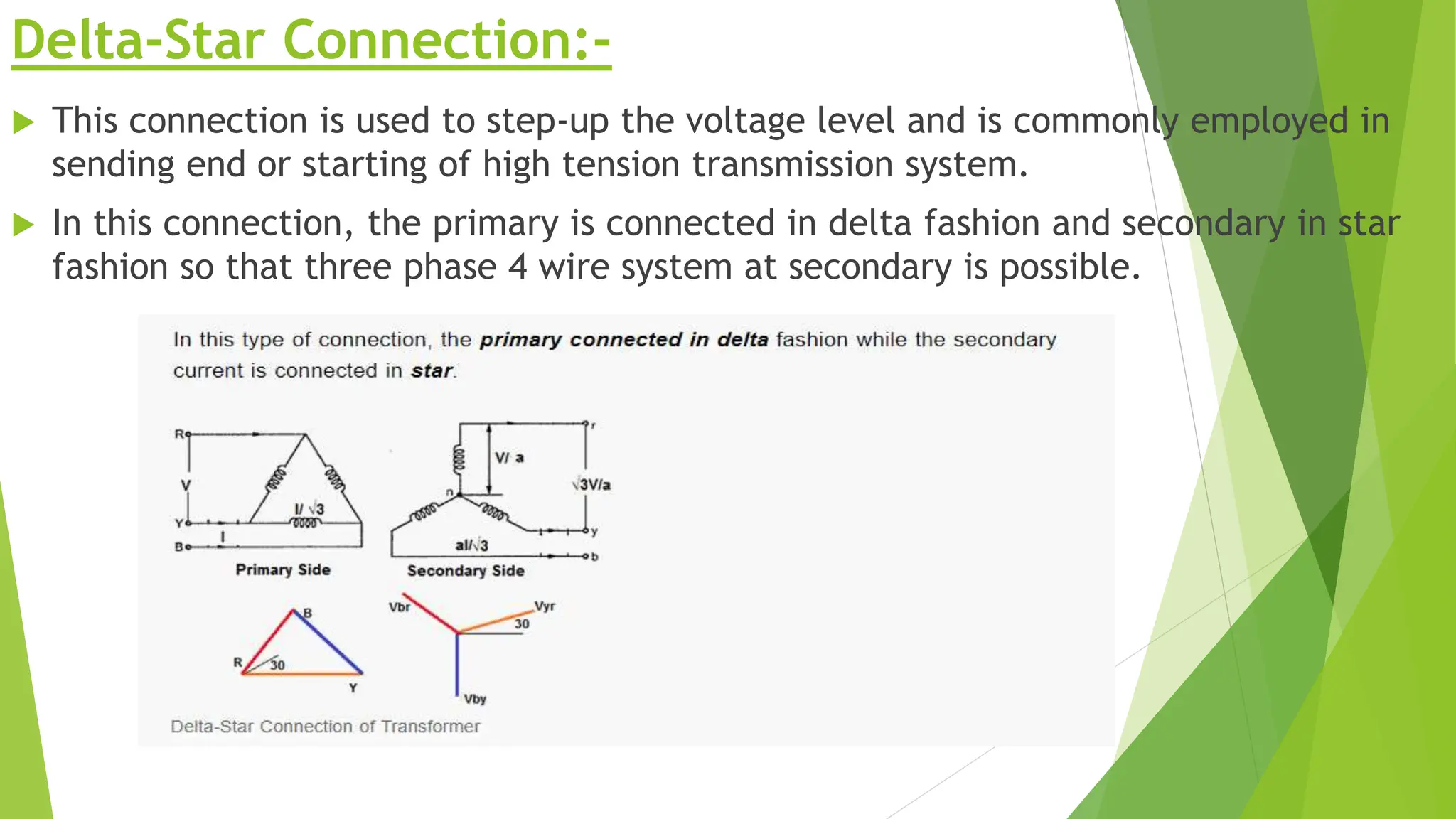
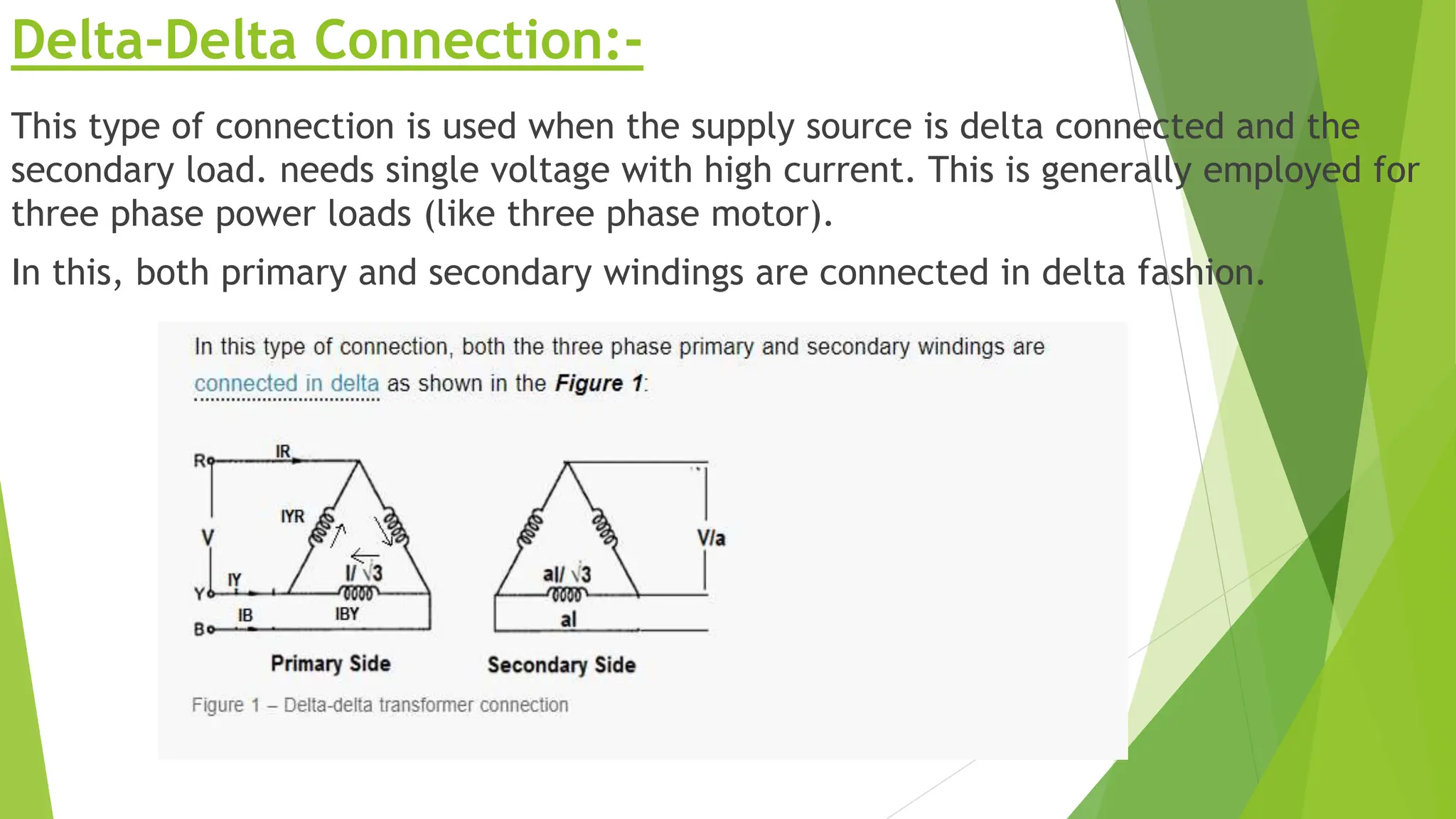
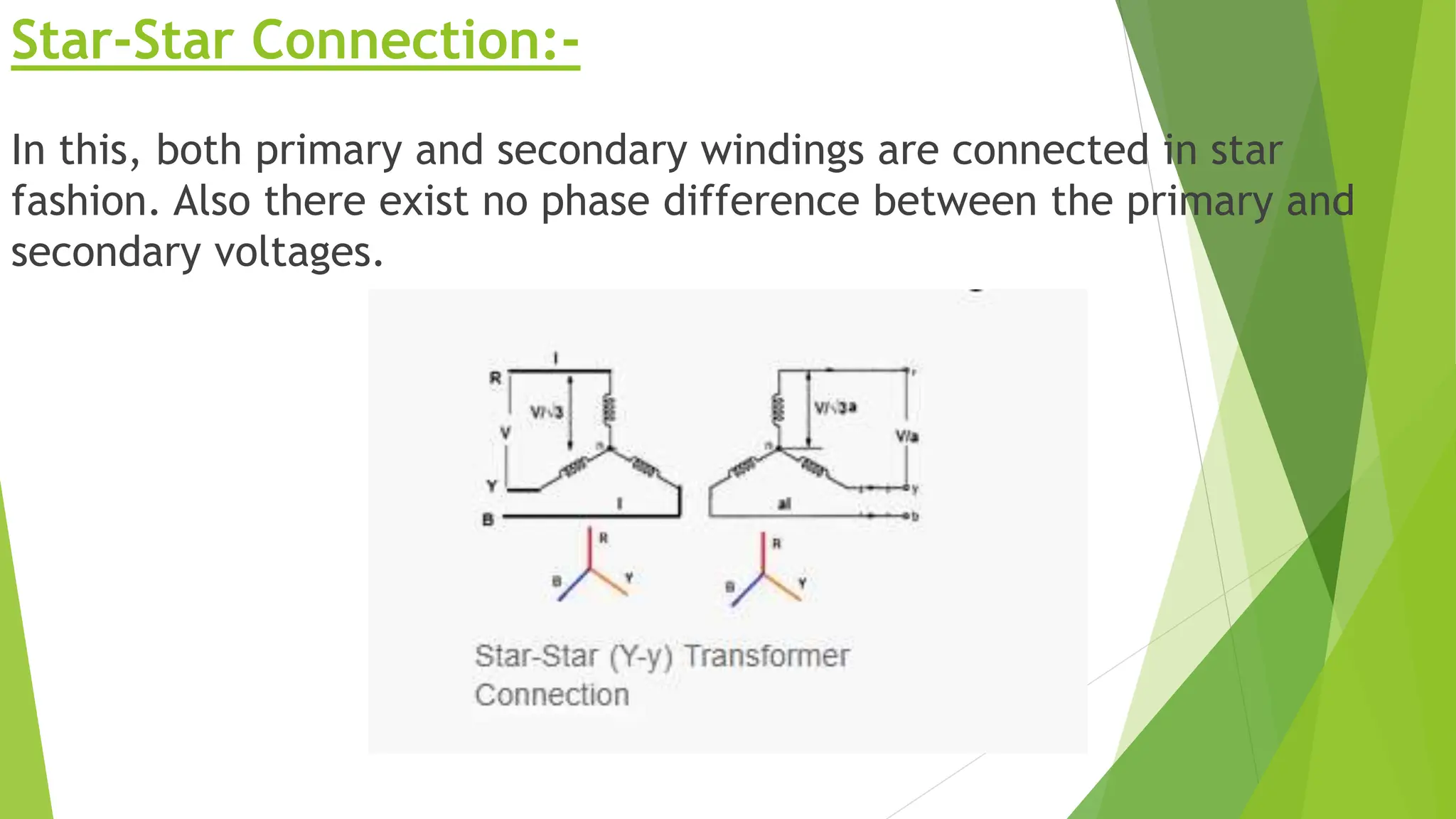
Three phase transformers are used to efficiently transmit power in three phase power systems. They have three coils on a single magnetic core that allow power to be transmitted at higher voltages to reduce transmission losses. Three phase transformers can be constructed as either core type, with a single core and coils, or shell type, with separate cores for each phase. They are commonly used in power generation, transmission and industrial applications to transform voltages for distribution or motor loads.