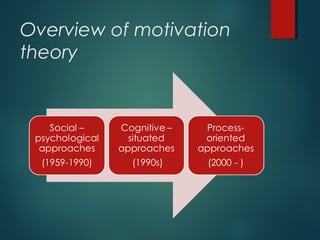
This document discusses motivation in language learning from several perspectives. It begins by defining motivation and outlining different approaches, including social-psychological models proposed by Gardner that focus on orientations and attitudes. It also discusses cognitive-situated approaches that emphasize the role of context in shaping motivation. Process-oriented models proposed by Dörnyei are then outlined, including the L2 Motivational Self System and ideal/ought-to selves. The document concludes by discussing strategies for motivating language learners based on a study by Dörnyei and Csizér, including setting a good example, developing relationships with learners, and promoting autonomy.









![The socio-educational
model
“The socio-educational model of second language
acquisition was developed […] in an attempt to
provide a fundamental basis for the role played by
different classes of variables […] It is intended to
provide a platform where the role of these variables
can be understood in the context of learning a
second language in a classroom context.”
Gardner 2010: 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appliedlinguisticslecture8-180423114152/85/Motivation-in-Second-Language-Acquisition-11-320.jpg)





















