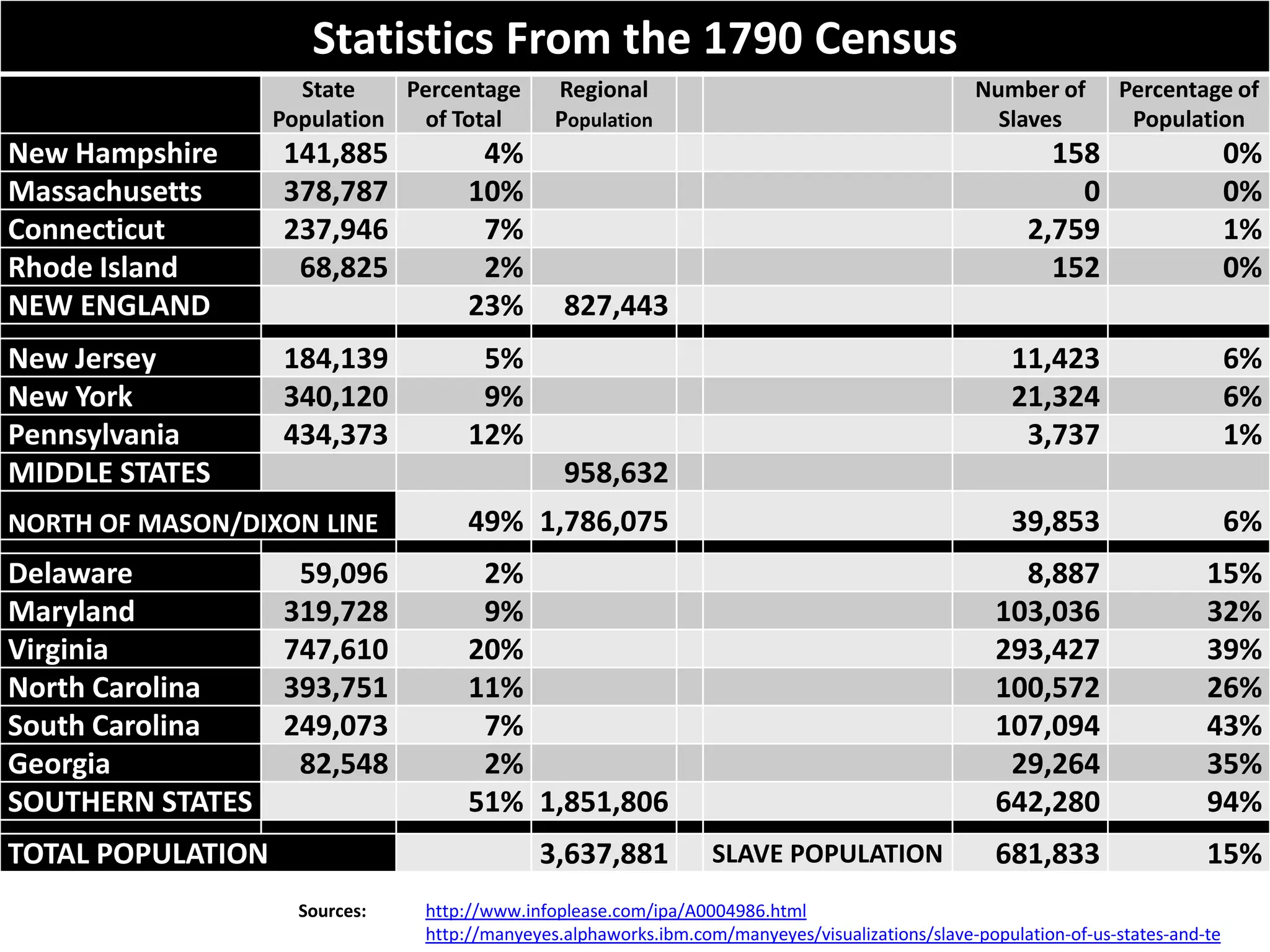
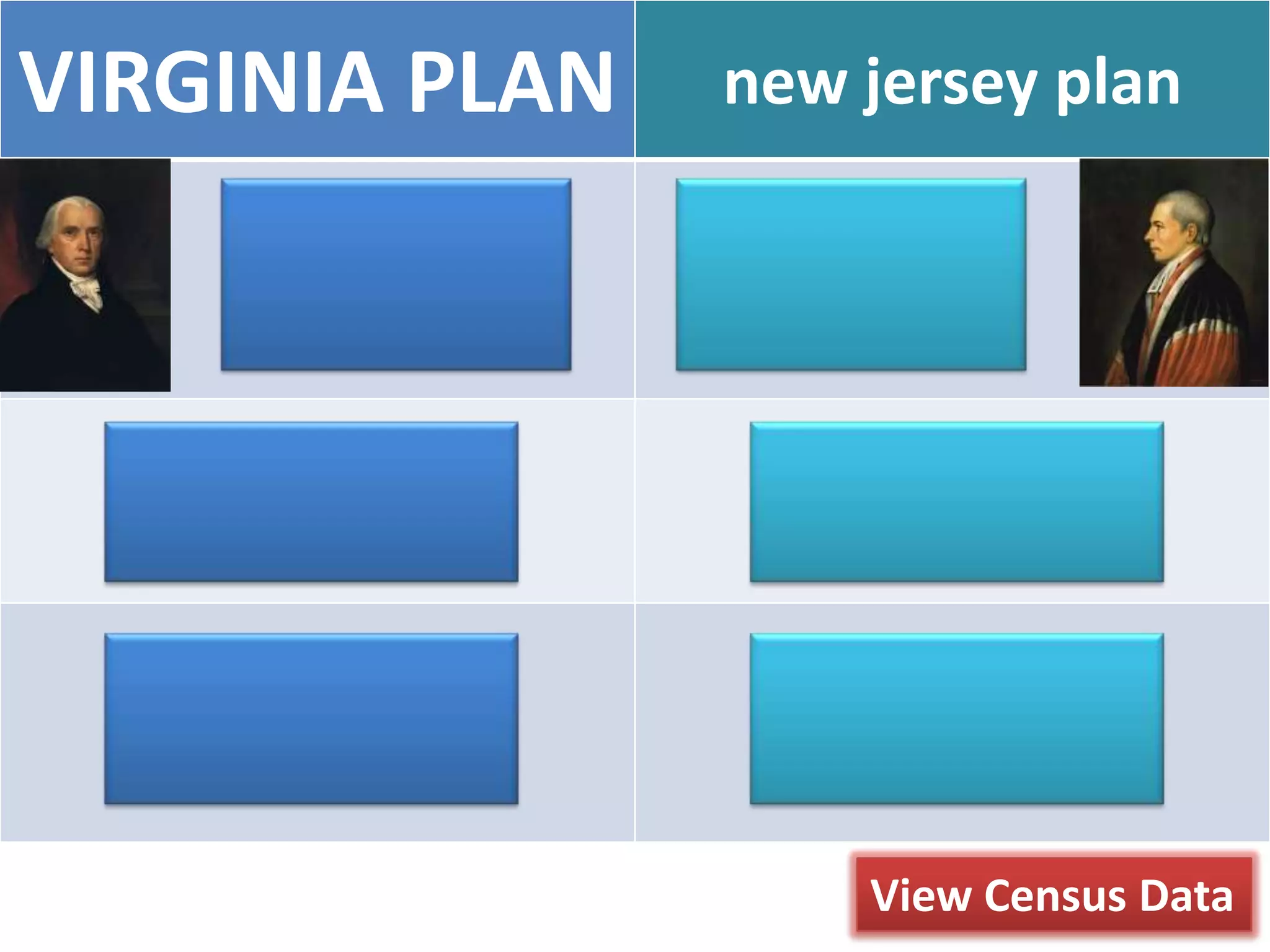
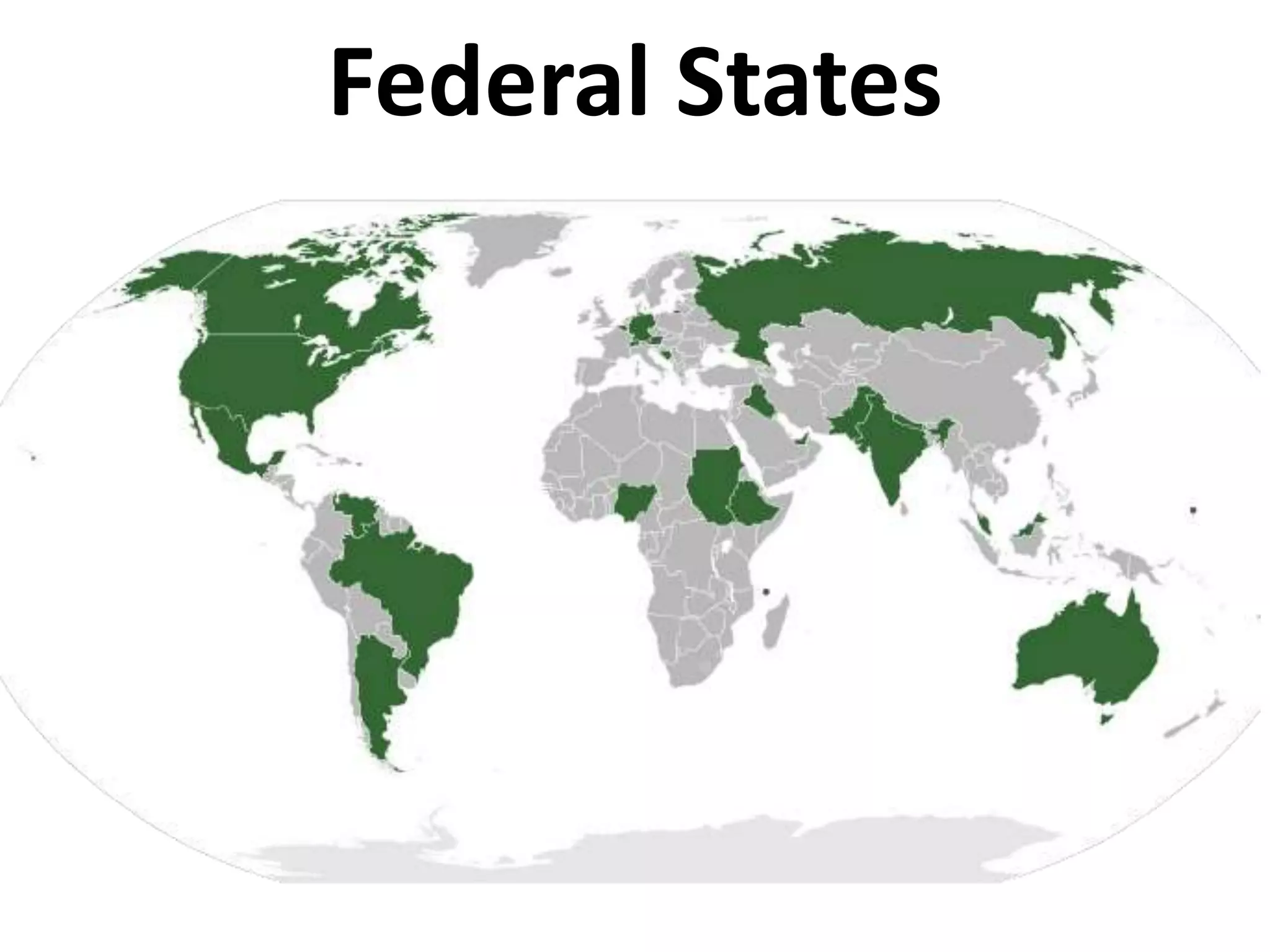
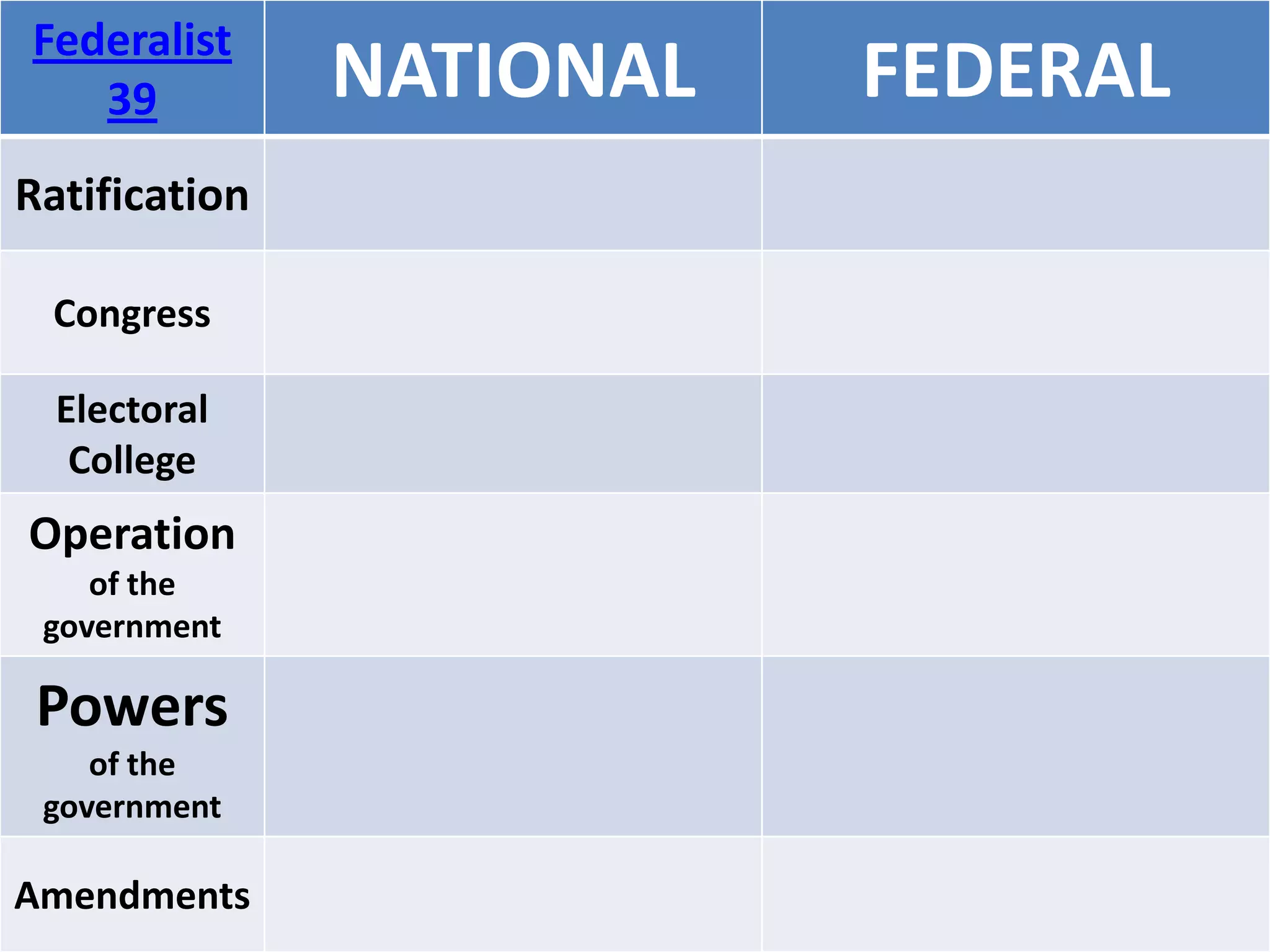
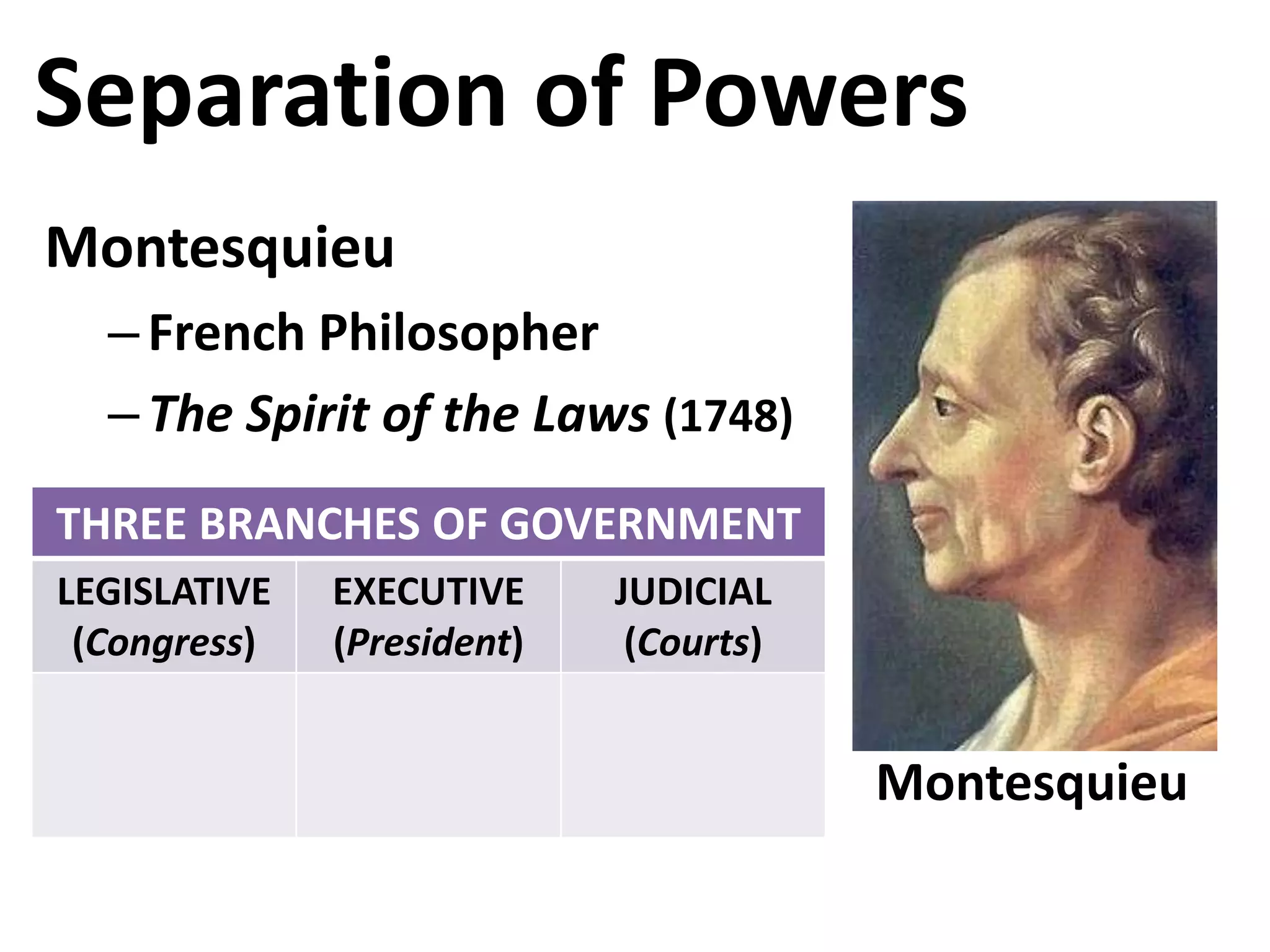
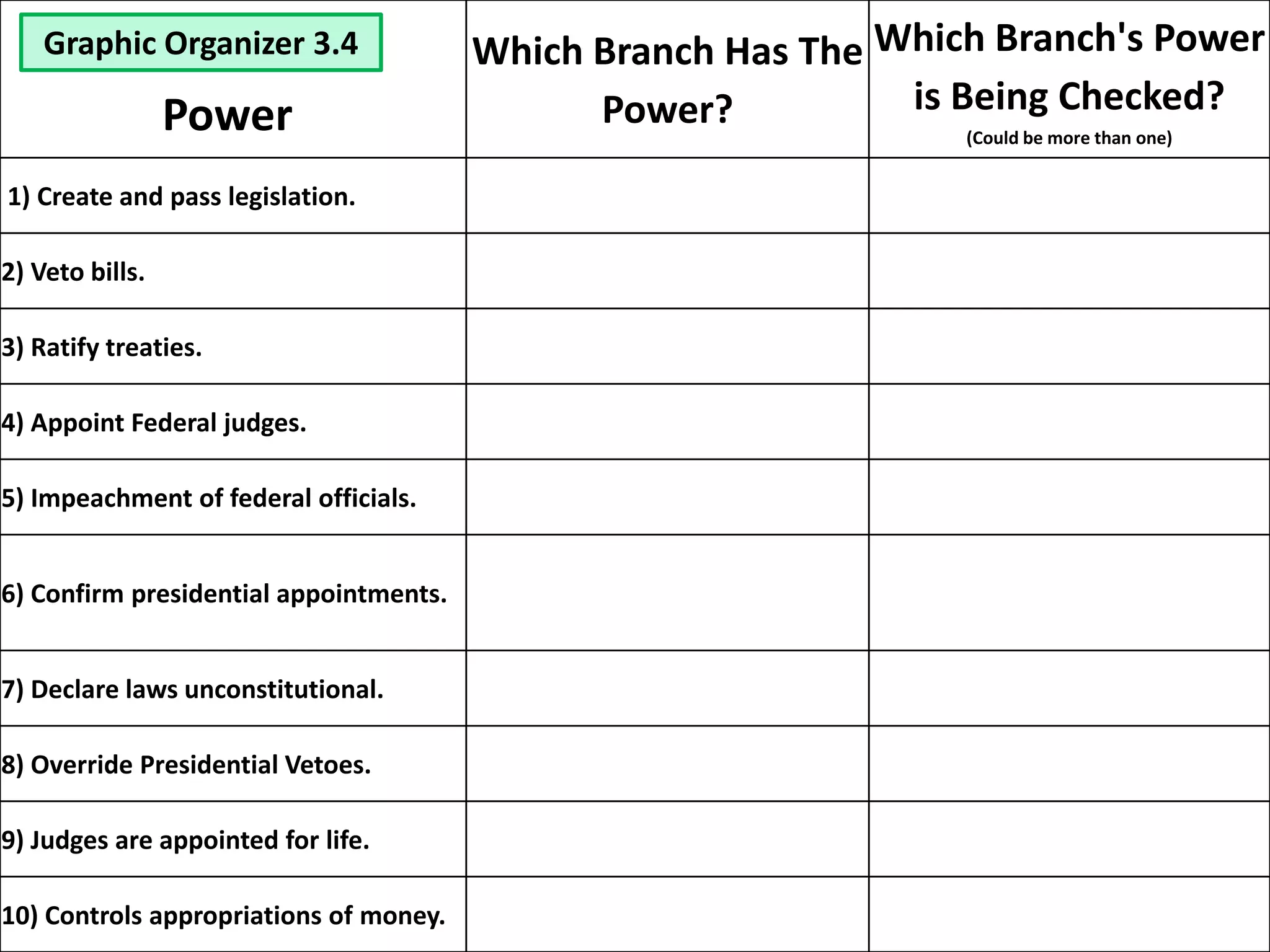
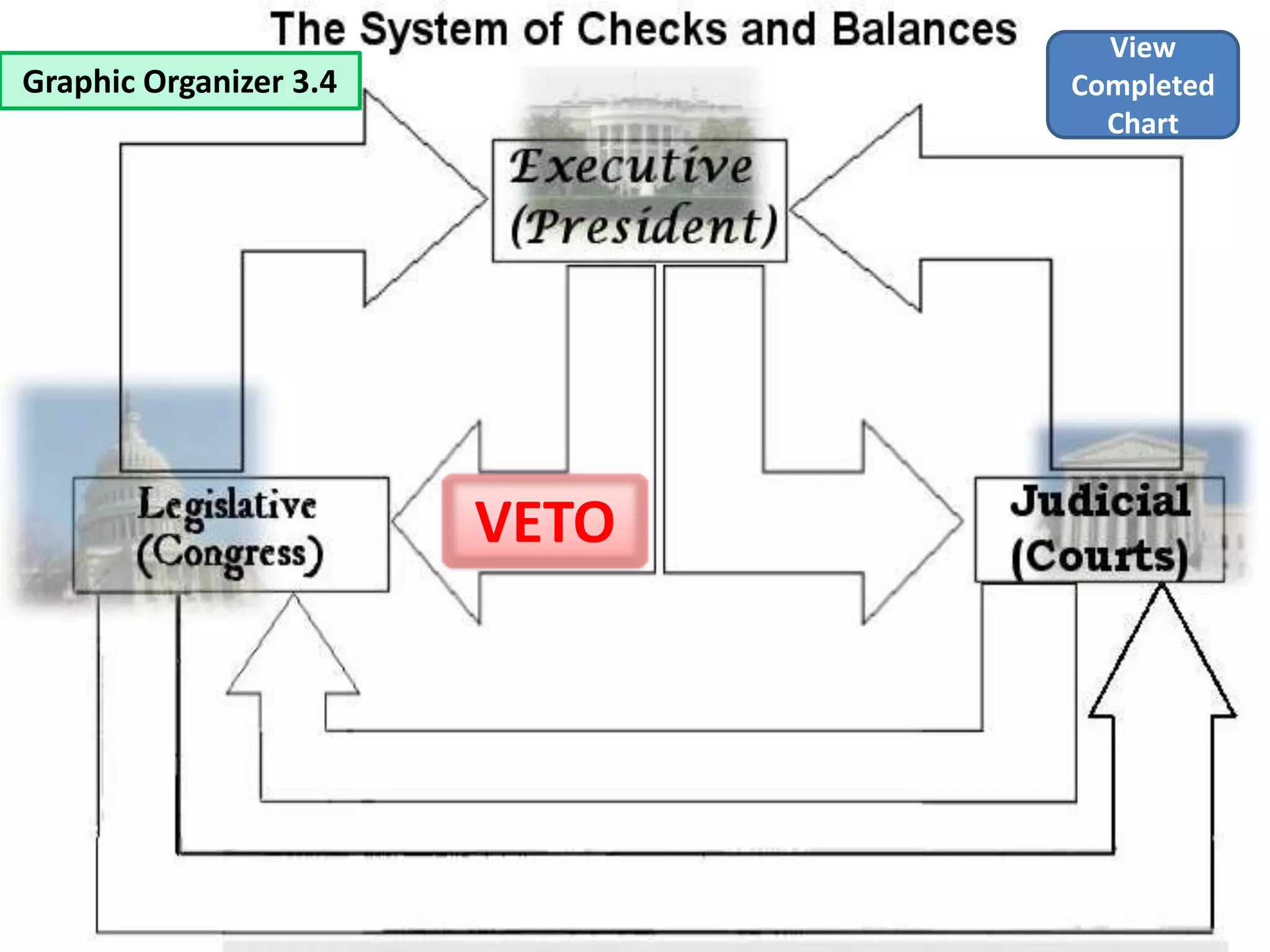
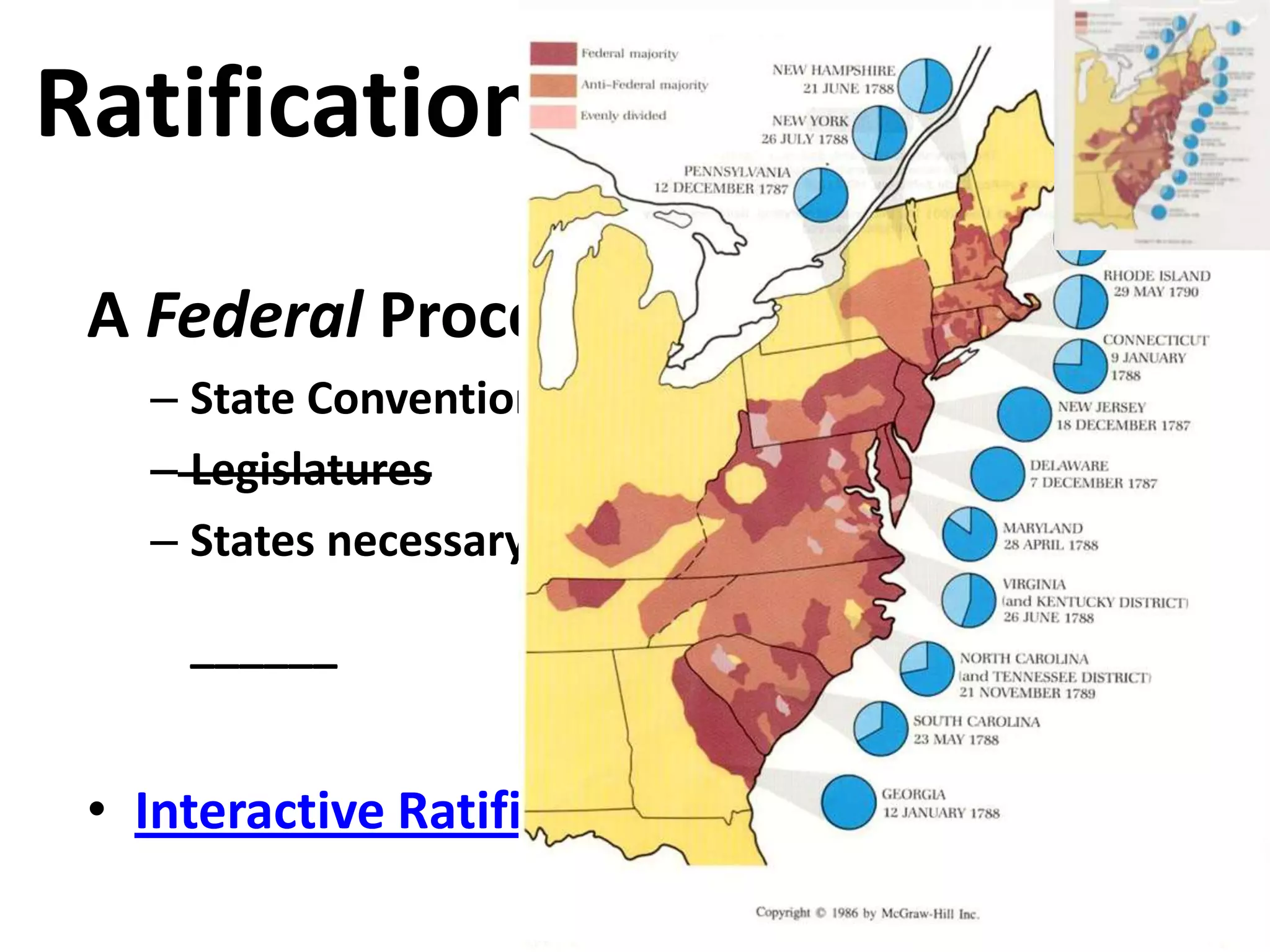
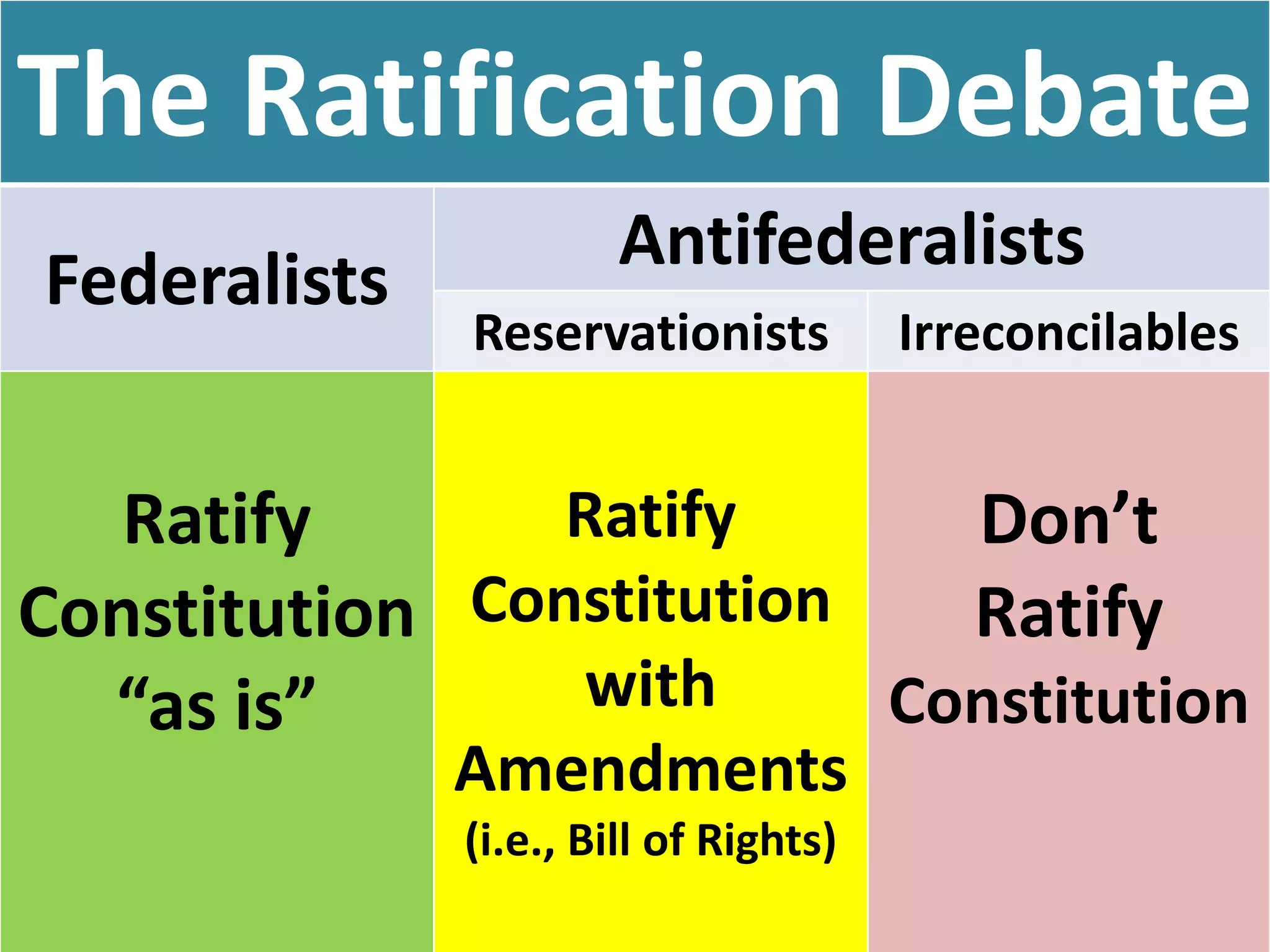
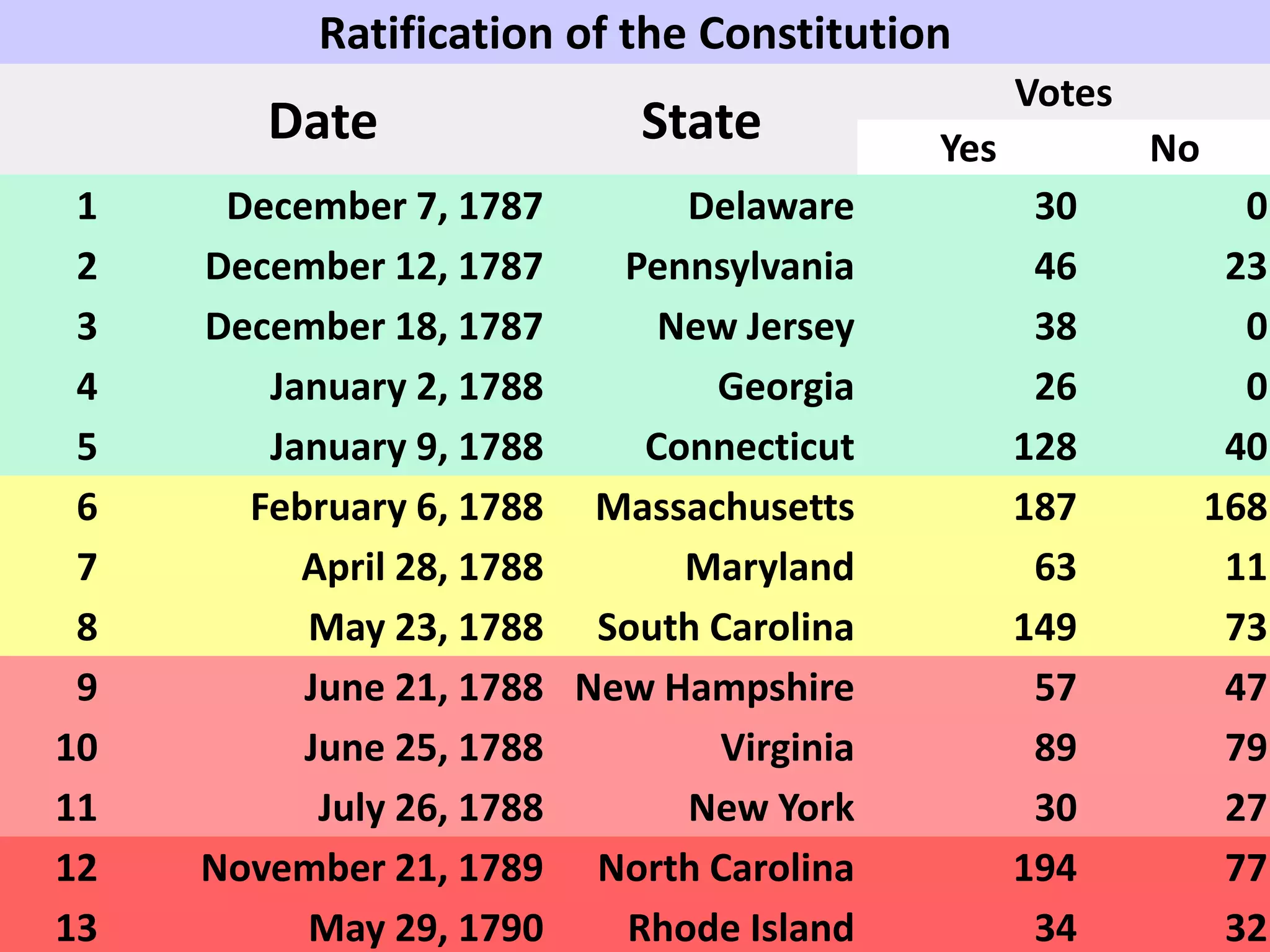
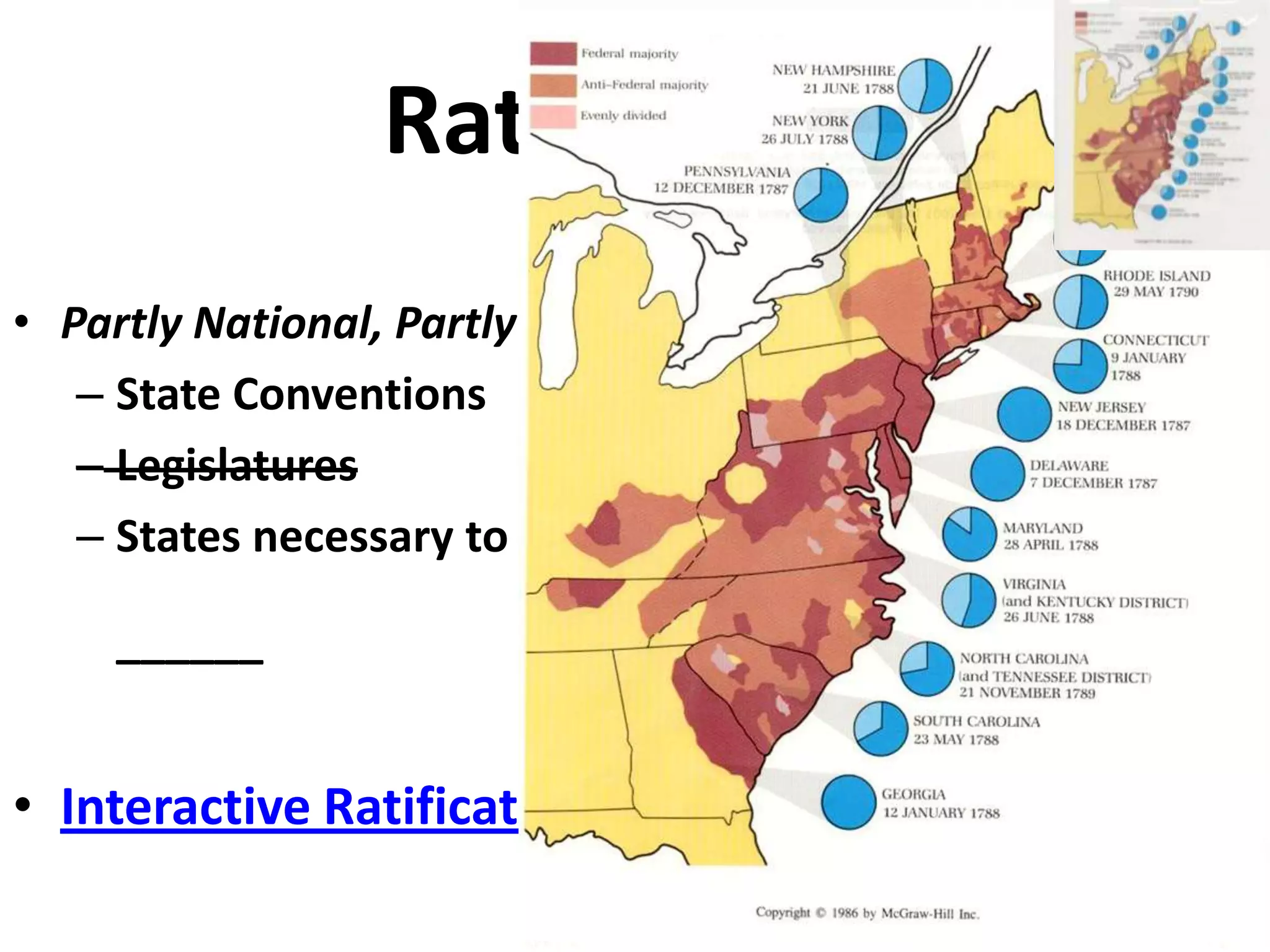
The document outlines the framing and ratification of the U.S. Constitution, emphasizing the dissatisfaction with the Articles of Confederation and the compromises made during the Philadelphia Convention, including the Virginia and New Jersey Plans. It discusses the key principles of limited government as safeguarded by the Constitution and the Bill of Rights, highlighting federalism, separation of powers, and checks and balances. Additionally, it covers the ratification debates between Federalists and Anti-Federalists, the various states' approval processes, and the importance of the Bill of Rights.







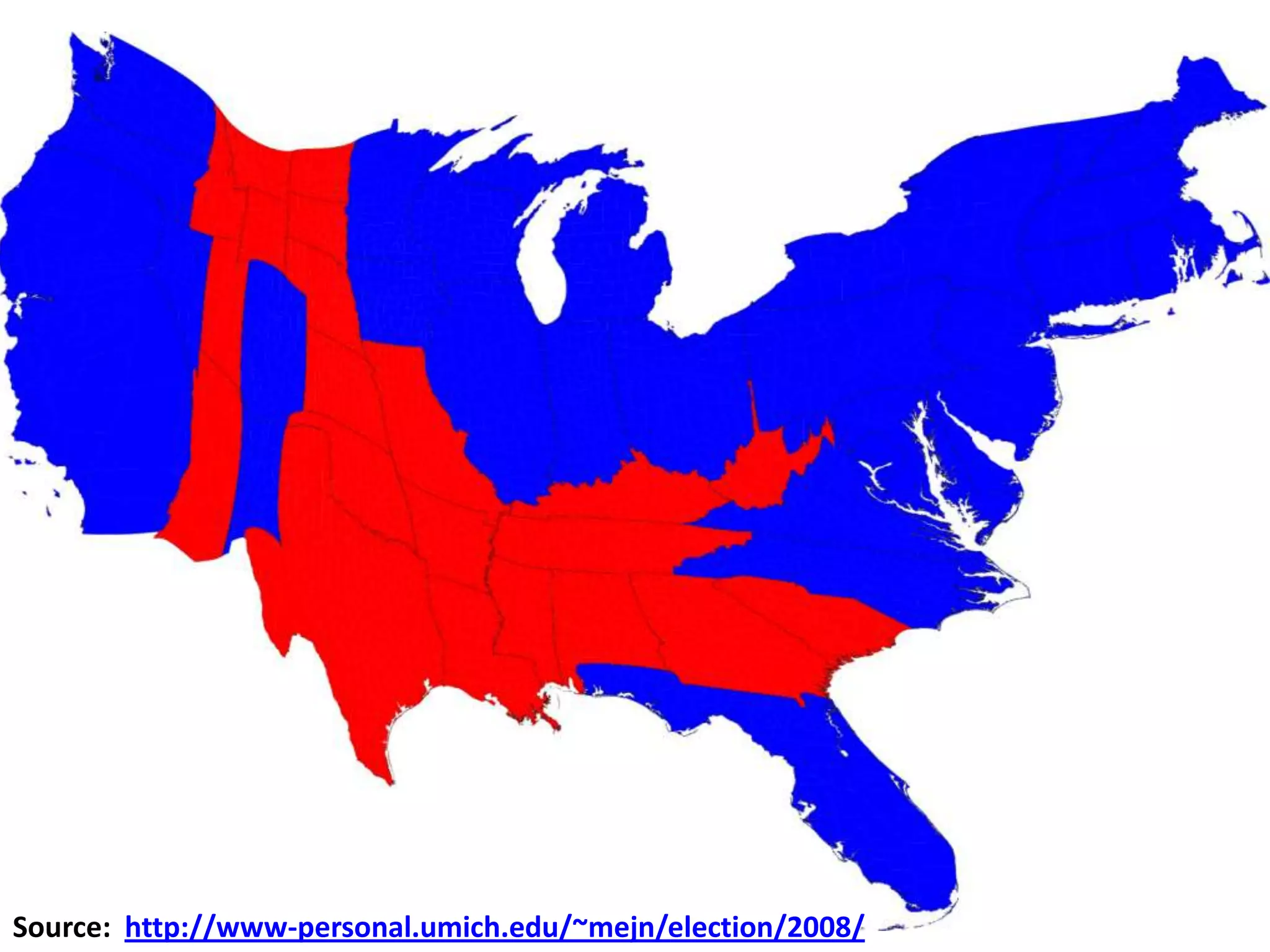
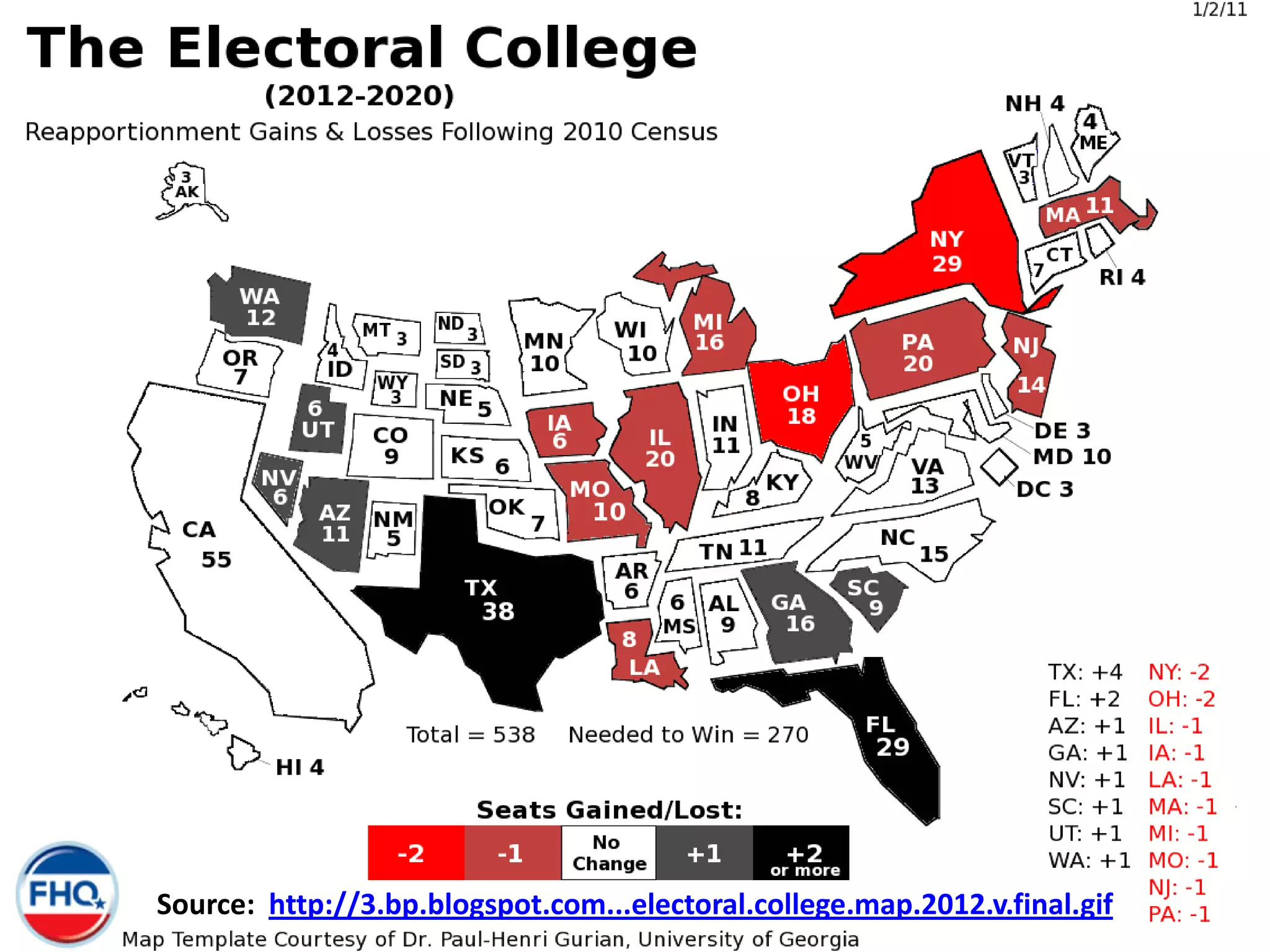


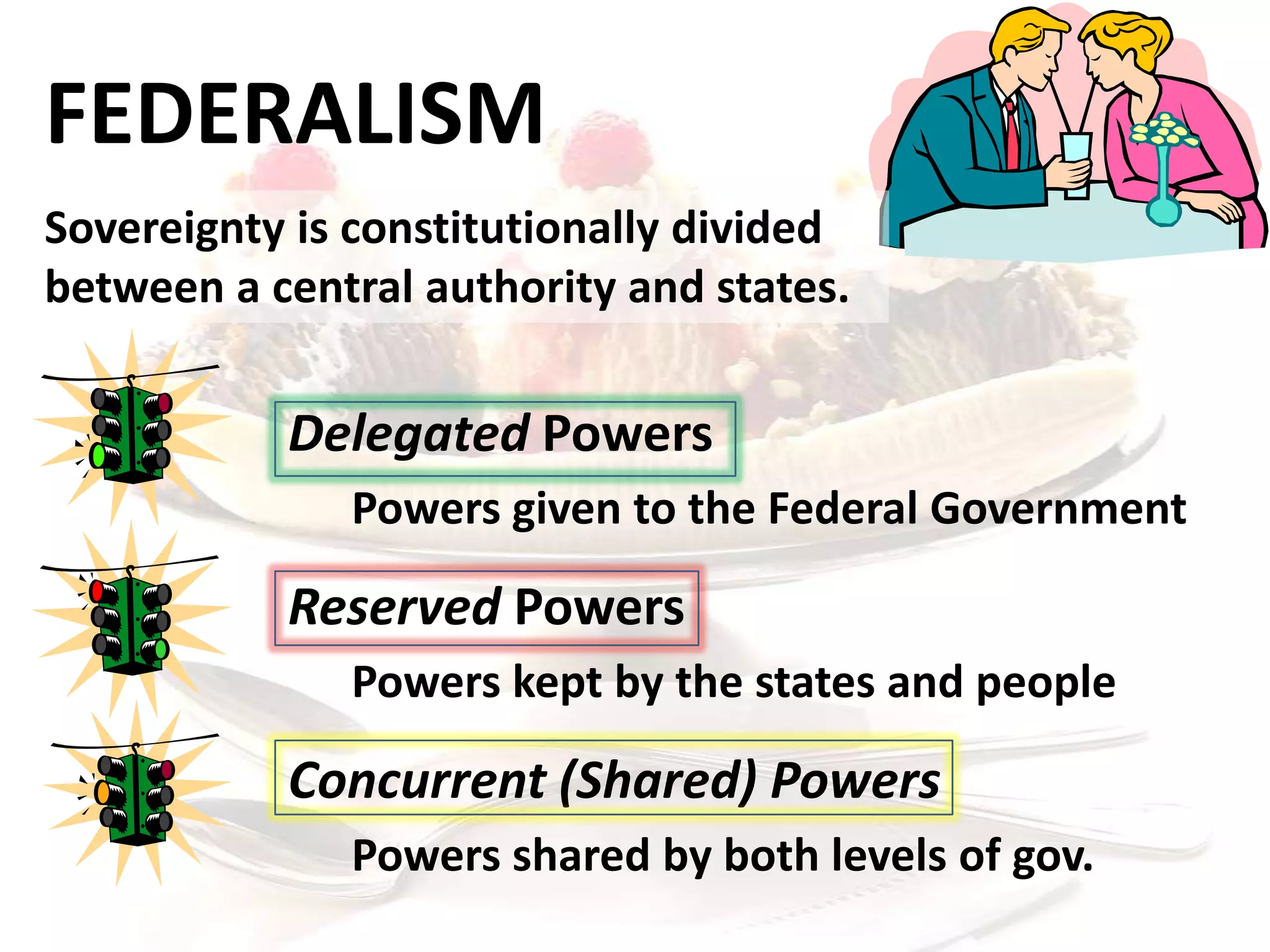

![Federal
[Delegated]
State
[Reserved]
Federalism
AMENDMENT X
The powers not delegated to the United States by the
Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the states, are reserved to
the states respectively, or to the people.
Concurrent
View
Completed
Chart
Graphic Organizer 3.3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-2-theconstitution-130624154504-phpapp01/75/The-U-S-Constitution-Framing-Principles-Ratification-20-2048.jpg)










![THE BILL OF RIGHTS
1ST Speech, Press, Assembly, Religion, Petition [Expression]
2ND Bear Arms
3RD Quartering Troops in Peacetime
4TH Unreasonable Searches and Seizures
5TH Rights of Accused Persons Self-Incrimination
6TH Speedy and Public Trial / Right to Counsel (Criminal)
7TH Trial By Jury in Civil Suits
8TH Cruel and Unusual Punishments Excessive Bails
9TH Protection of Un-enumerated Rights
10TH Powers of States and People](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-2-theconstitution-130624154504-phpapp01/75/The-U-S-Constitution-Framing-Principles-Ratification-41-2048.jpg)