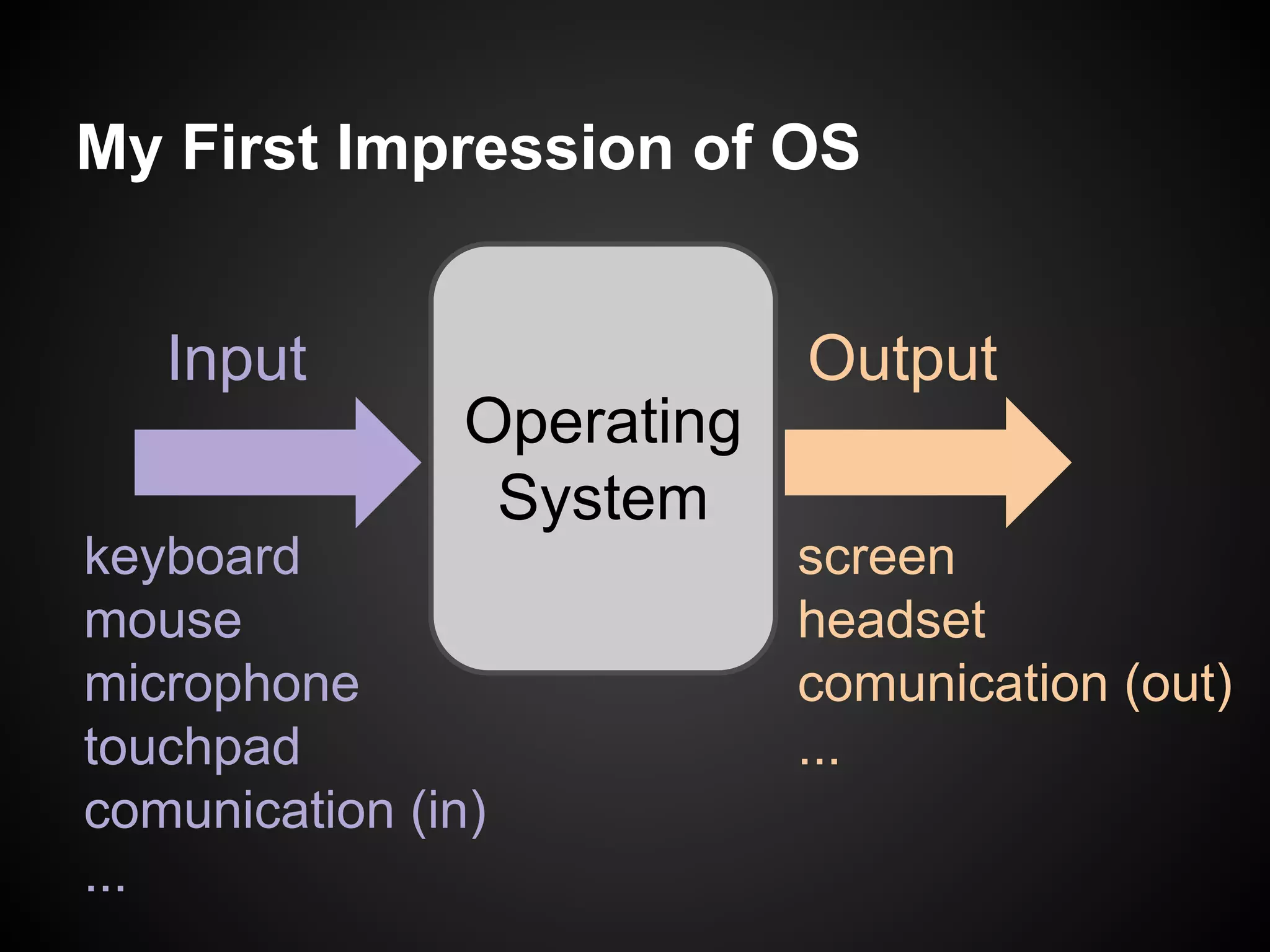
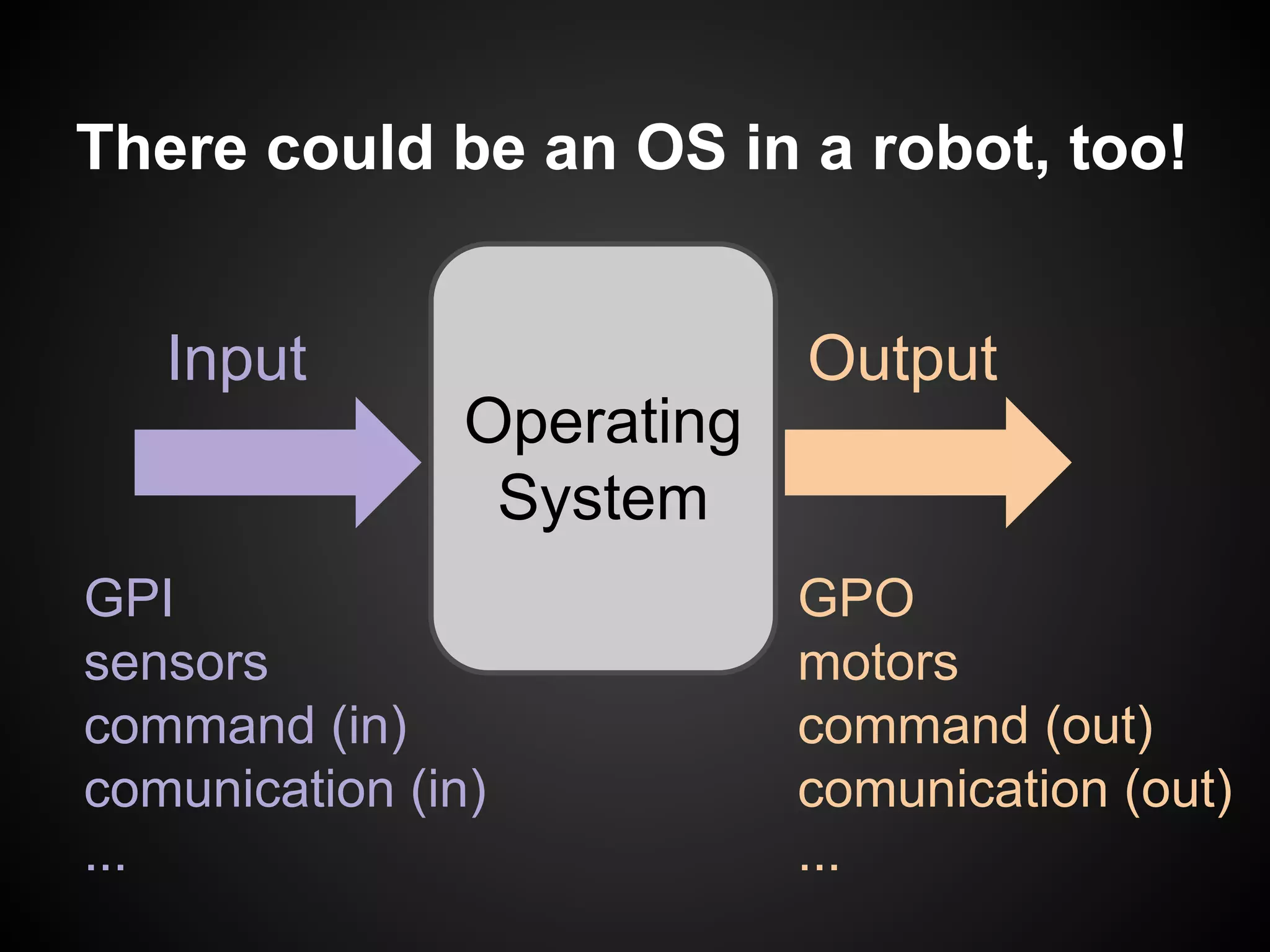
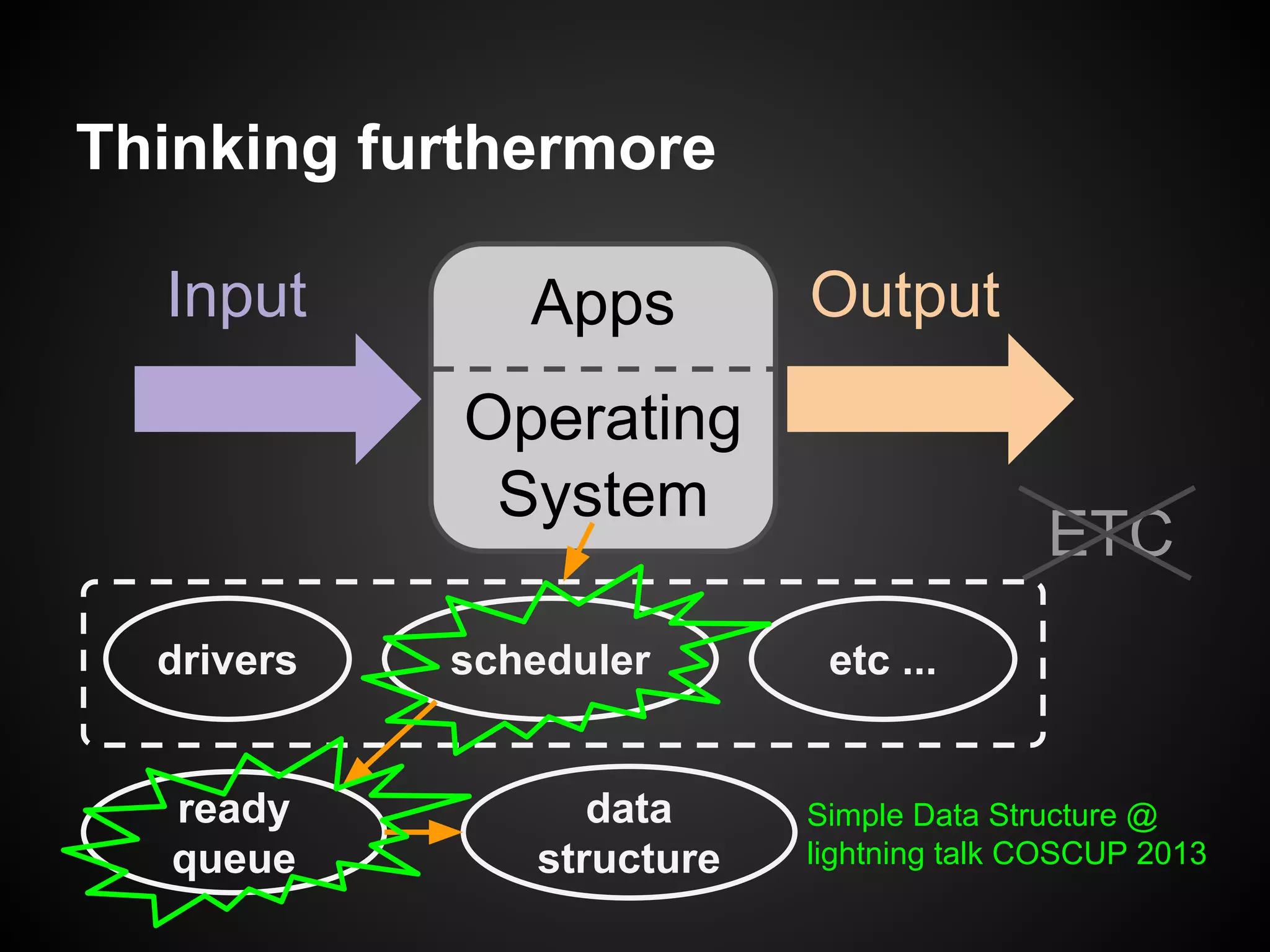
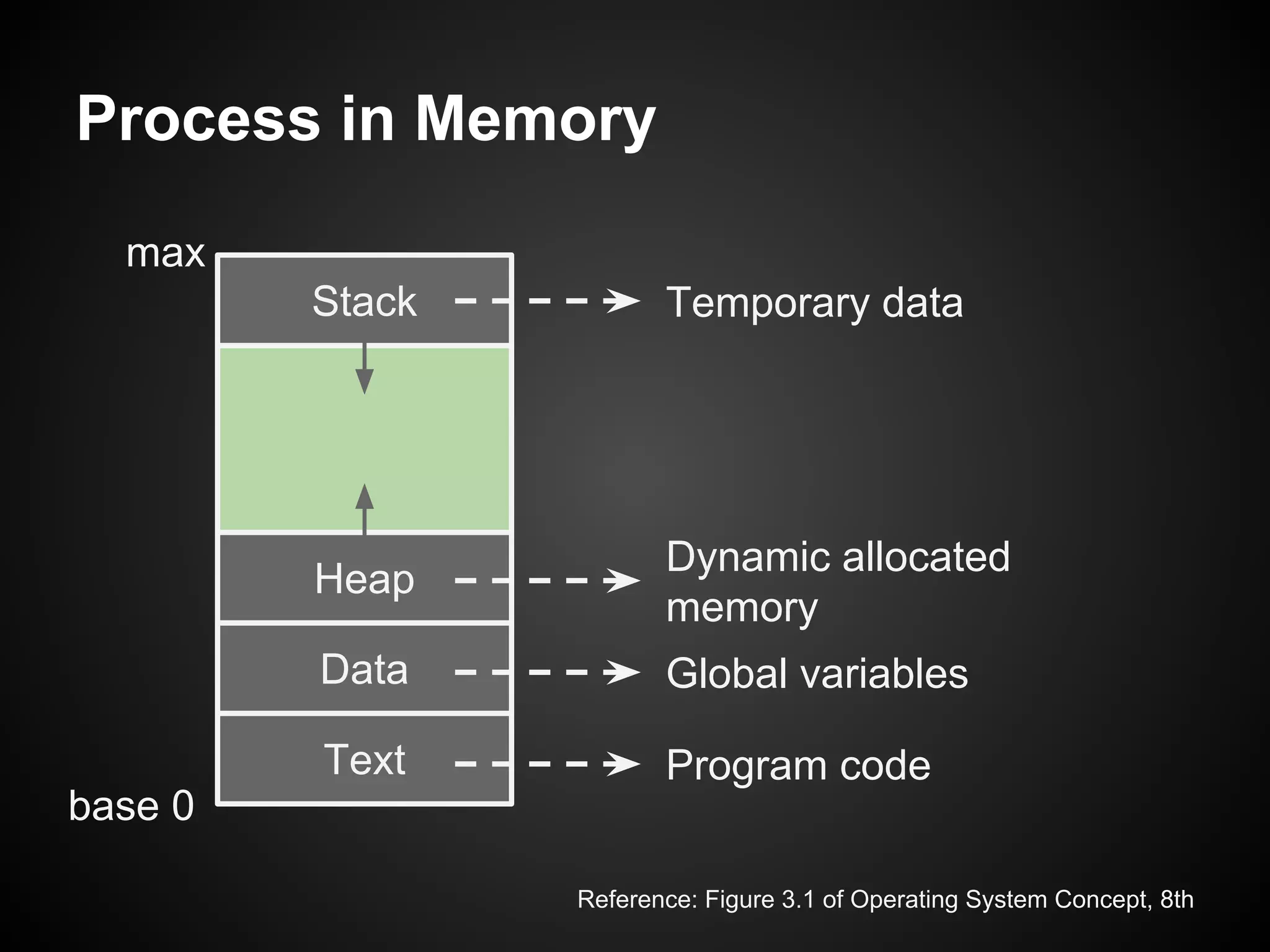
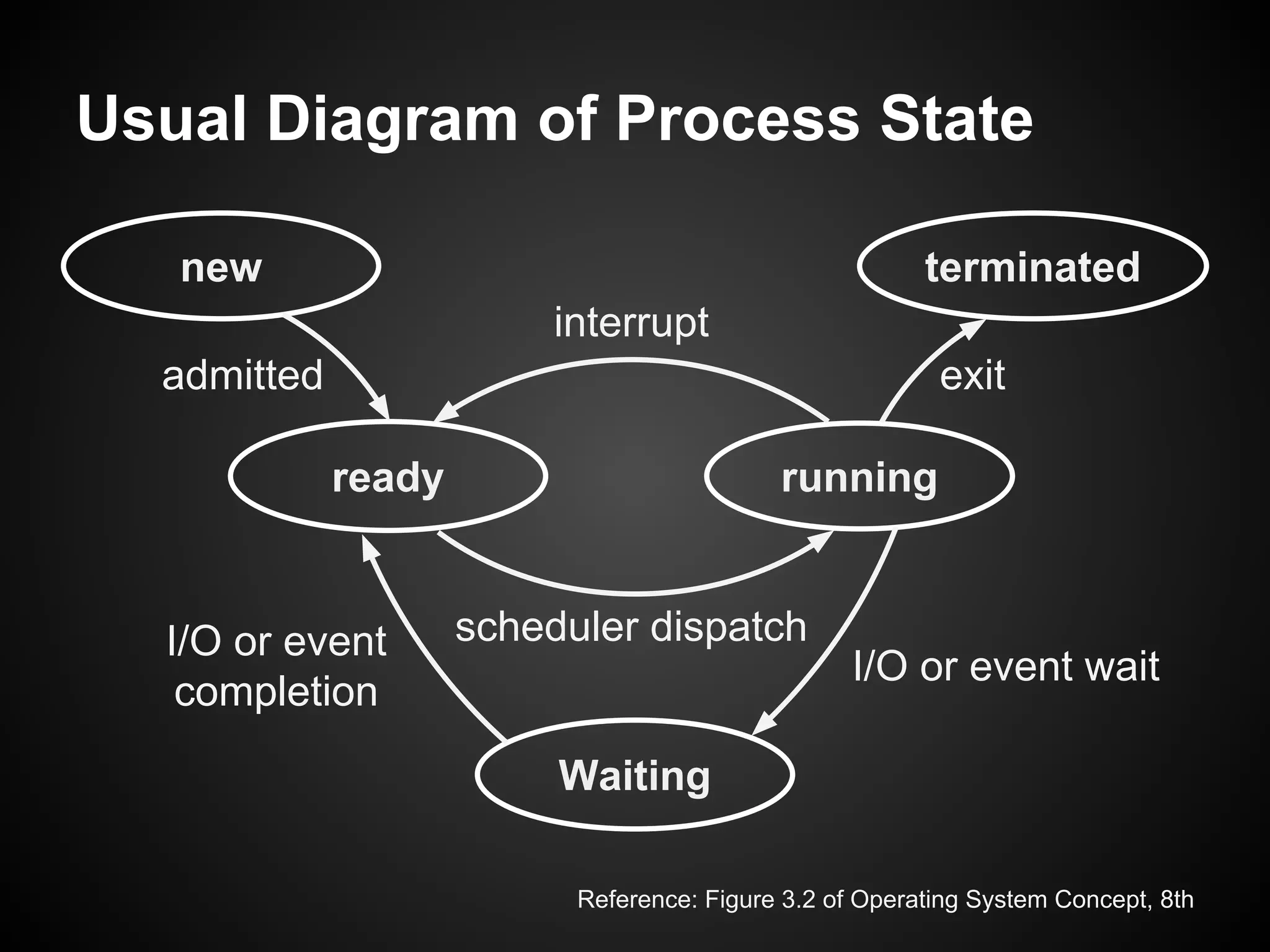
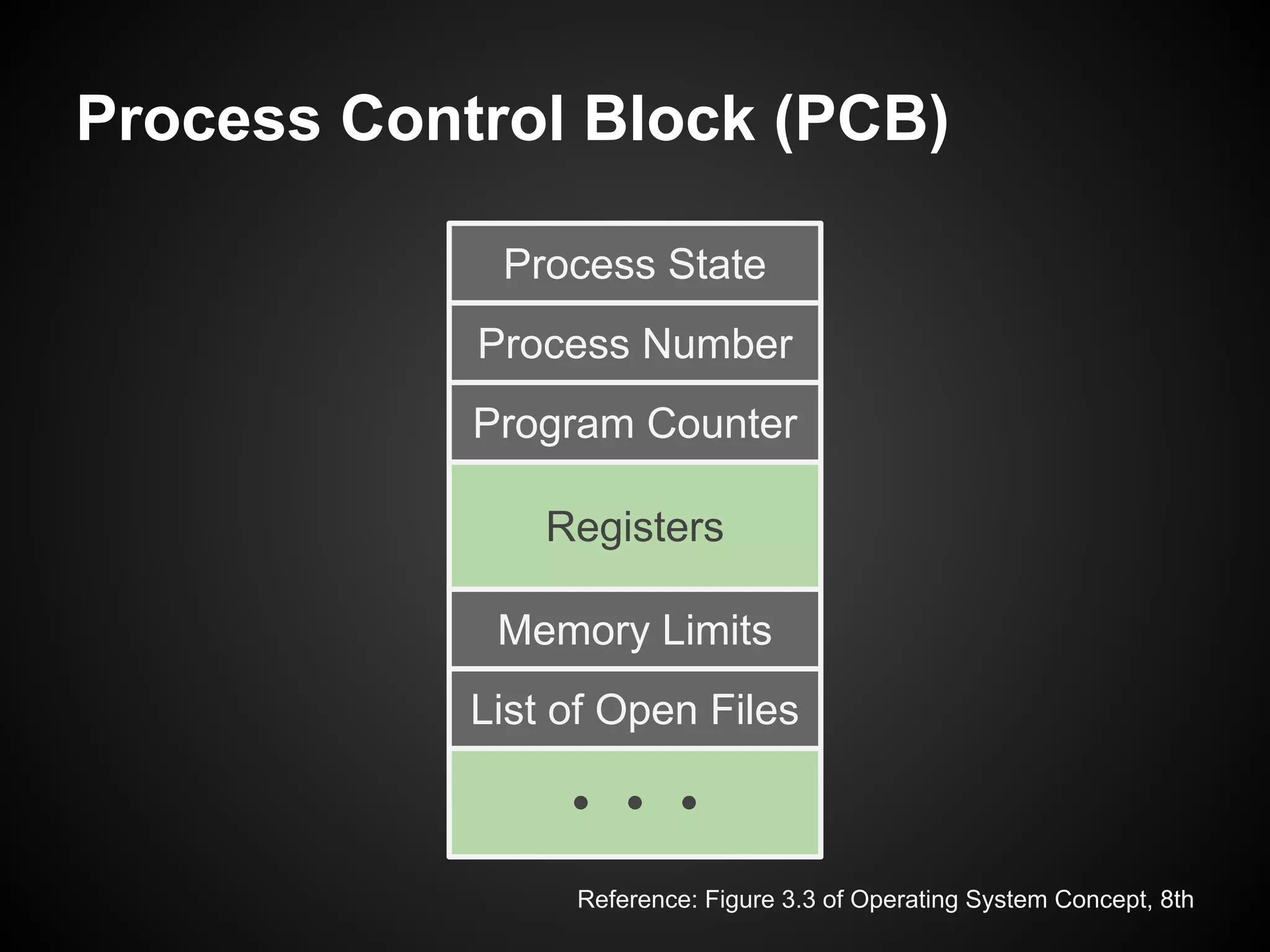
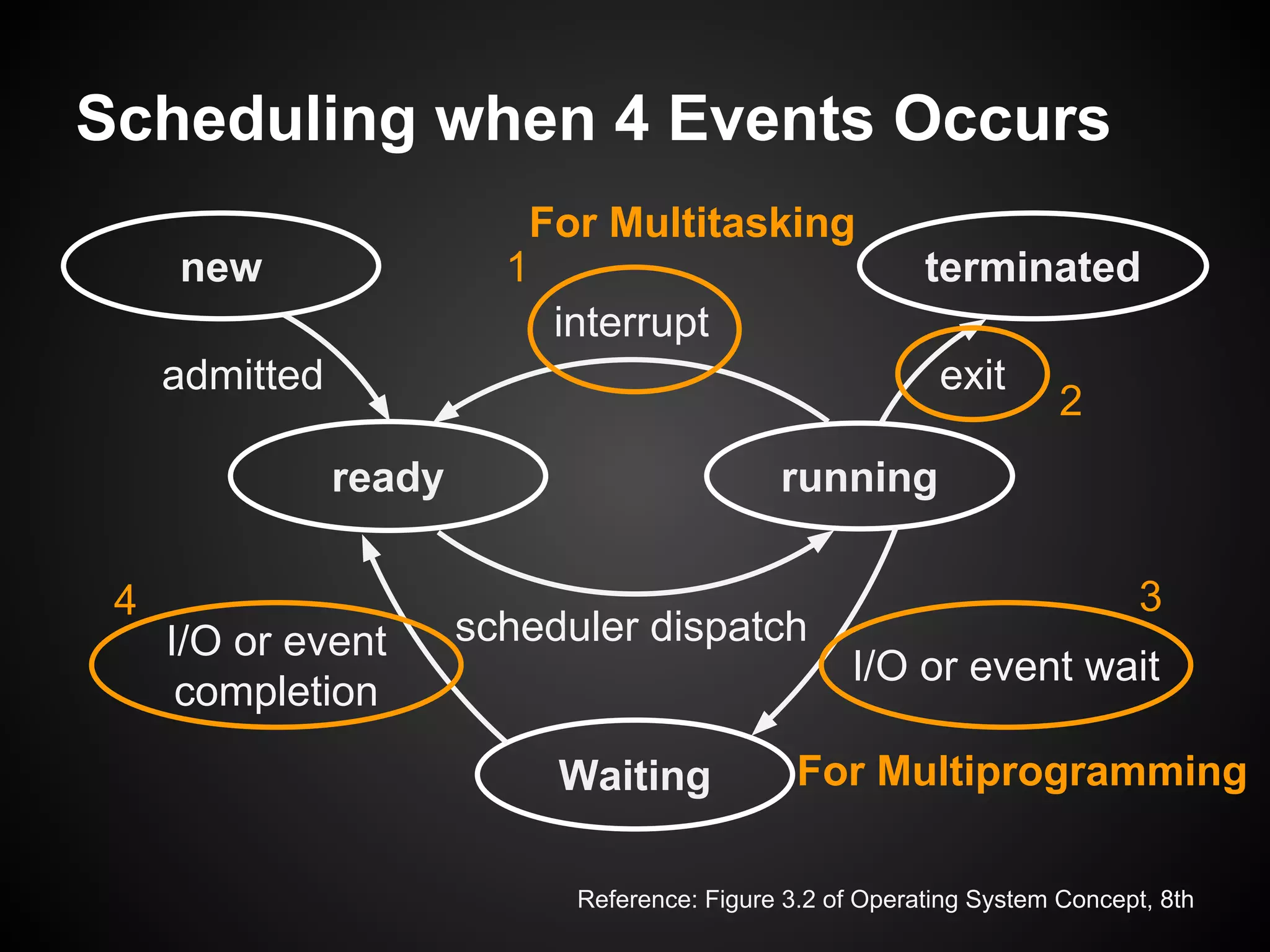
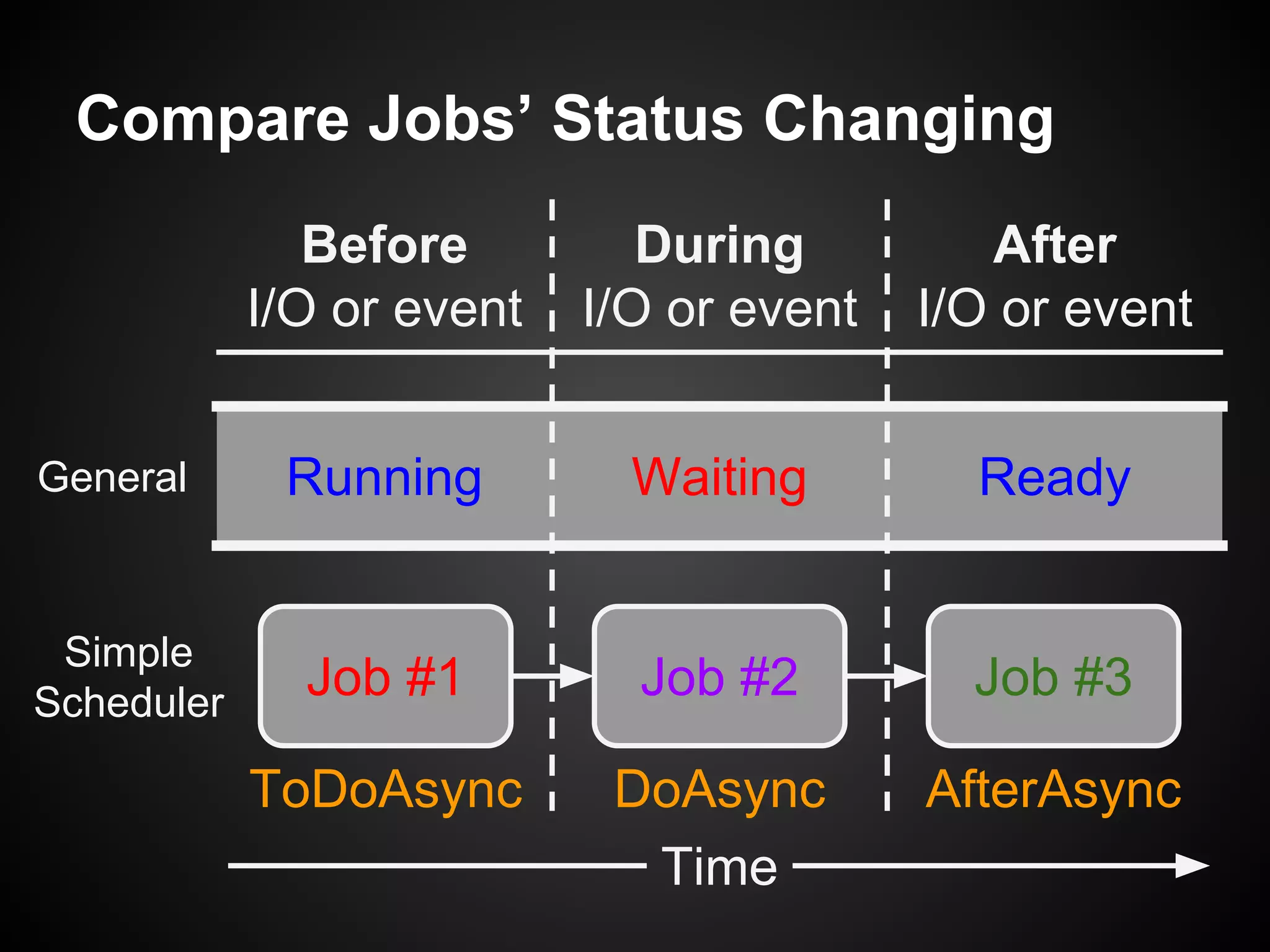
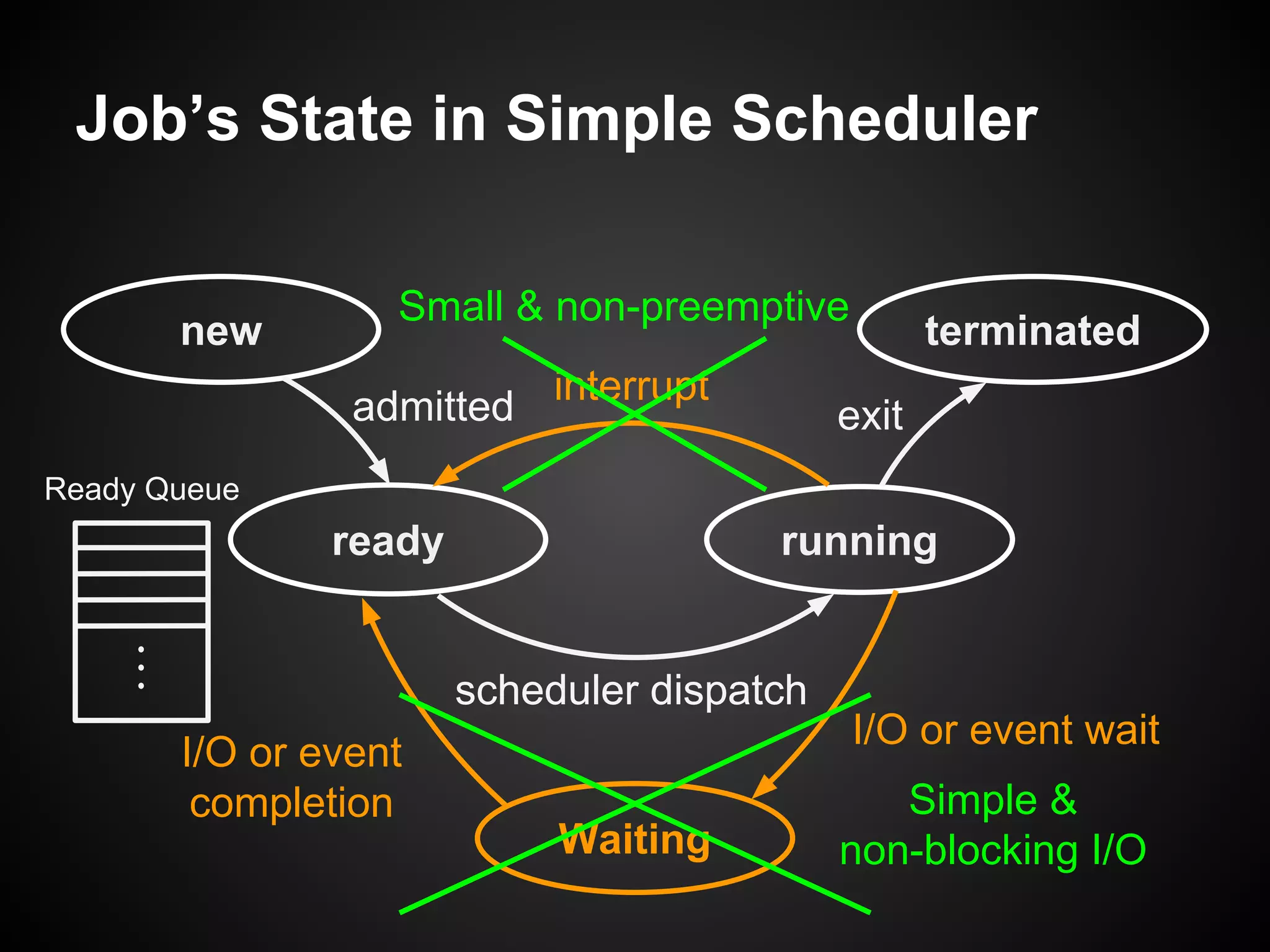
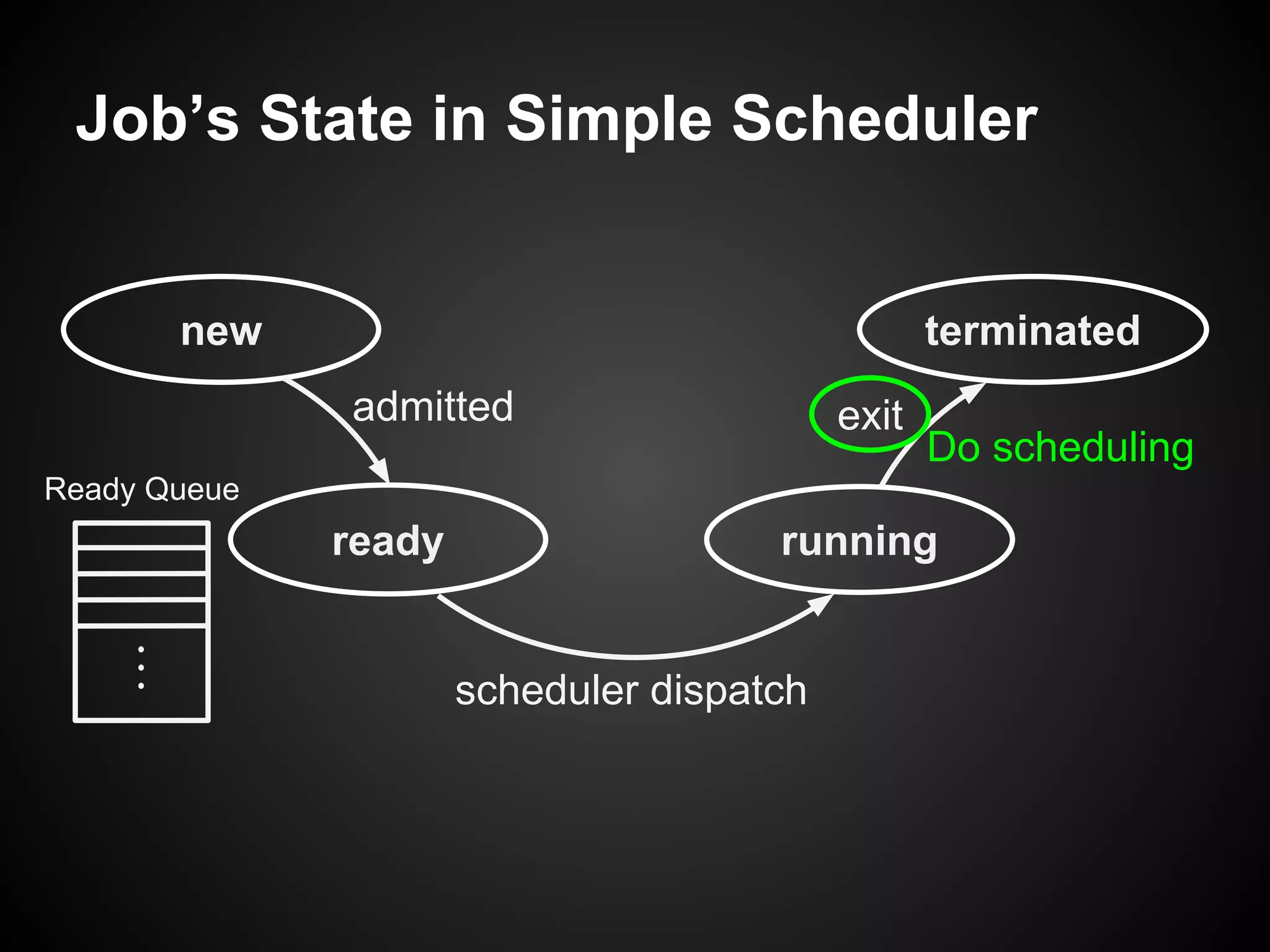
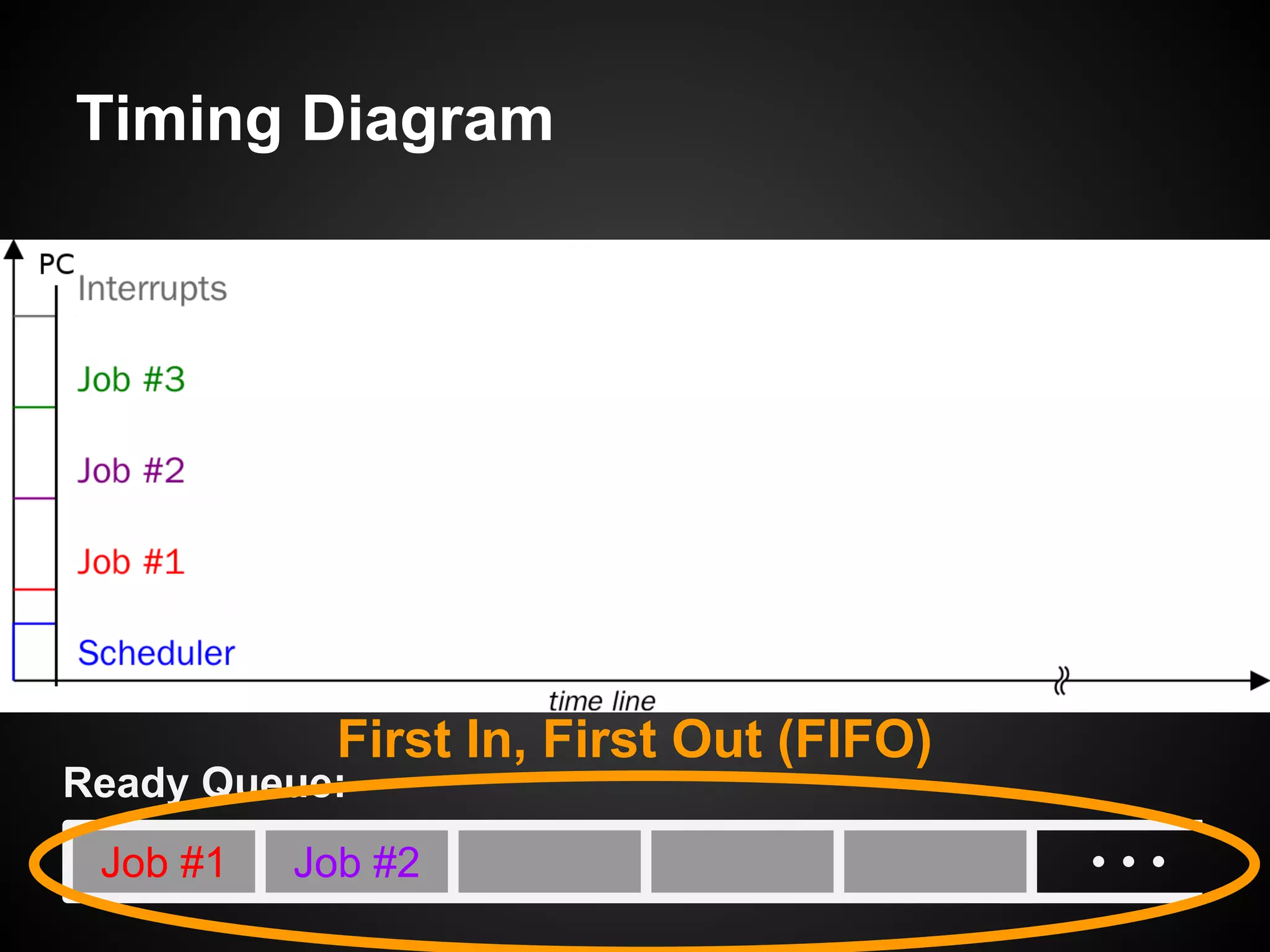
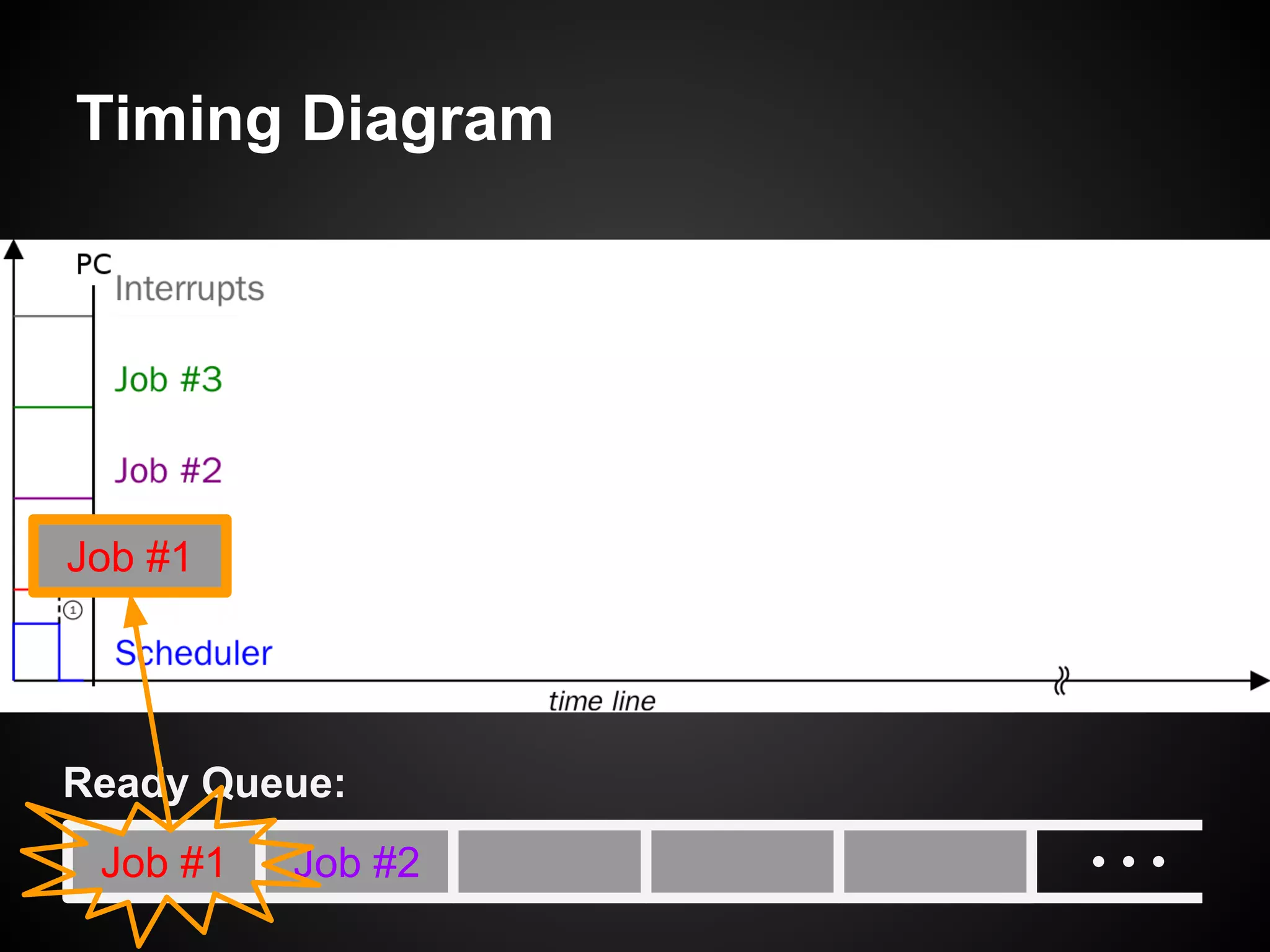
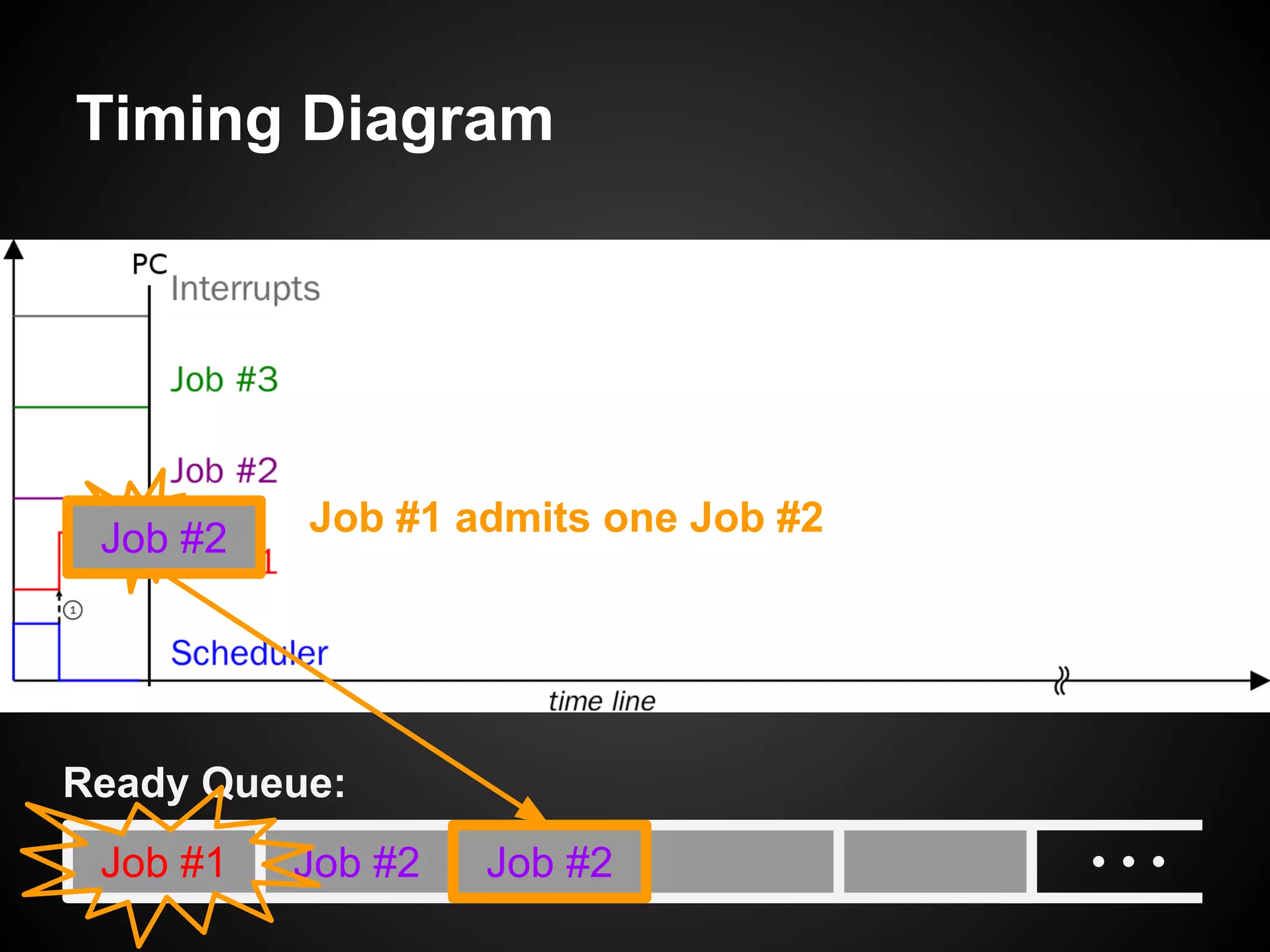
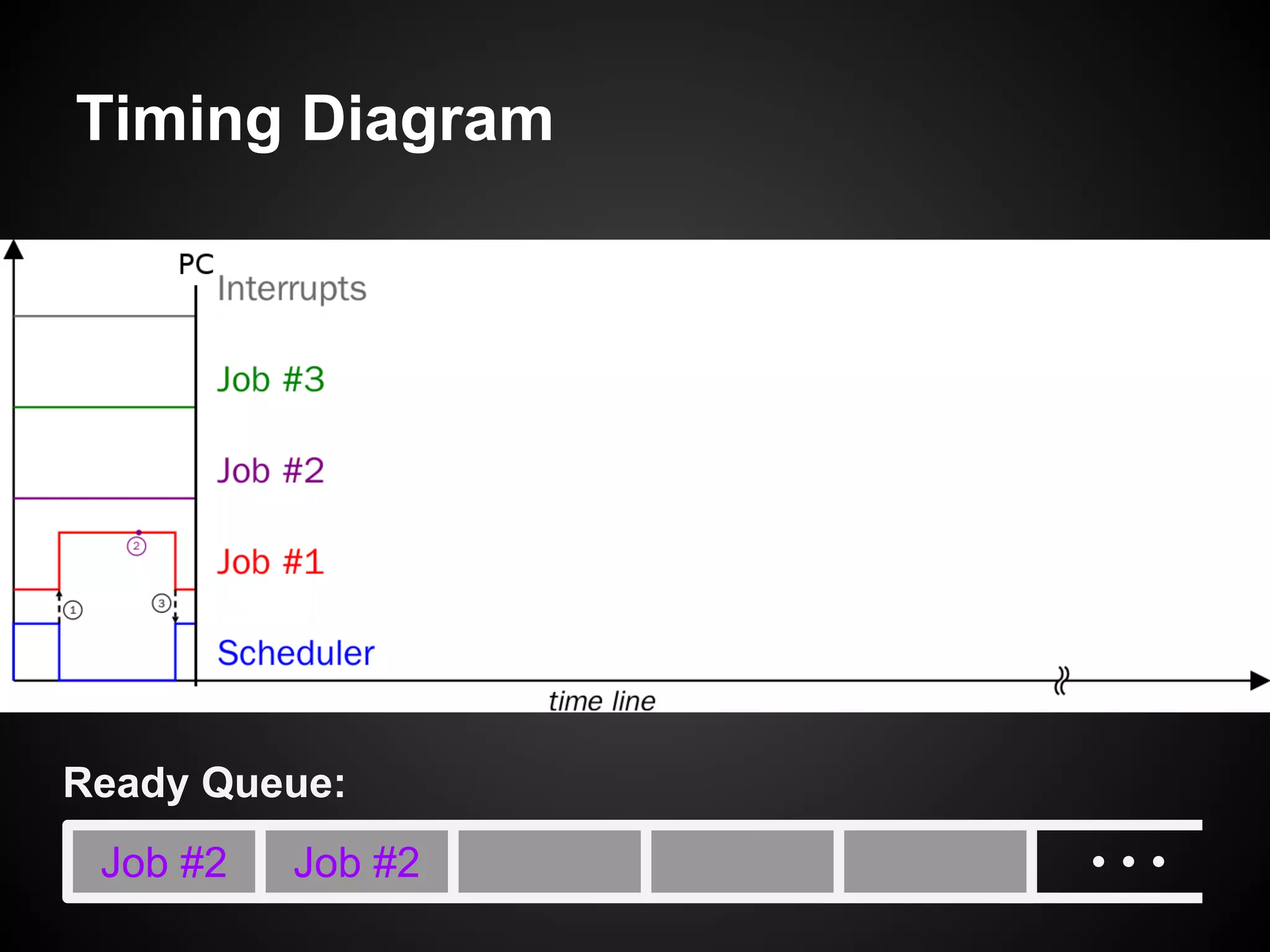
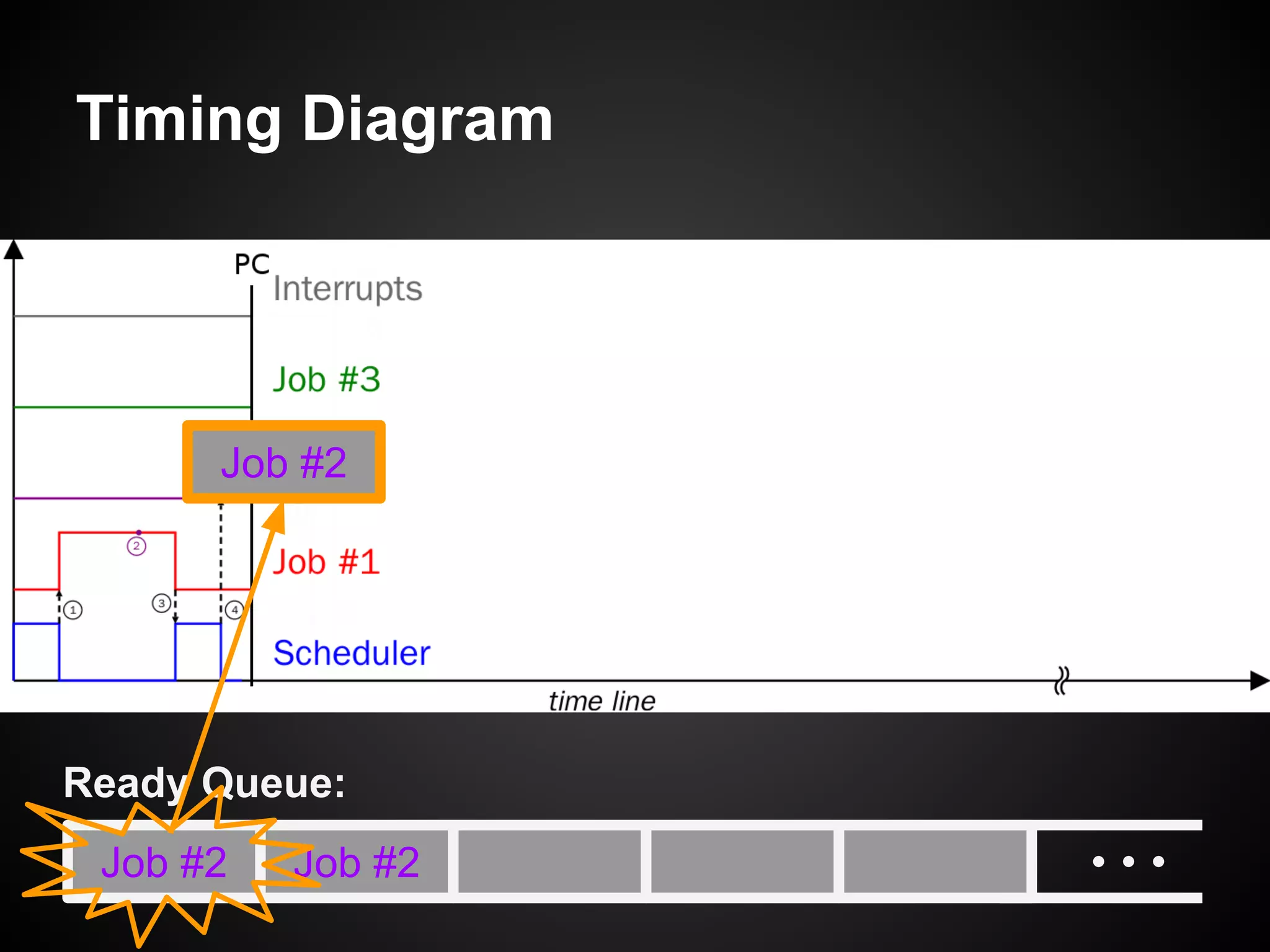
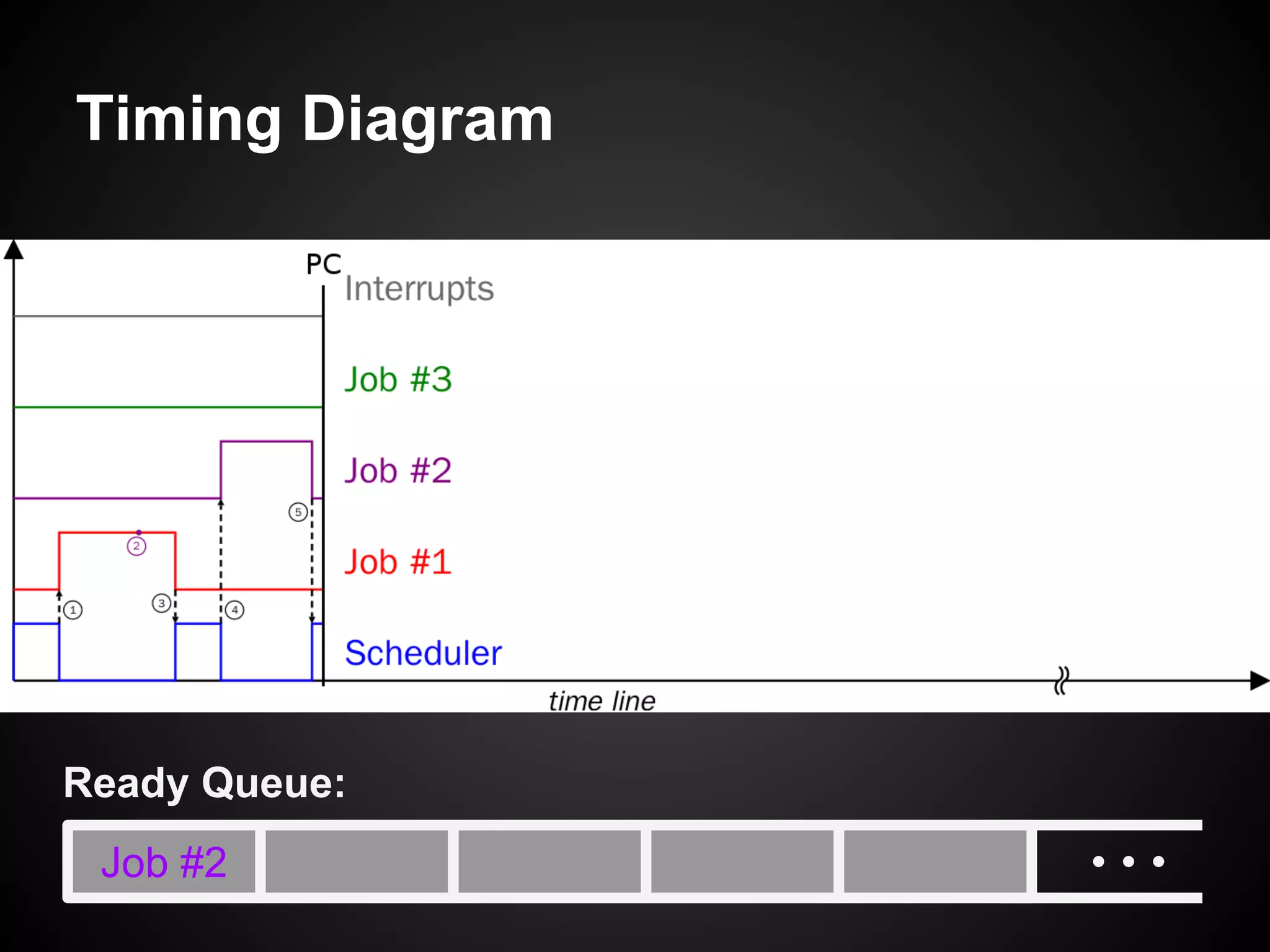
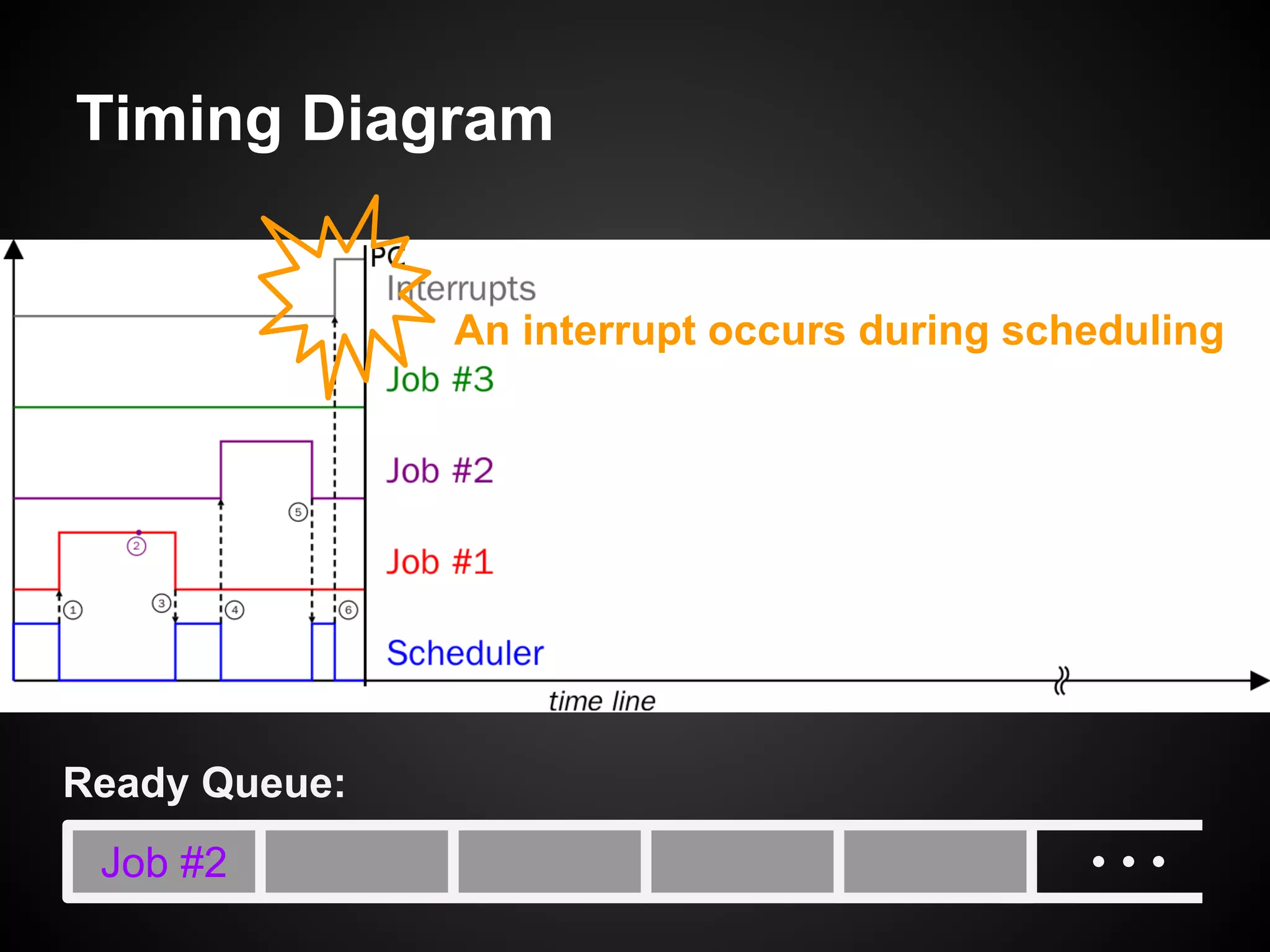
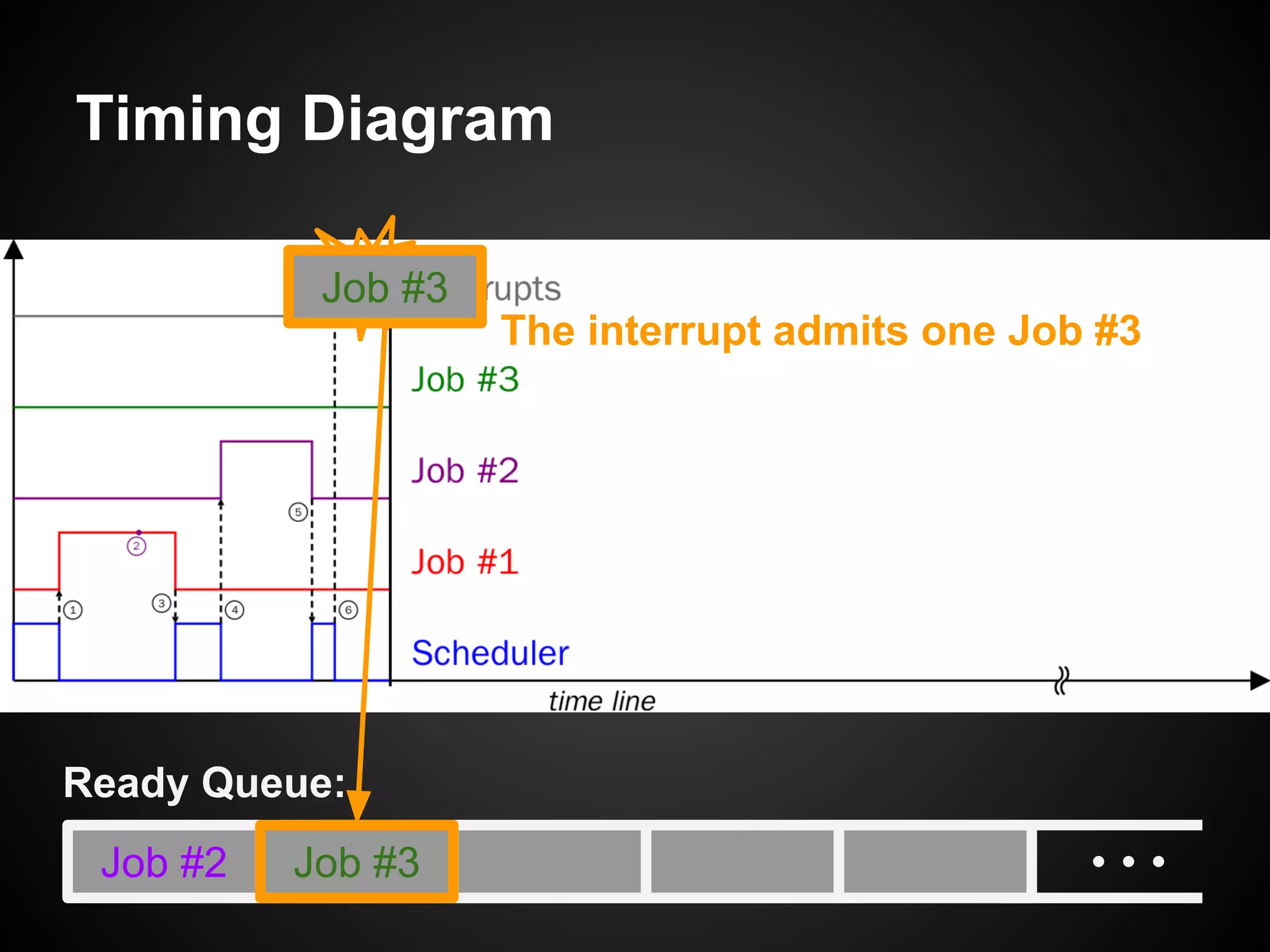
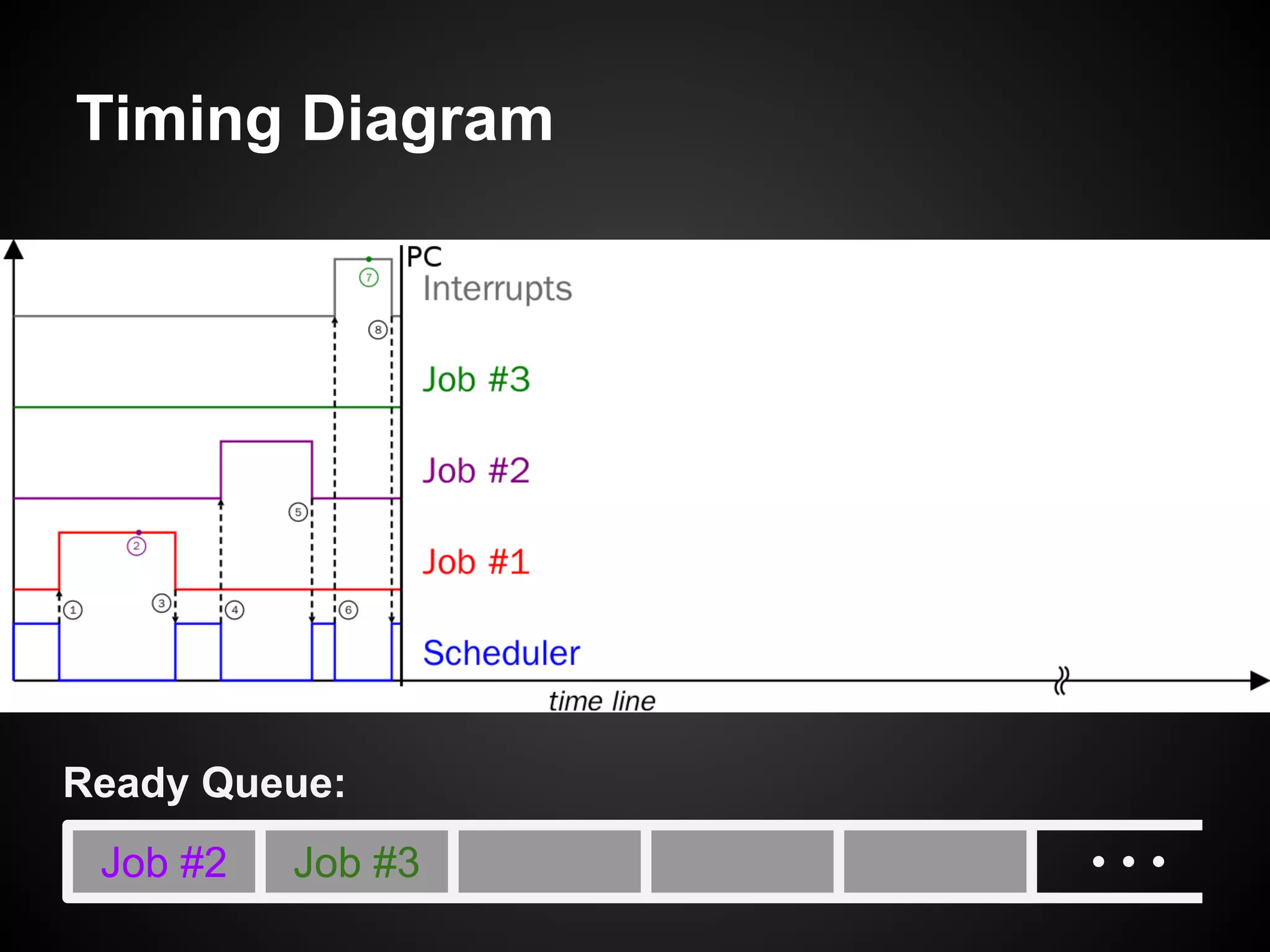
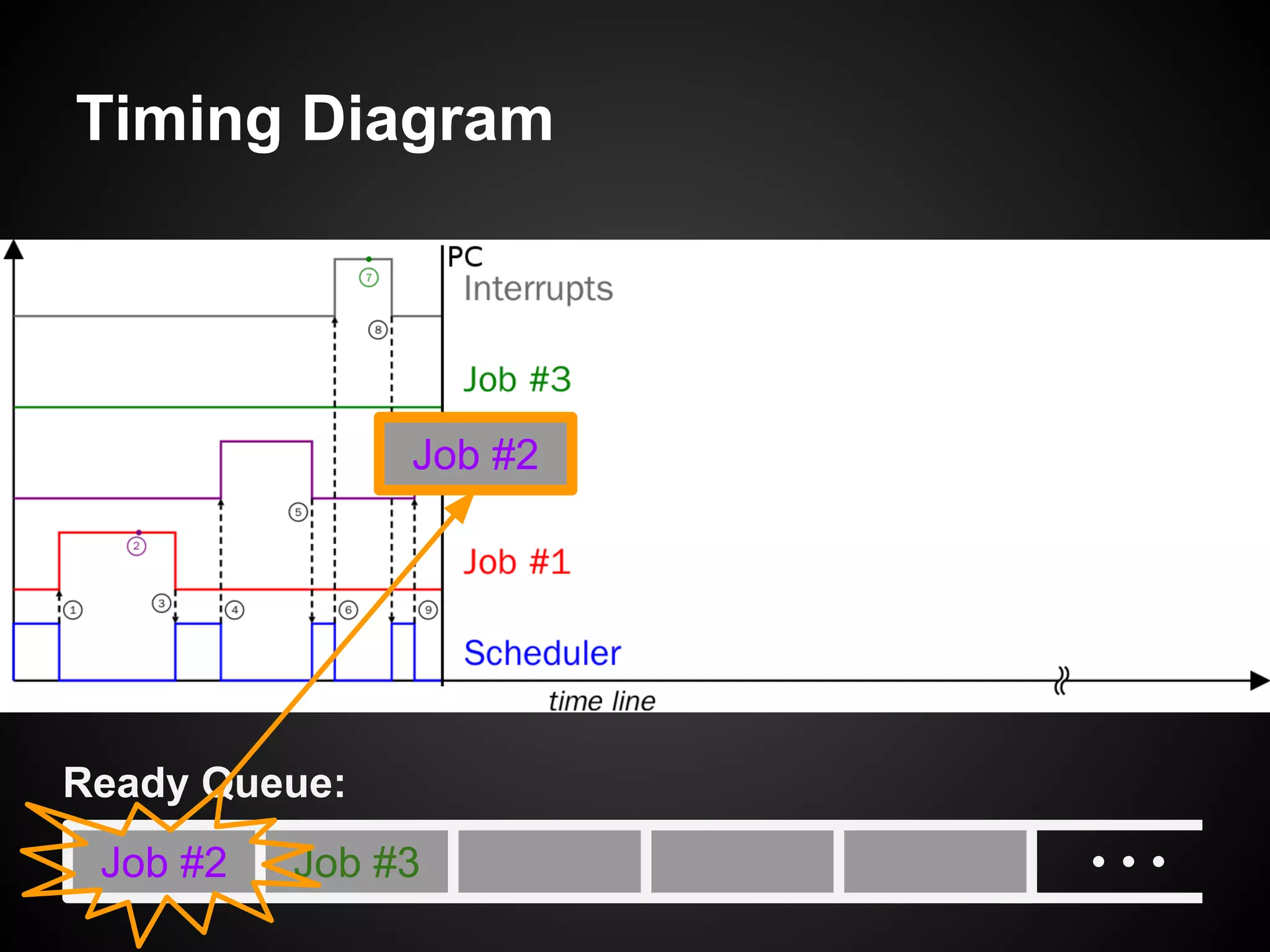
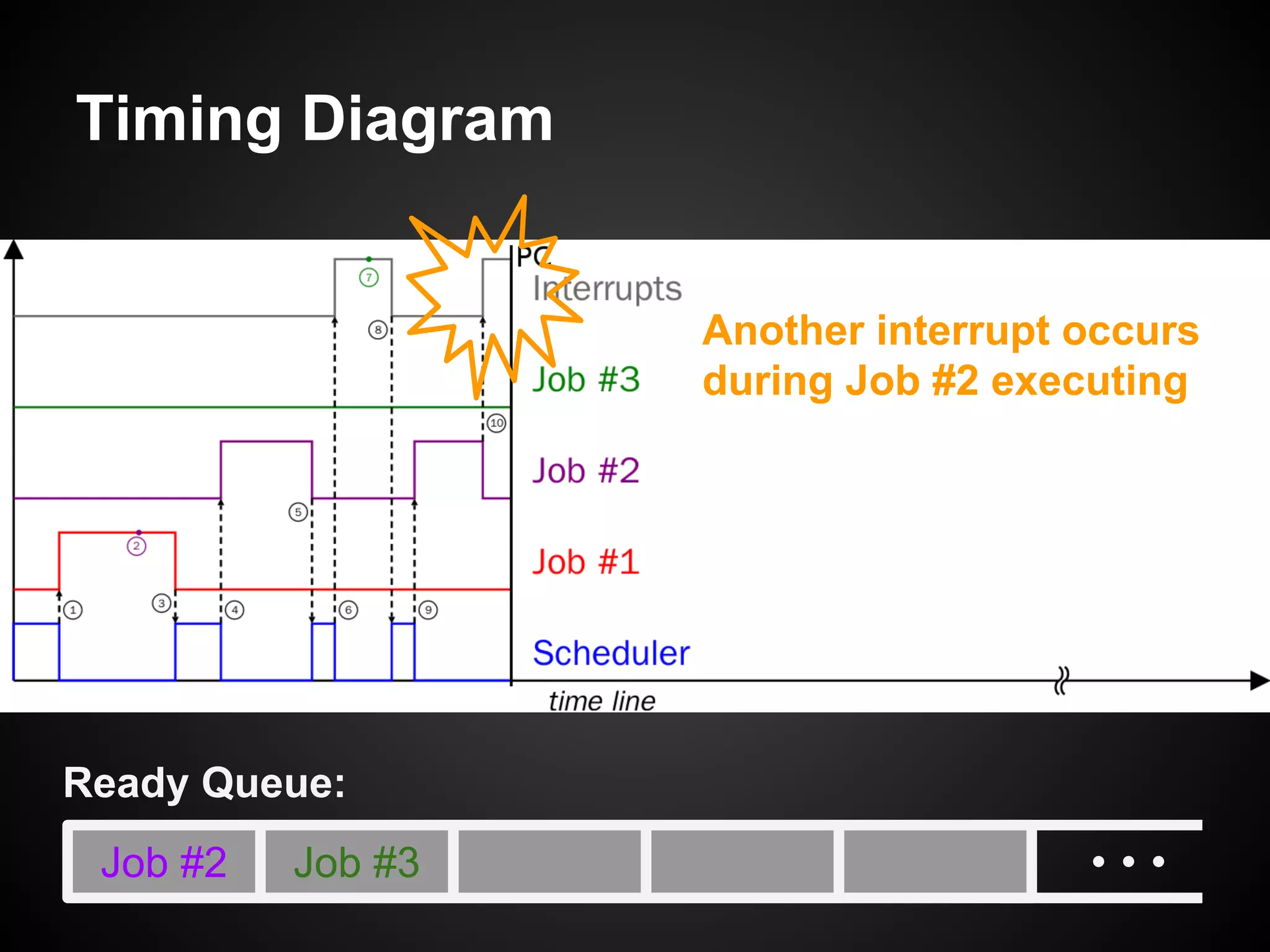
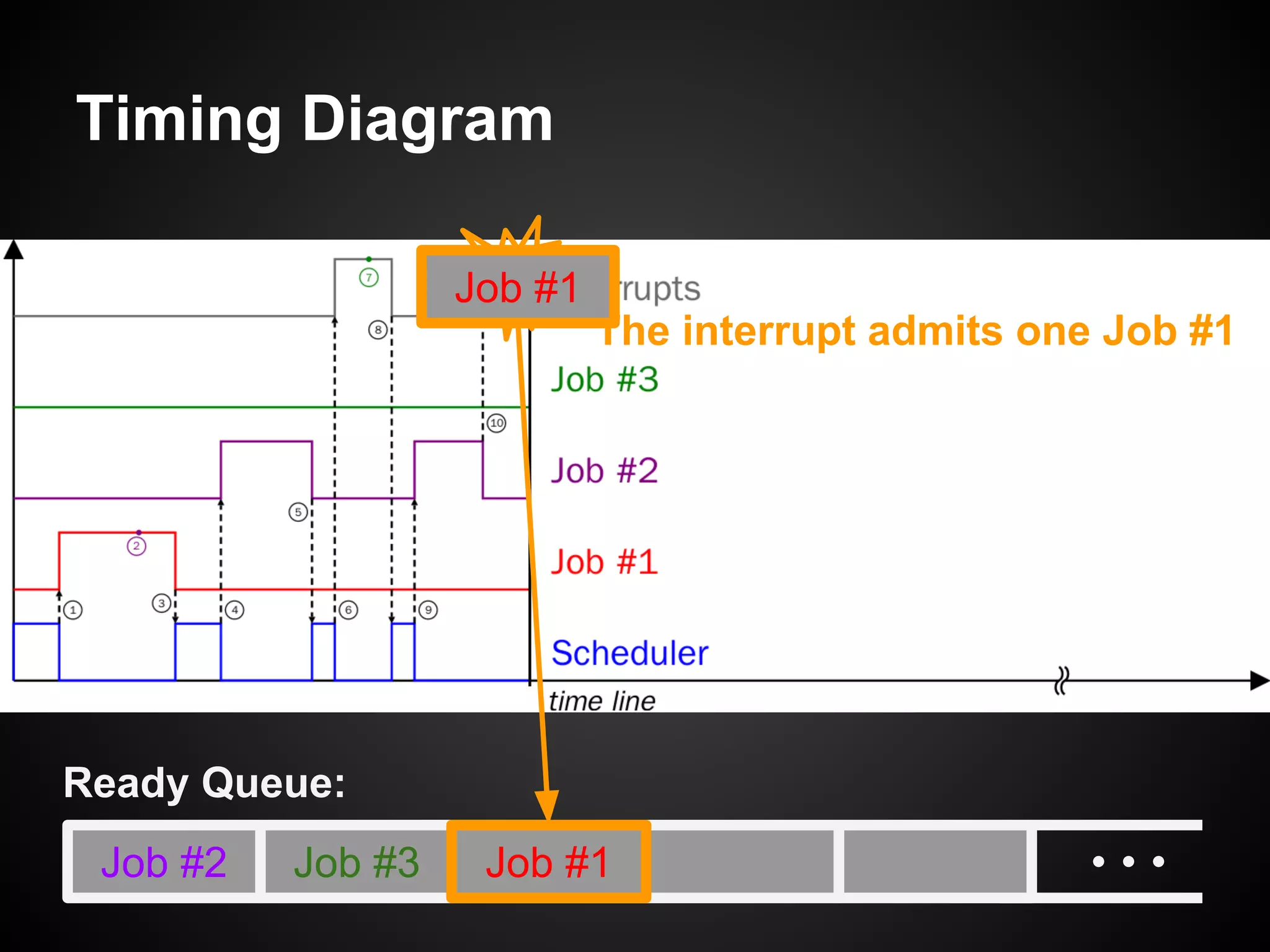
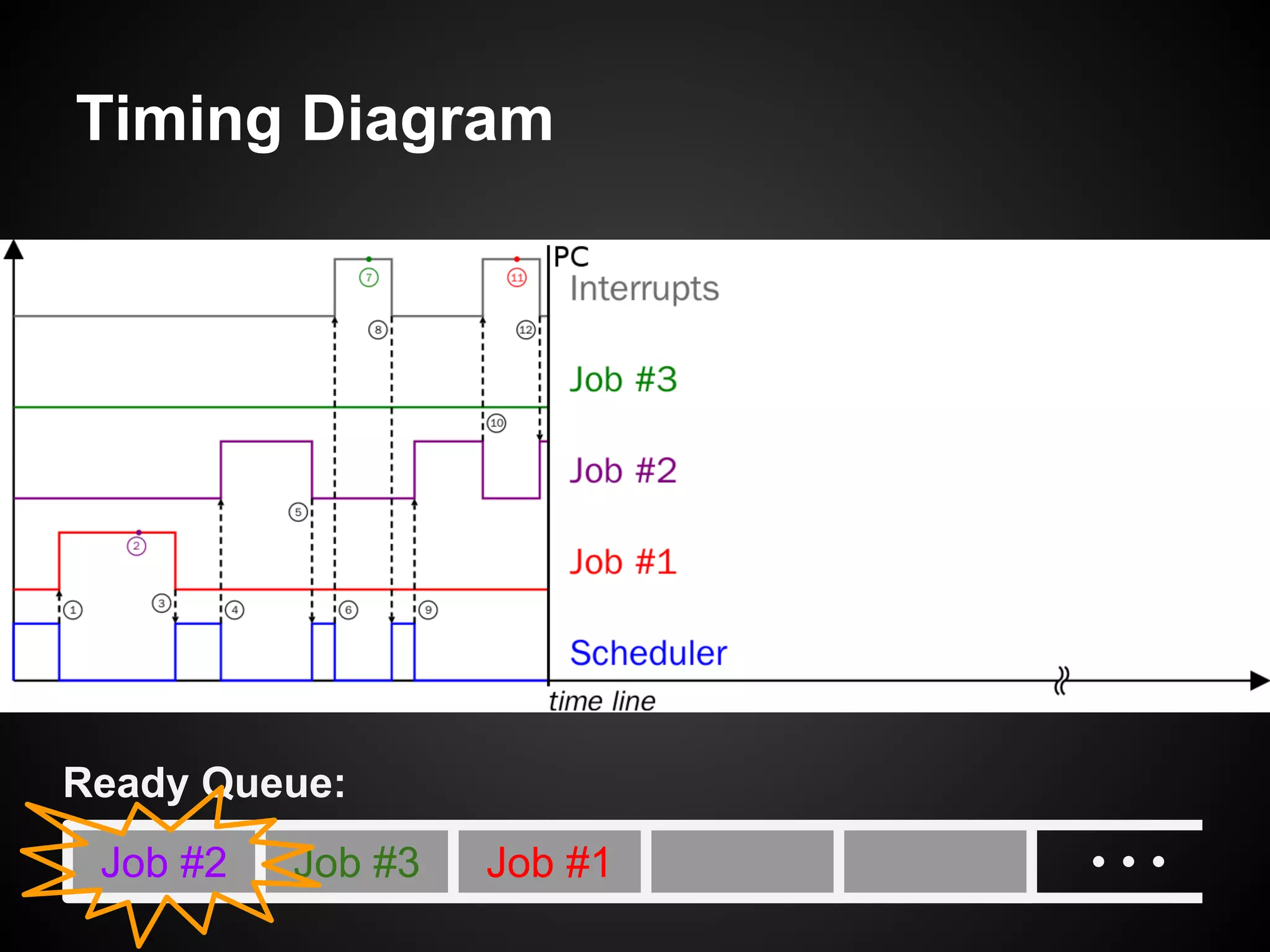
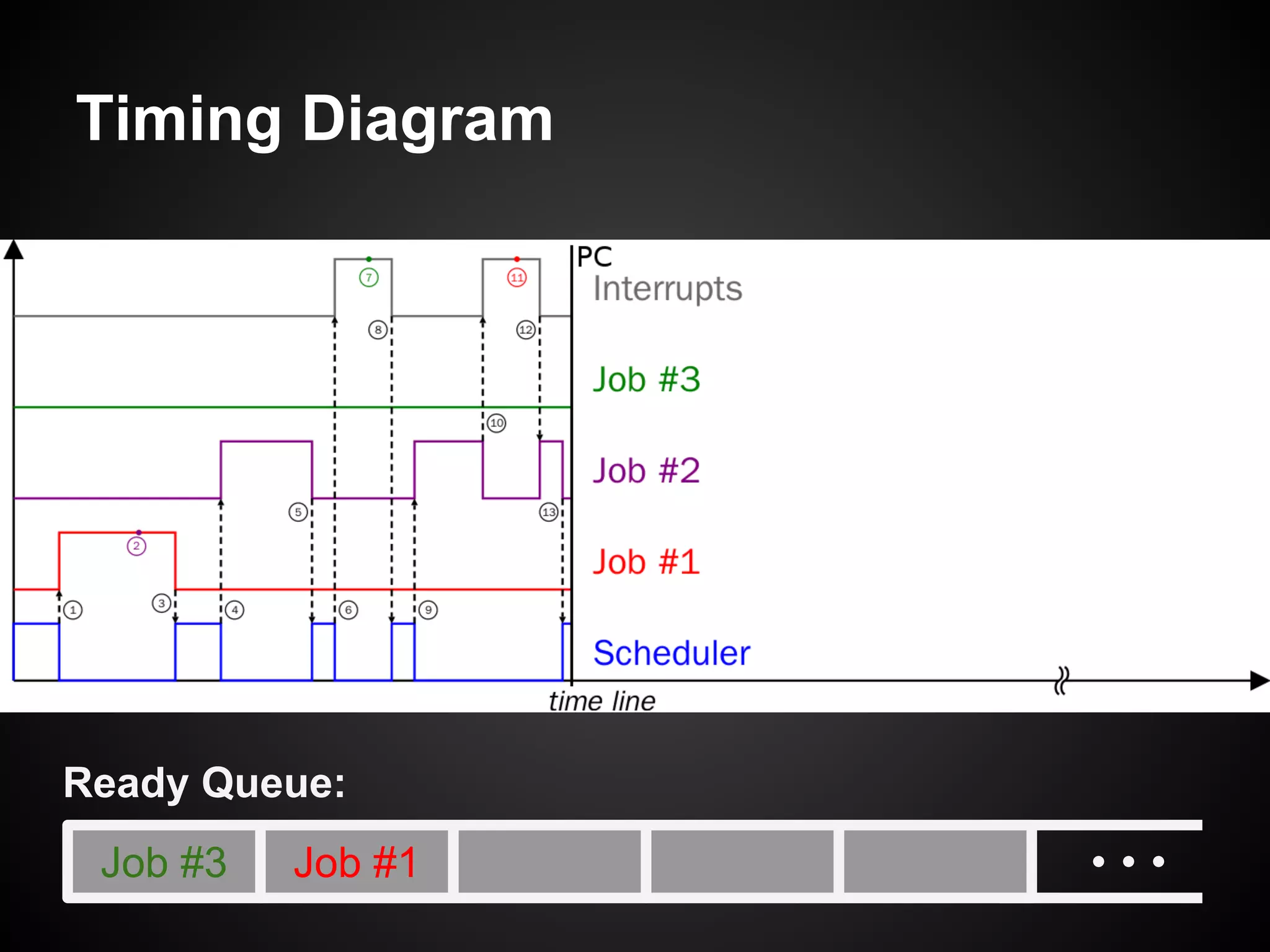
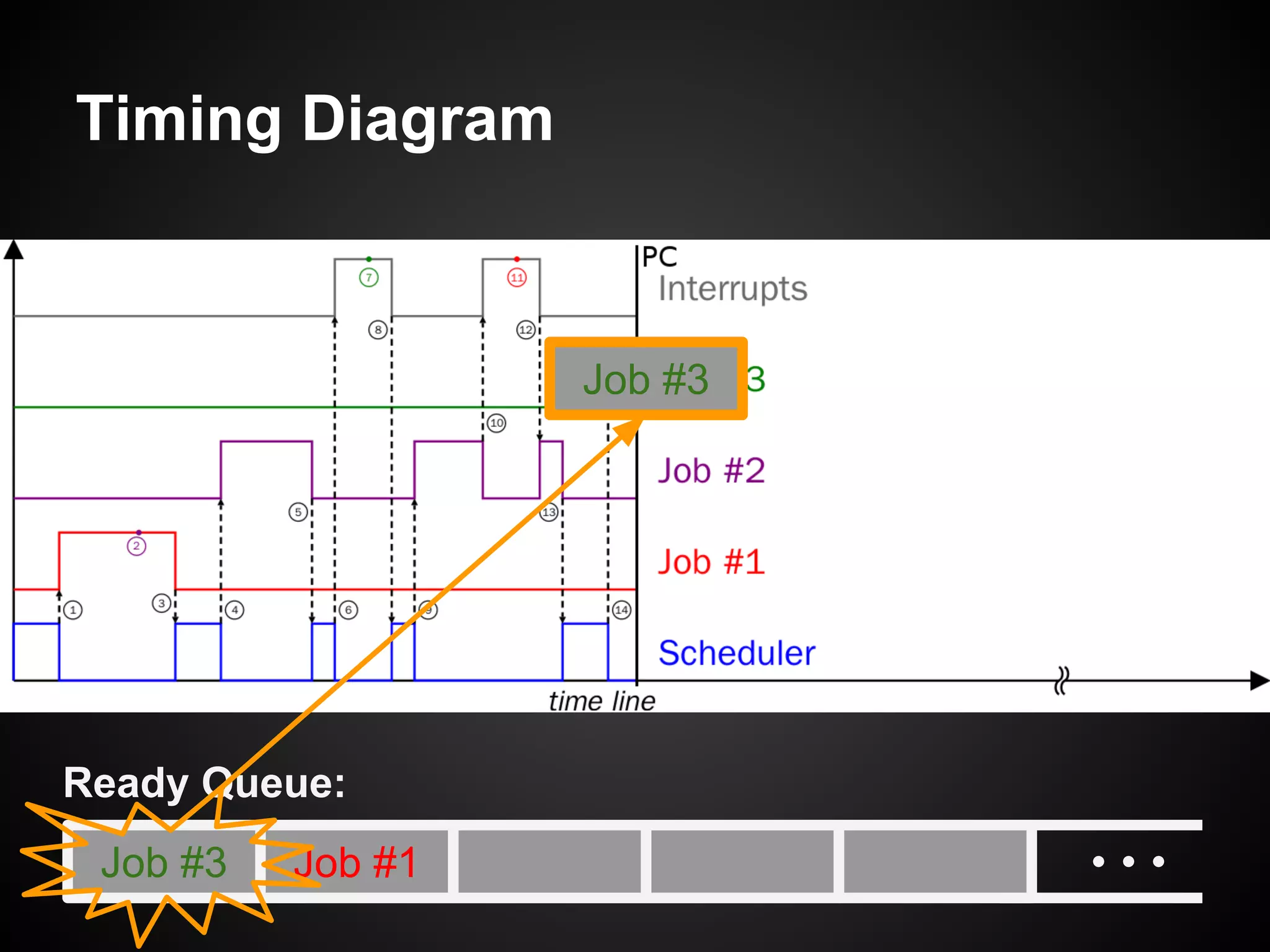
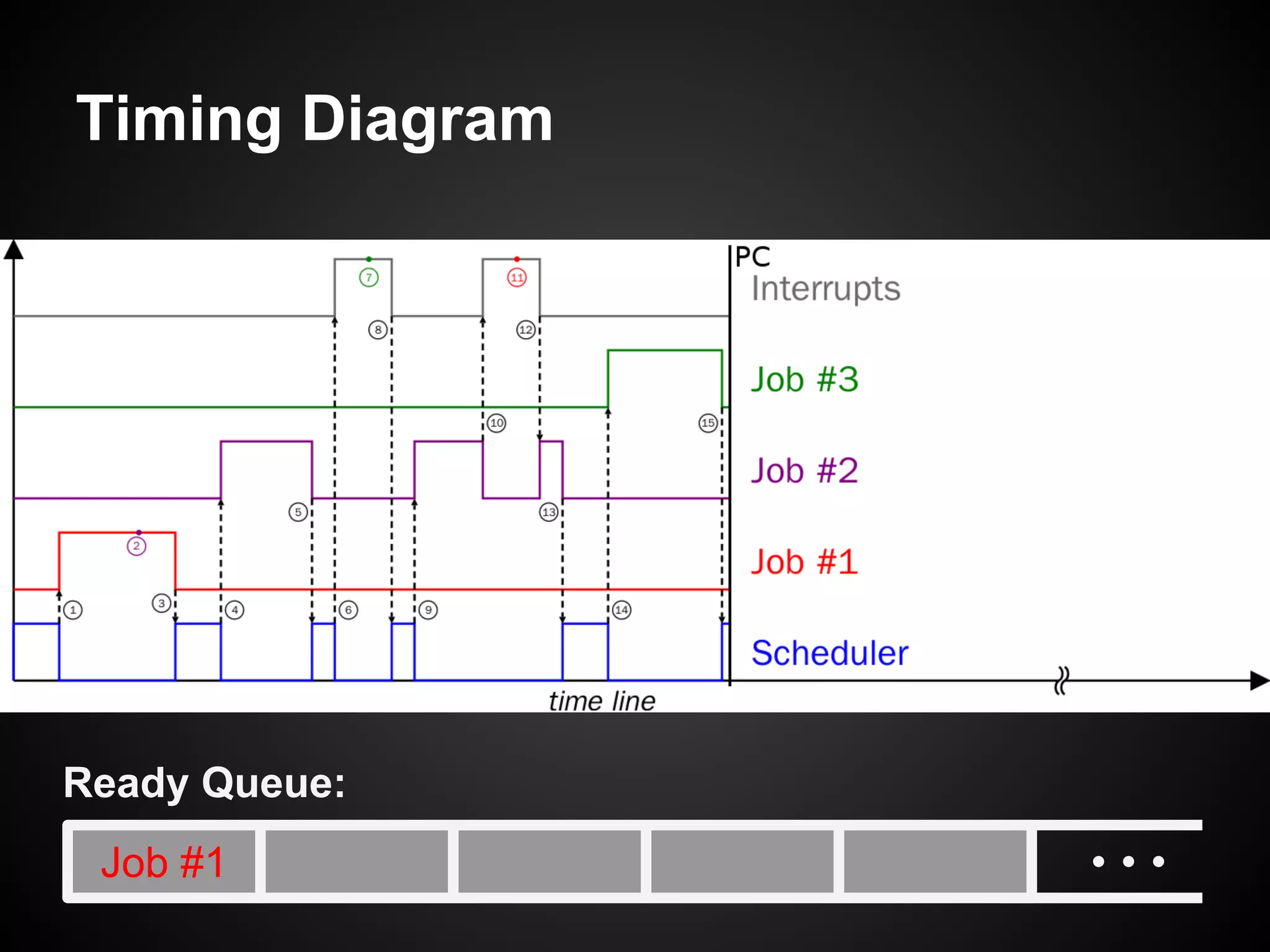
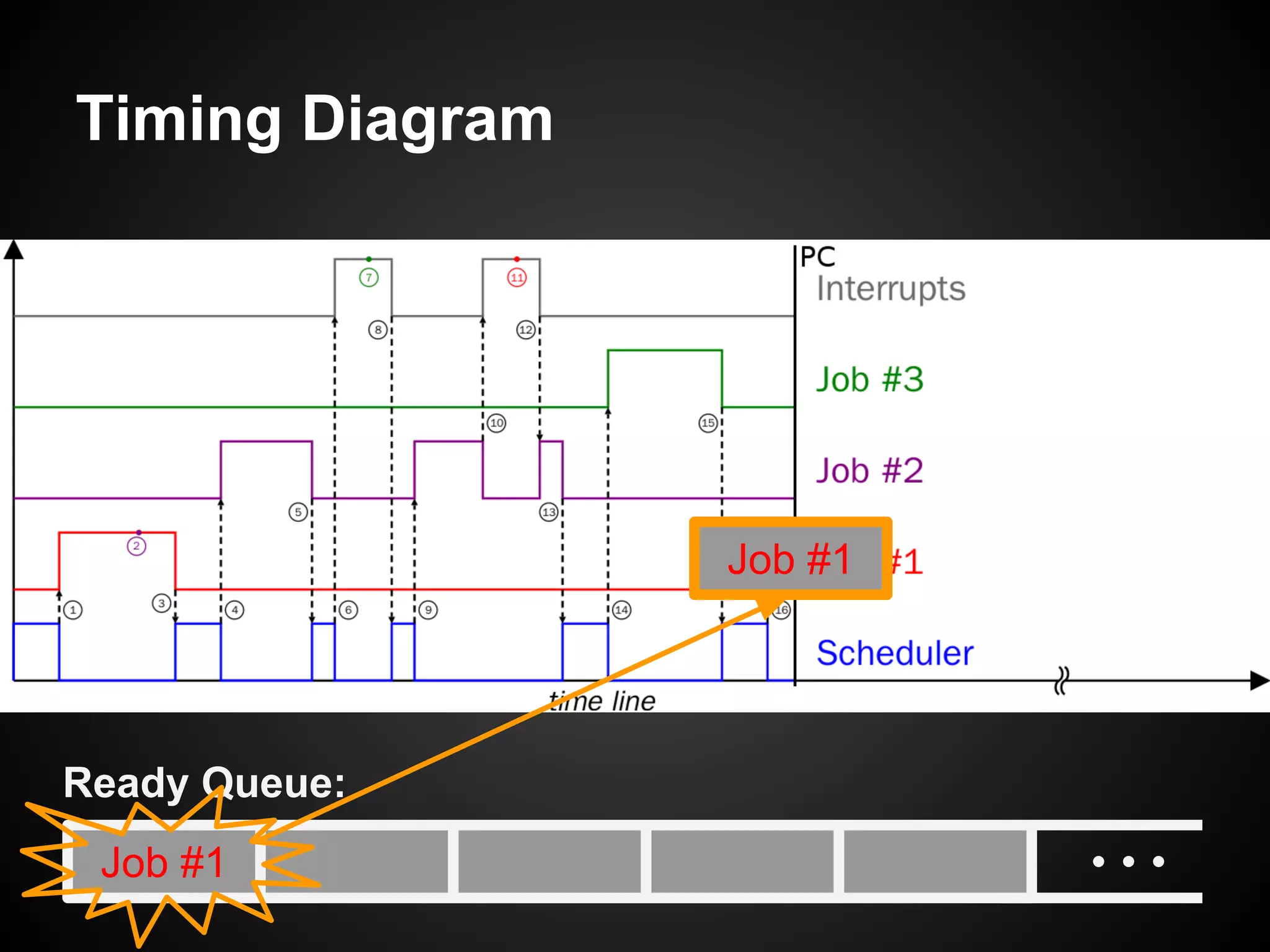
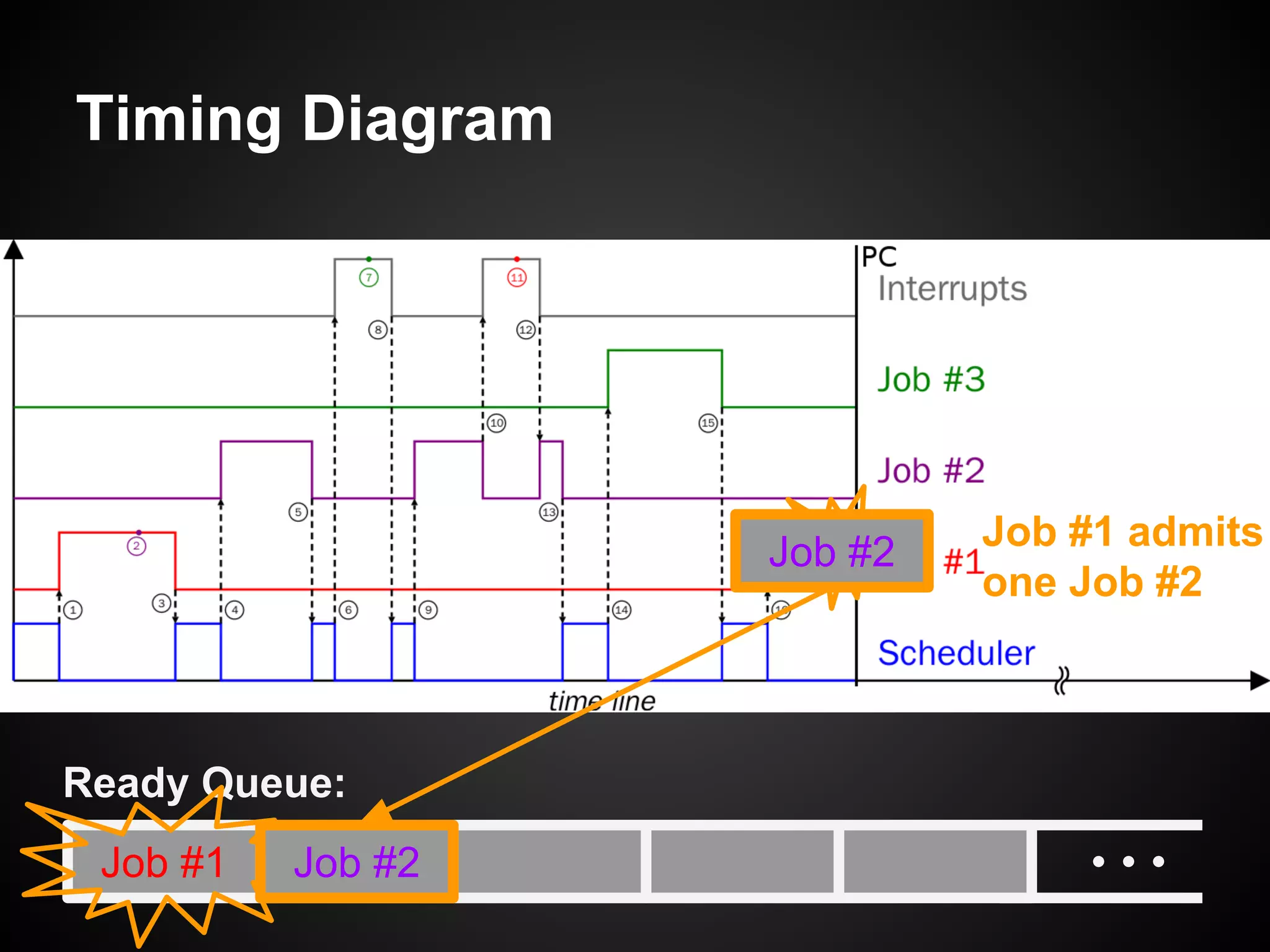
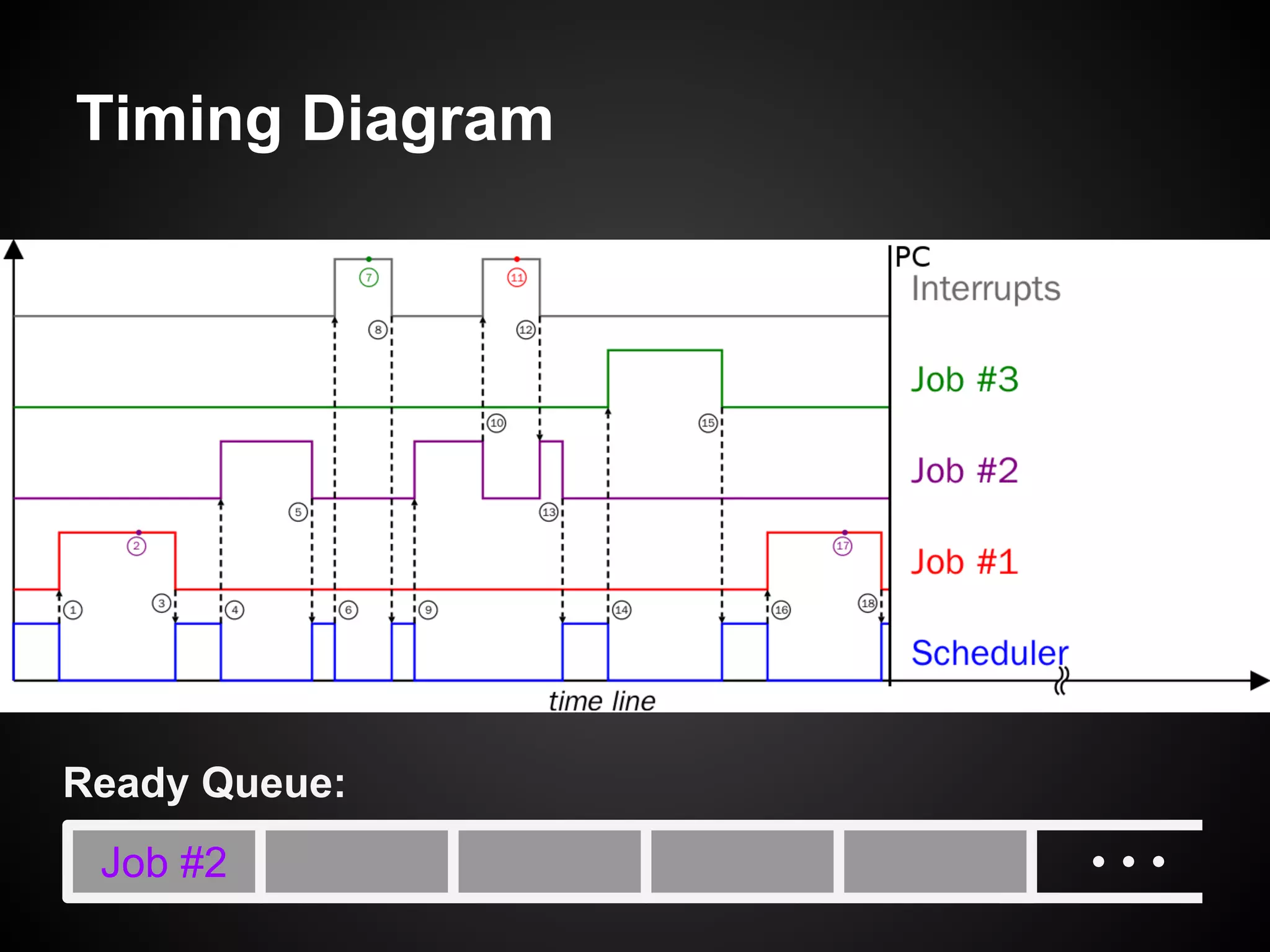
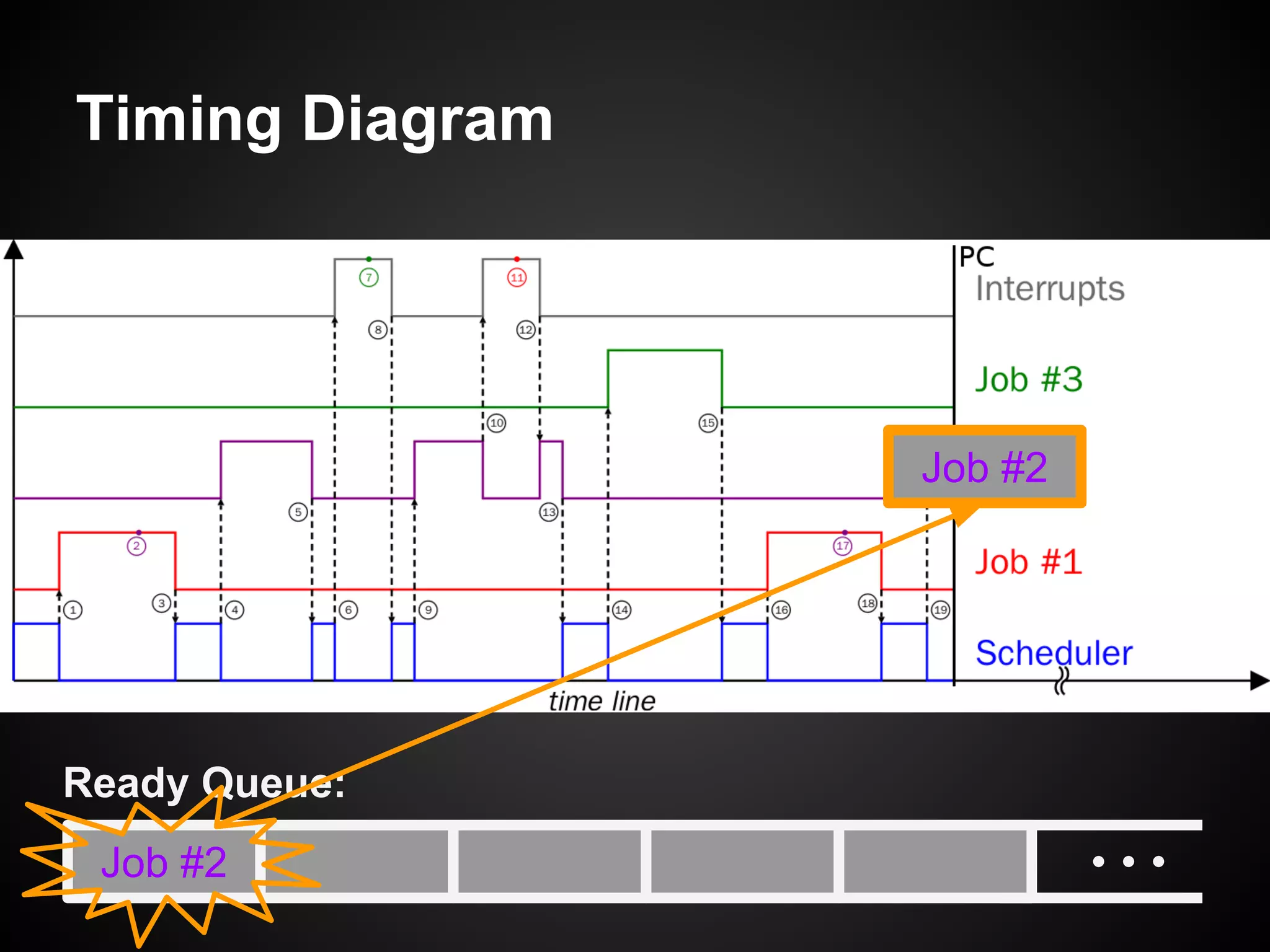
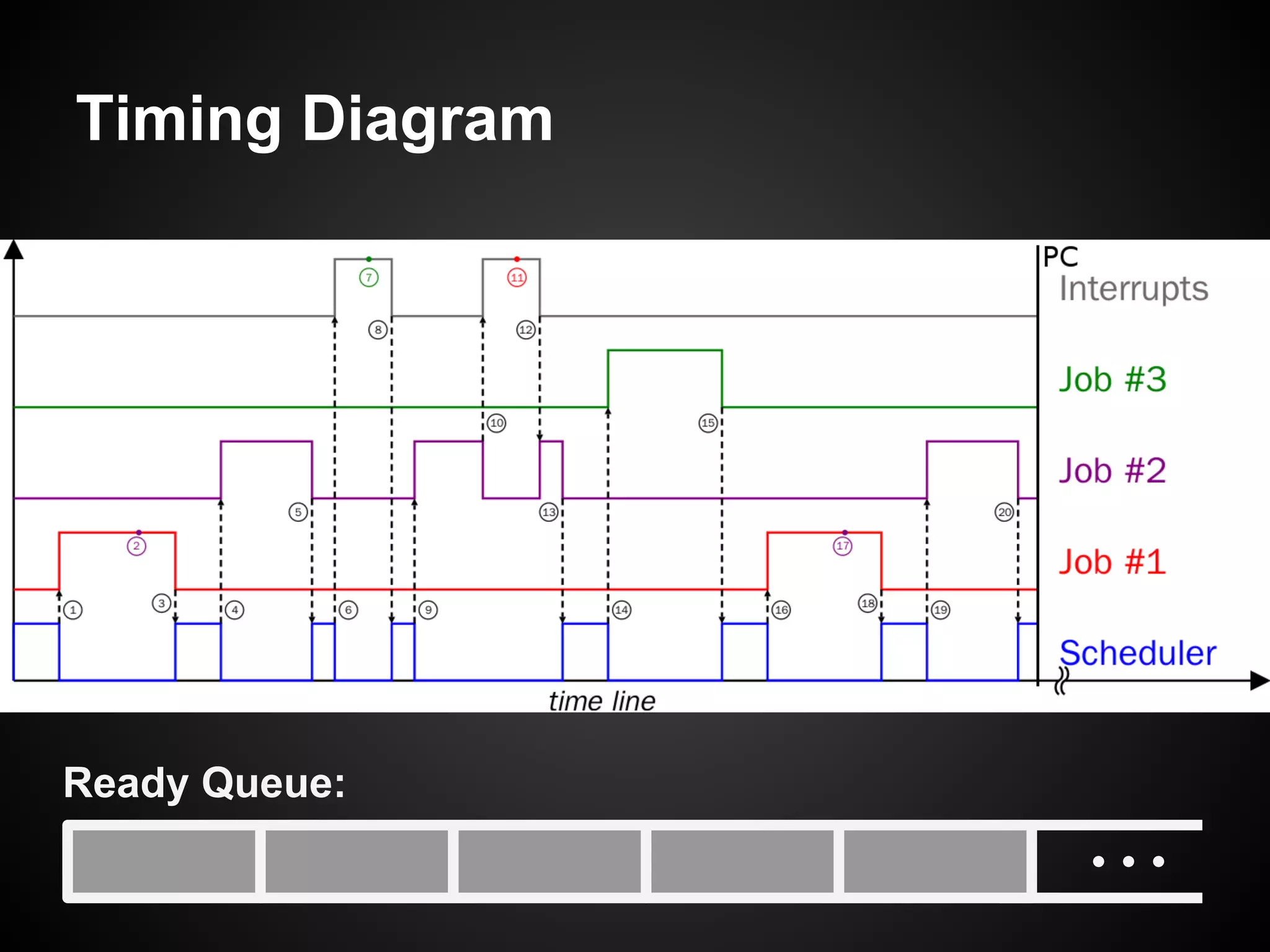
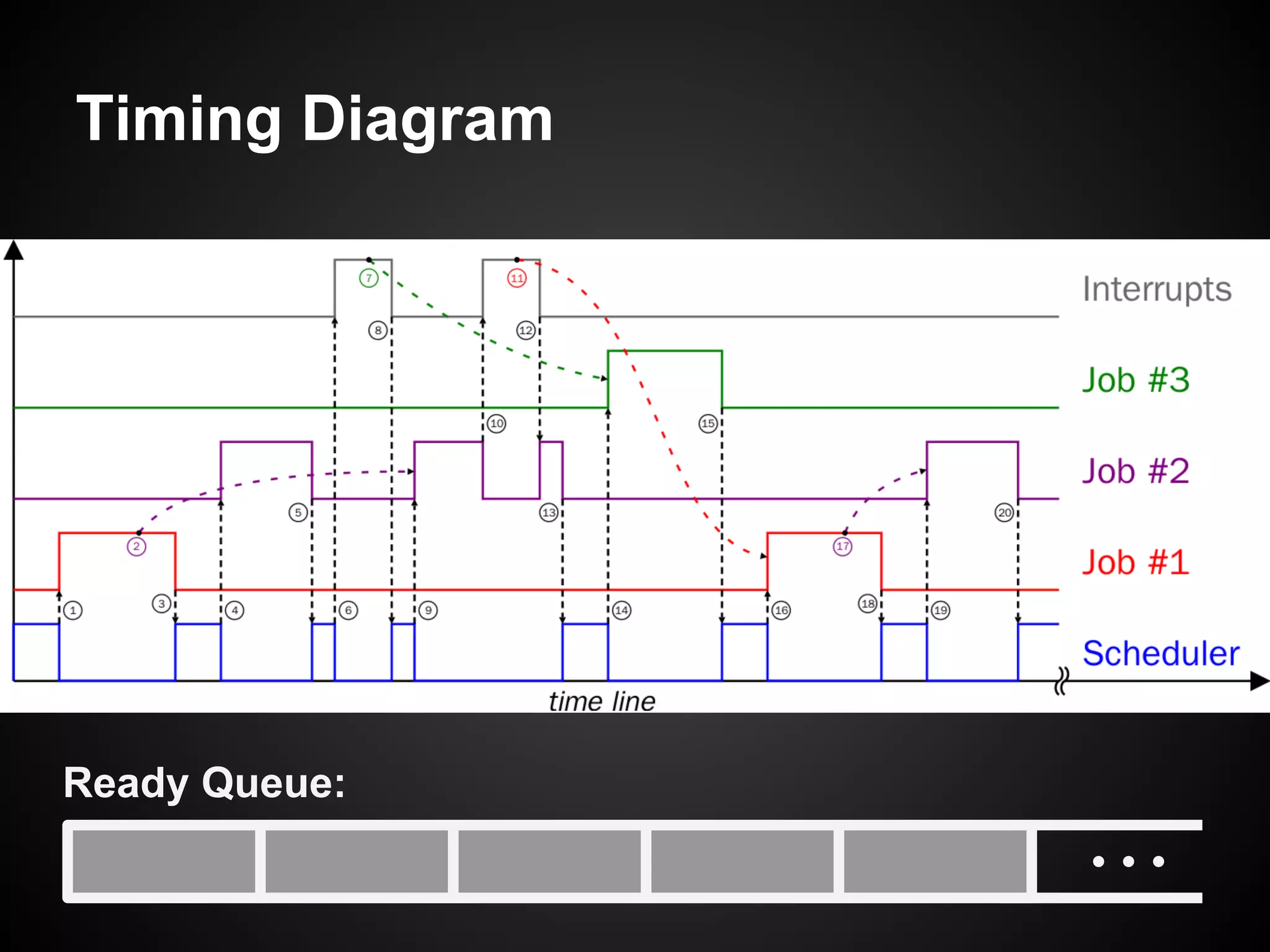
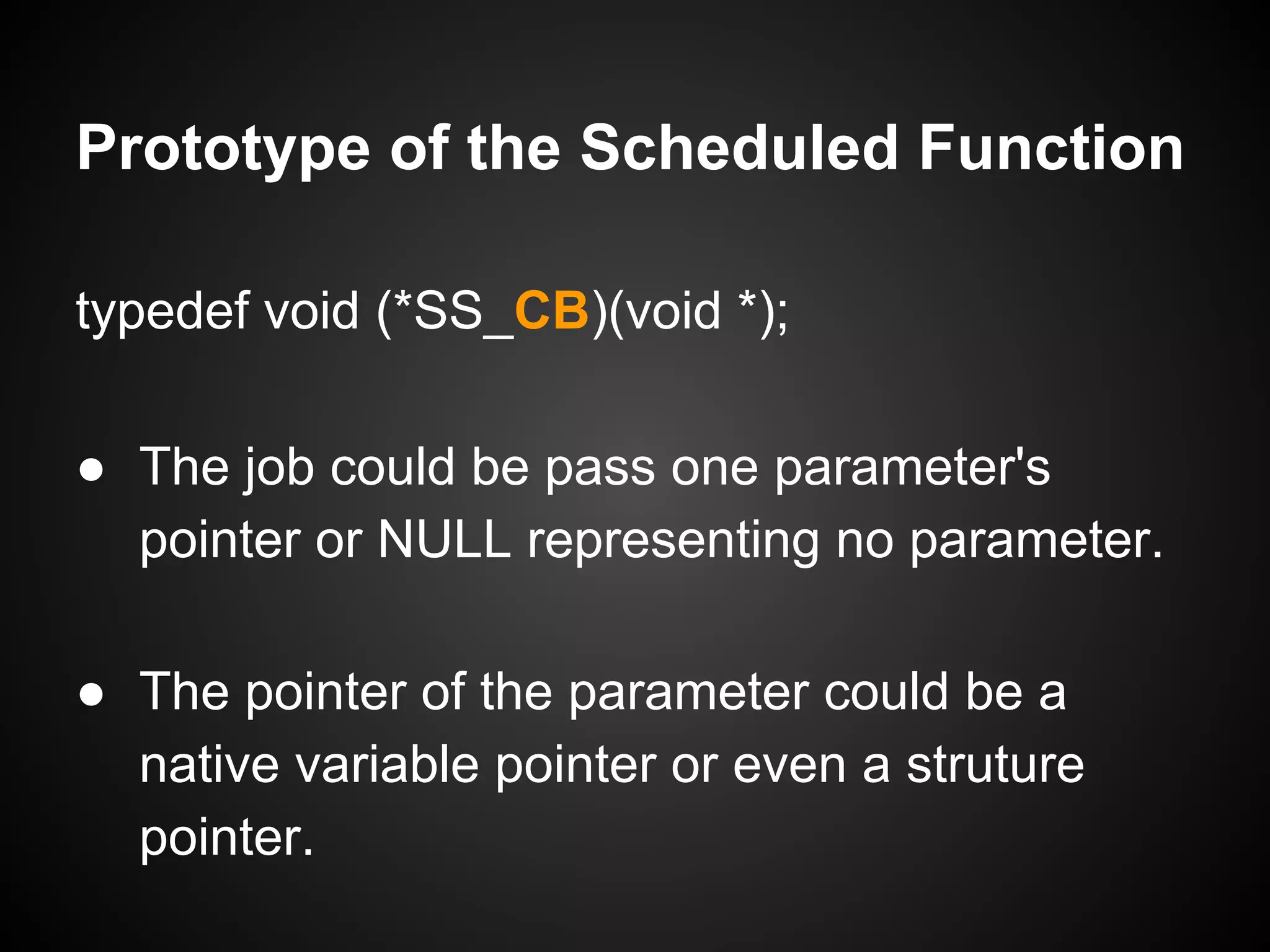
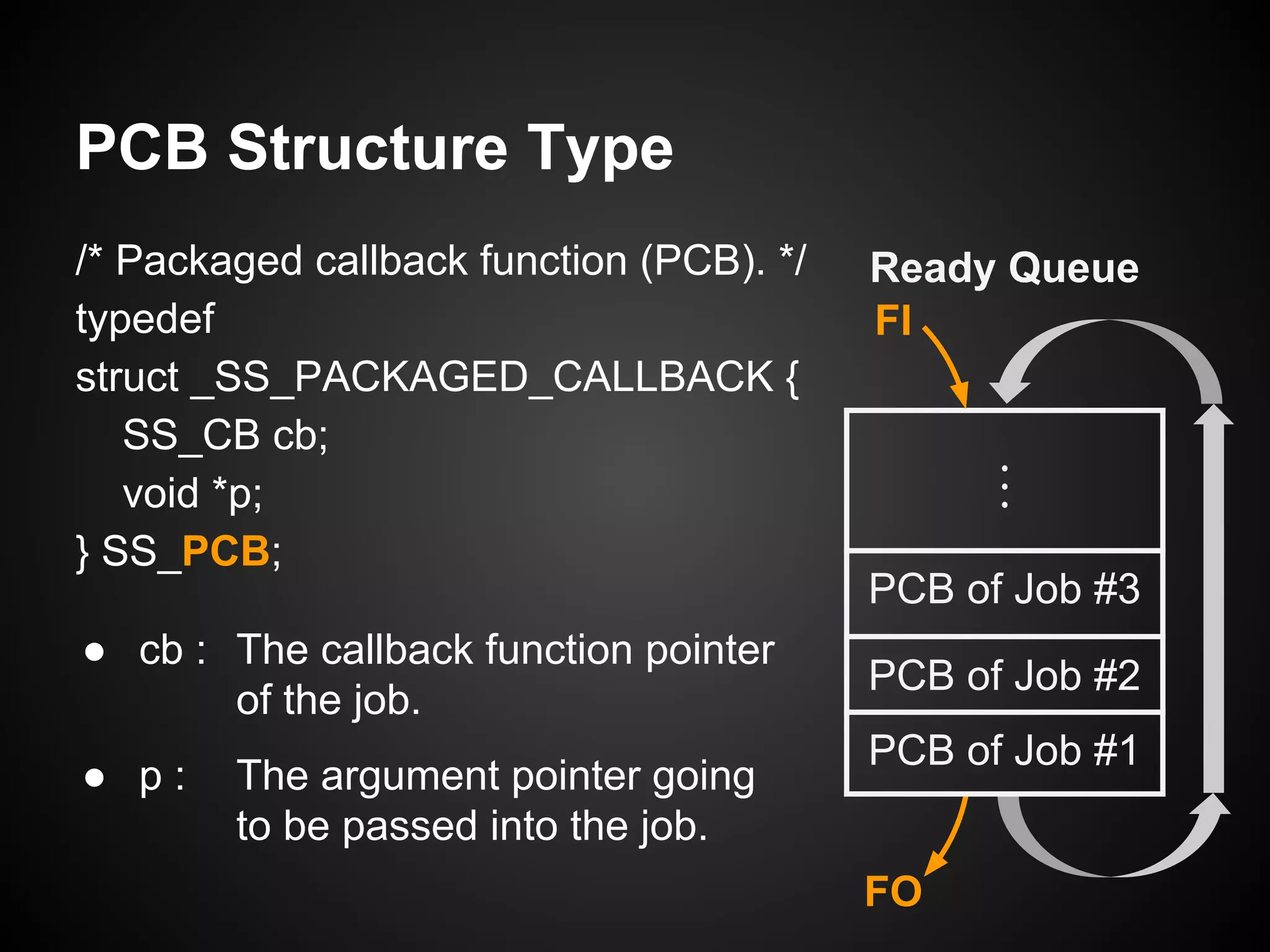
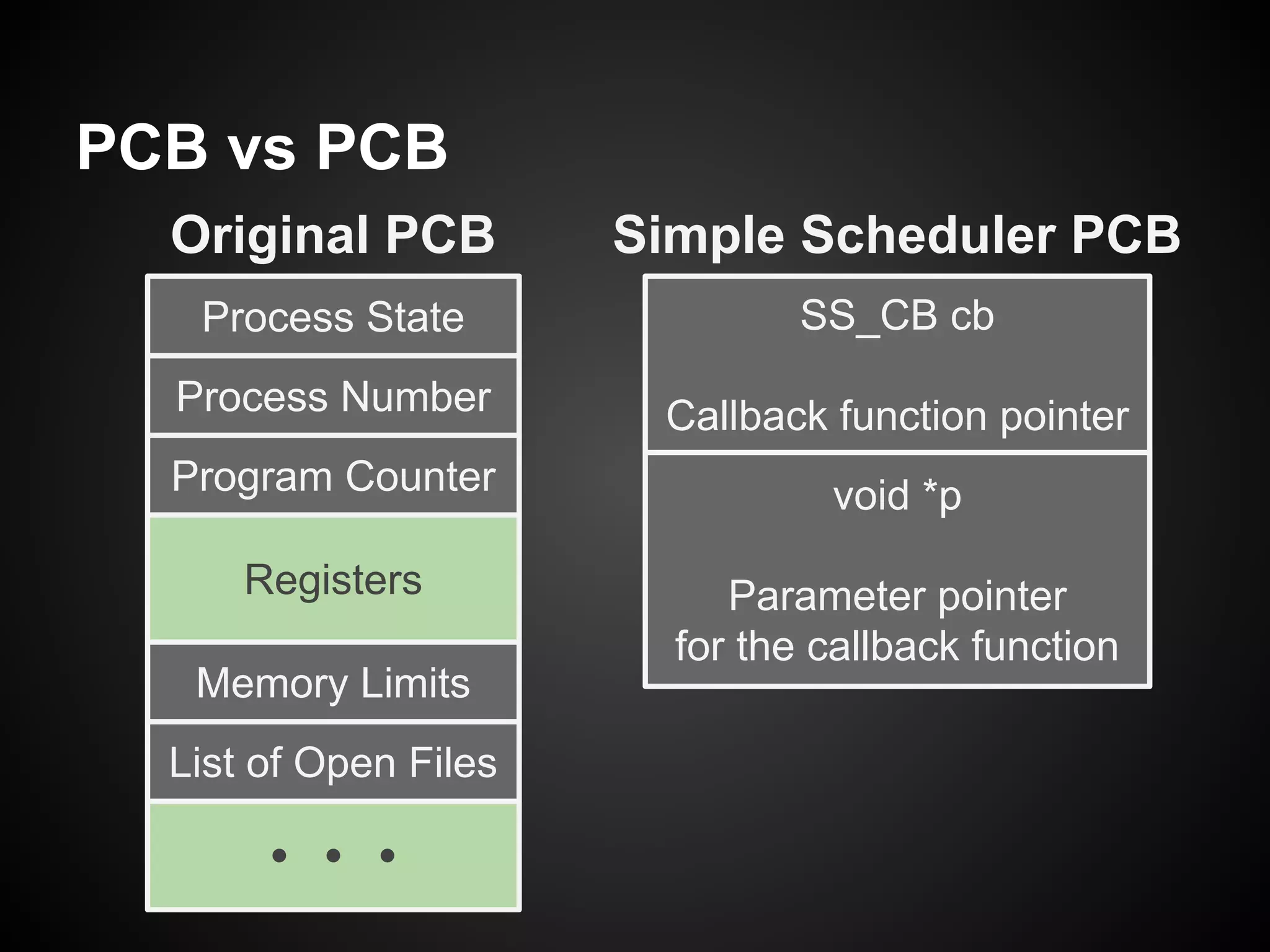
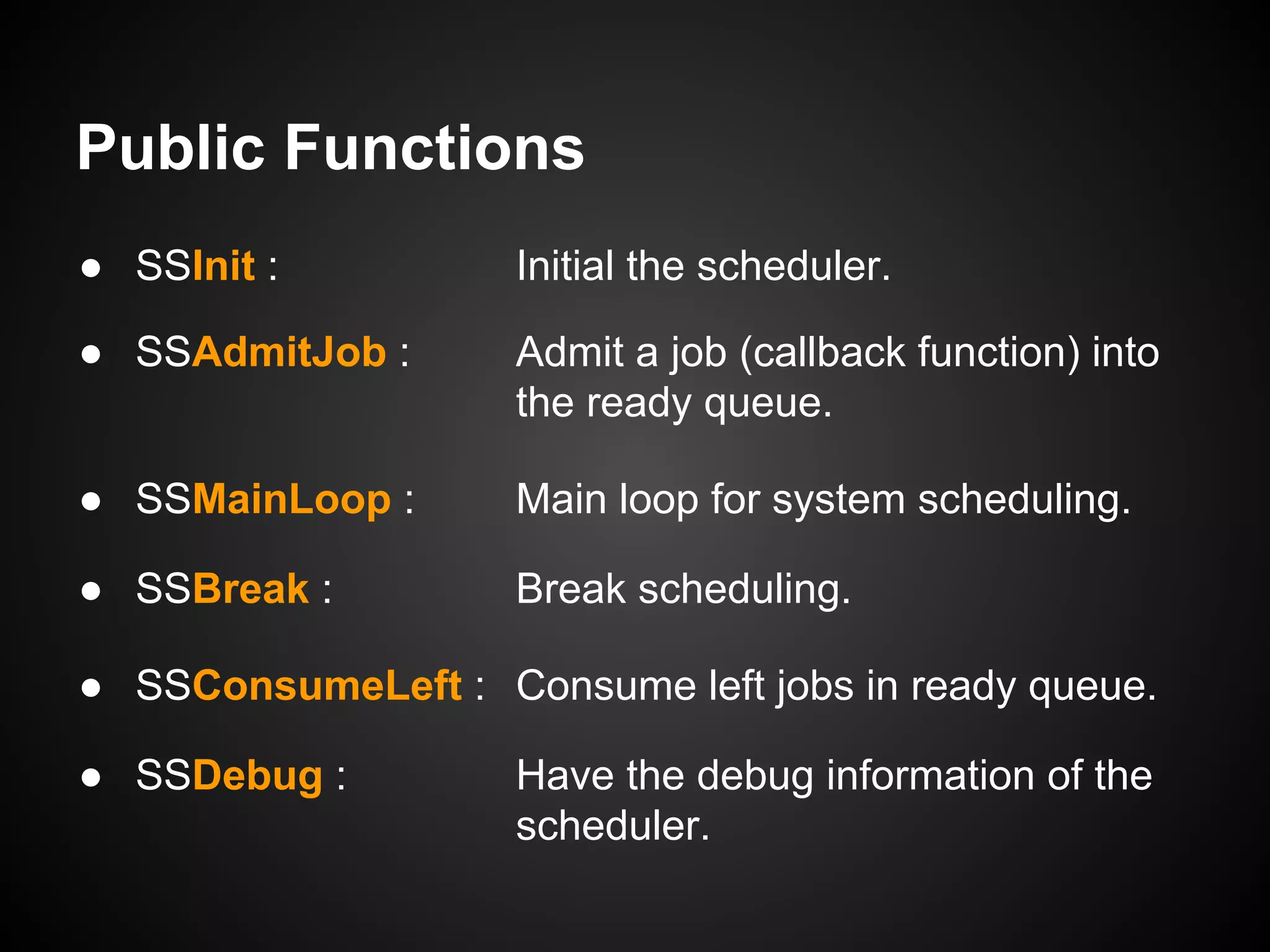
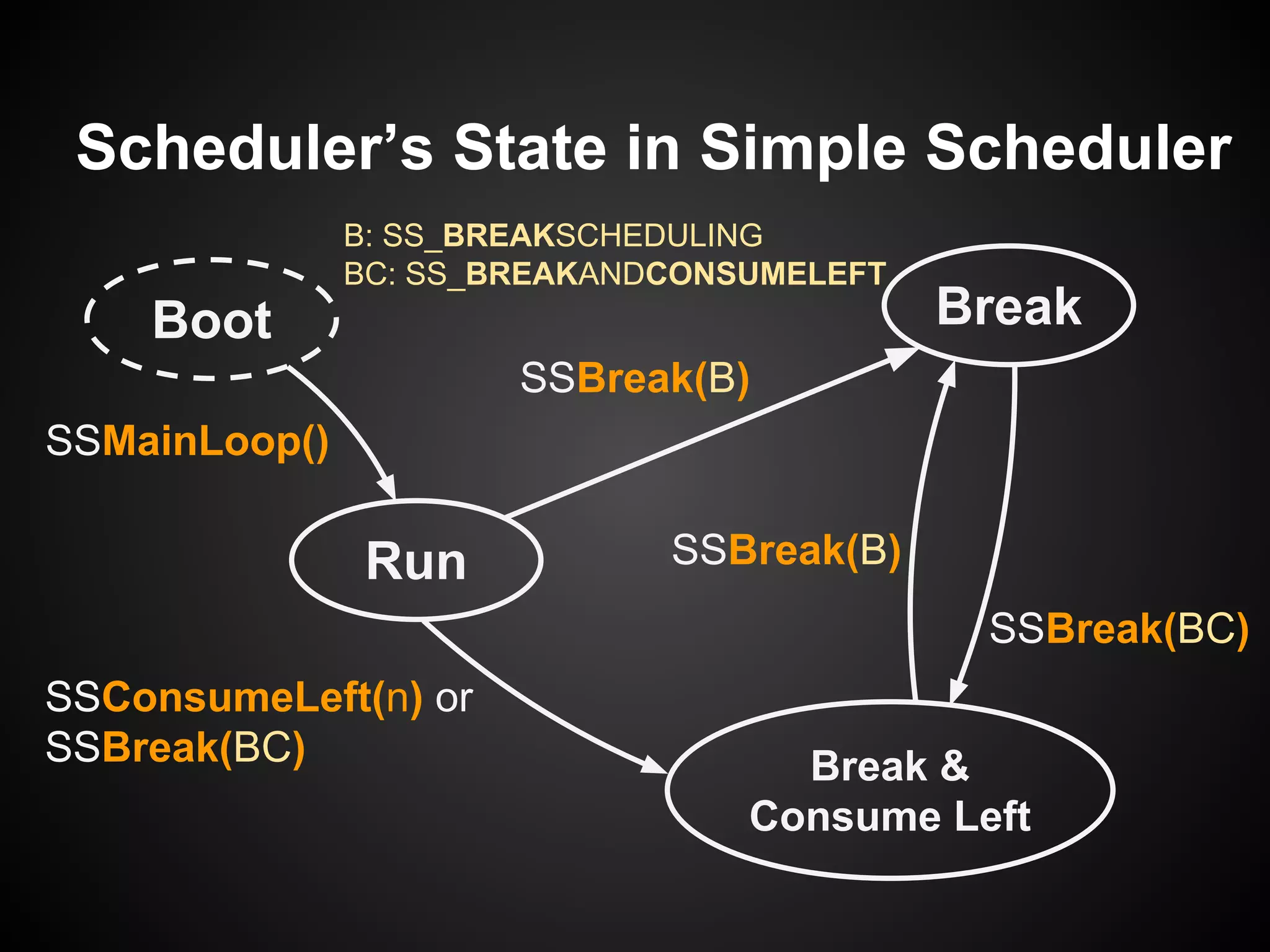
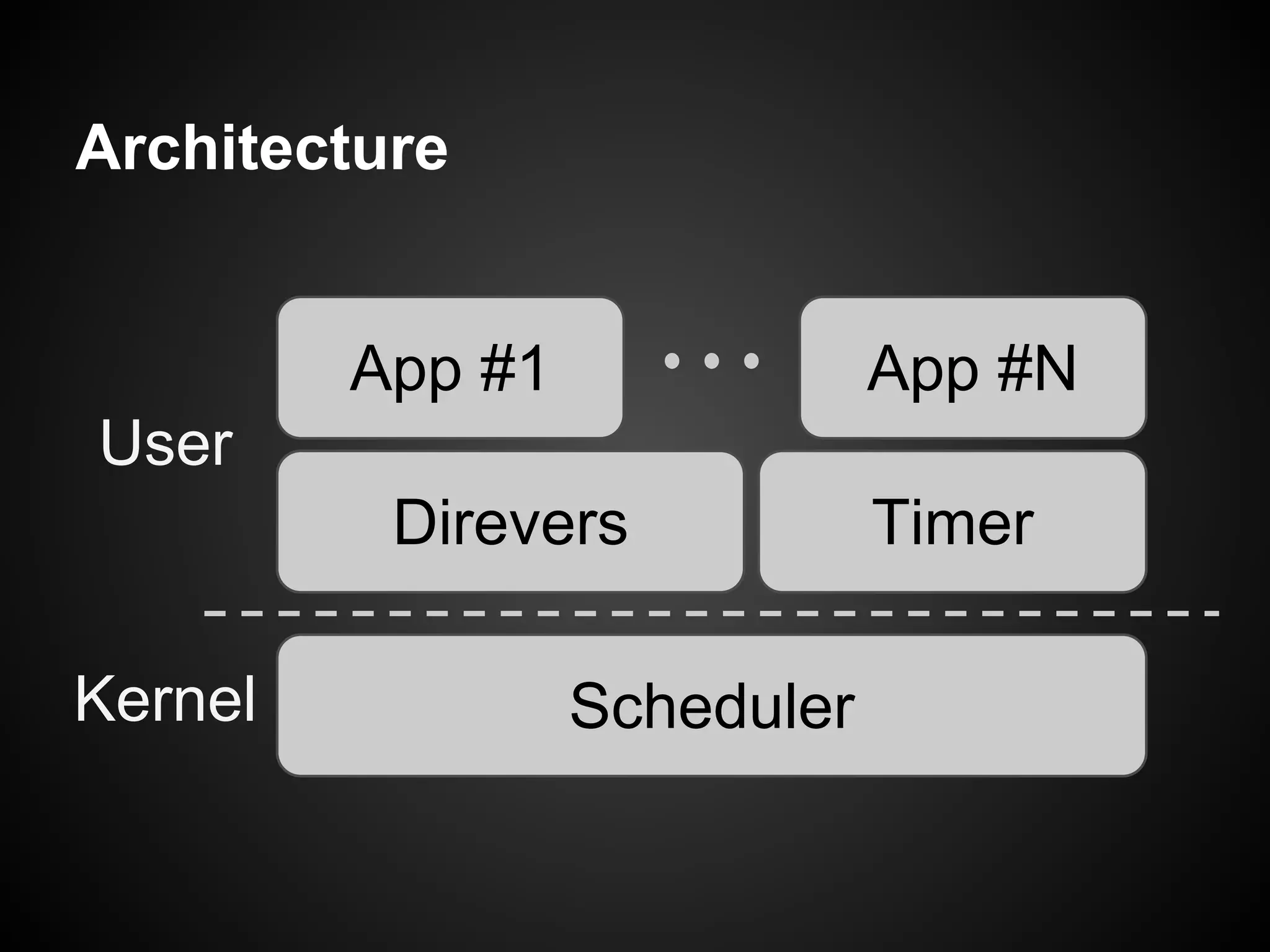
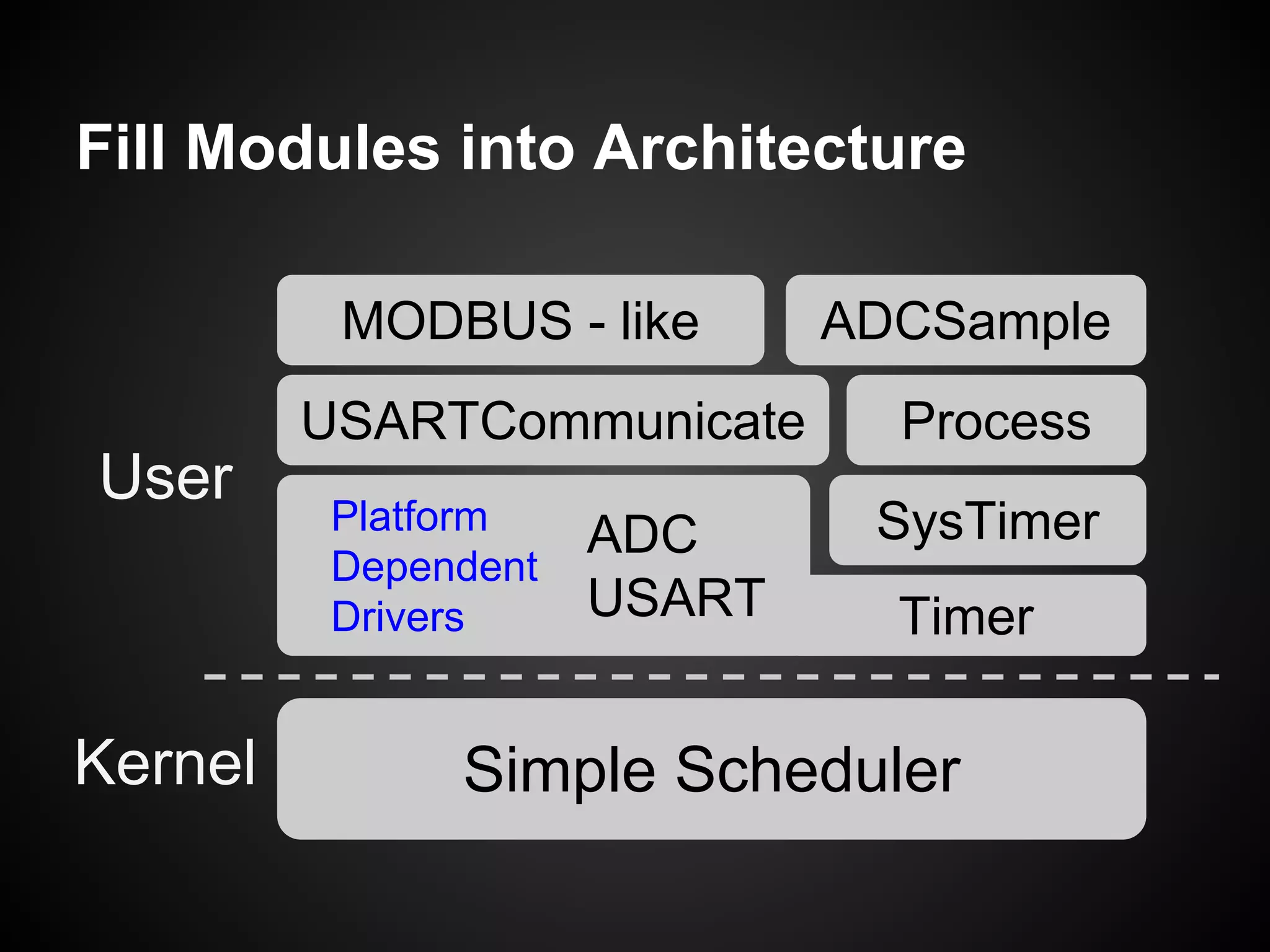
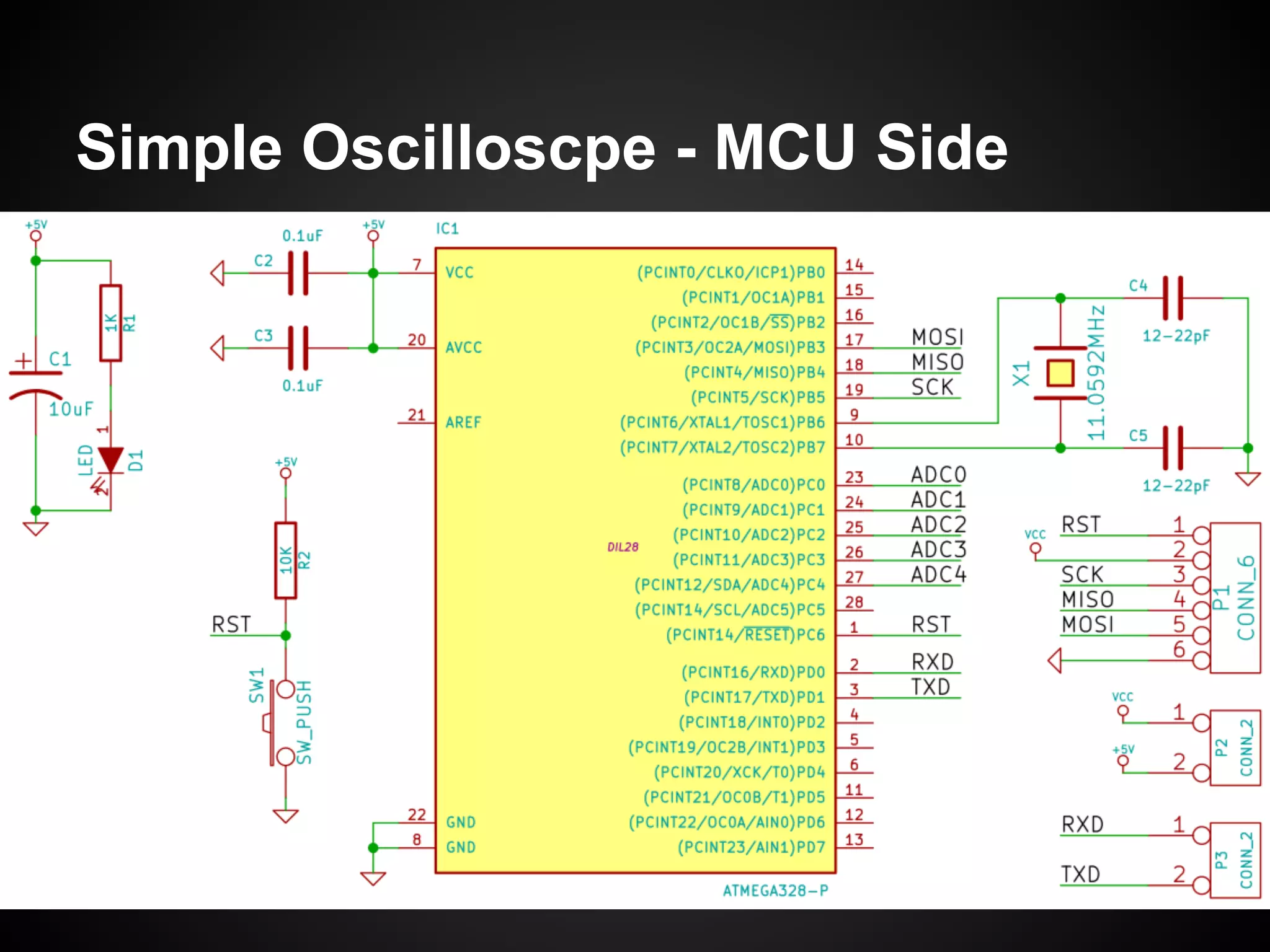
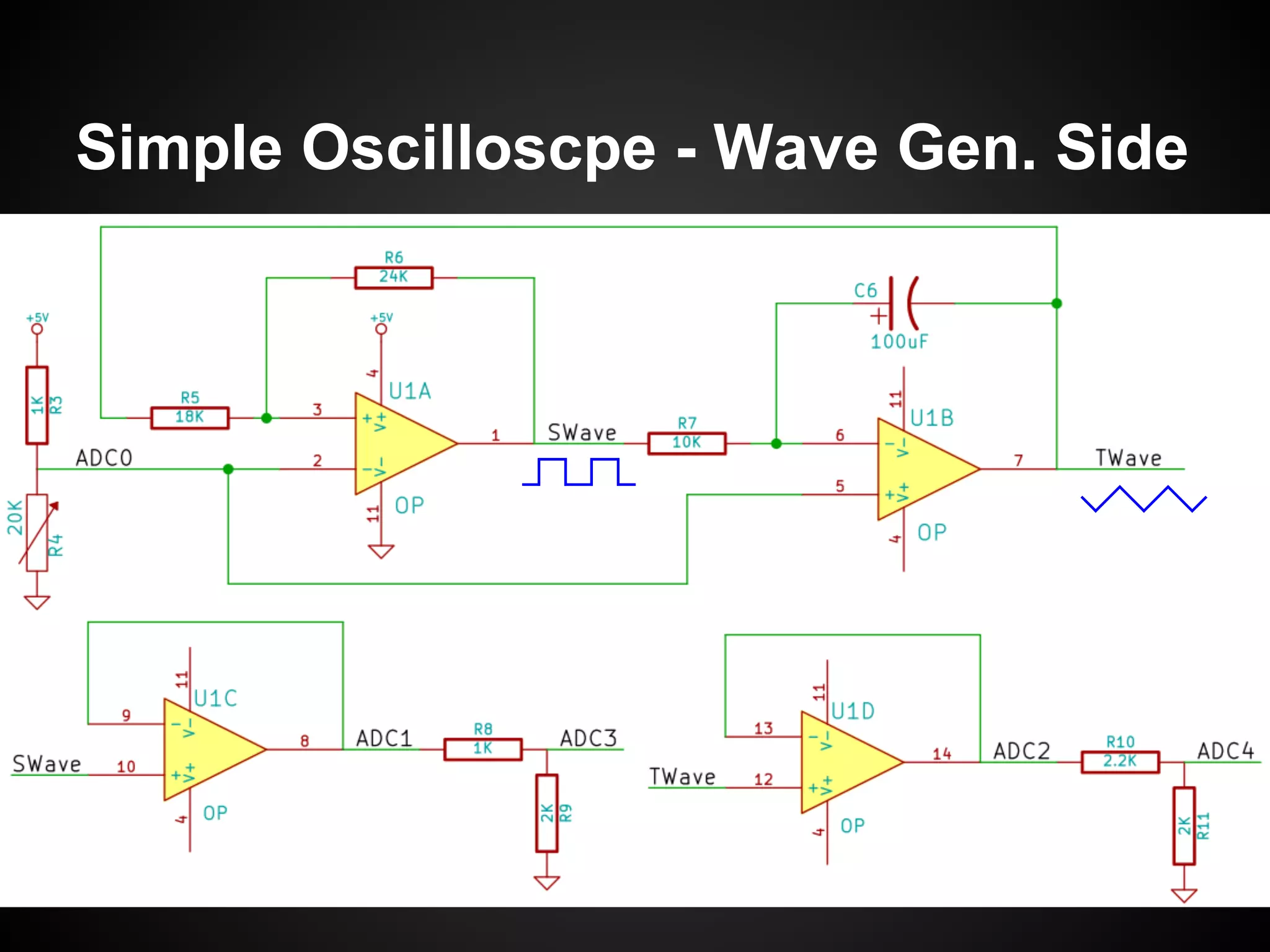
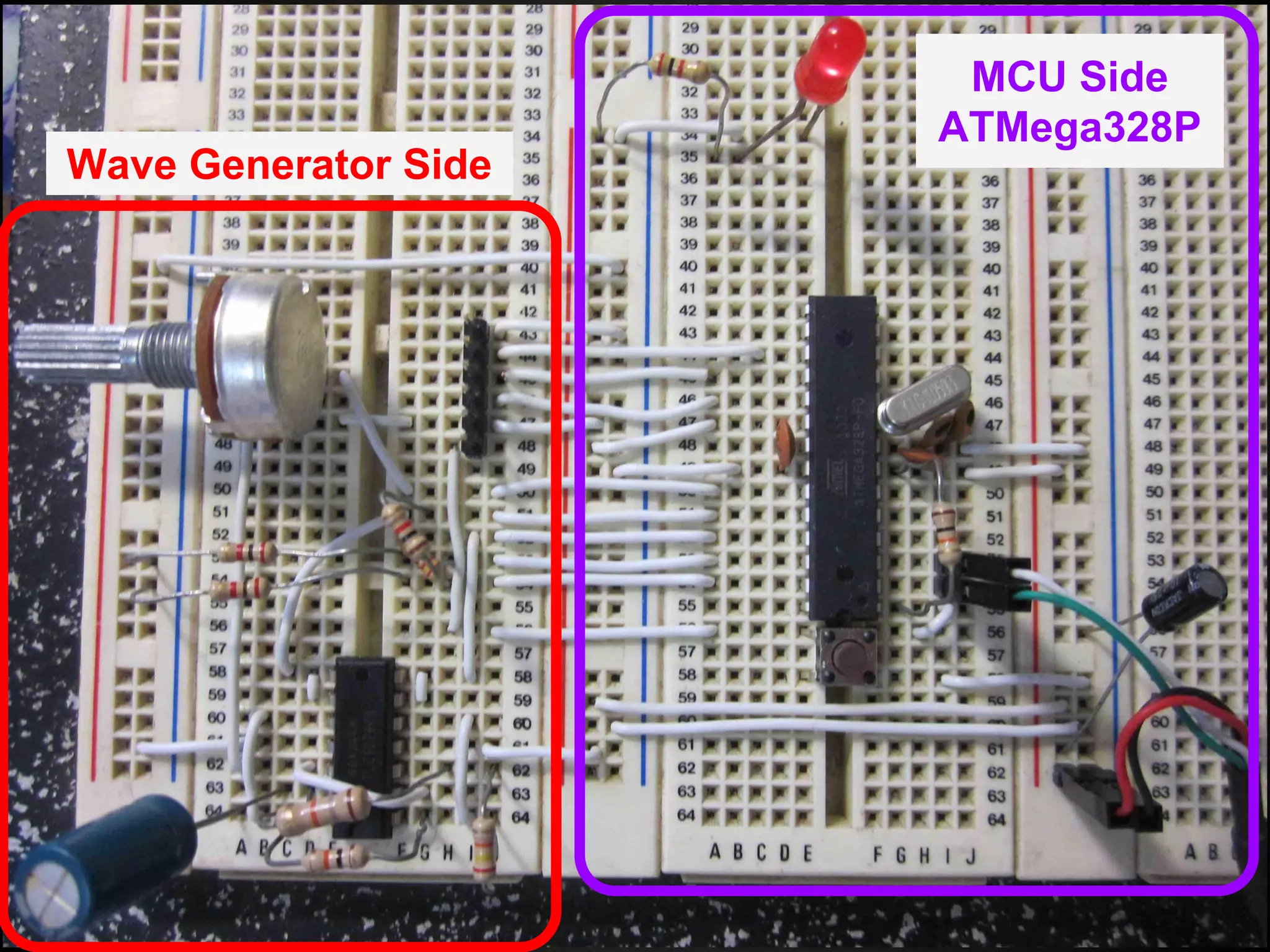
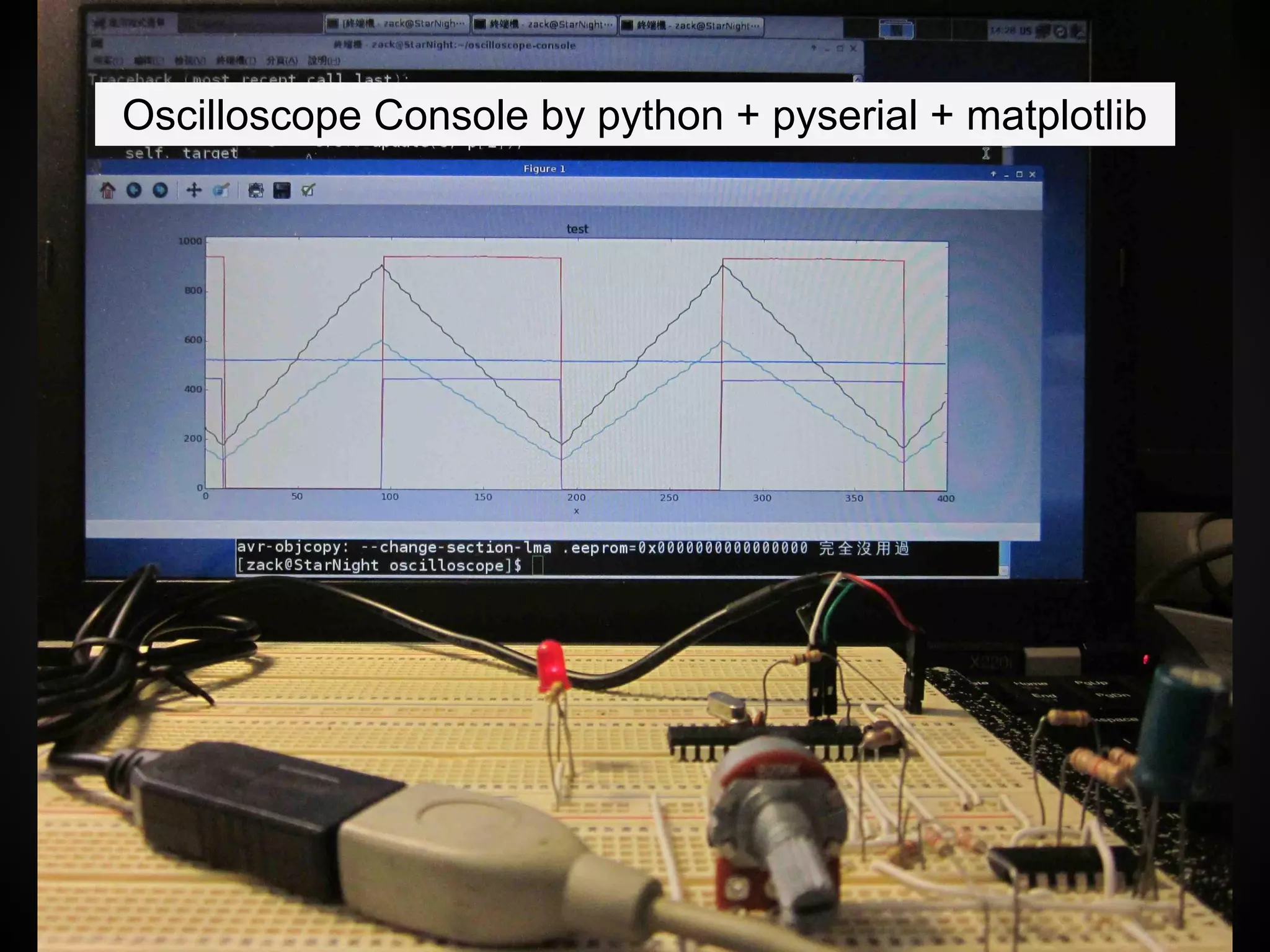
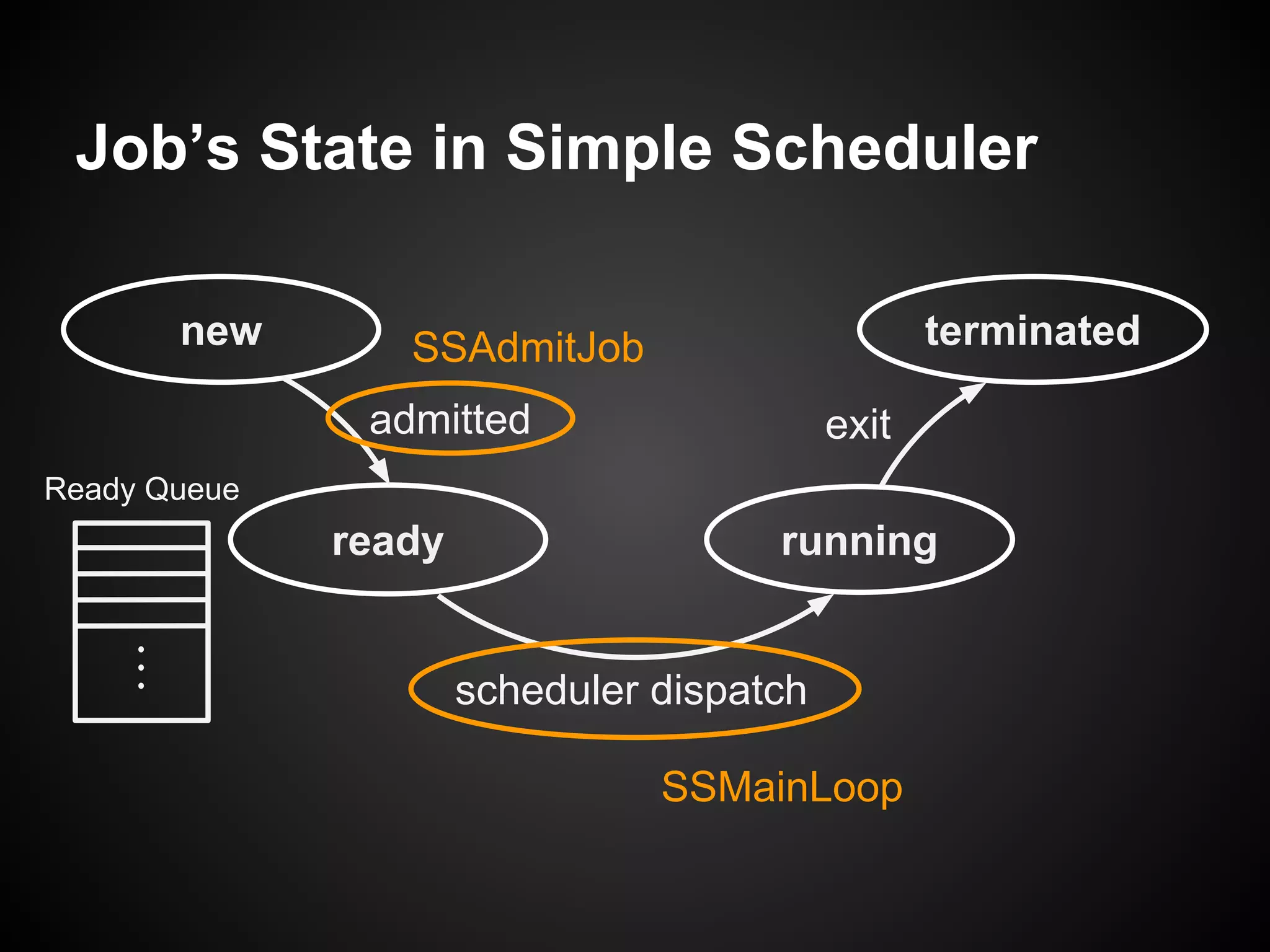
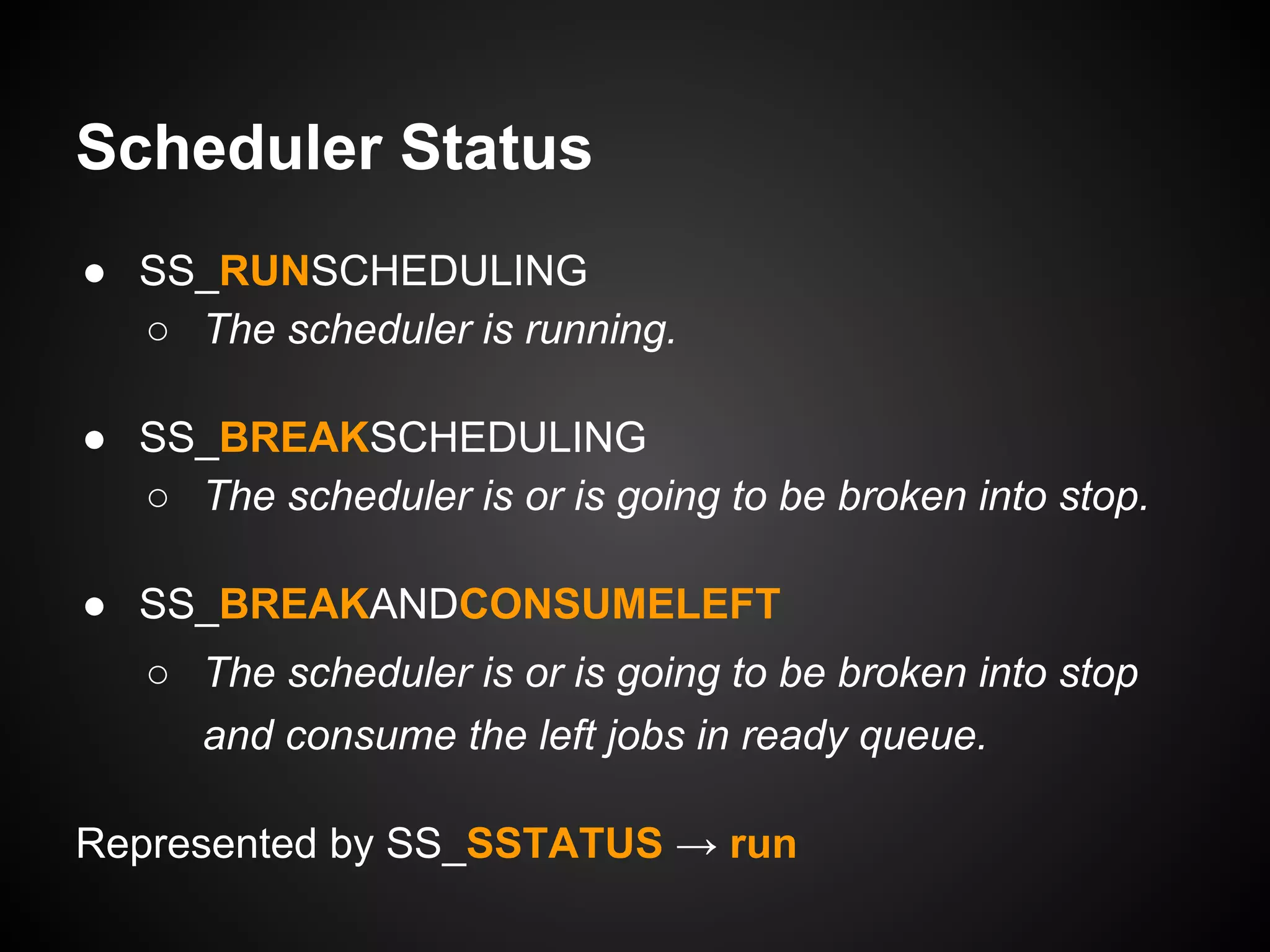
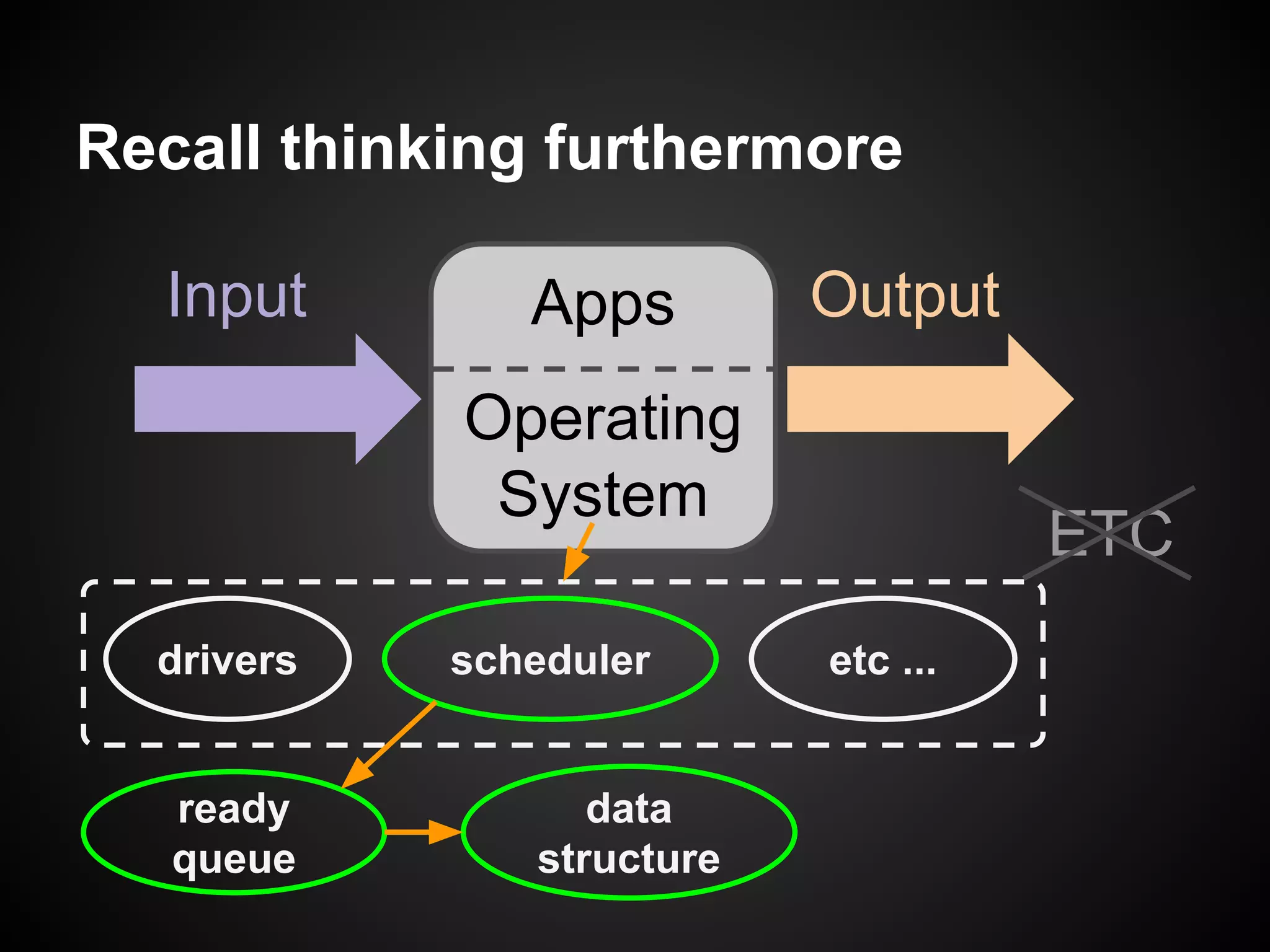
The document describes a simple scheduler module implemented in C for embedded systems. It breaks processes into small jobs represented by functions that are scheduled in a first-in, first-out queue without preemption. This allows embedding an operating system concept into simple systems using only functions and a ready queue. Interrupts can add jobs to the queue. The scheduler and example oscilloscope application demonstrate scheduling without process state using only callbacks.