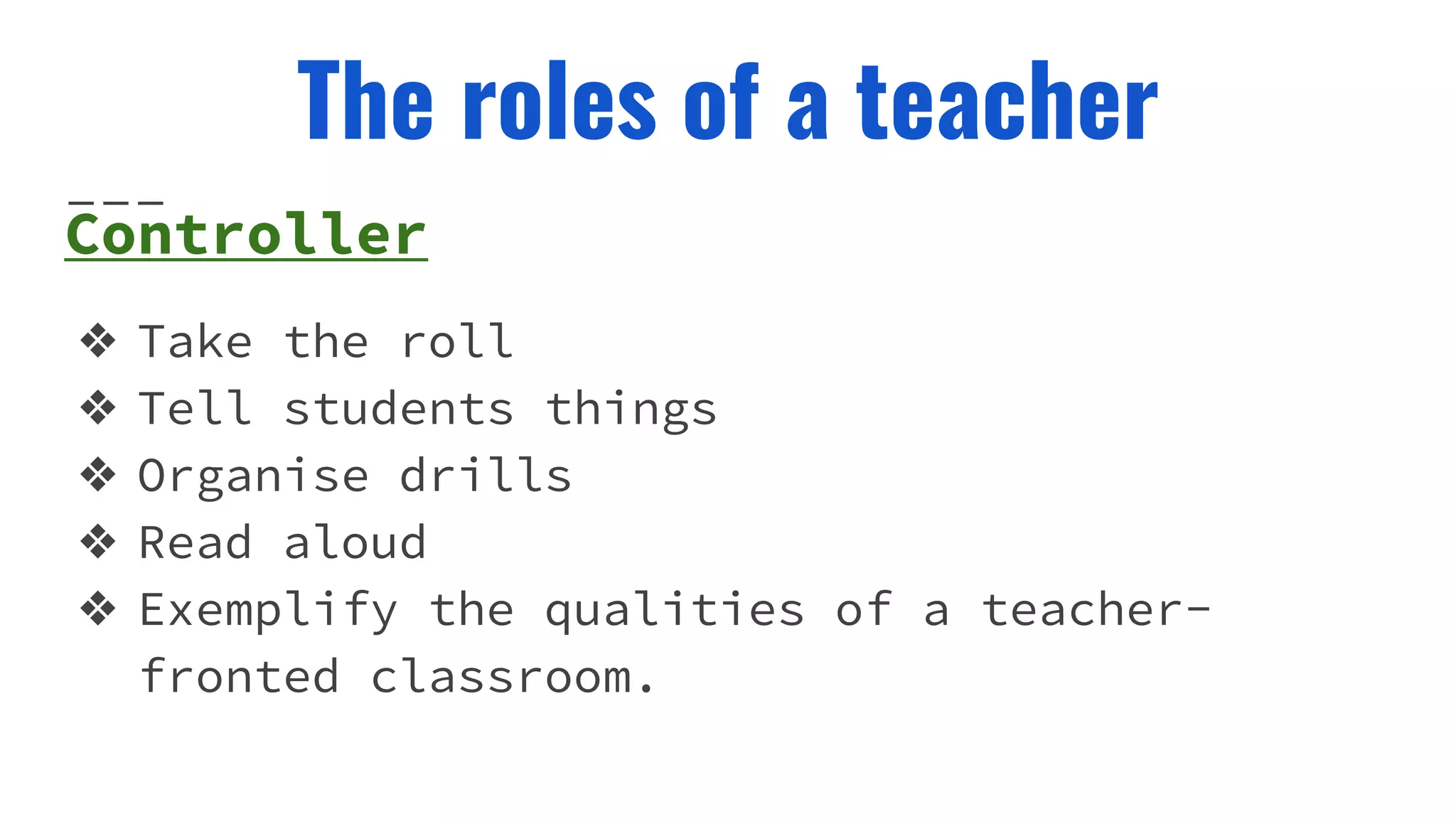
The document discusses the various roles of an English language teacher, including being an actor, orchestrator, gardener, controller, organizer, assessor, prompter, participant, resource, tutor, observer, and provider of comprehensible input. It also covers how teachers should perform in different classroom activities and how they can use mime, gestures, language models, and materials to aid teaching. The key roles revolve around directing lessons, giving feedback, supporting students, and providing comprehensible language input.