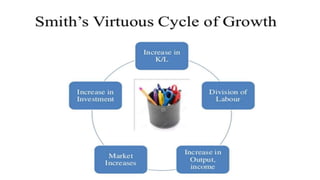
The document summarizes several classical theories of economic development:
1) Adam Smith, David Ricardo, and J.S. Mill believed that economic growth would slow or stop due to increasing population and limited resources.
2) Thomas Malthus argued that population growth alone does not lead to development and that capital accumulation is necessary for continued growth.
3) Walt Rostow proposed a model of economic growth occurring in five stages: traditional society, preconditions for take-off, take-off, drive to maturity, and high mass consumption.
4) John Stuart Mill viewed economic development as dependent on land, labor, and capital, and distinguished between productive and unproductive consumption.