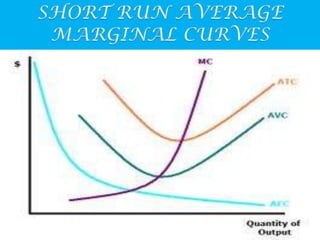
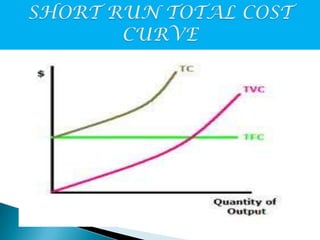
The document defines short-run and long-run costs, and explains the relationships between total, fixed, and variable costs. It also defines average and marginal costs. Specifically, it states that in the short-run, output can be increased or decreased while fixed costs remain unchanged. Total cost equals fixed plus variable cost. Average and marginal cost curves are also discussed, with average cost initially declining and then increasing due to diminishing returns.

![
Cost function may be defined as
the relationship between costs of a
product and output.
C = F [Q]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/costfunction-131130093102-phpapp02/85/Cost-function-Managerial-Economics-2-320.jpg)





![UNITS OF OUTPUT
TFC
[Rs.]
TVC
[Rs.]
TC
[Rs.]
0
60
60 -60 = 0
60
1
60
100 -60 = 40
100
2
60
120 – 60 = 60
120
3
60
70
130
4
60
100
160
5
60
160
220
6
60
300
360](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/costfunction-131130093102-phpapp02/85/Cost-function-Managerial-Economics-9-320.jpg)


![
AFC is the per unit fixed cost of
producing a commodity. It is obtained by
dividing the total fixed cost by the
quantity of output [Q].
AFC =
TFC
Q](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/costfunction-131130093102-phpapp02/85/Cost-function-Managerial-Economics-13-320.jpg)



![Units of TFC
producti [Rs]
on
TVC
[Rs]
TC
[Rs]
AFC
[Rs]
AVC
[Rs]
ATC
[Rs]
MC
[Rs]
O
60
0
60
-
-
-
-
1
60
40
10
60
40
100
40
2
60
60
120
30
30
60
20
3
60
70
130
20
23.3
43.3
10
4
60
100
160
15
25
40
30
5
60
160
220
12
32
44
60
6
60
300
360
10
50
60
140](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/costfunction-131130093102-phpapp02/85/Cost-function-Managerial-Economics-17-320.jpg)