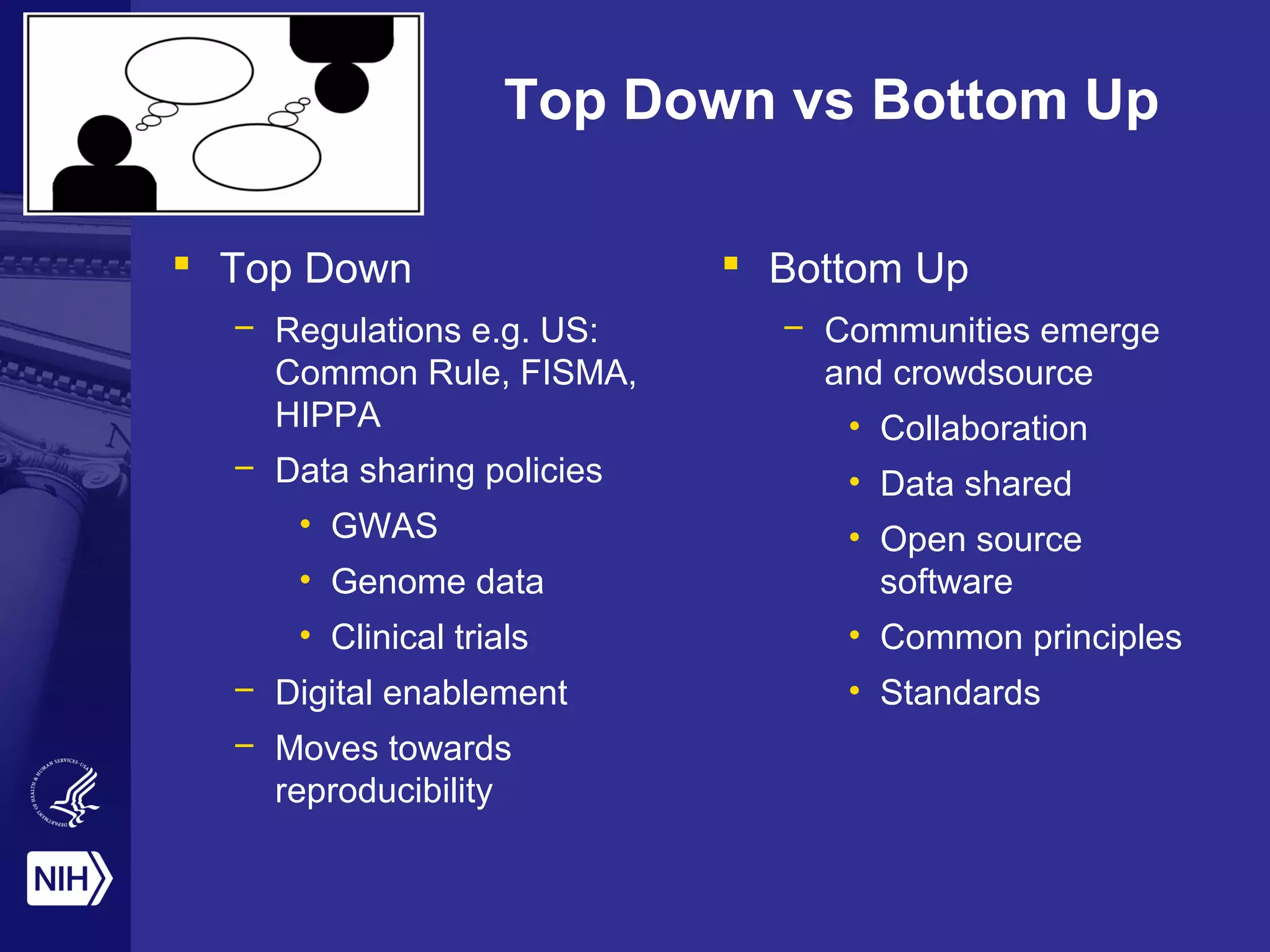
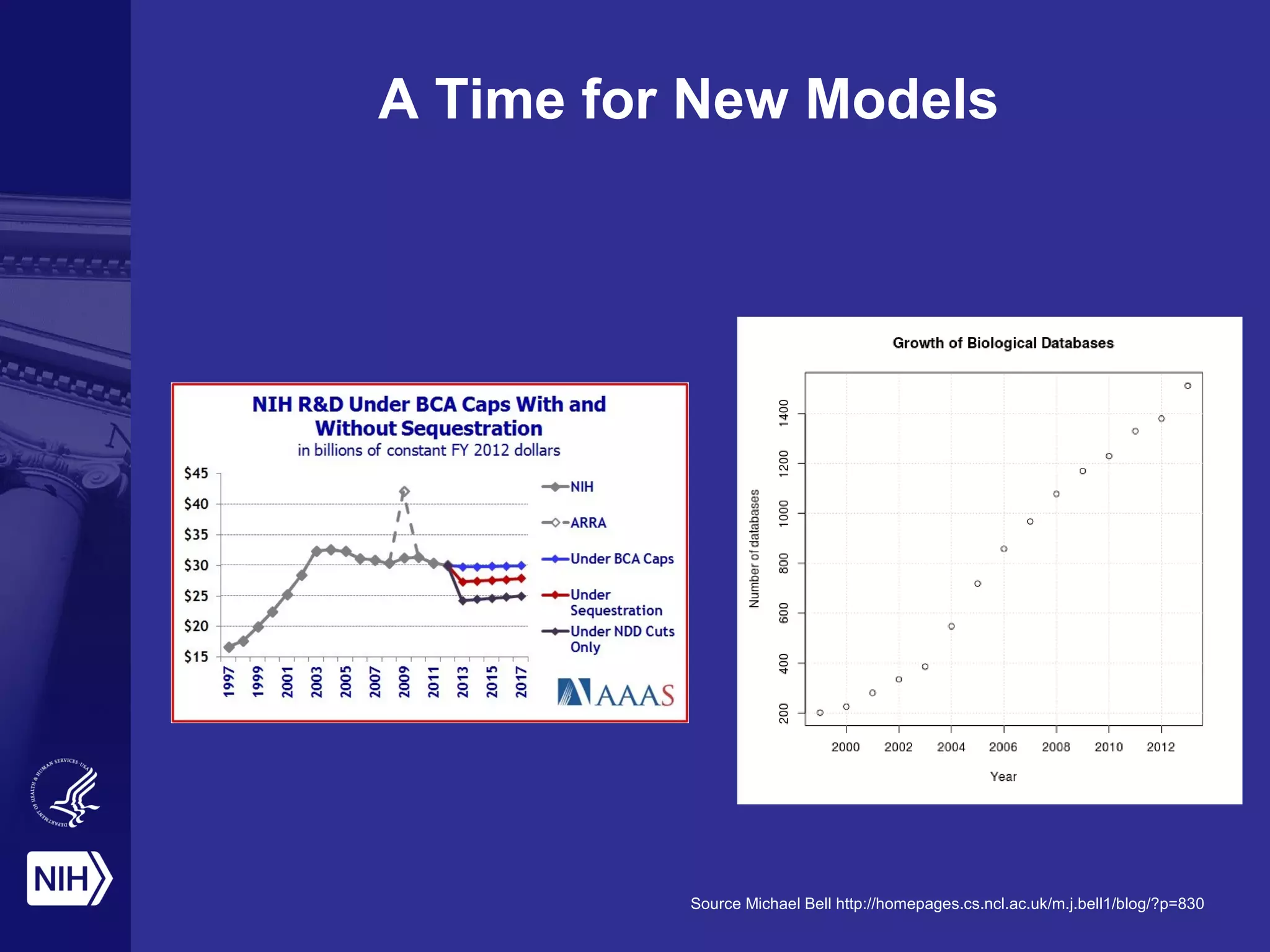
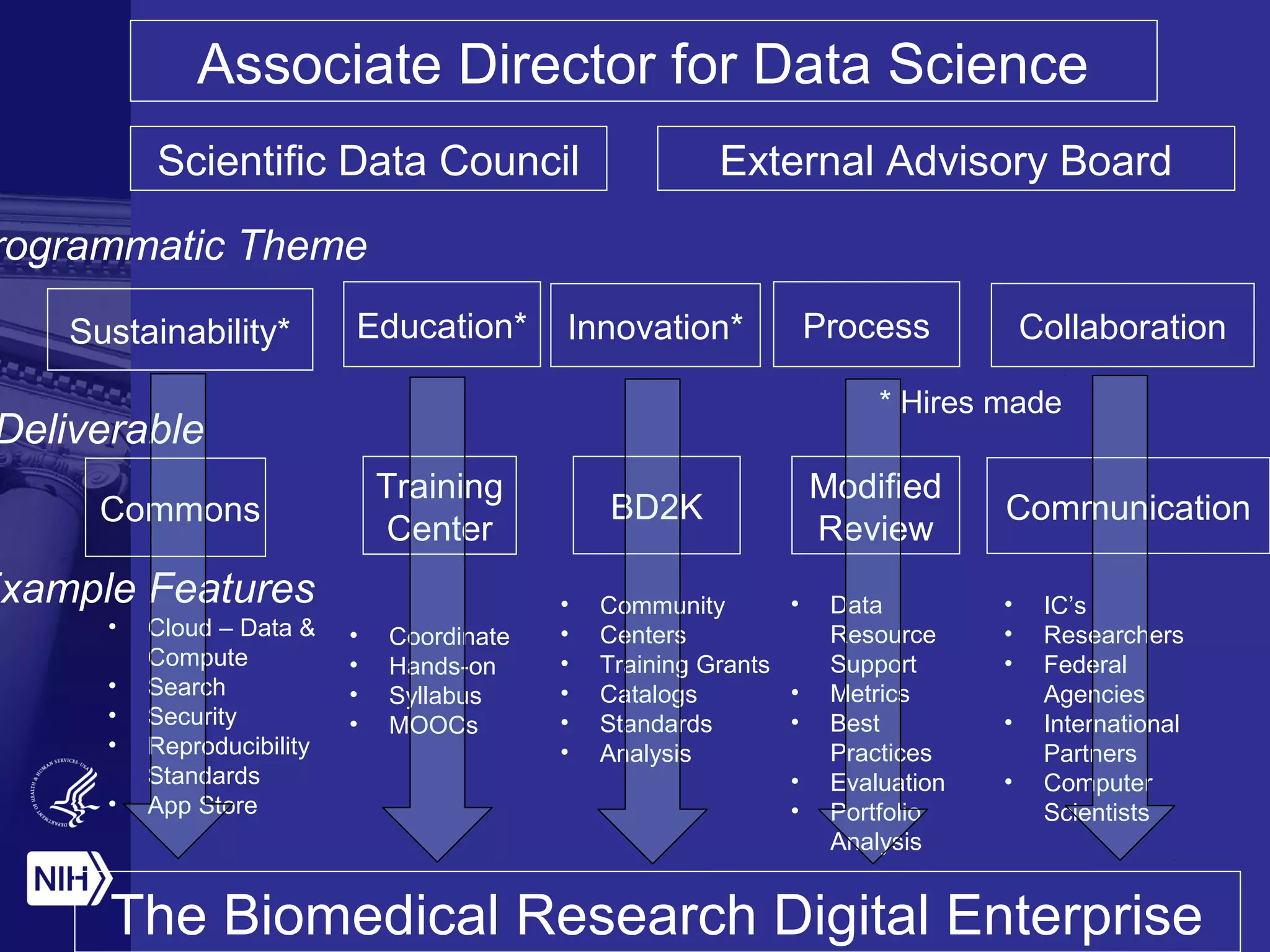
The document discusses the challenges and opportunities in scientific research amidst limited funding and rapid technological advancement, emphasizing the importance of automated function prediction and data sharing. It outlines the need for new collaborative models and best practices to enhance research outputs while fostering innovation and reproducibility. The concept of 'the commons' is introduced as a framework for collaborative research, enabling better resource sharing and functional annotation through open environments and community engagement.








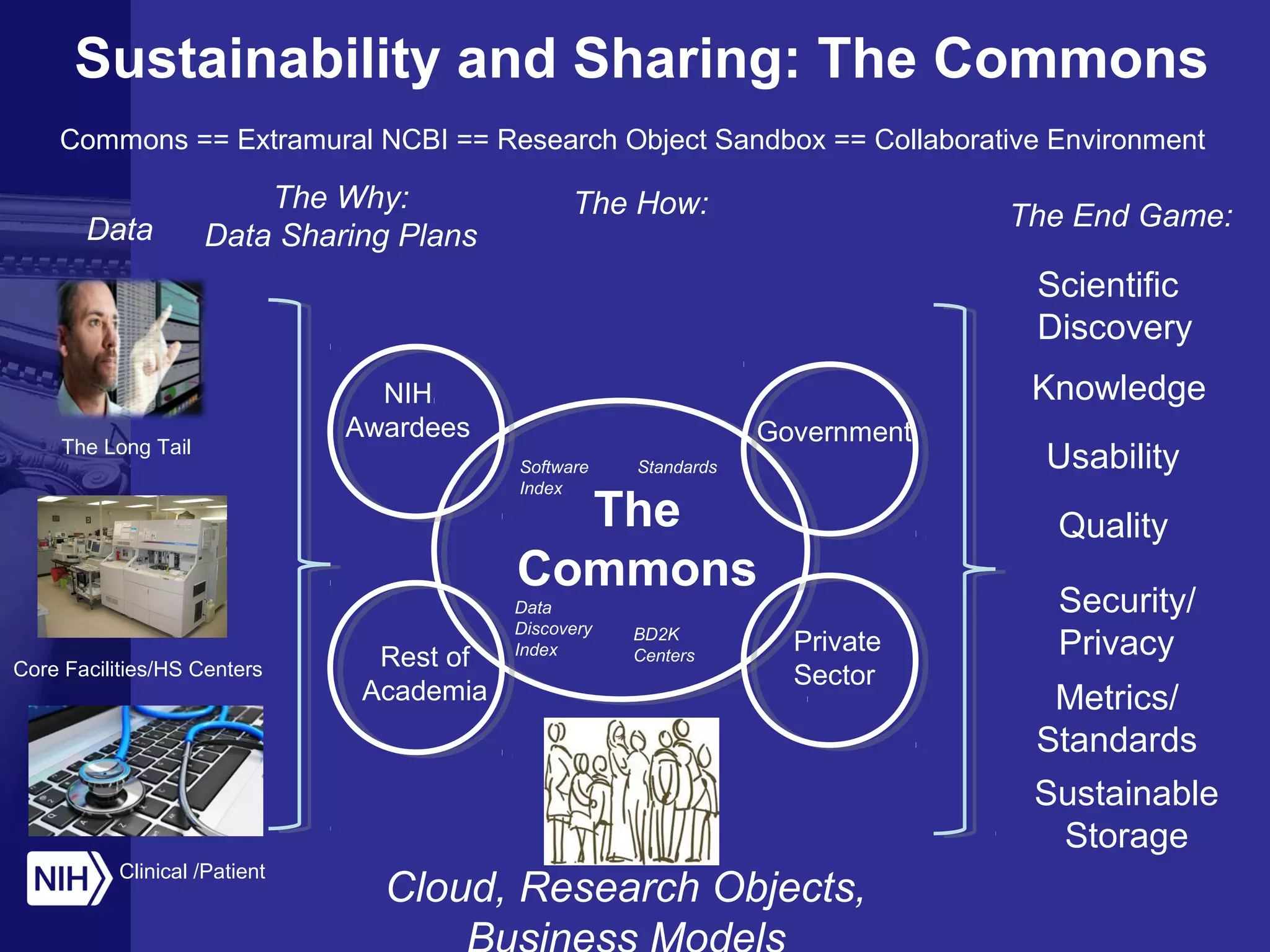


![[Adapted from George Komatsoulis]
One Possible Commons Business Model
HPC, Institution …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/afp2014-140710200031-phpapp02/75/The-Role-of-Automated-Function-Prediction-in-the-Era-of-Big-Data-and-Small-Budgets-16-2048.jpg)