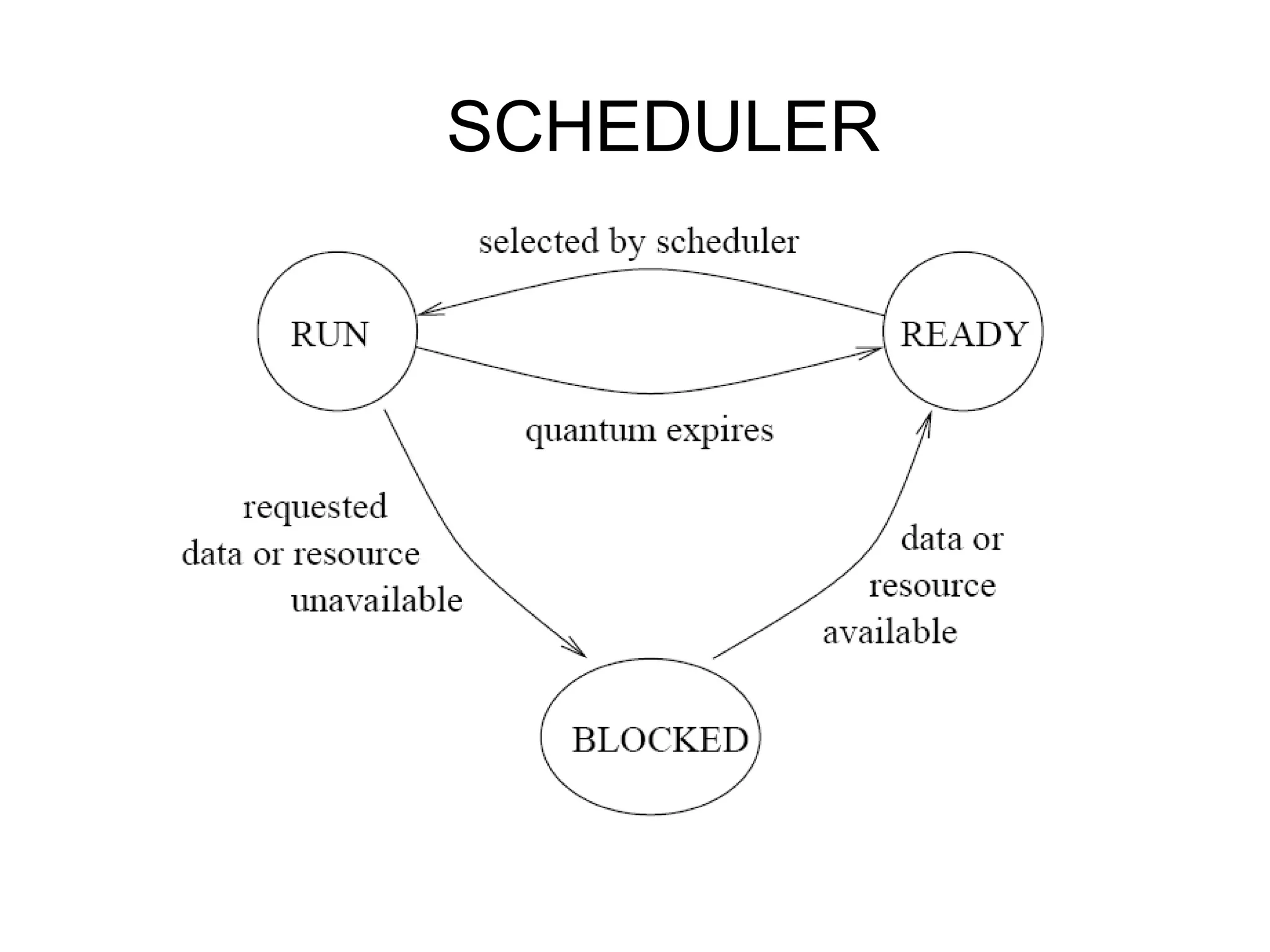
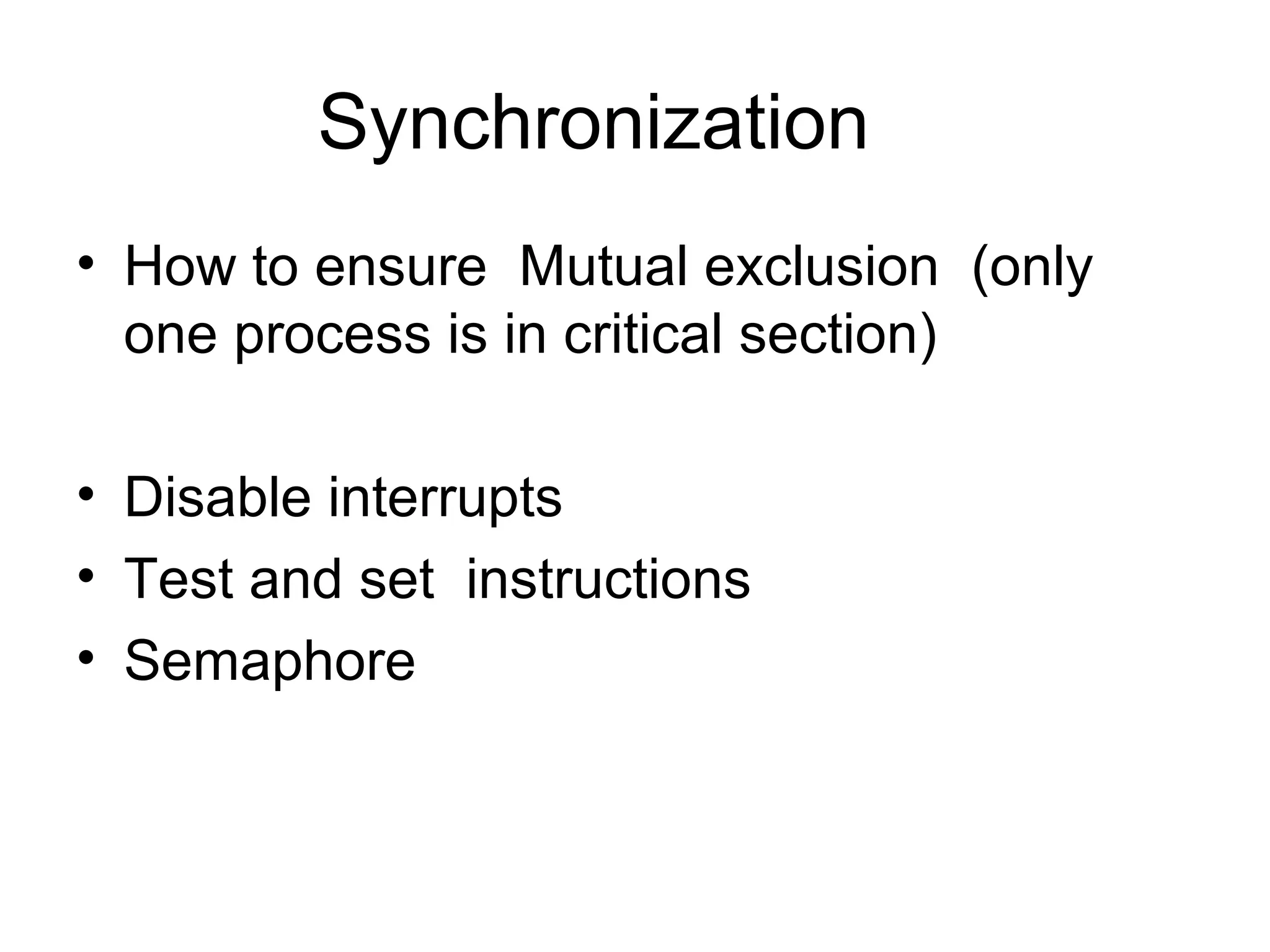
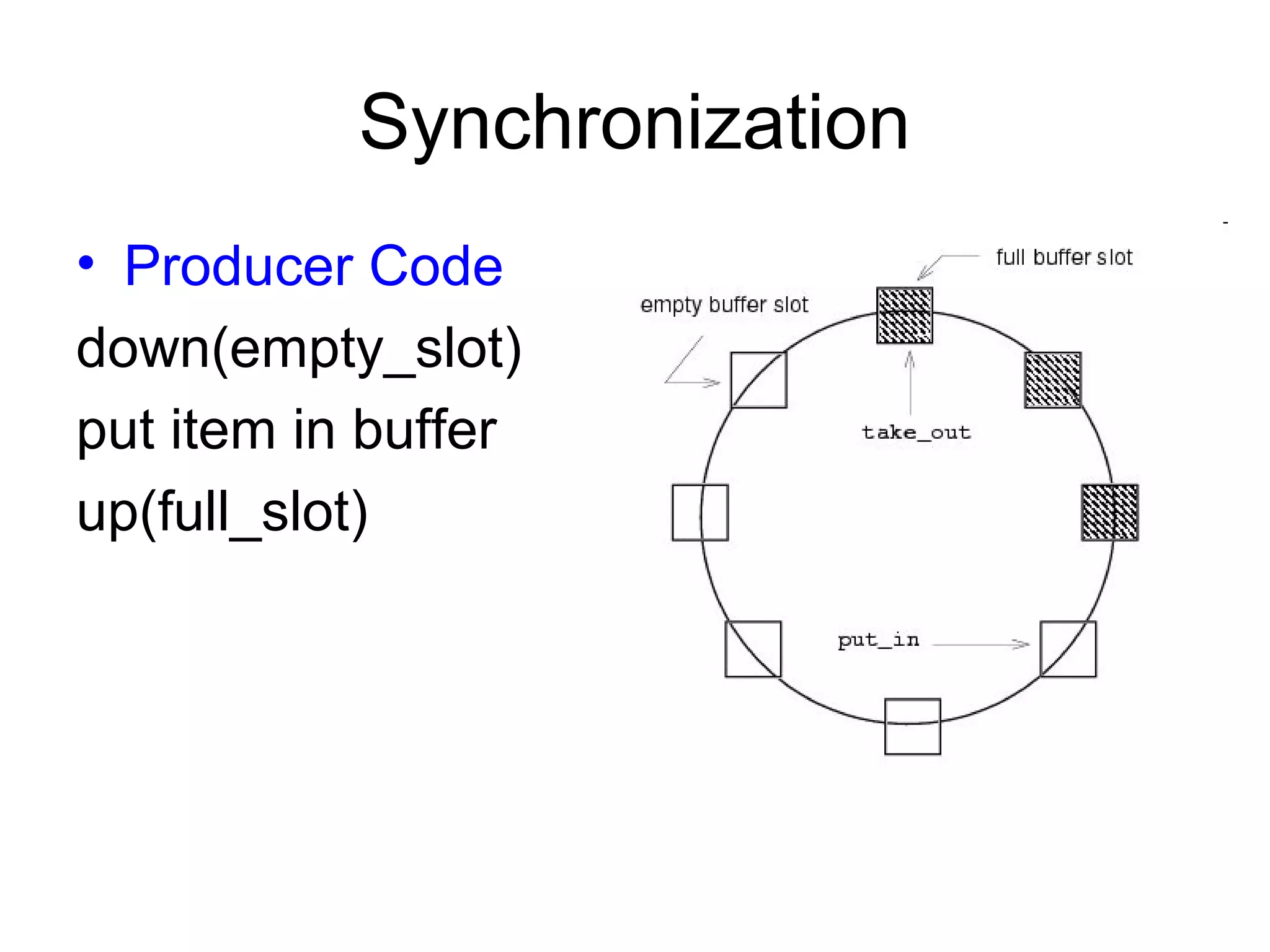
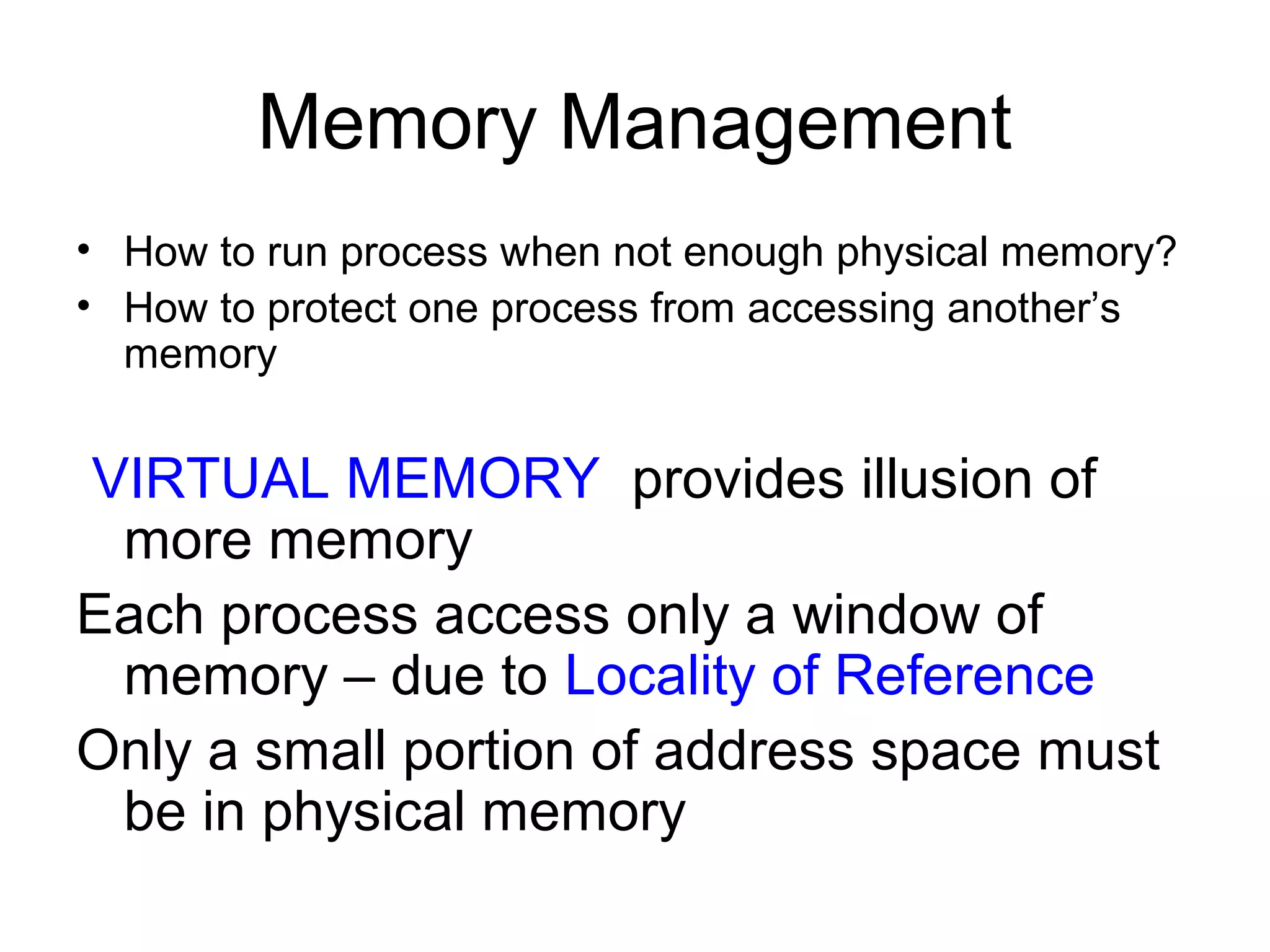
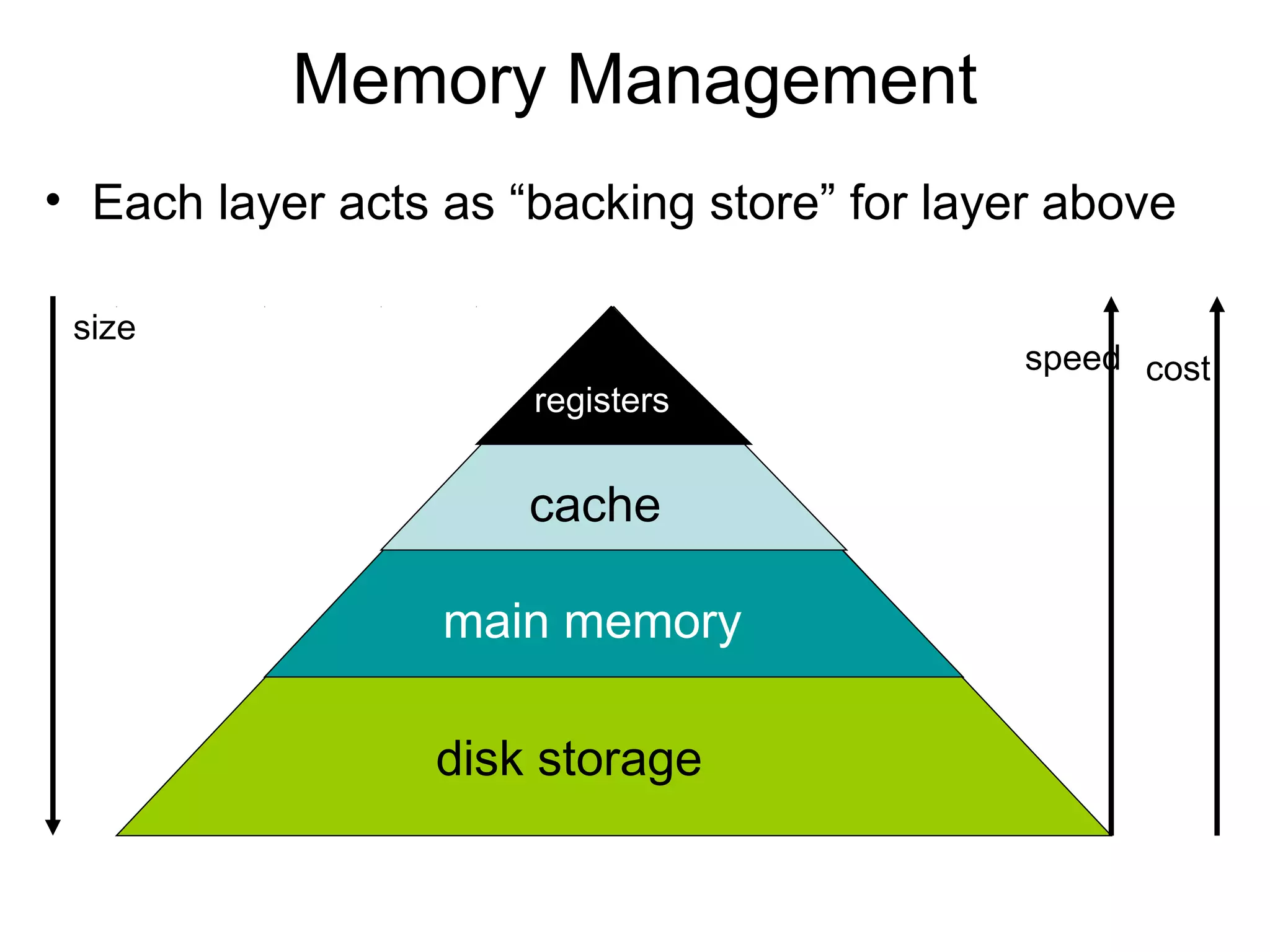
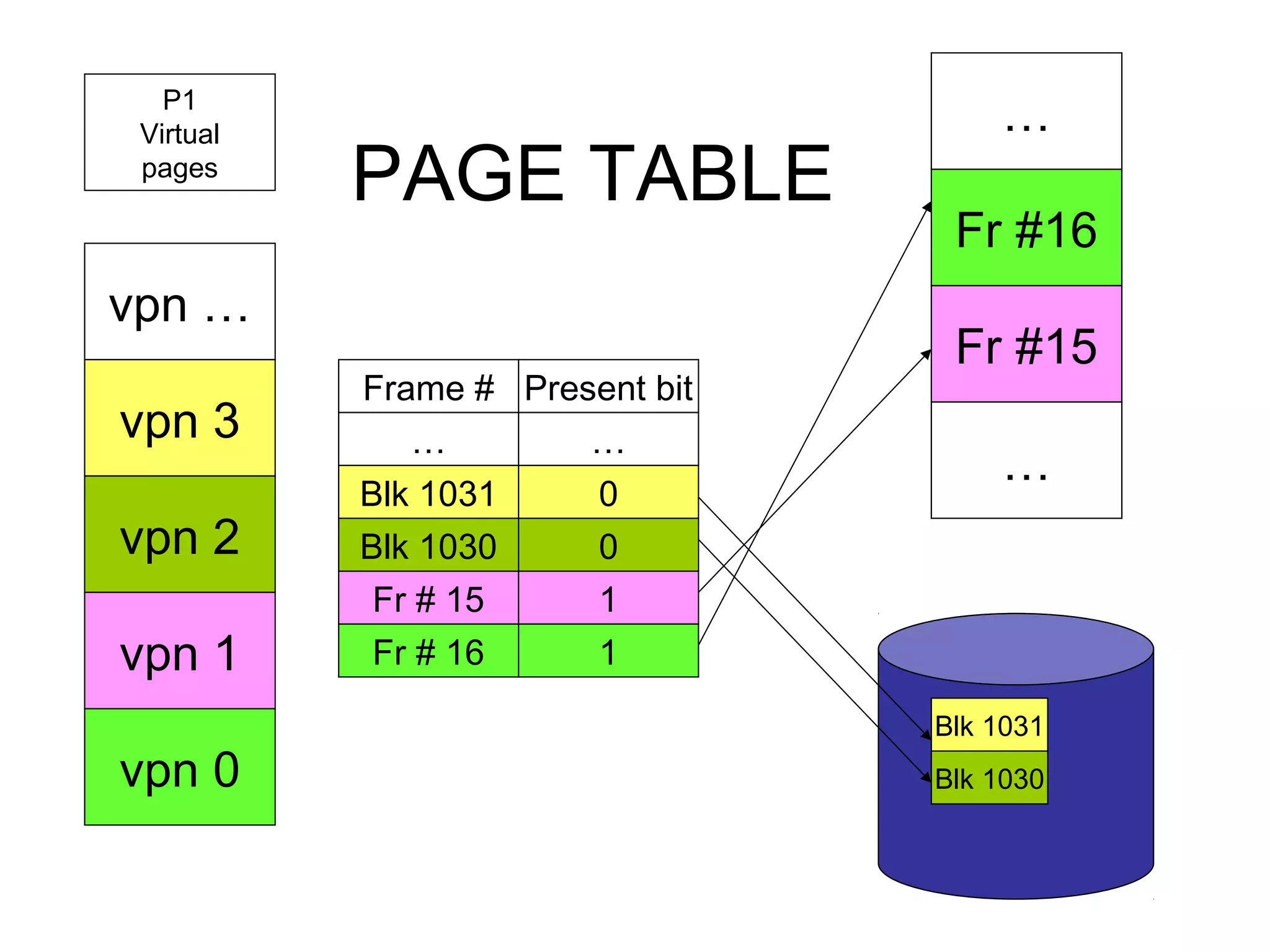
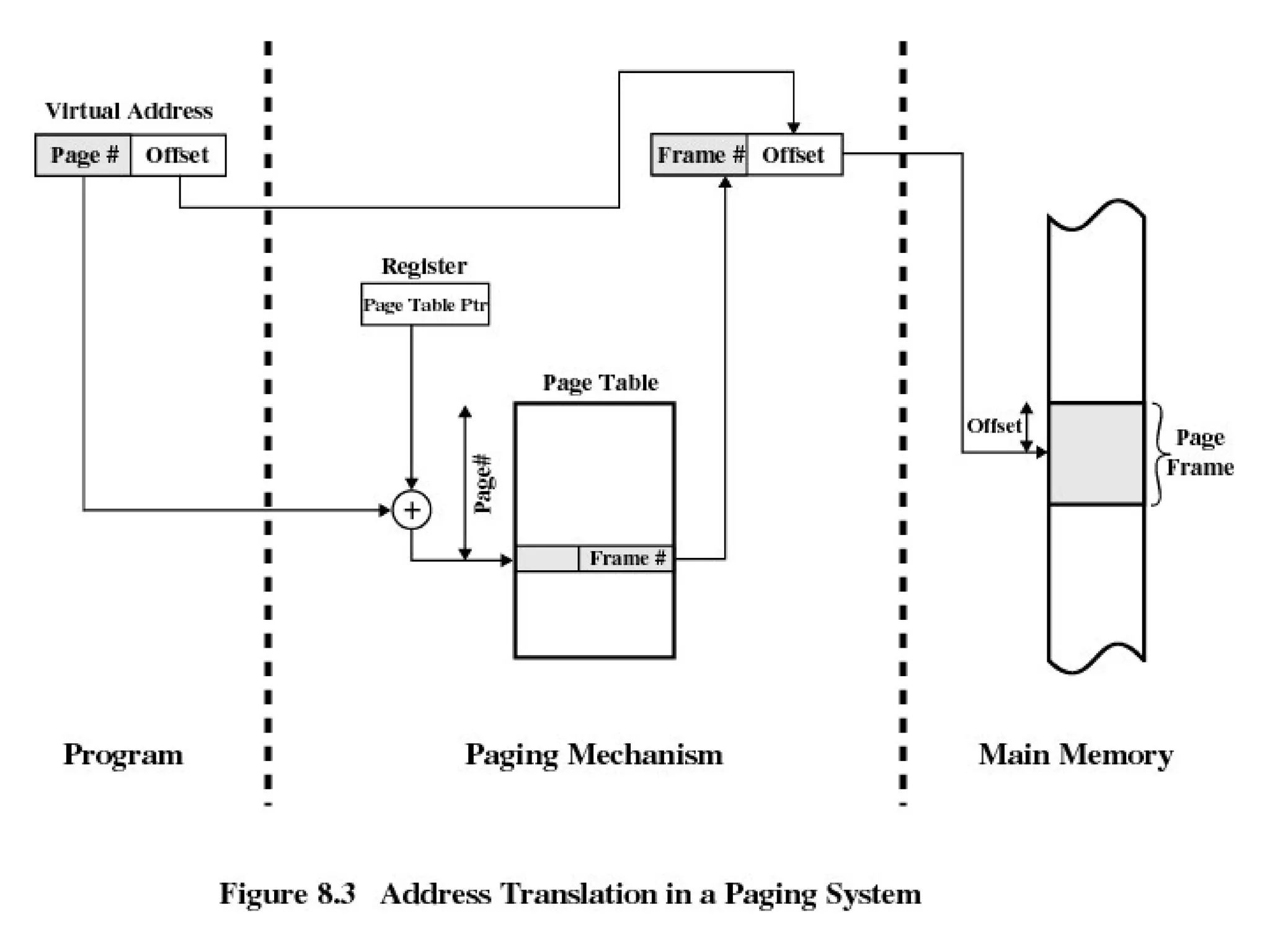
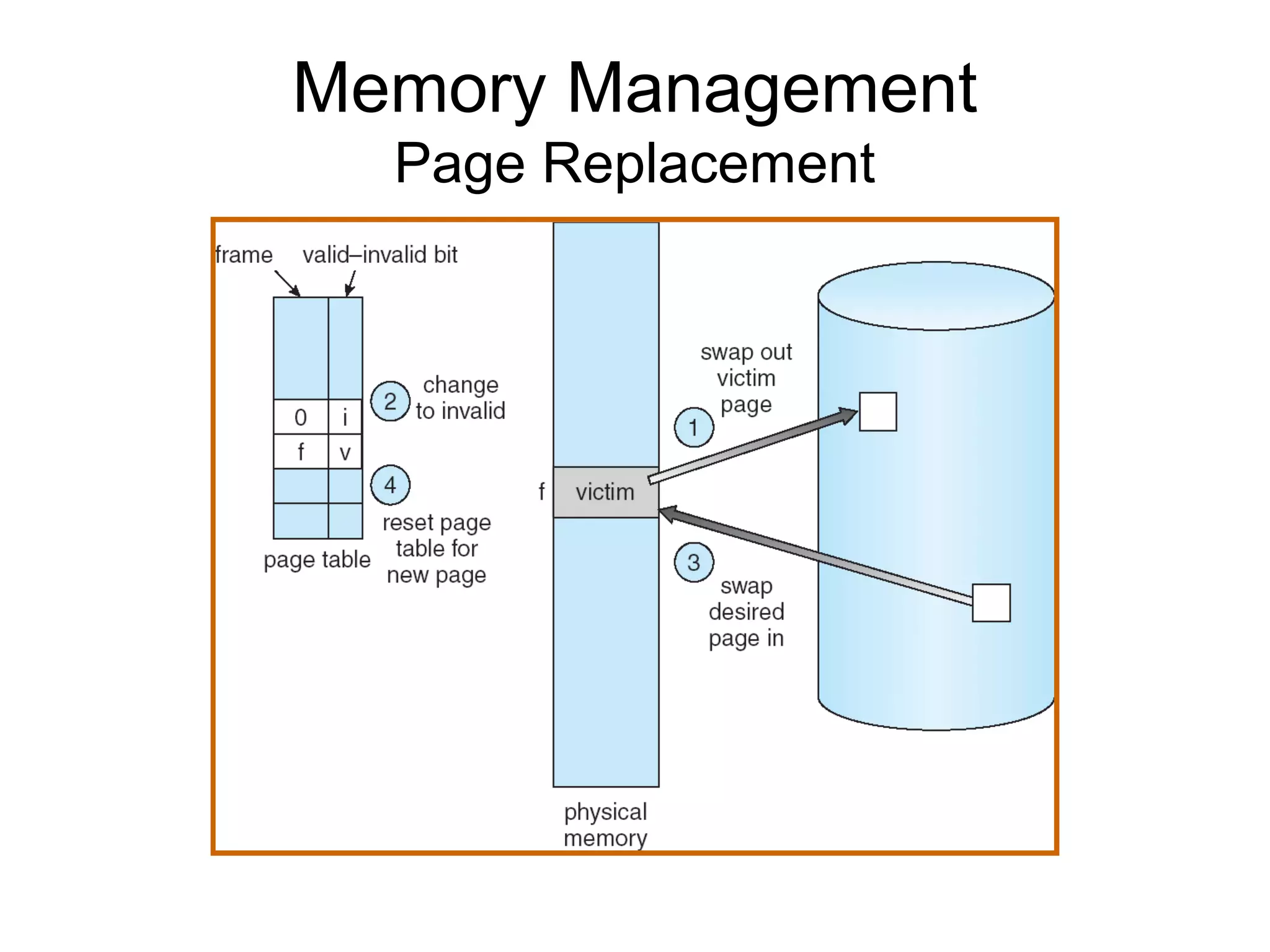
The operating system performs key functions like scheduling, synchronization, and memory management. Scheduling involves allocating time to programs and switching between threads. Synchronization ensures mutual exclusion so only one process accesses shared resources at a time using techniques like semaphores. Memory management uses virtual memory to allow processes to access more memory than physically available by swapping pages between disk and RAM.