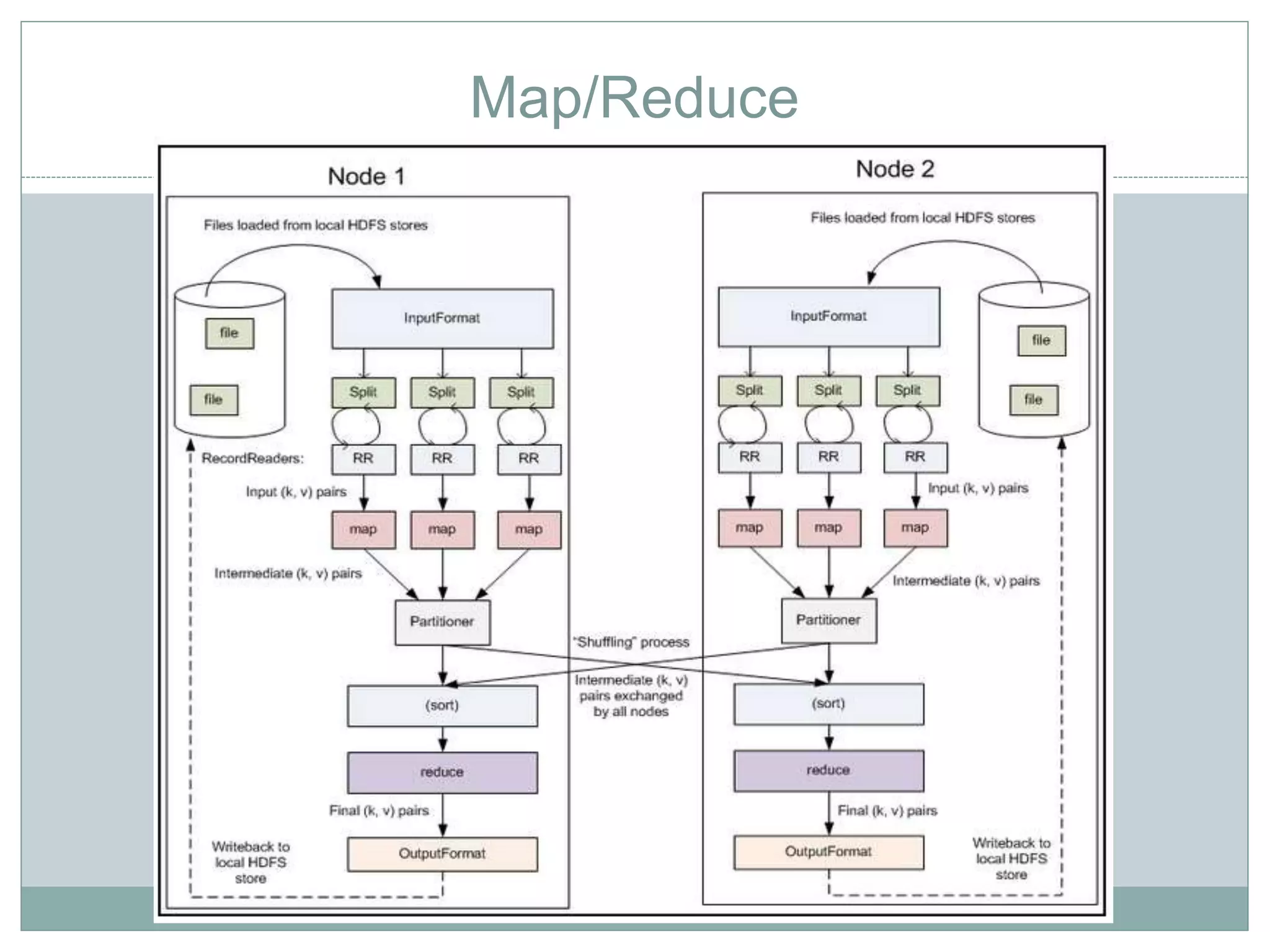
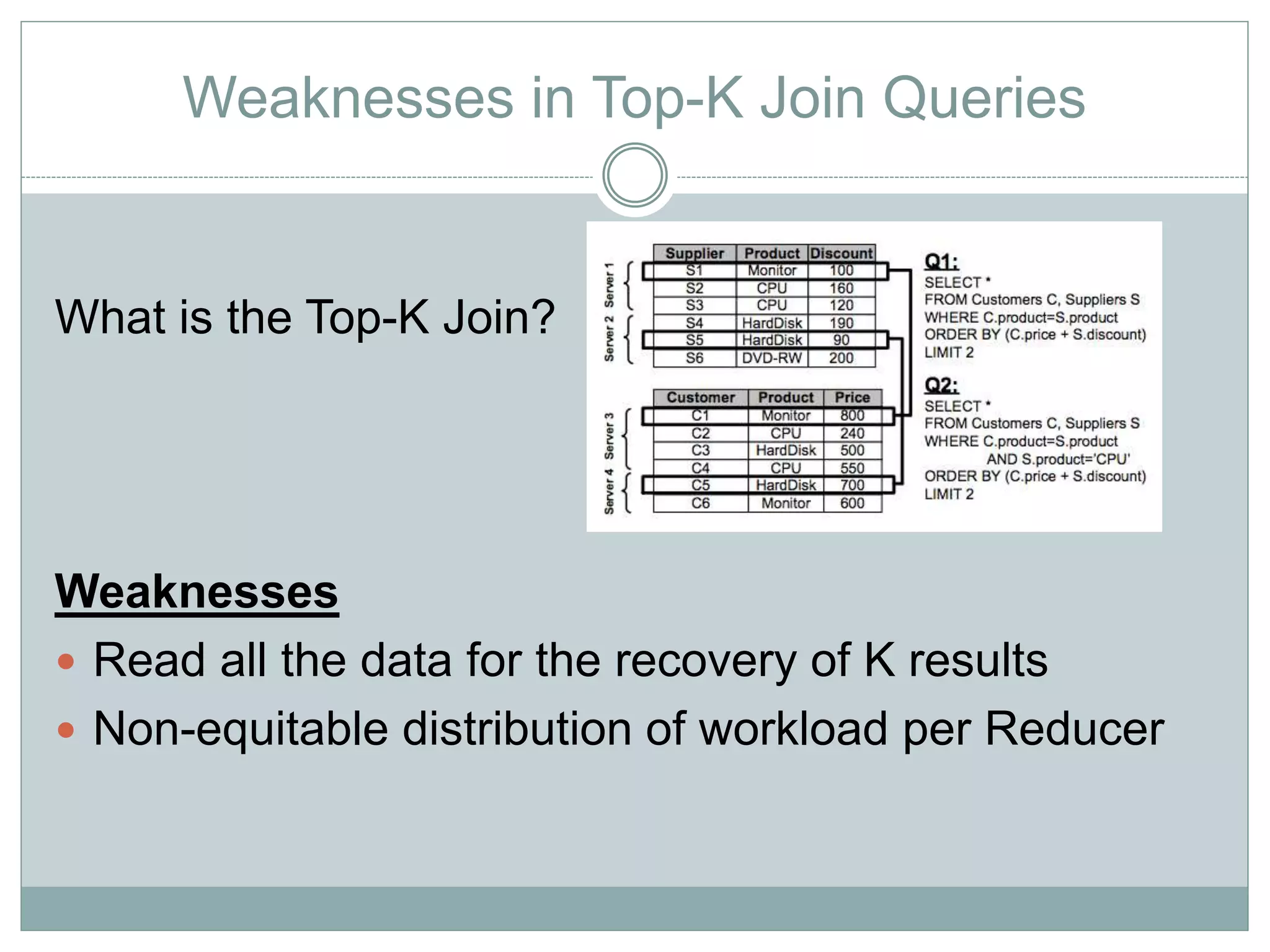
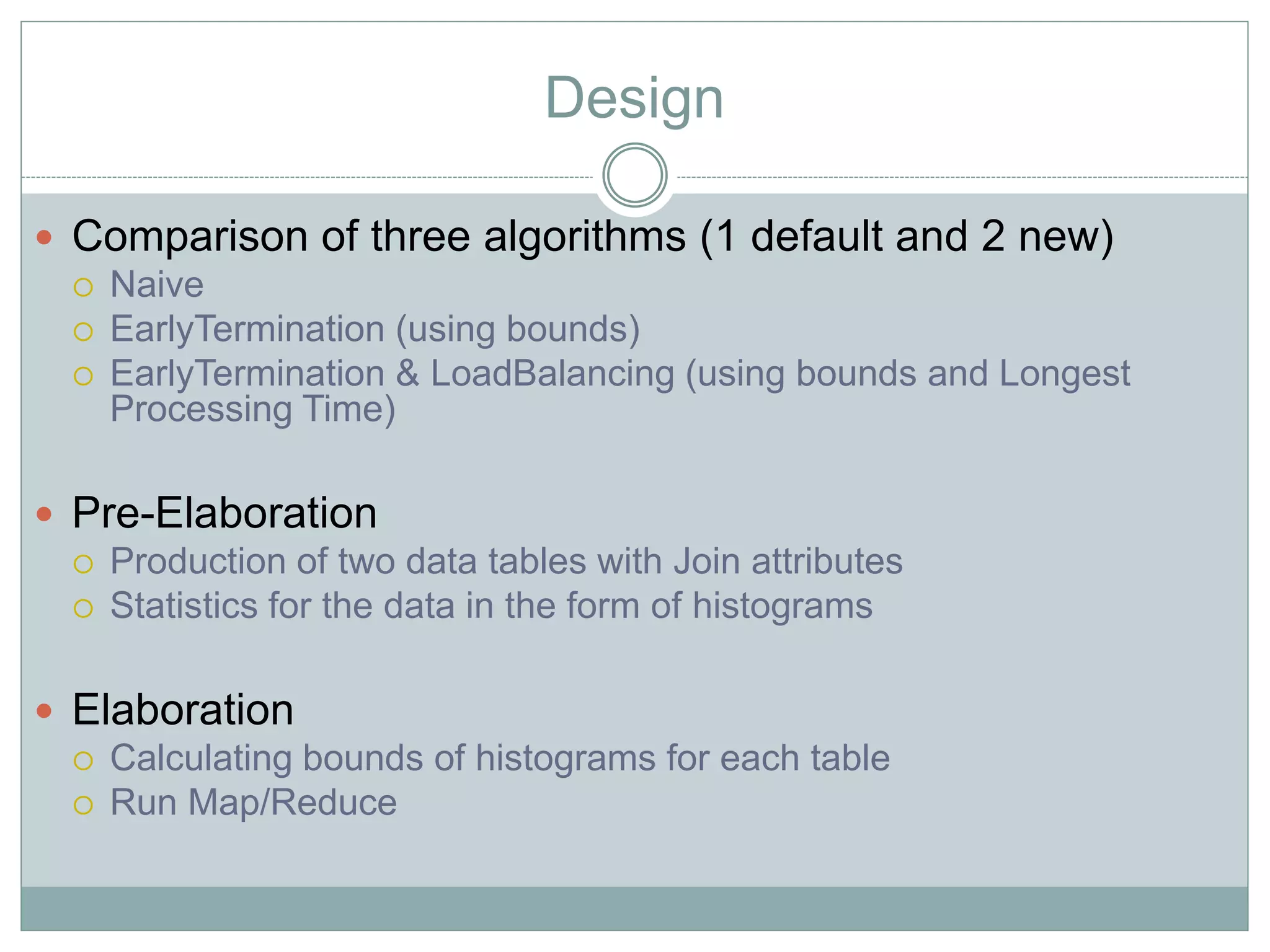
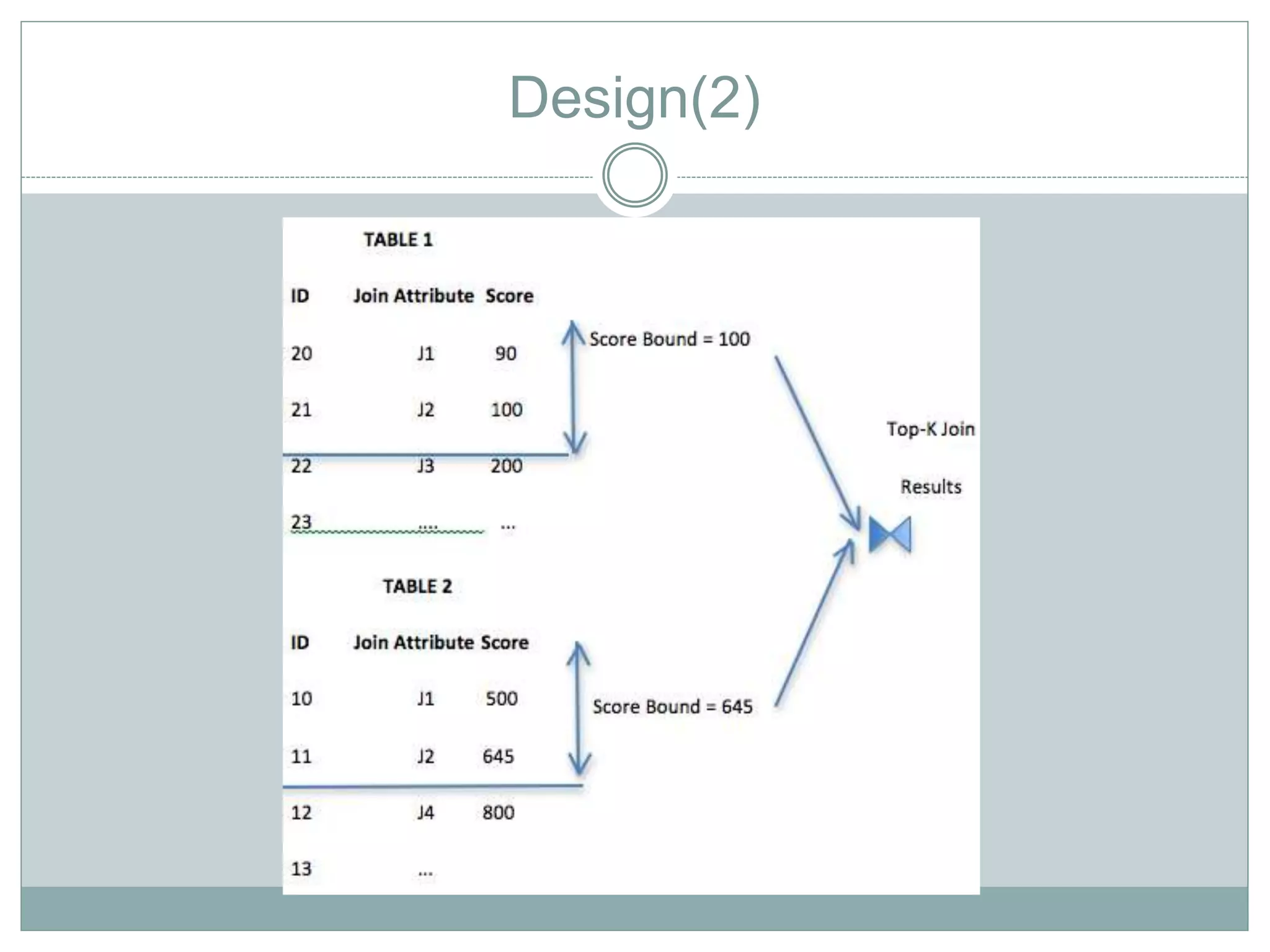
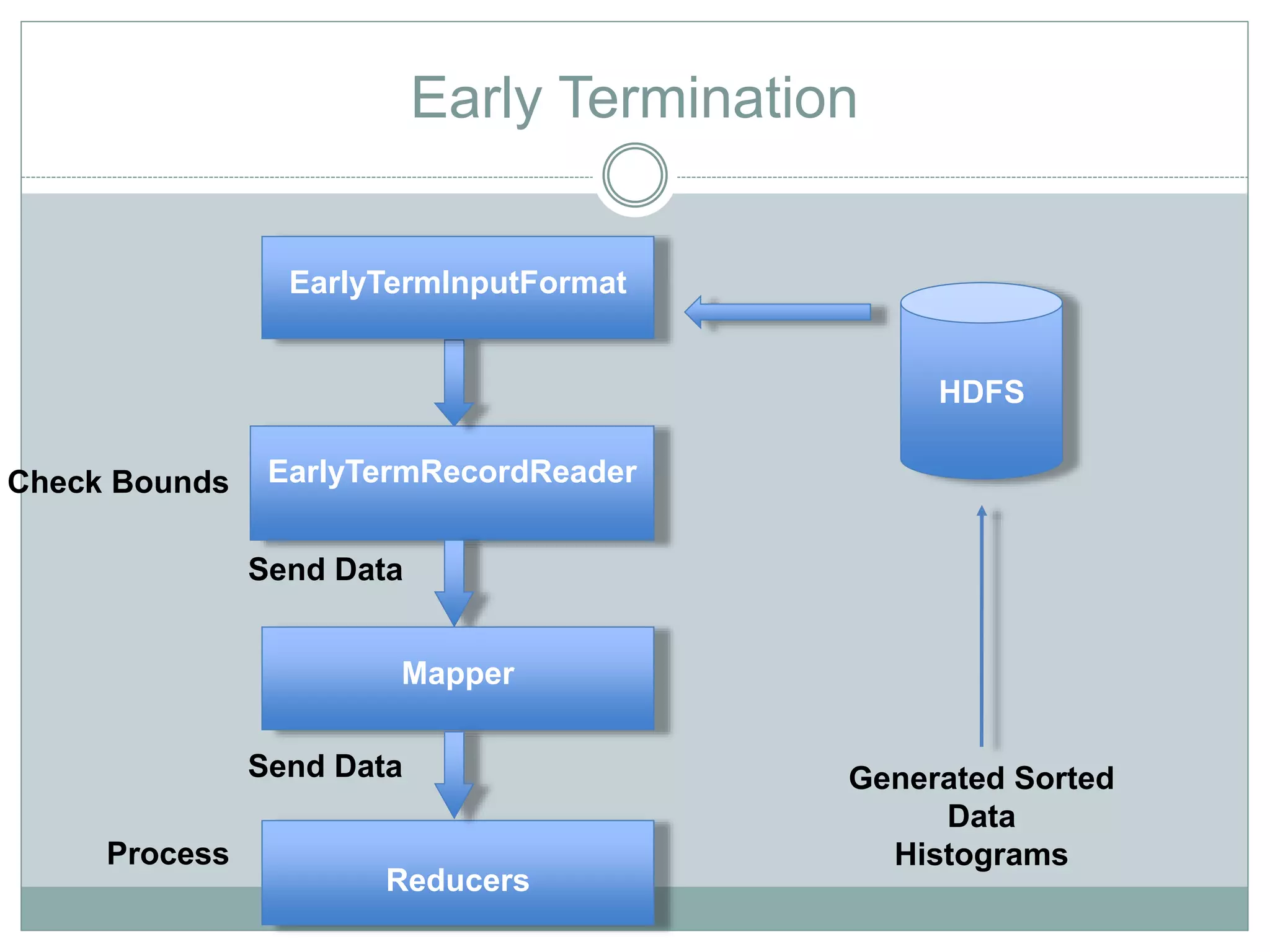
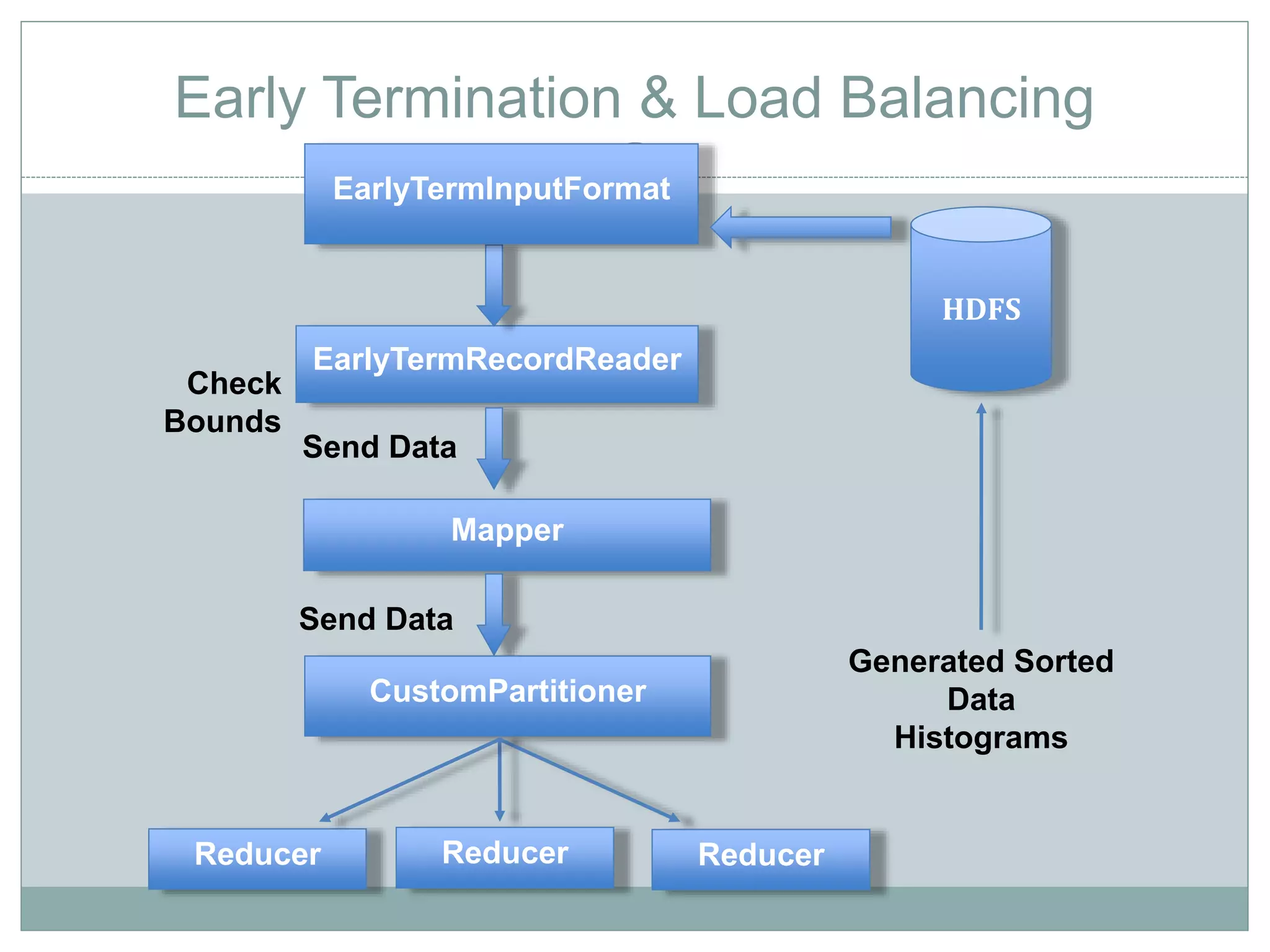
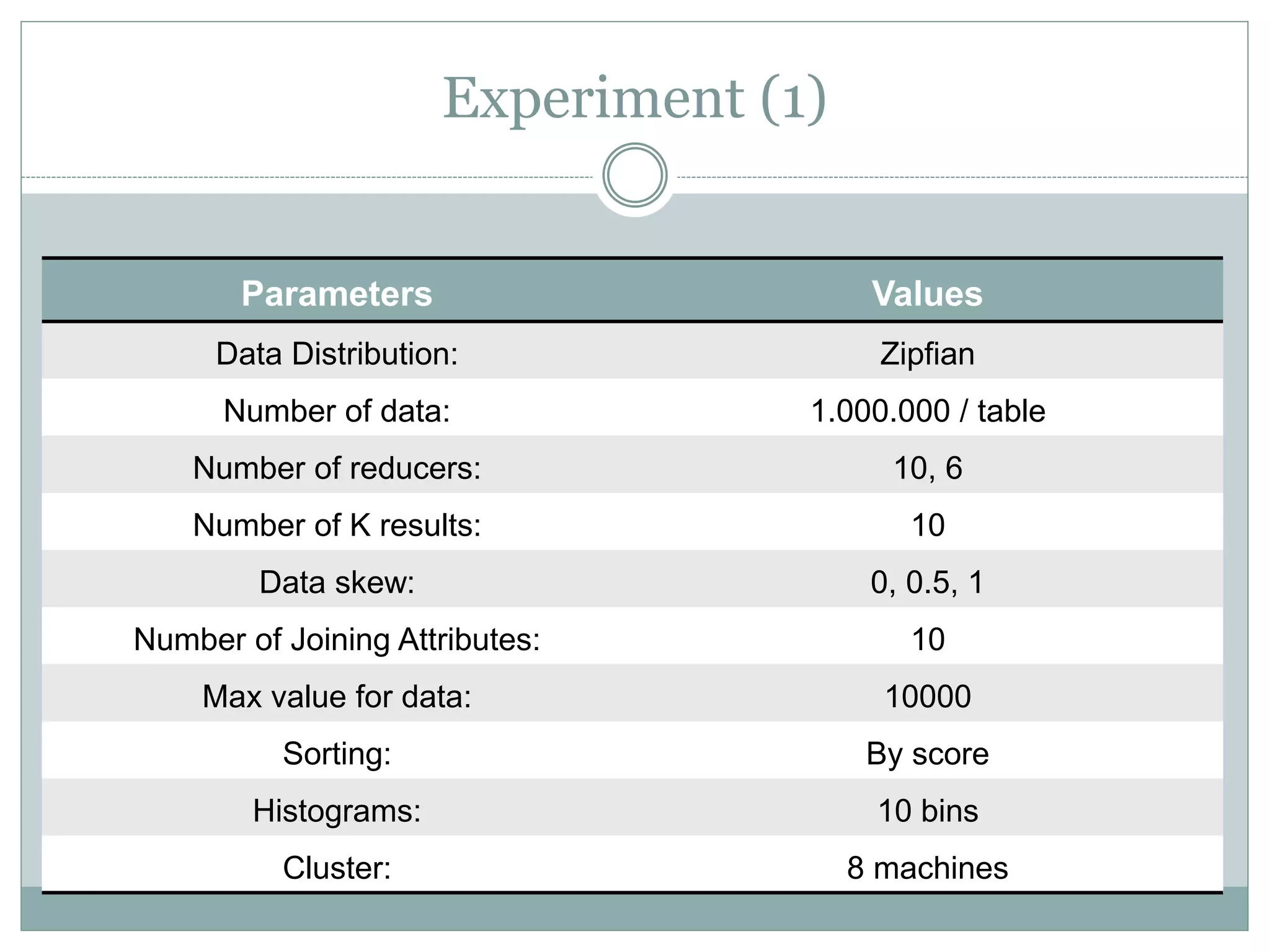
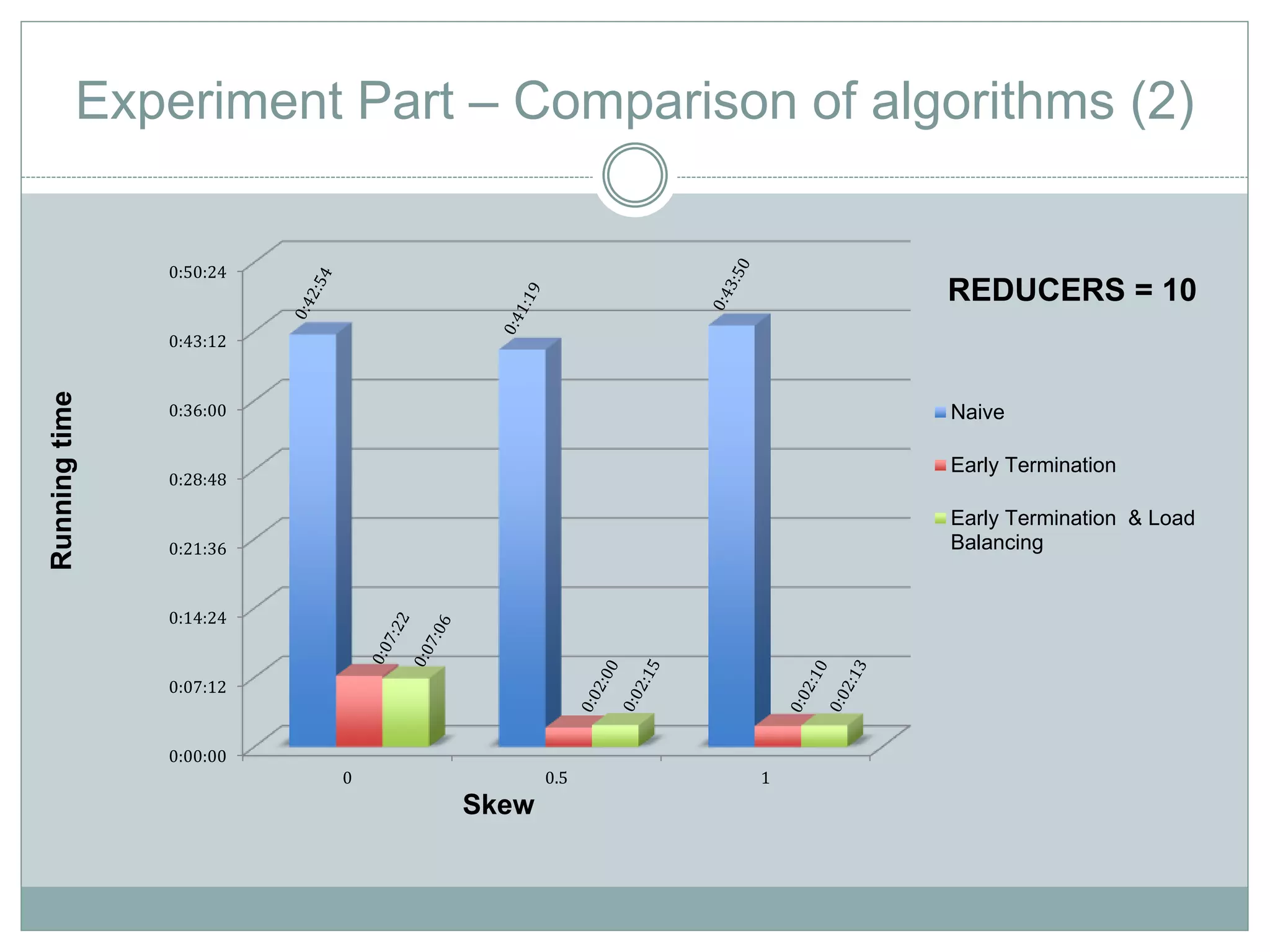
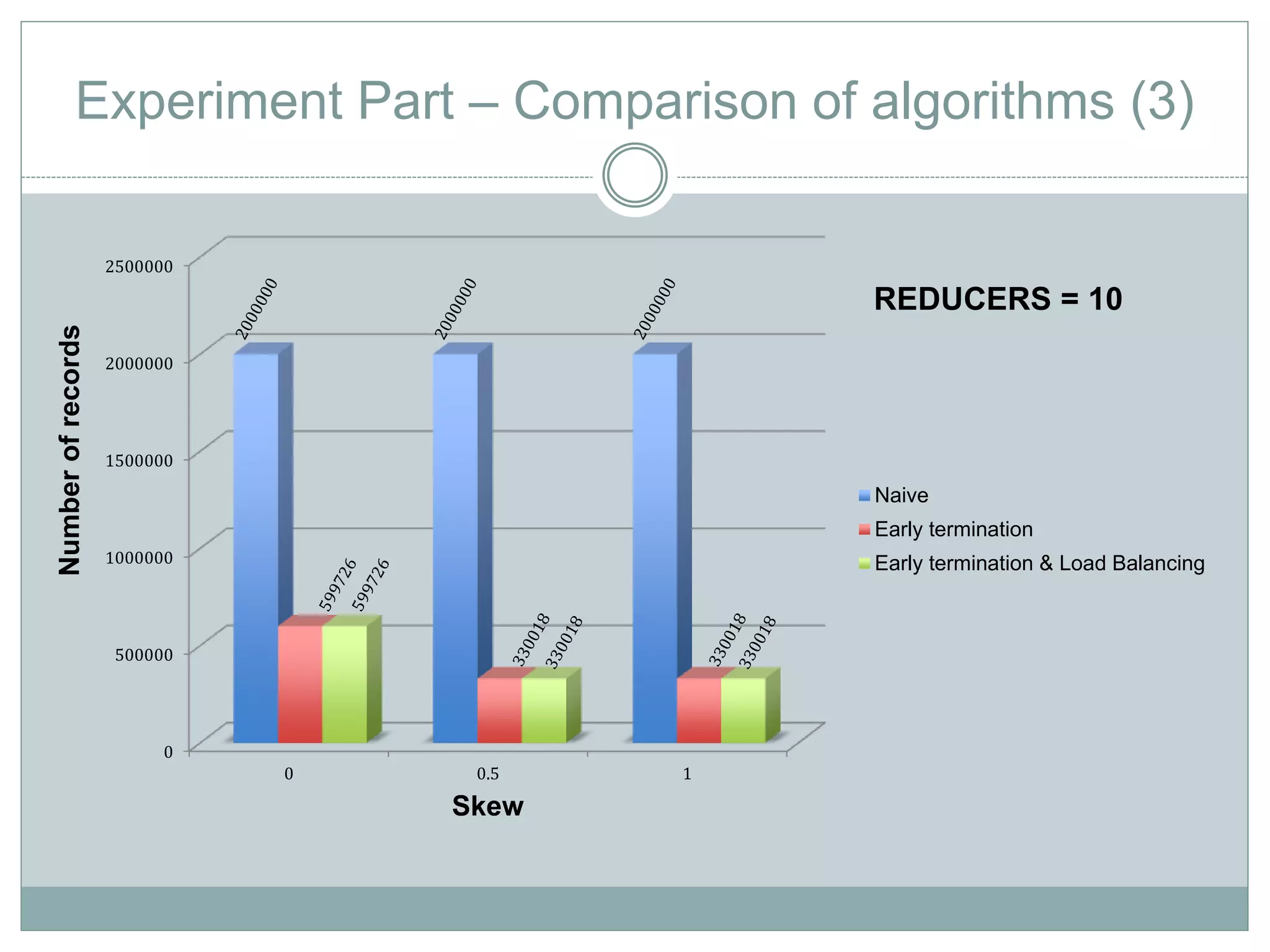
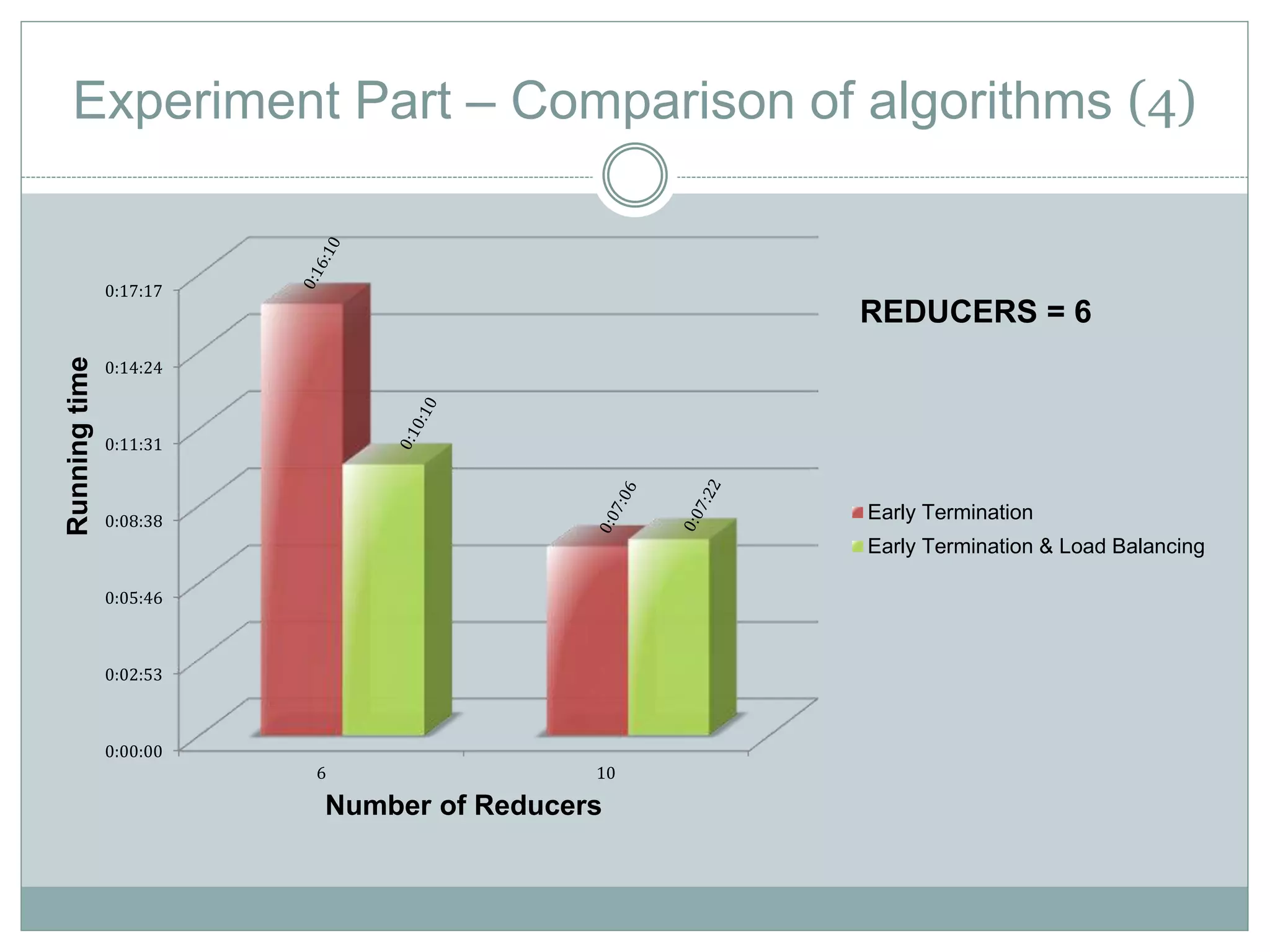
The document discusses the implementation of efficient processing for rank-aware top-k join queries within the Map/Reduce model. It highlights the need for rapid data analysis and scalability due to exponential data growth while addressing weaknesses in current methods, including load balancing and early termination techniques. Experimental results compare three algorithms for improving performance in processing these queries, demonstrating the advantages of the proposed methods.