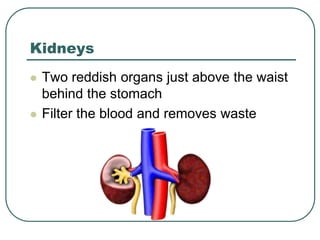
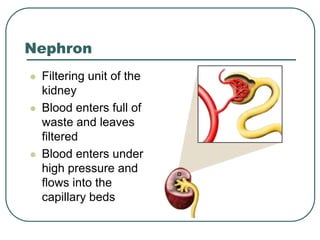
The kidneys control water levels in the body and remove waste from the bloodstream. The kidneys filter the blood, reabsorbing useful nutrients while producing urine containing waste products like urea and excess water. This urine travels from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder for storage before being excreted through the urethra. In this way, the kidneys play a vital role in regulating water balance and removing toxins from the body.