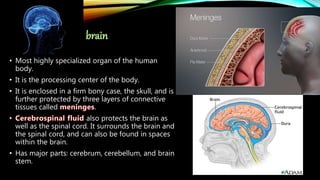
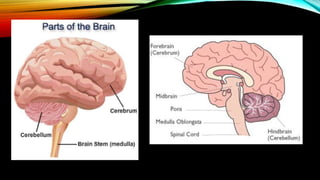
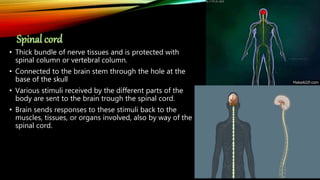
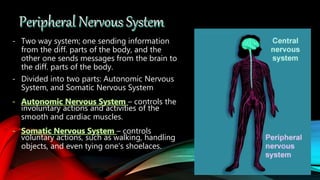
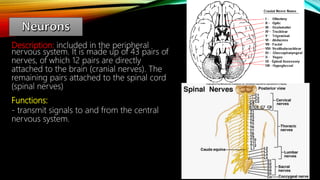
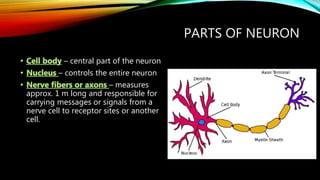
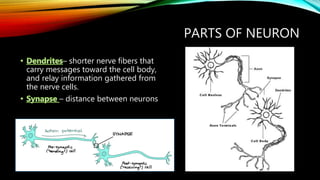
The nervous system is composed of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It is responsible for coordinating all functions of the body and controlling thoughts, actions, and vital signs. The brain acts as the control center, interpreting stimuli and directing organs and muscles. The spinal cord connects the brain to the rest of the body and transmits signals back and forth. Within the nervous system, neurons are specialized cells that transmit electrical signals and allow communication between different parts of the body.