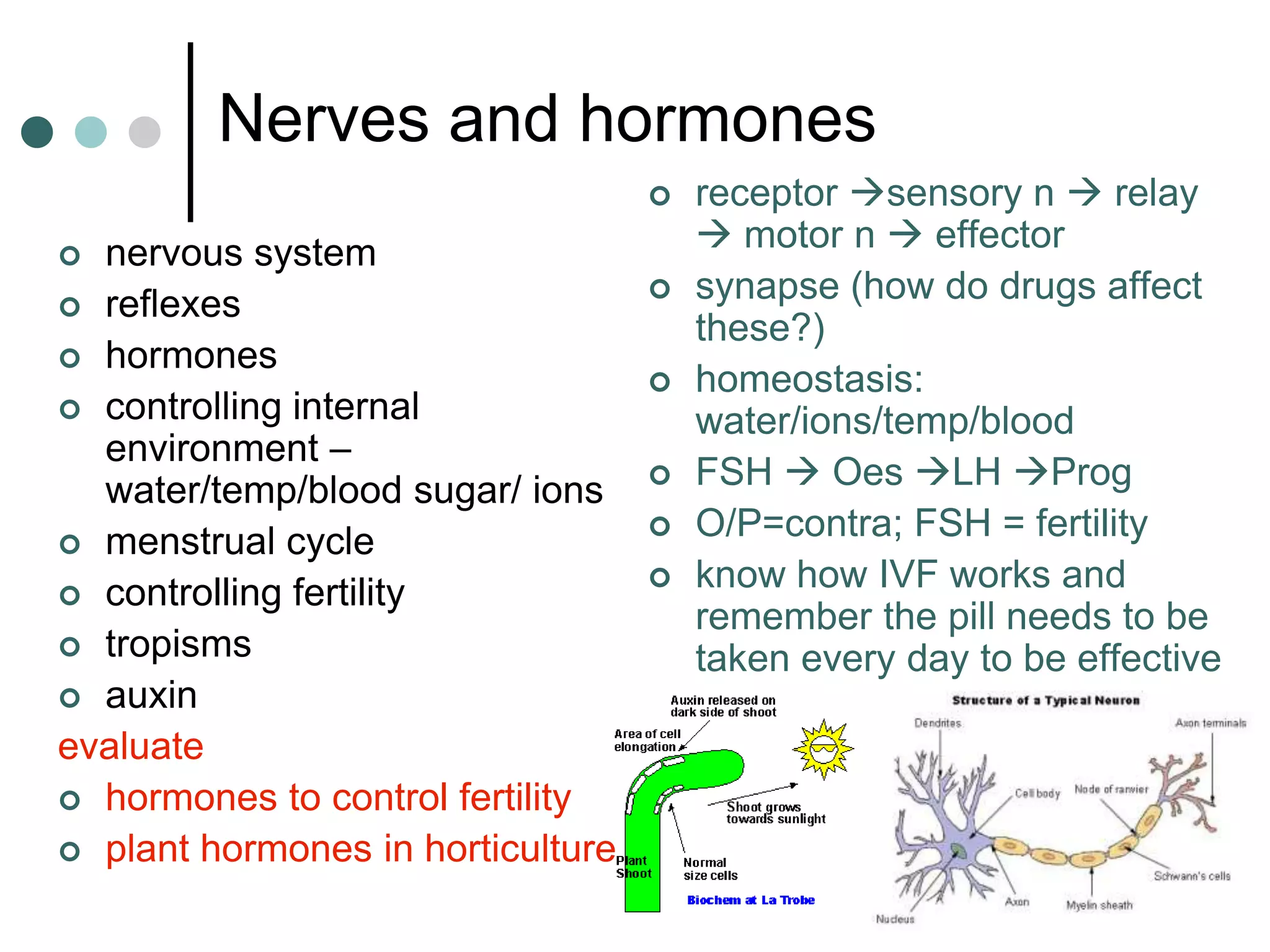
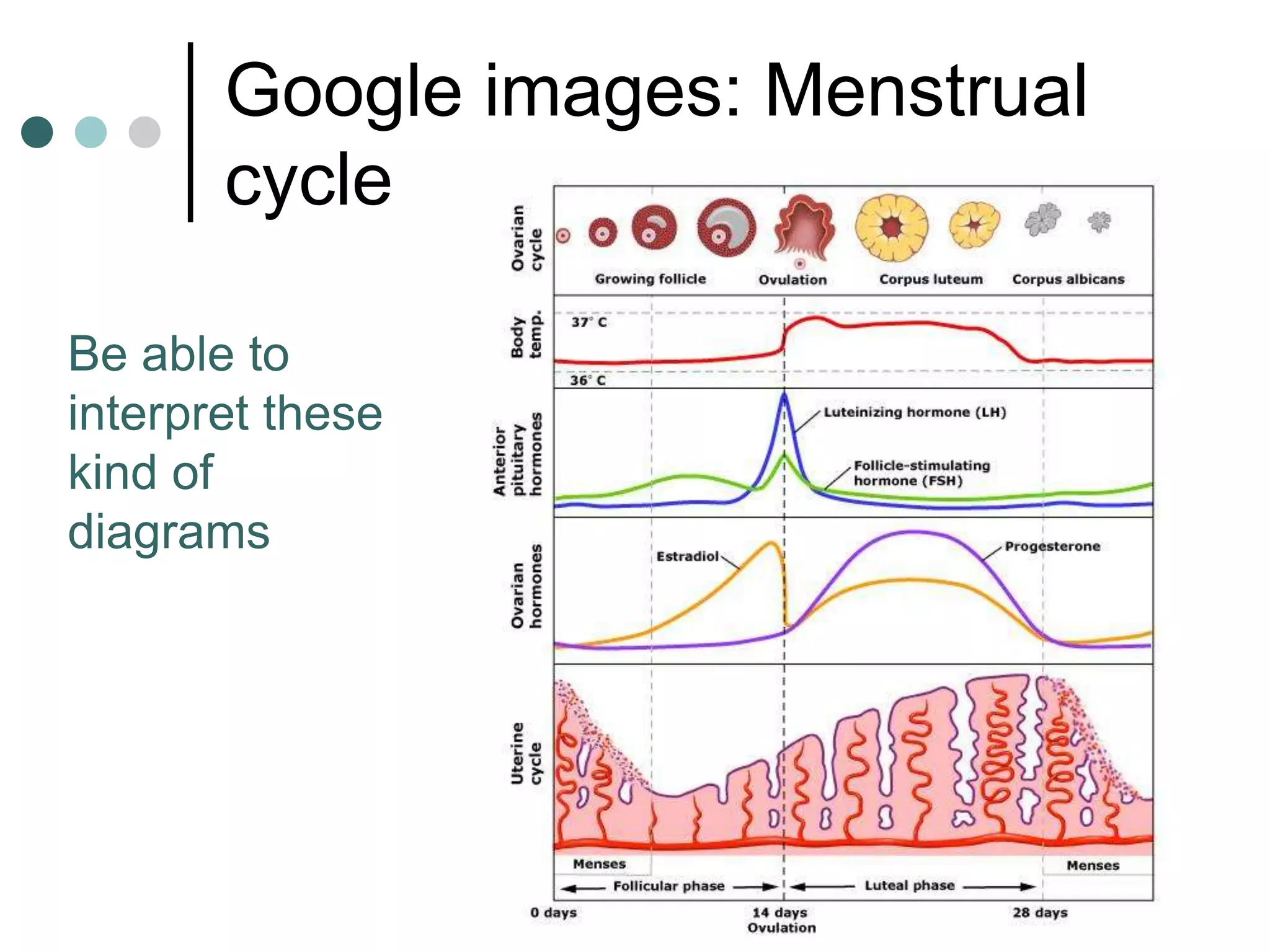
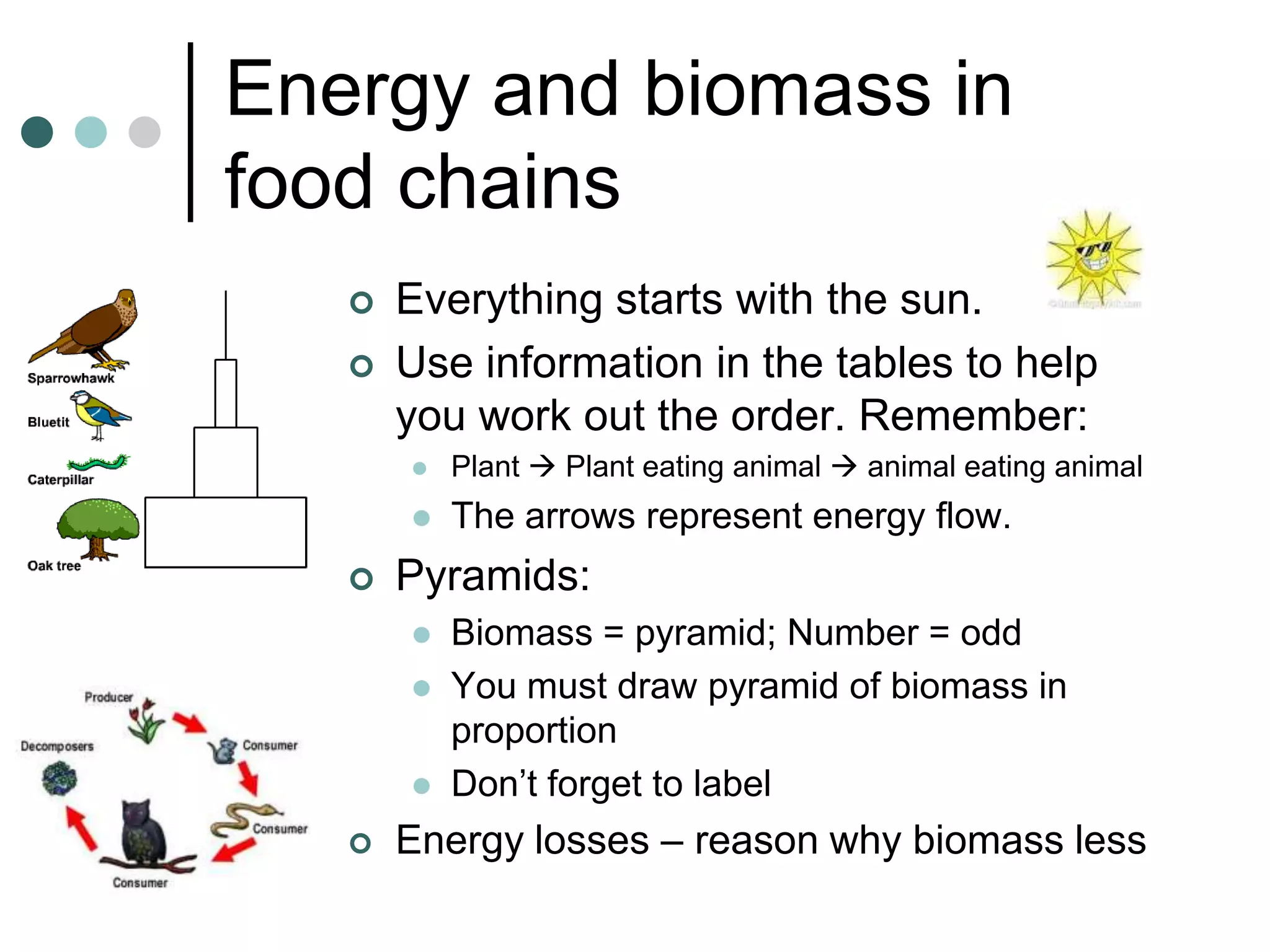
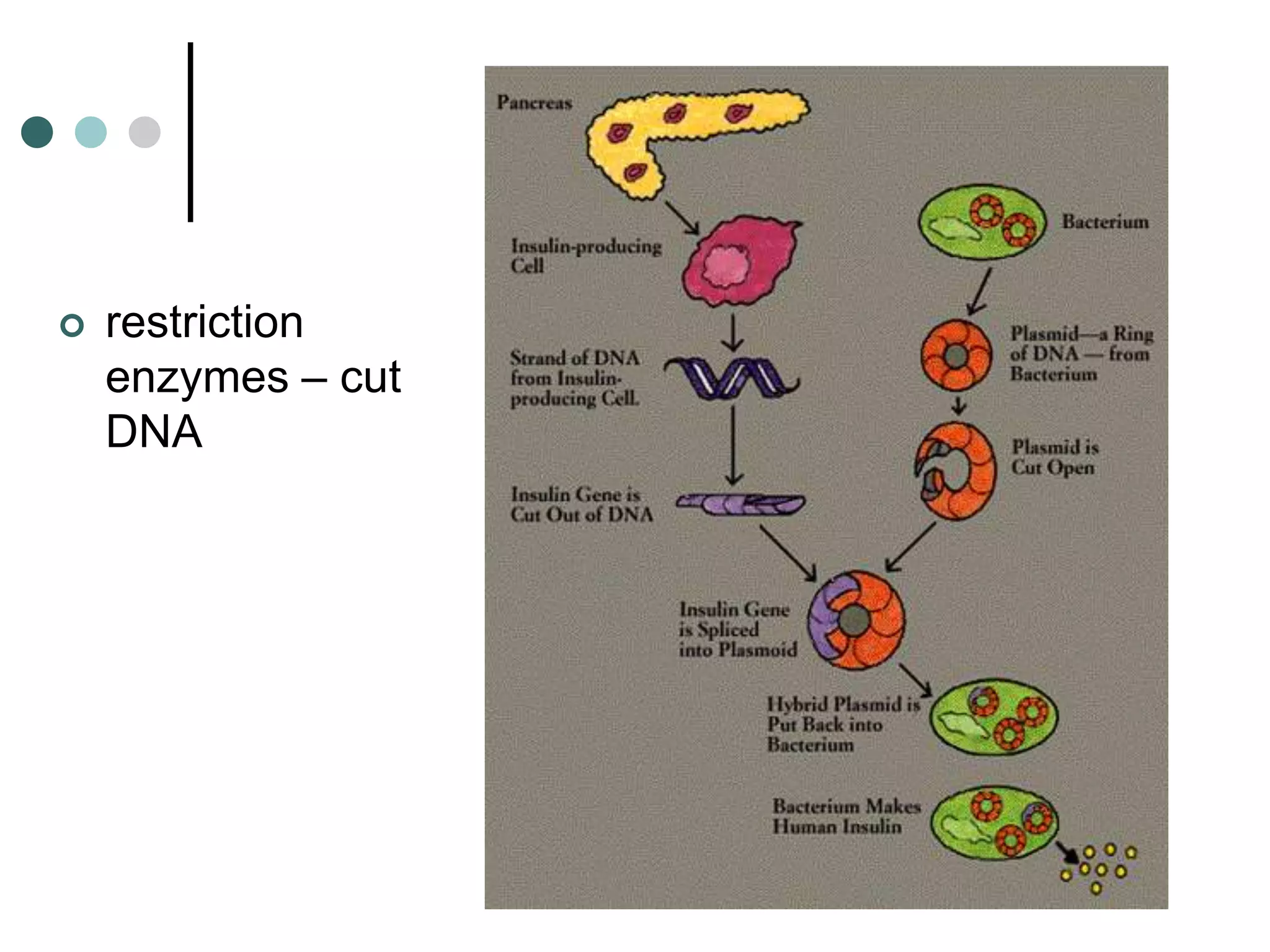
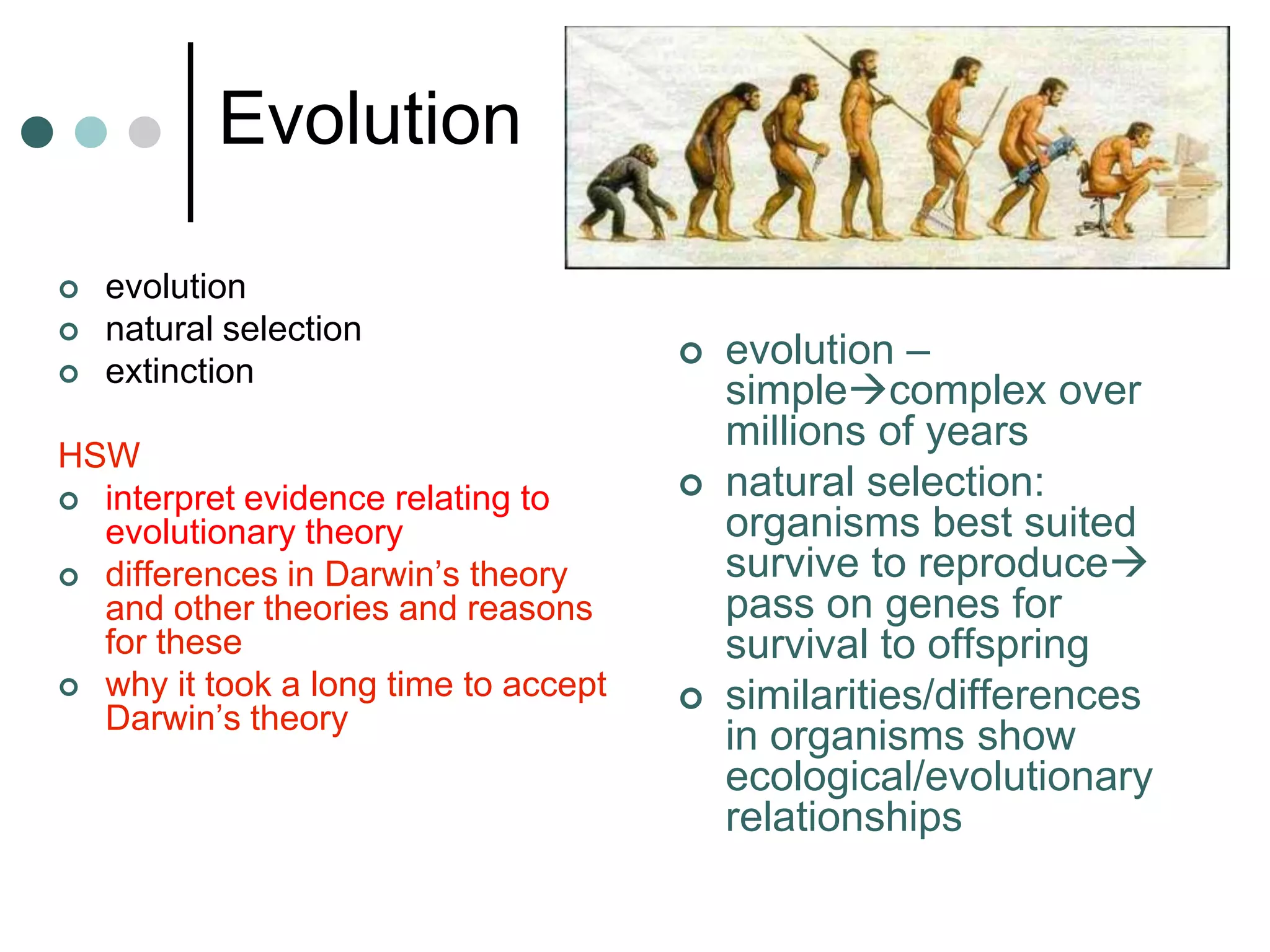
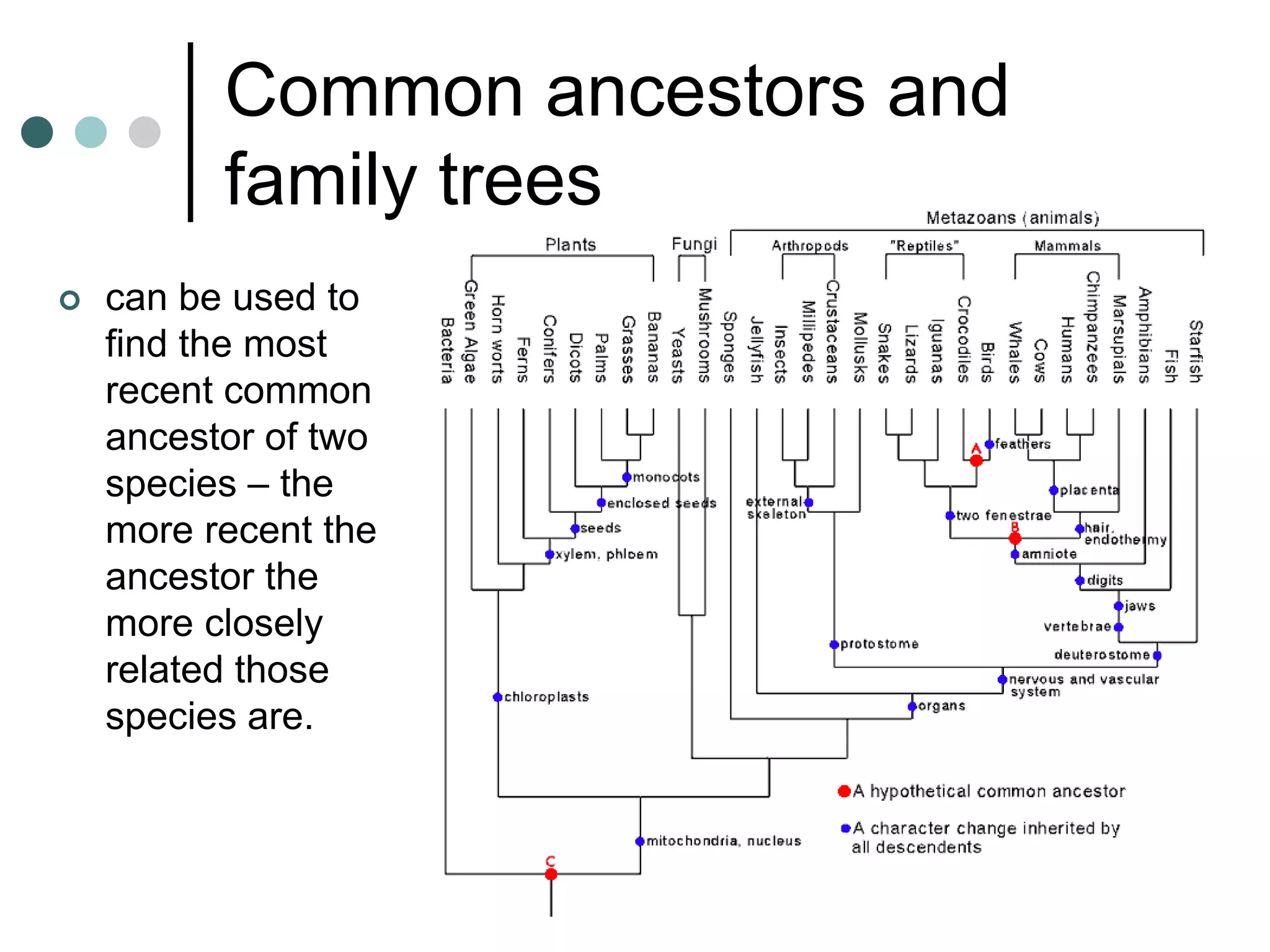
This document provides an overview of the core biology syllabus including topics such as keeping healthy, infectious disease, nerves and hormones, use and abuse of drugs, adaptation, food chains, waste materials, genetic variation, evolution, and common ancestors. Key concepts are outlined for each topic in bullet points along with evaluation points to consider. Diagrams are referenced to help interpret processes like the menstrual cycle.