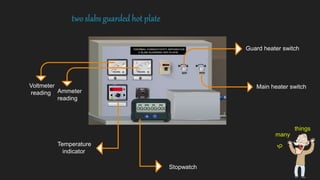
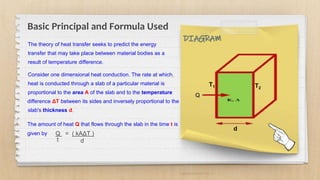
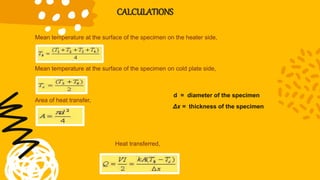
Conduction is the transfer of heat between objects in direct contact. Heat flows from the higher temperature object to the lower temperature object through the vibration of molecules. Solids are the most conductive as molecules are tightly packed, while gases are the least conductive as molecules are farther apart. The rate of heat flow is measured in watts and the ability of a material to conduct heat is called its thermal conductivity. Thermal conductivity can be measured using a two slab guarded hot plate method which involves measuring the heat transferred through a material over time for a given temperature difference and surface area.