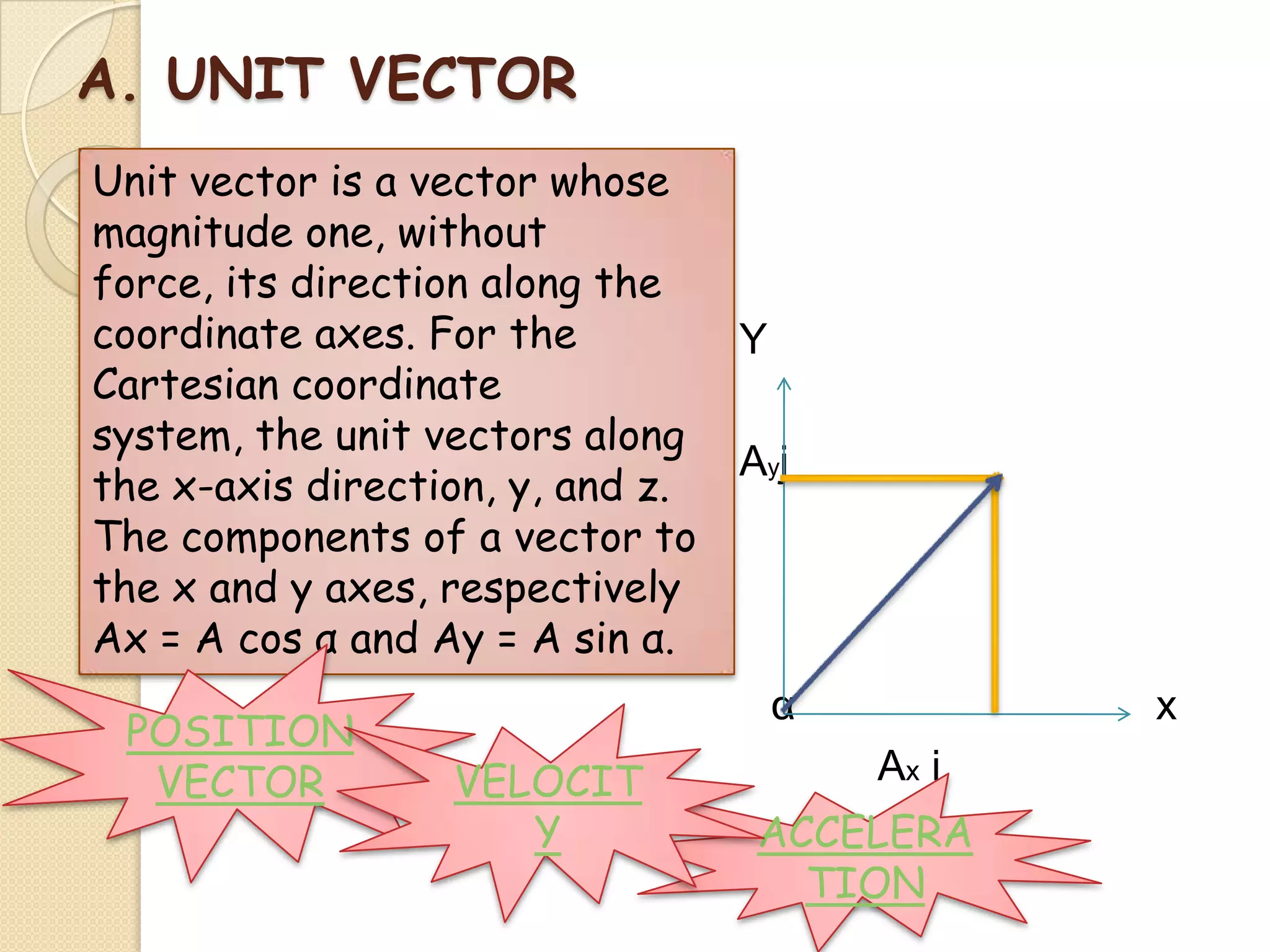
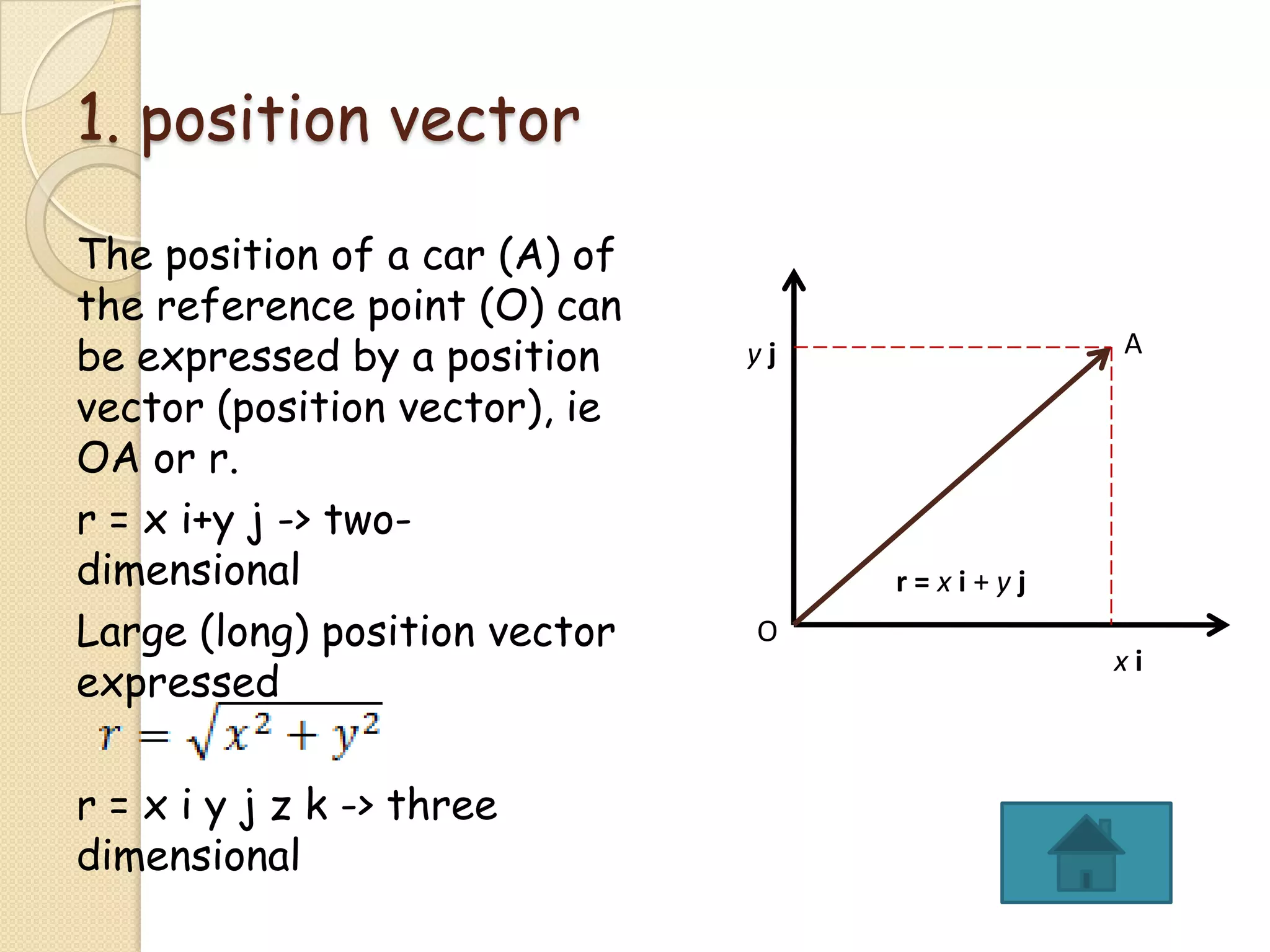
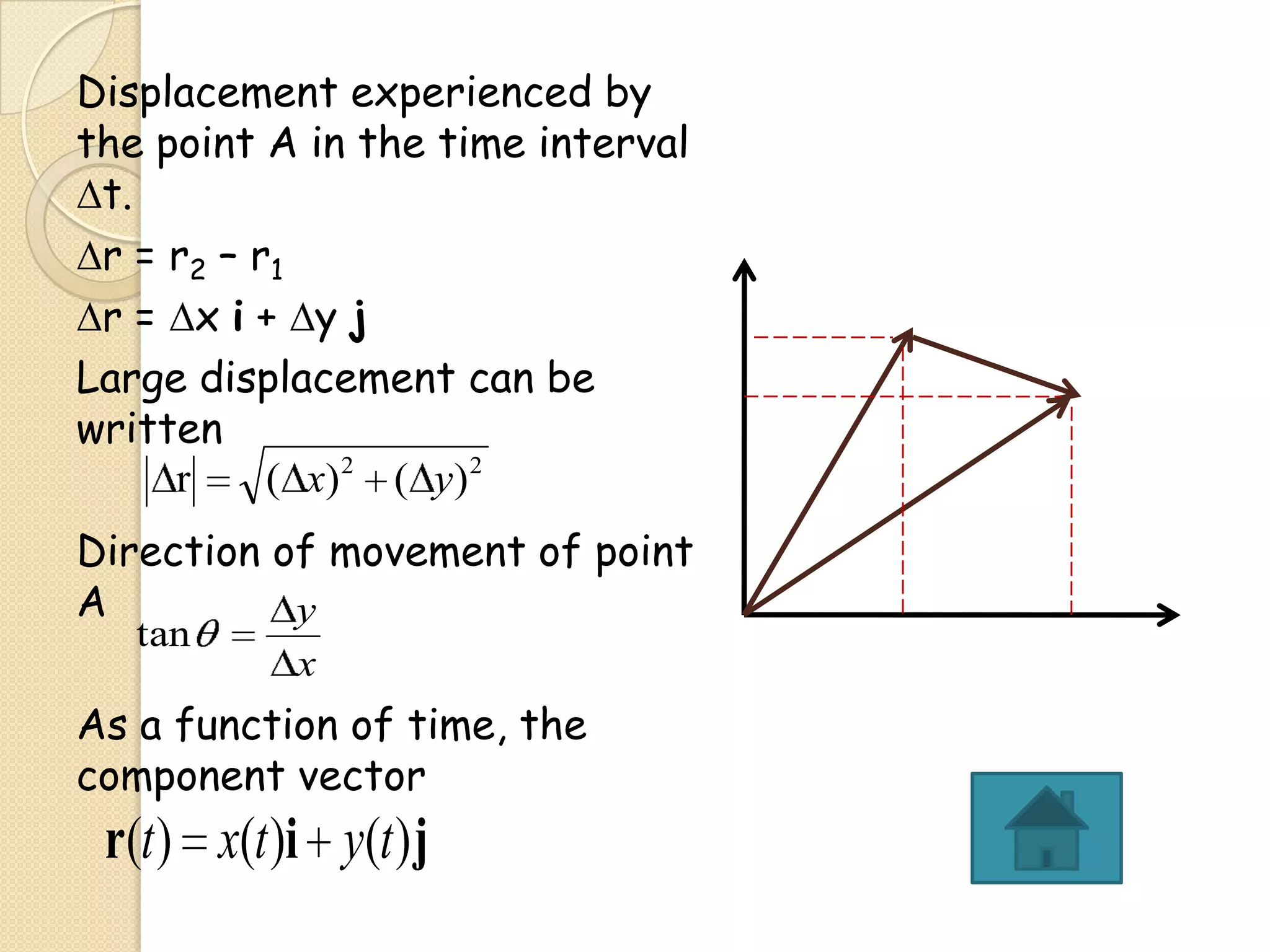
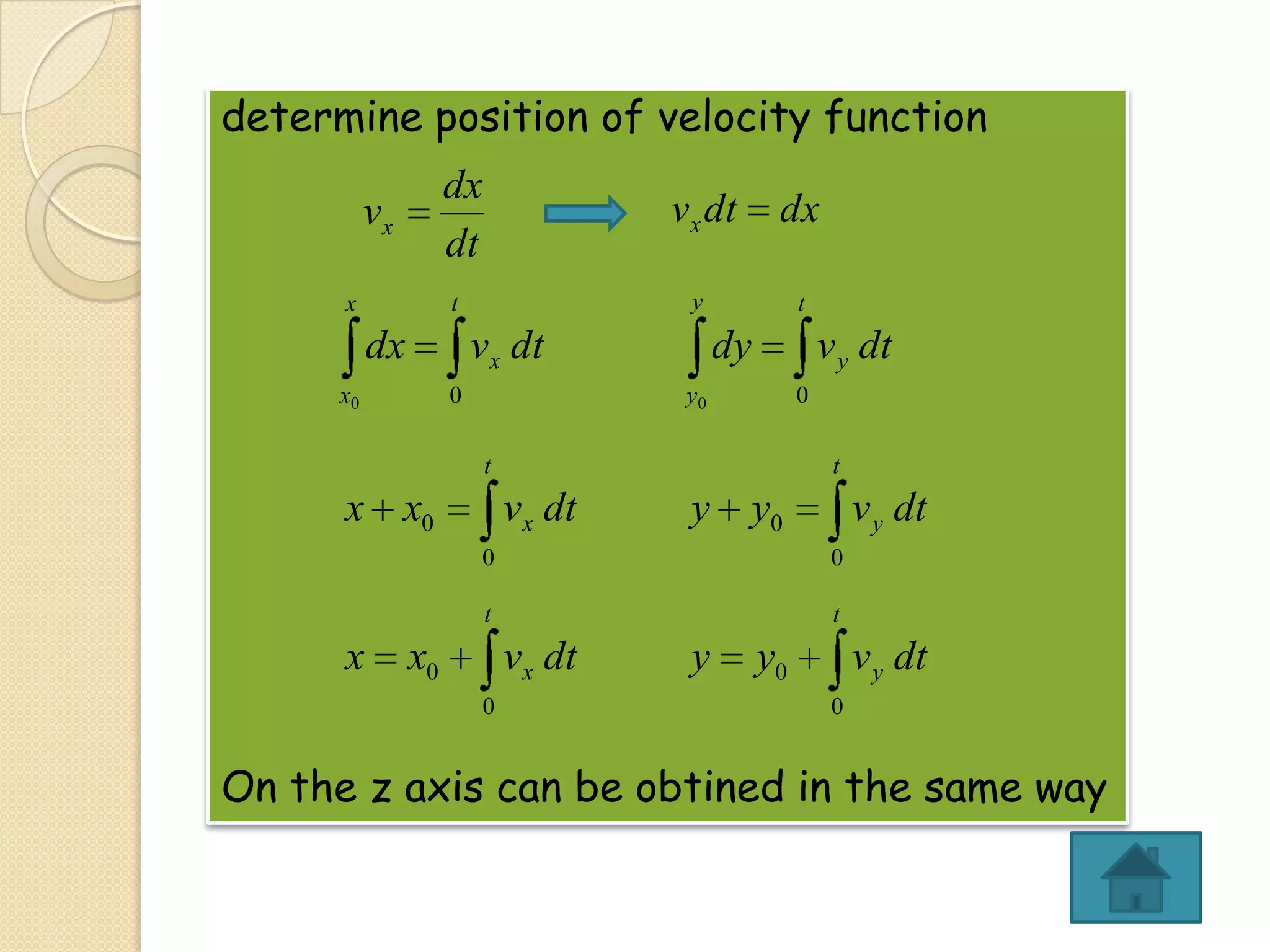
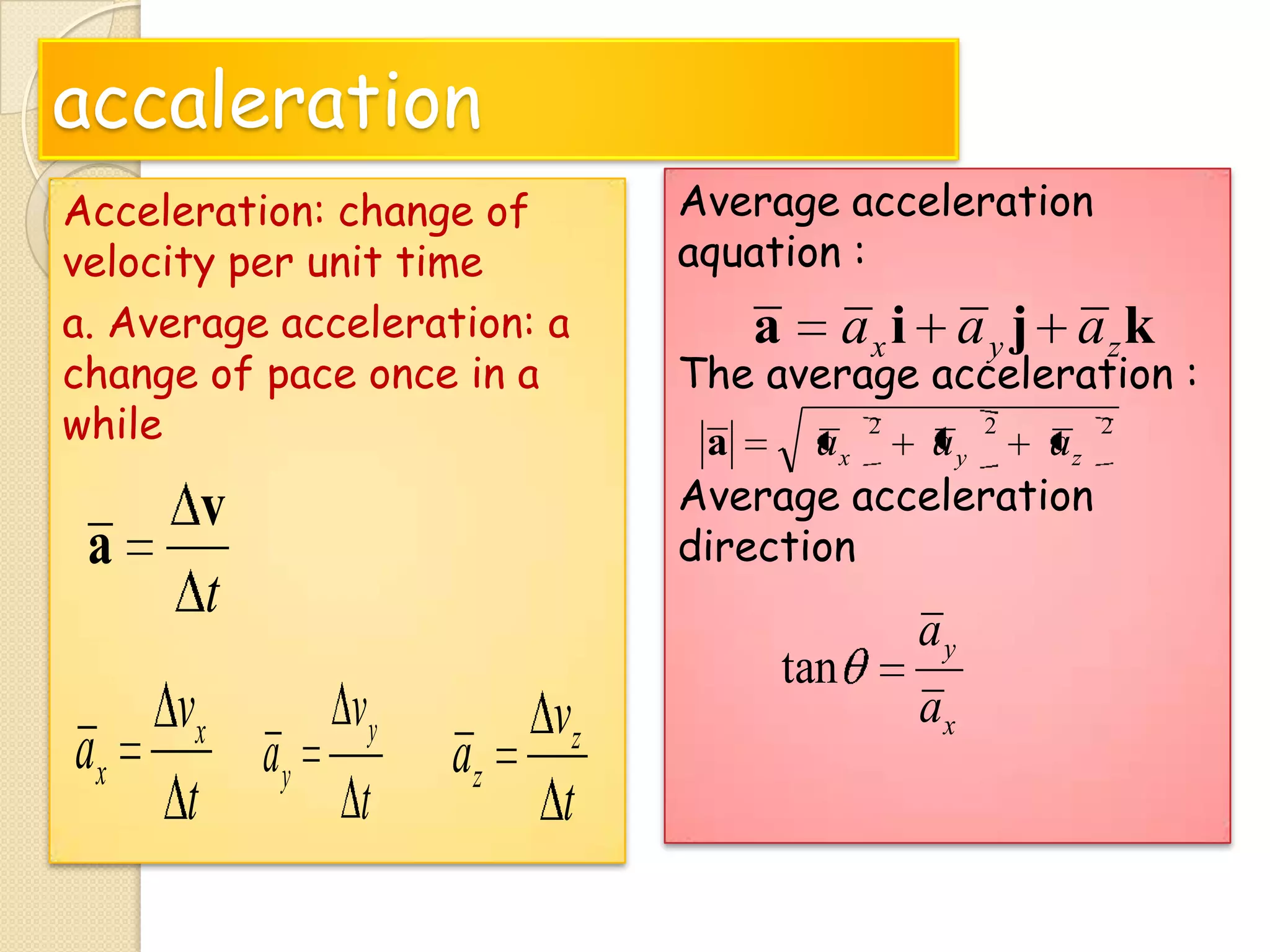
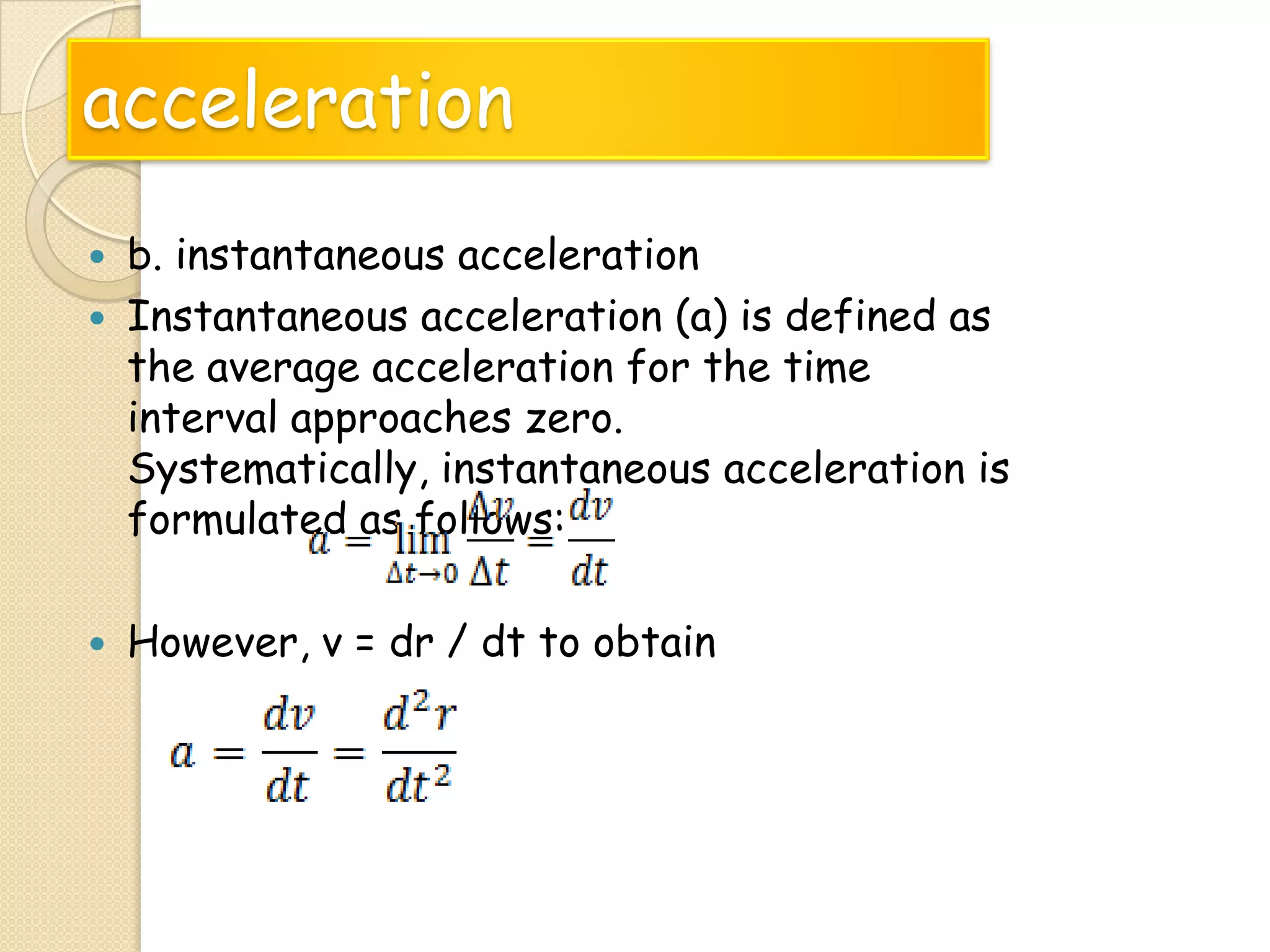
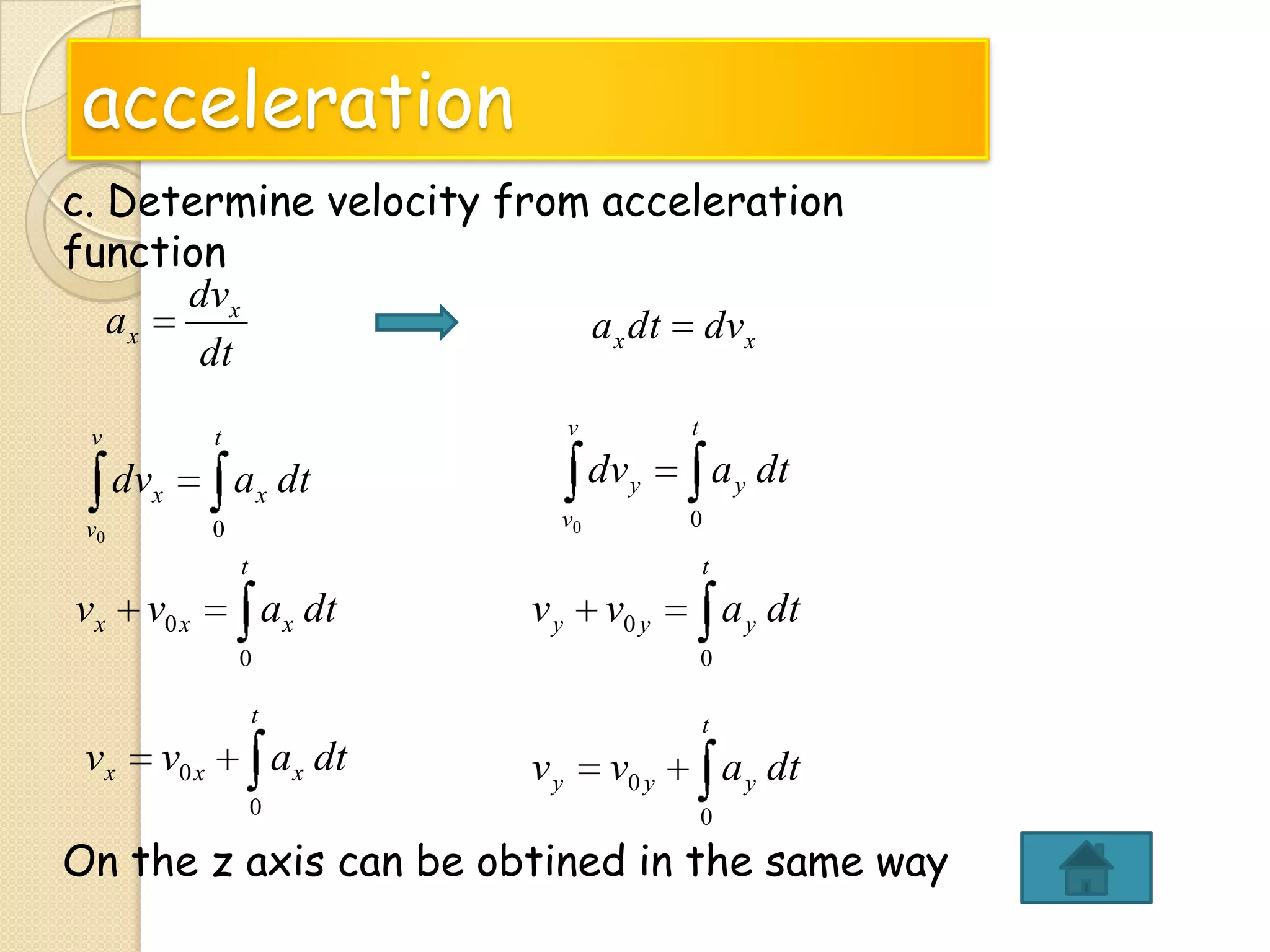
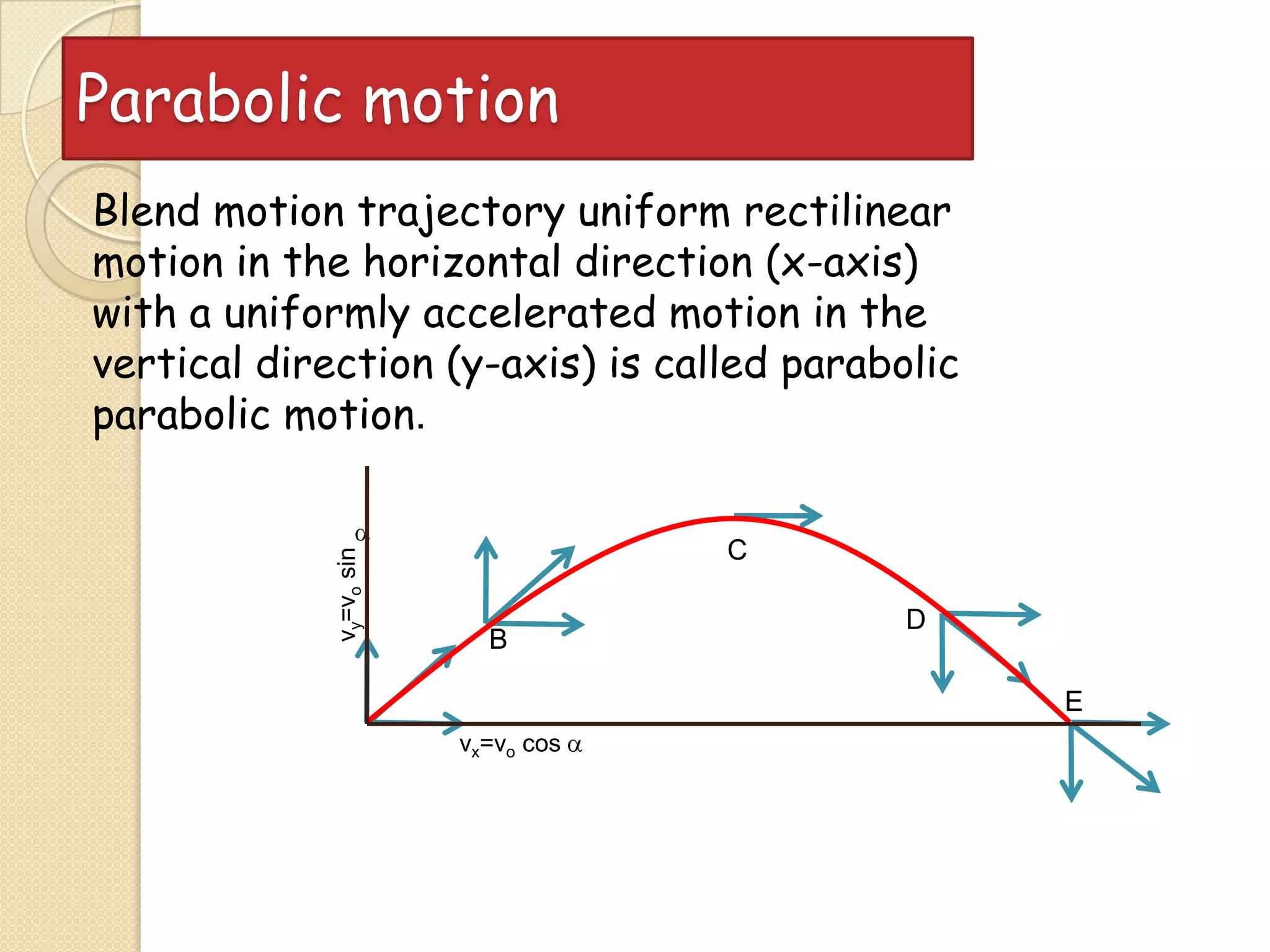
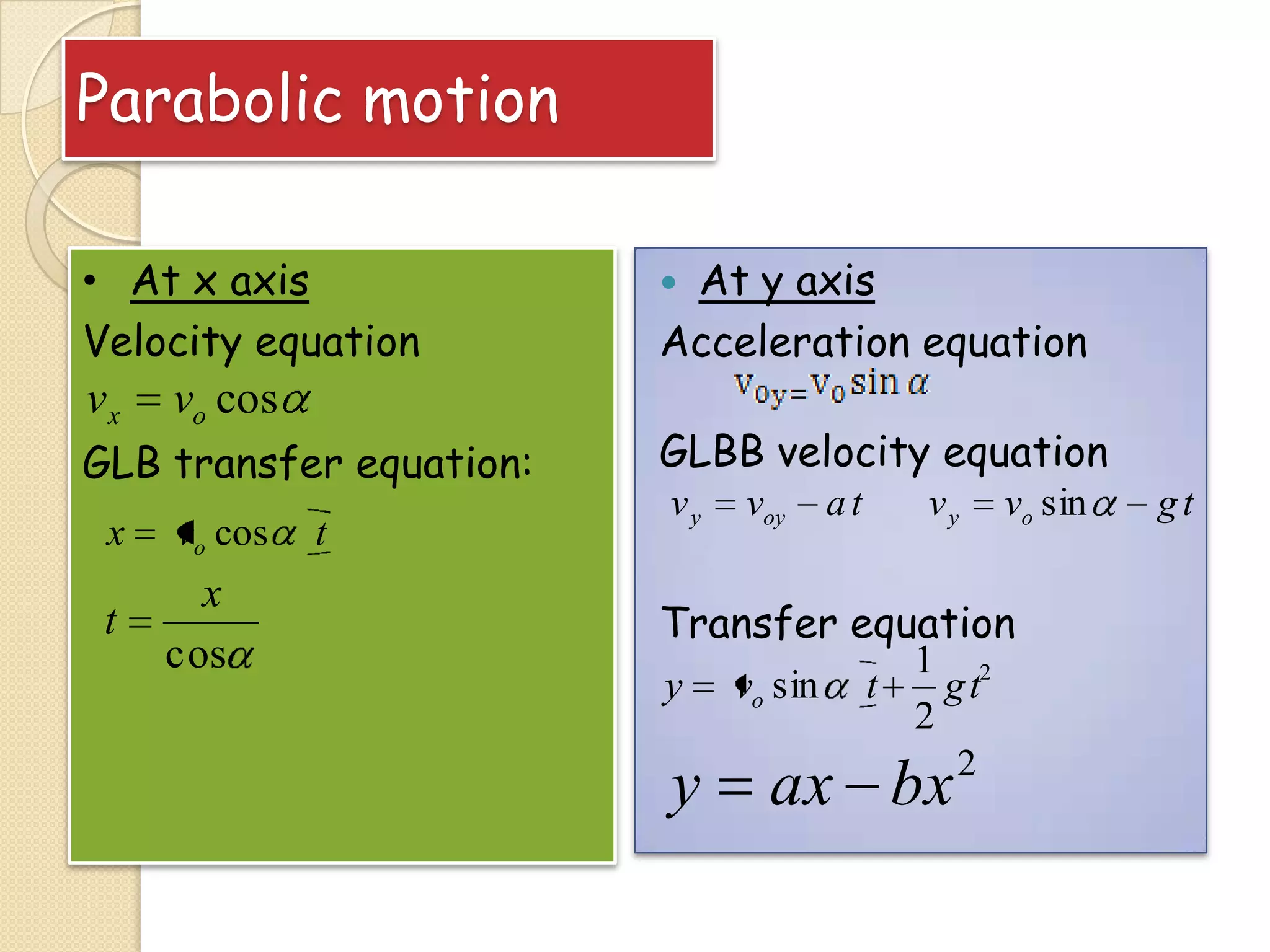
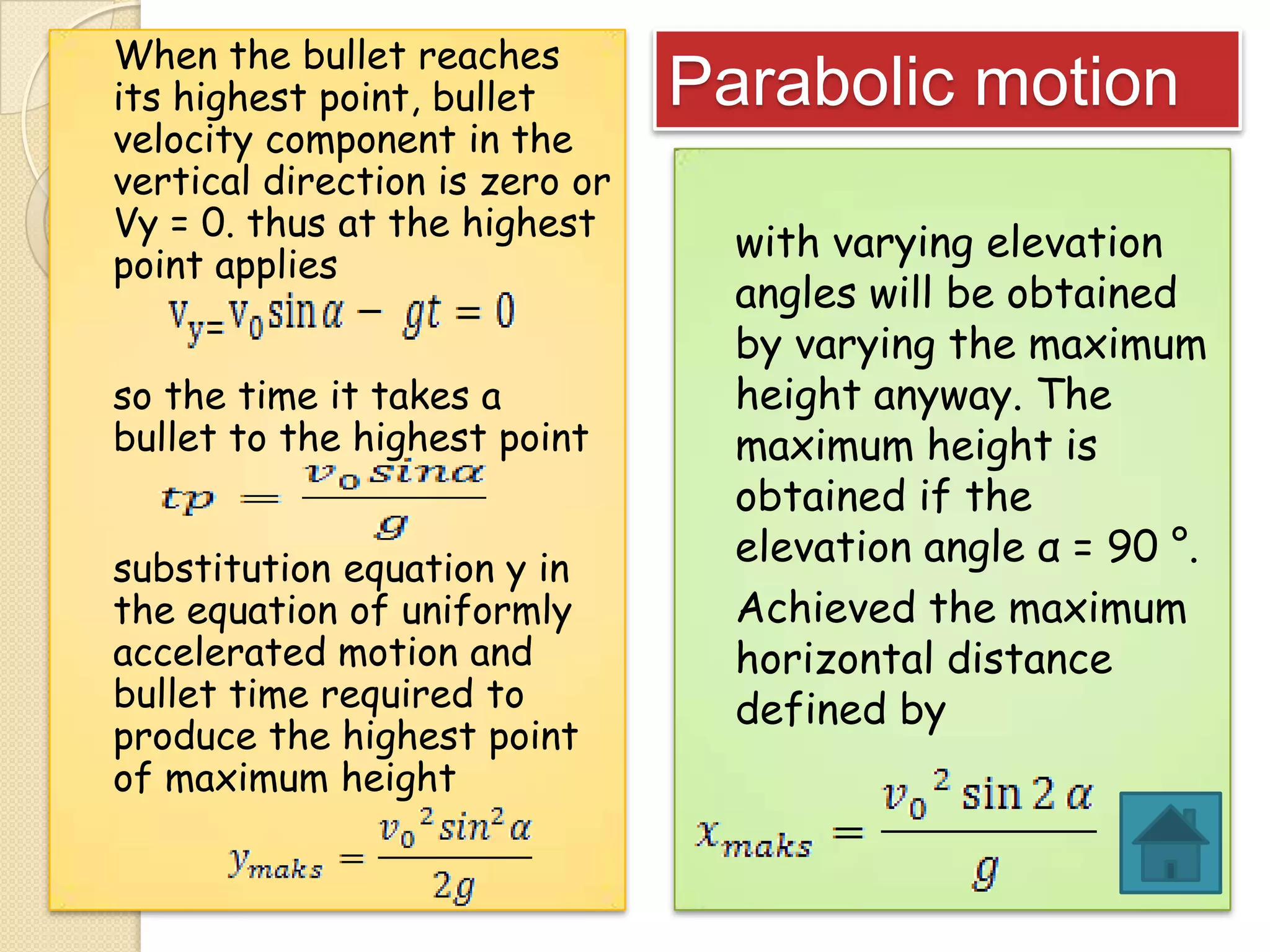
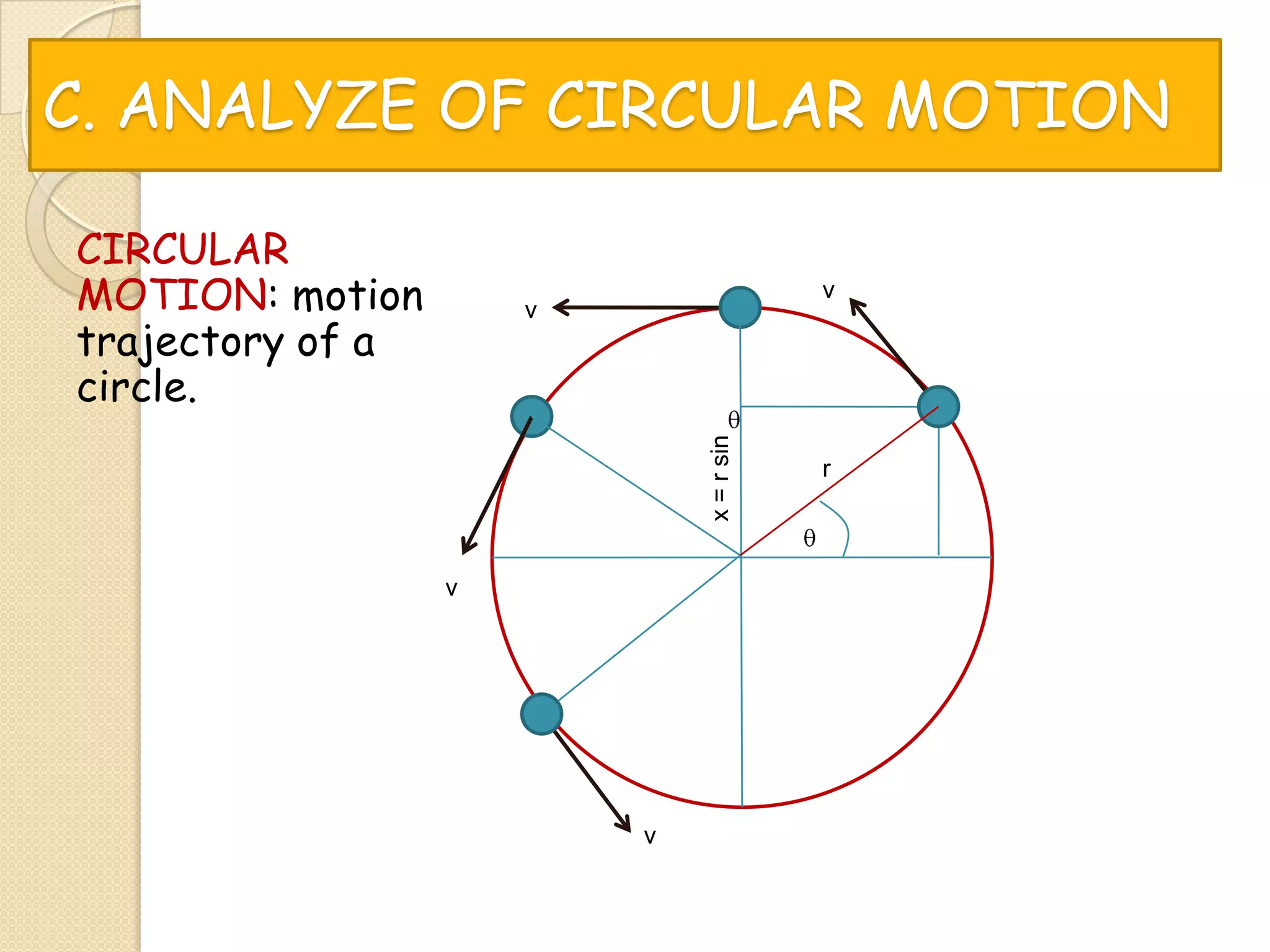
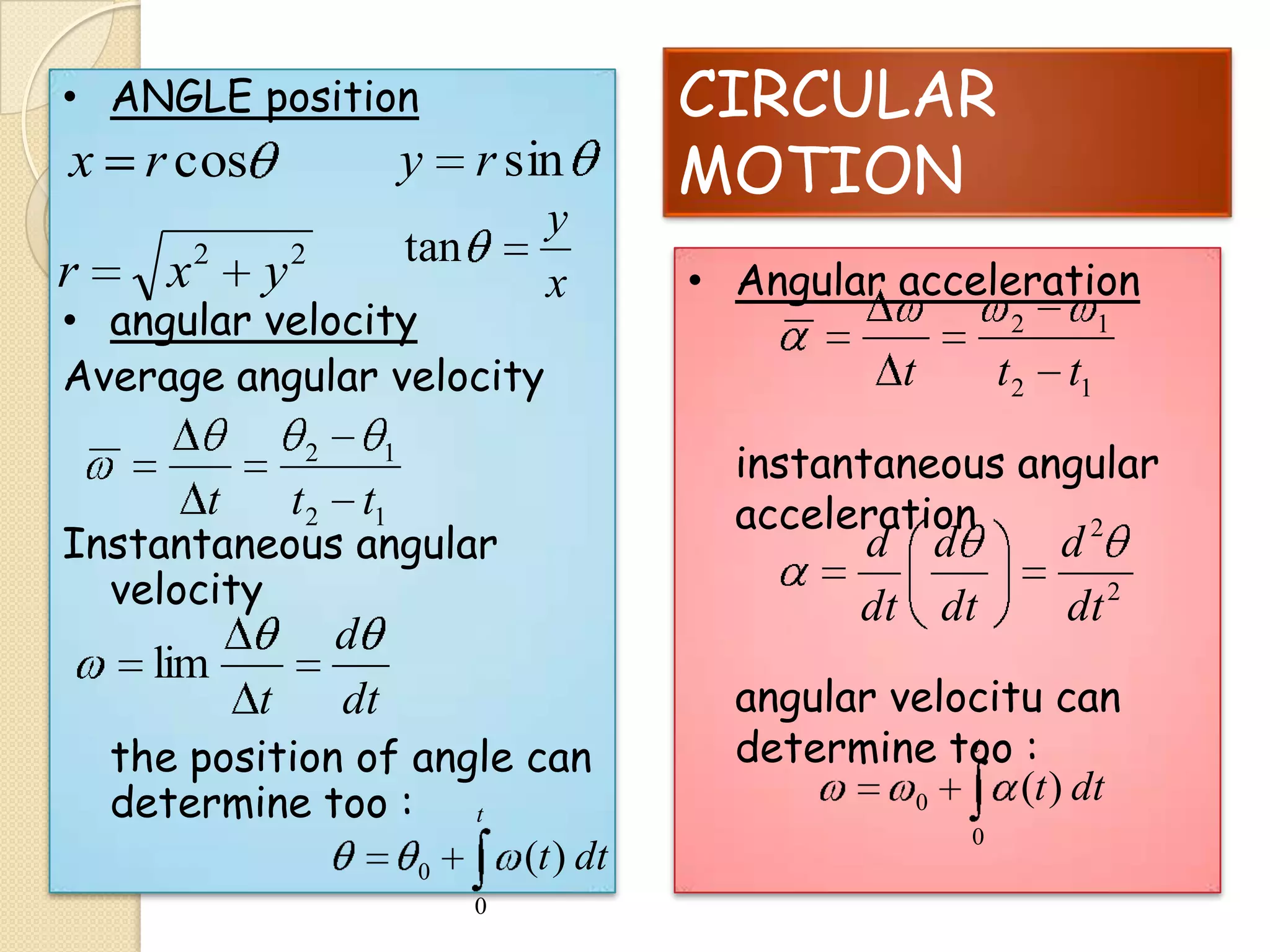
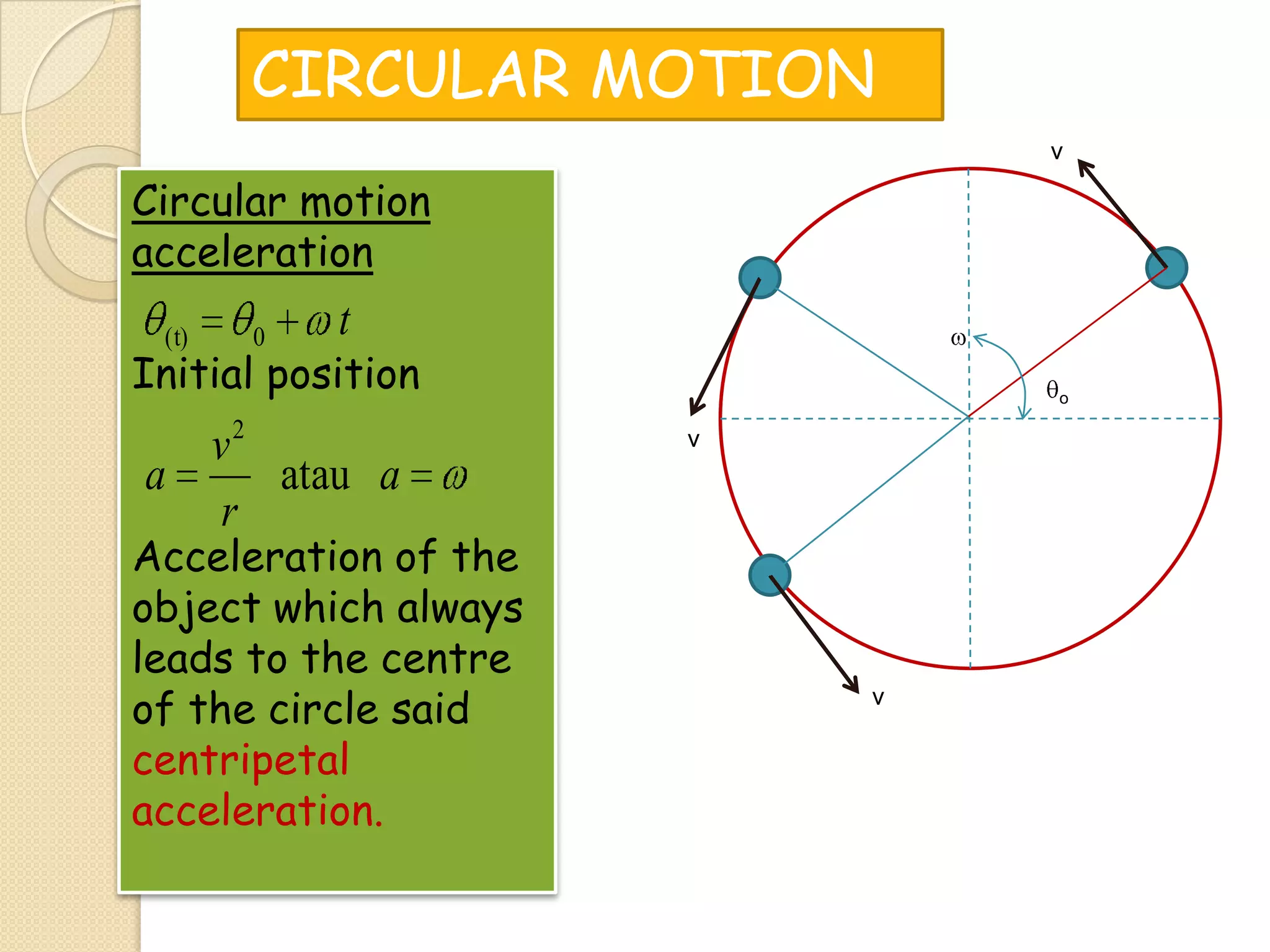
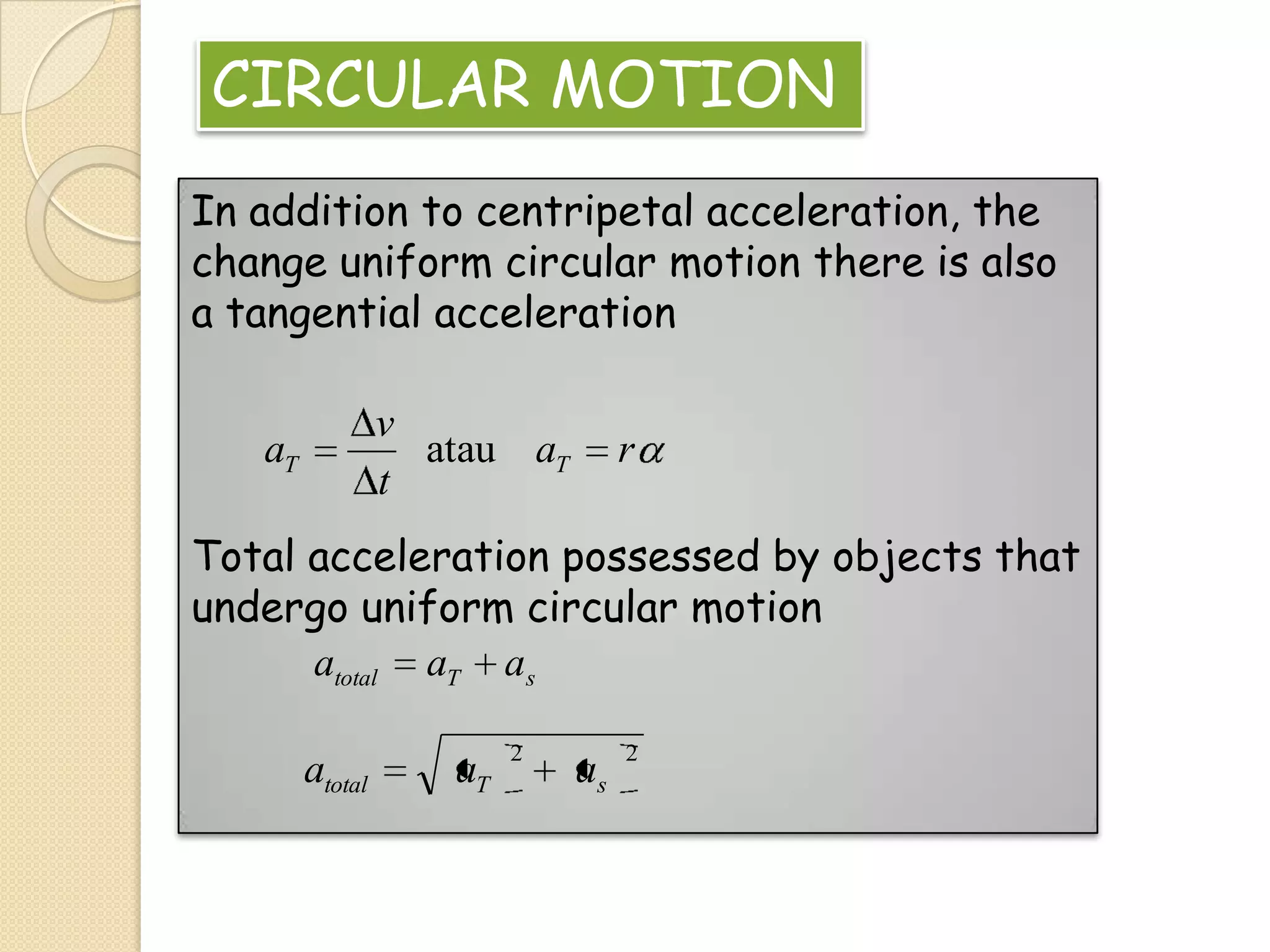
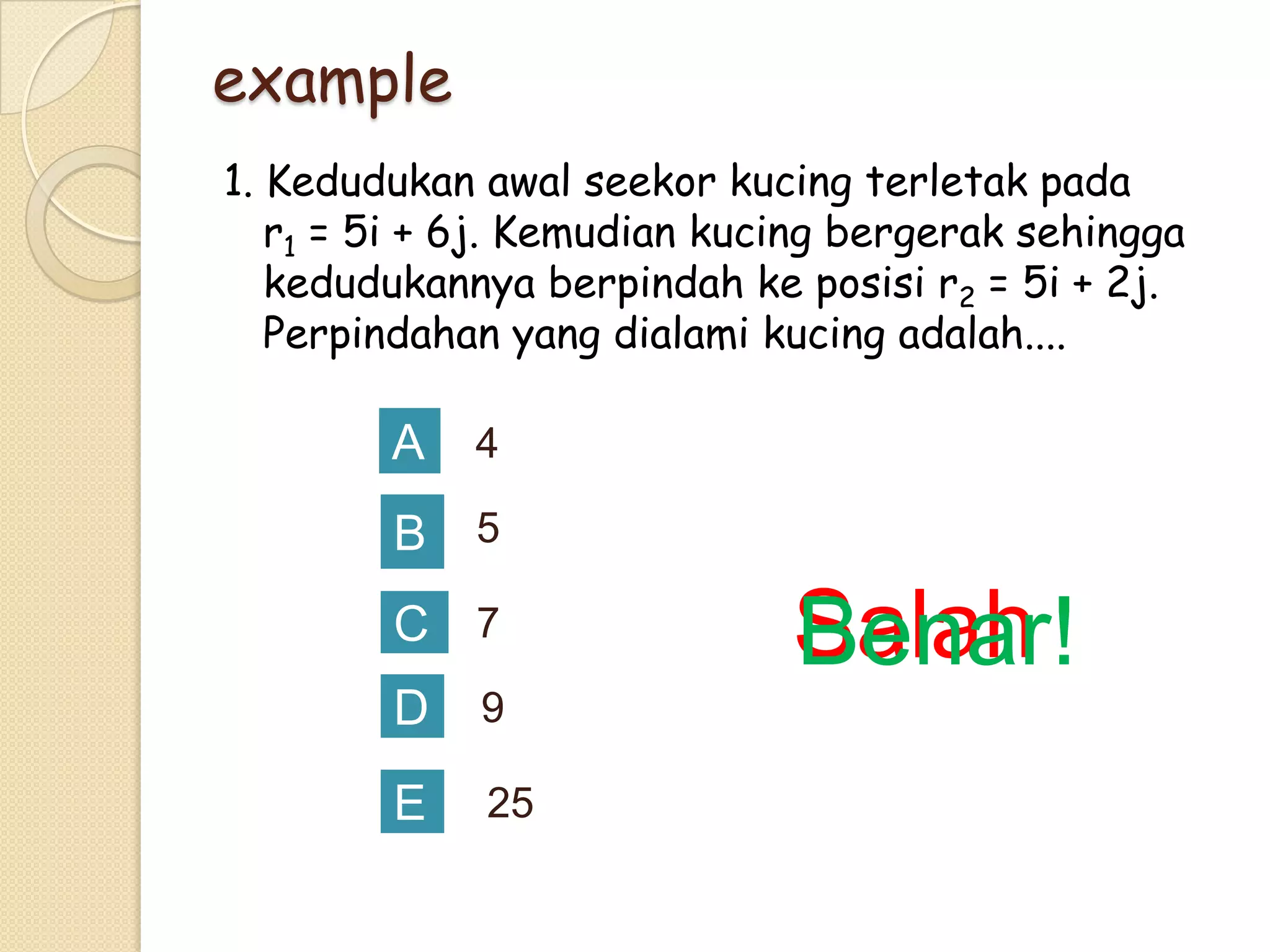
This document provides instructional materials on analyzing motion using vectors. It begins with definitions of motion and discusses rectilinear, parabolic, and circular motion. Rectilinear motion is analyzed using position, velocity, and acceleration vectors. Parabolic motion results from horizontal rectilinear motion combined with vertically accelerated motion. Circular motion is described using angular position, velocity, and acceleration. Examples are provided to demonstrate analyzing different types of motions using vectors.