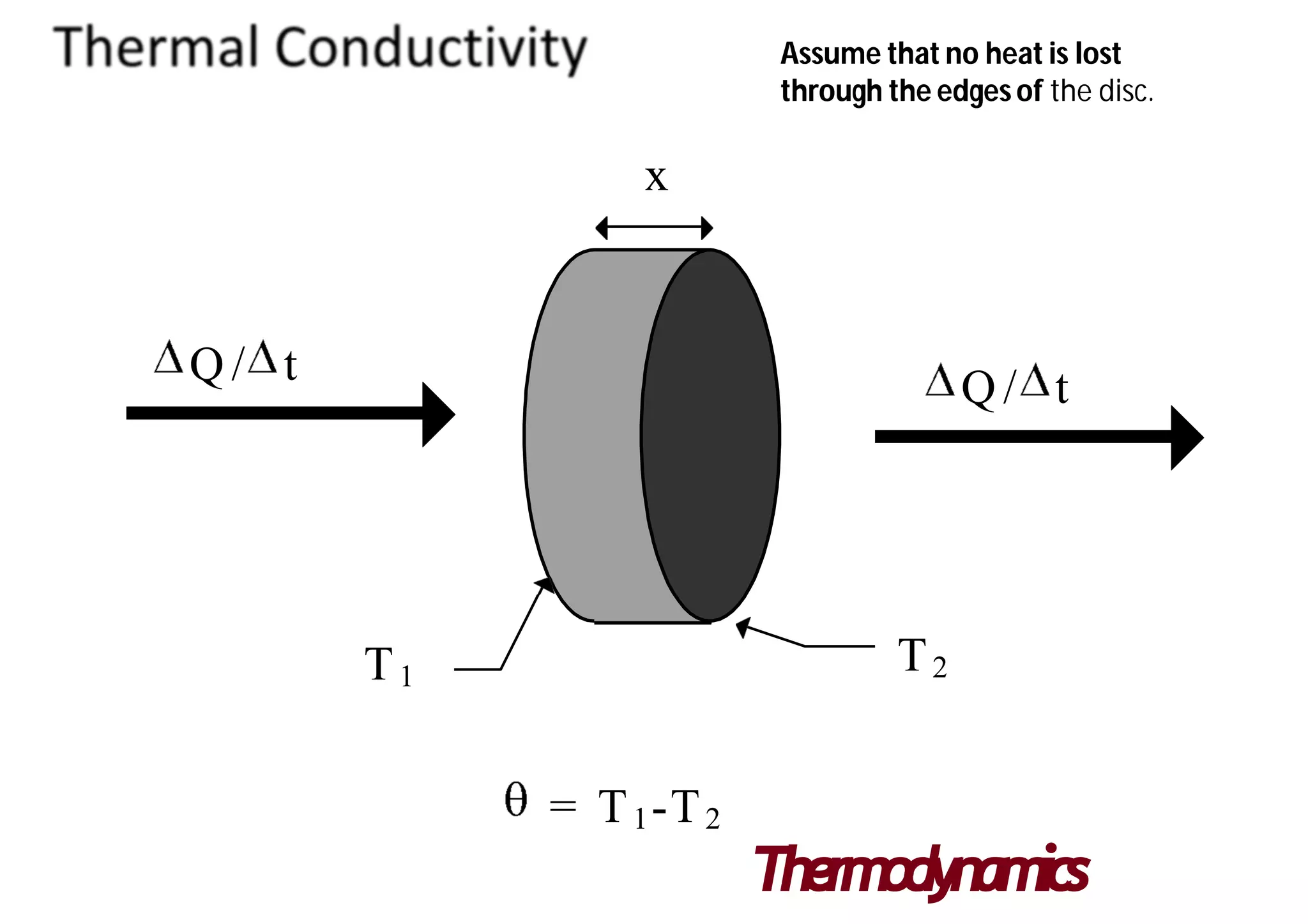
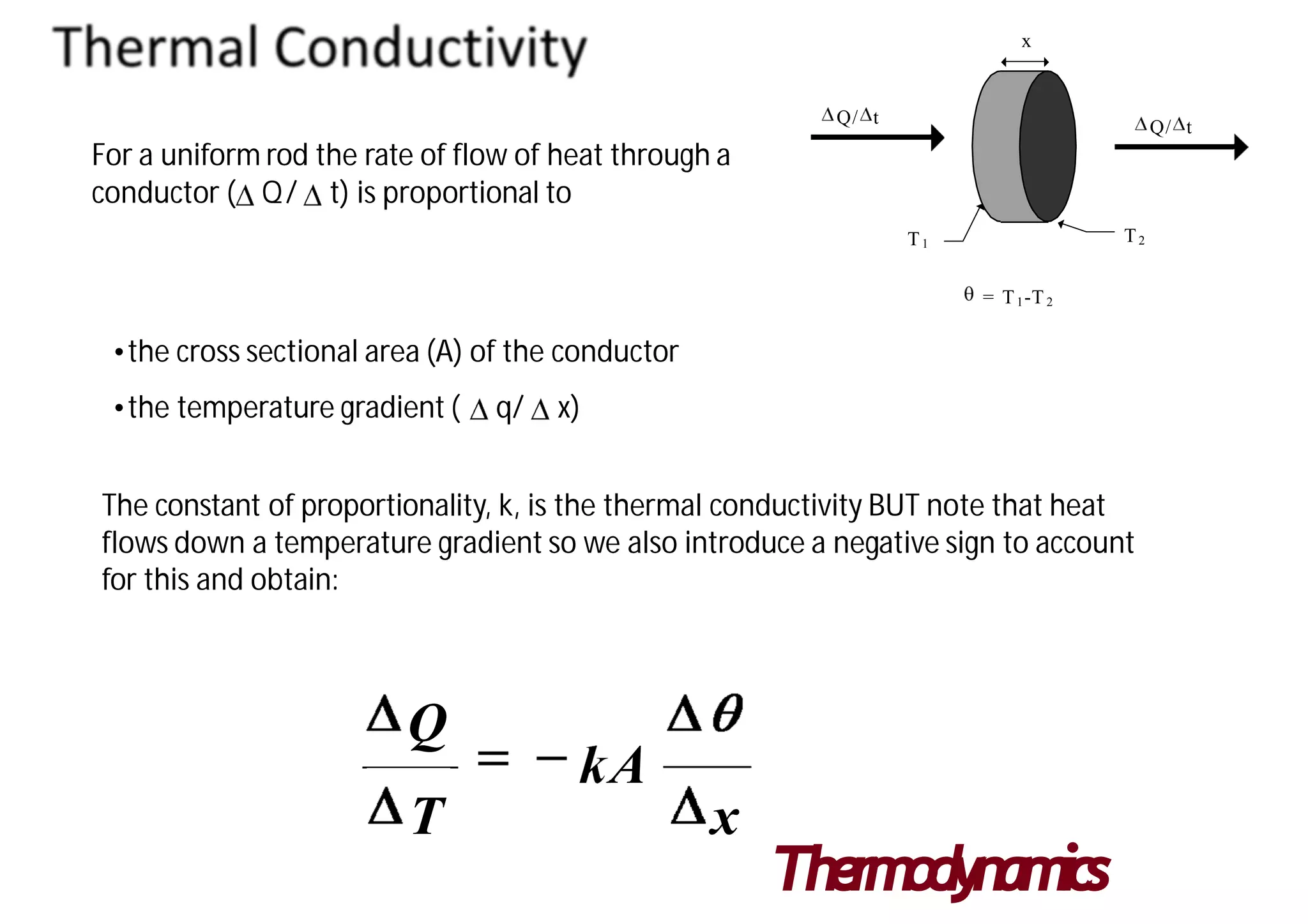
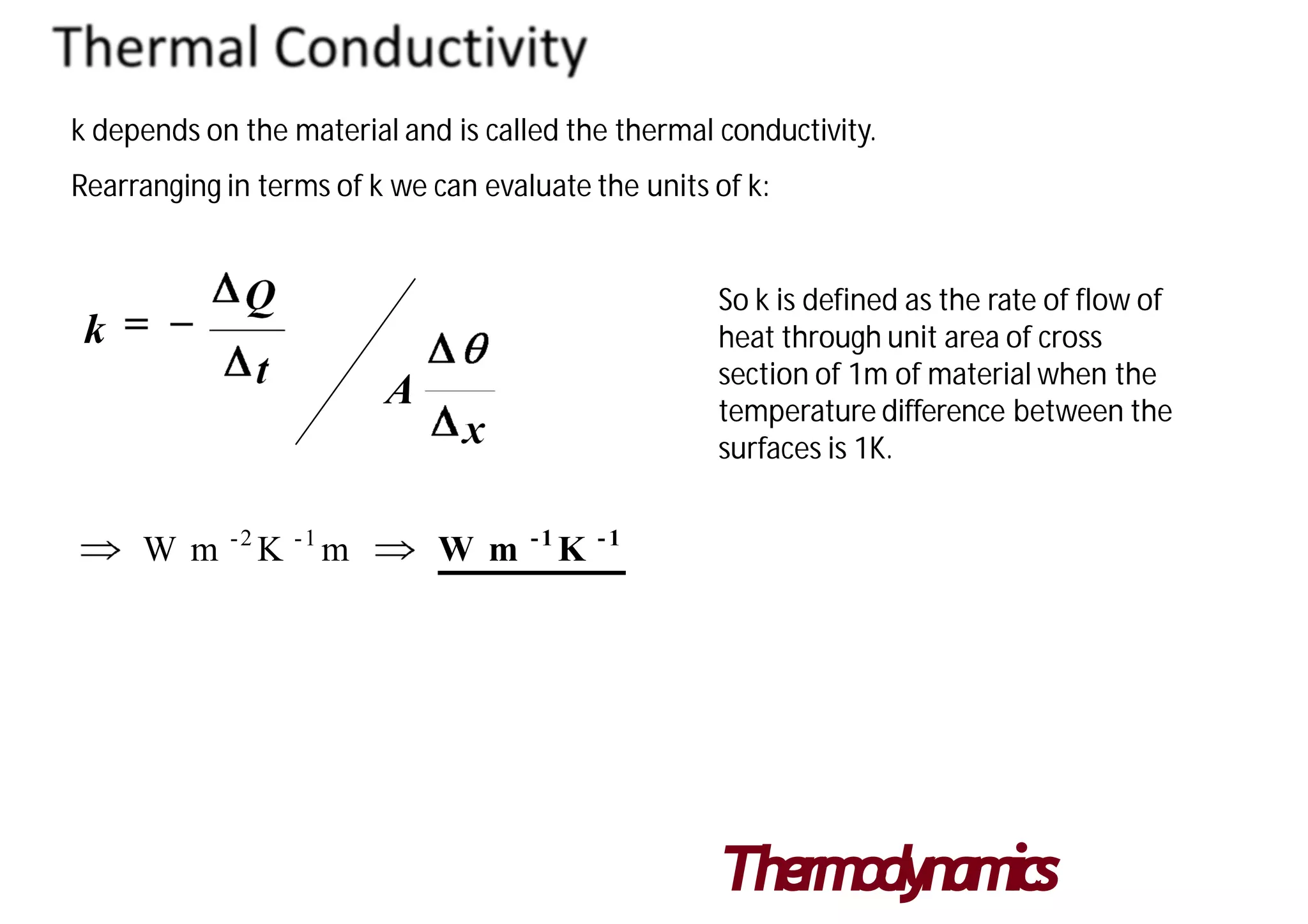
Thermal conductivity is a material property that indicates its ability to conduct heat. It is represented by k and measured in watts per kelvin per meter. There are two main methods to measure thermal conductivity - steady state methods which measure materials at thermal equilibrium, and transient state methods which measure during heating. Steady state is more accurate but slower, while transient state does not require equilibrium but has more difficult analysis. Thermal conductivity values vary widely between materials from over 400 W/K-m for metals like silver to below 0.1 W/K-m for insulators like styrofoam.