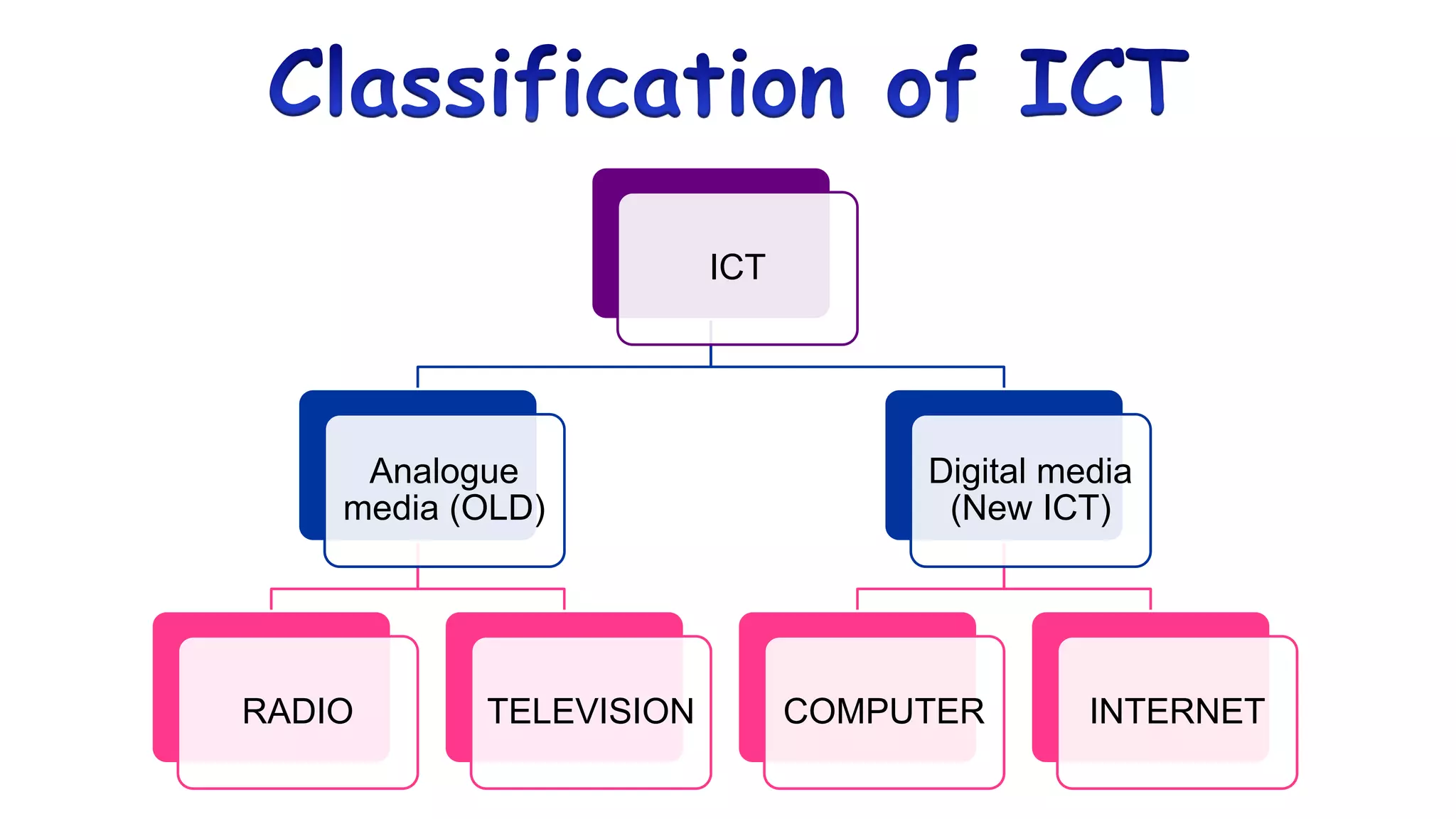
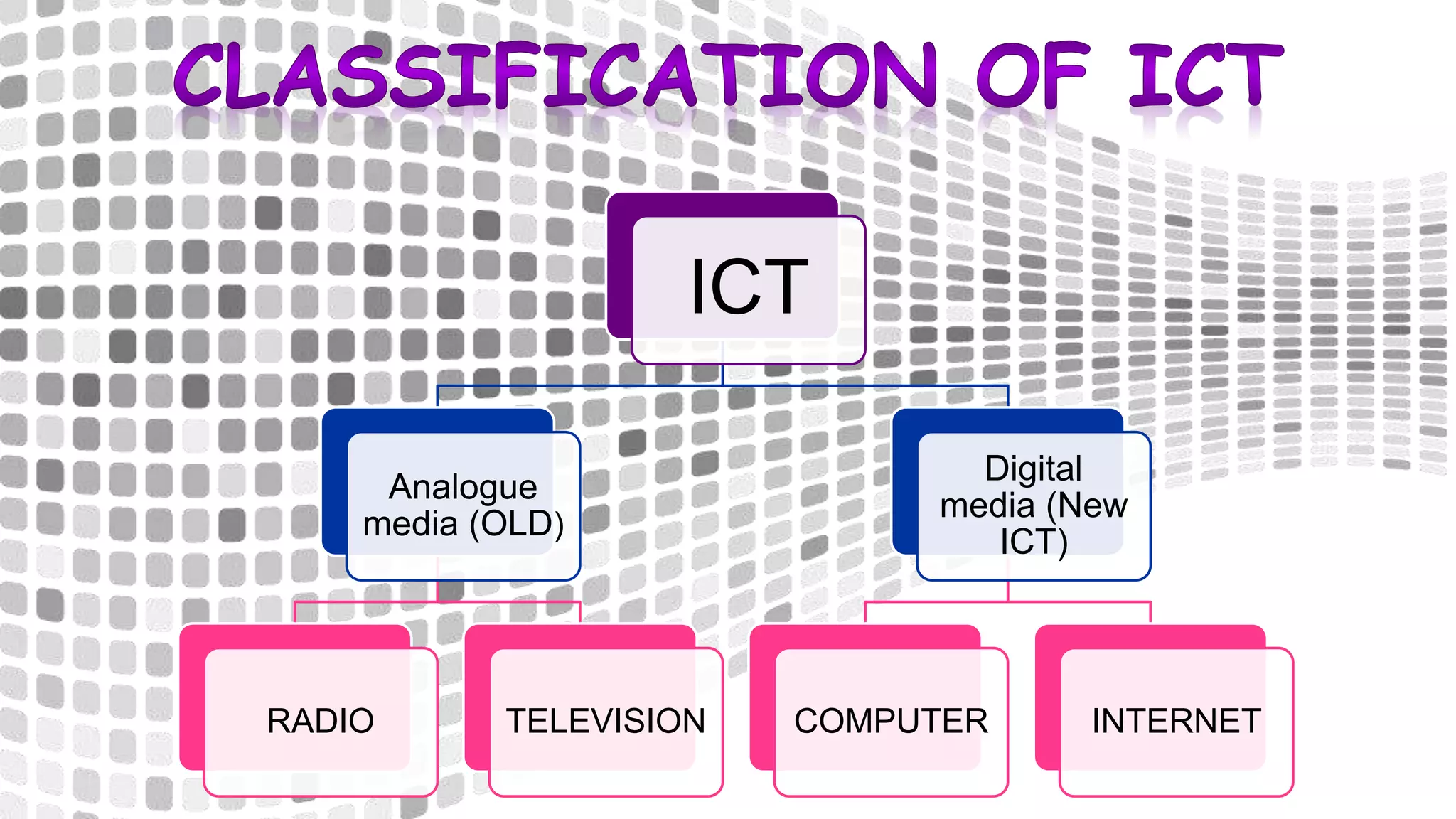
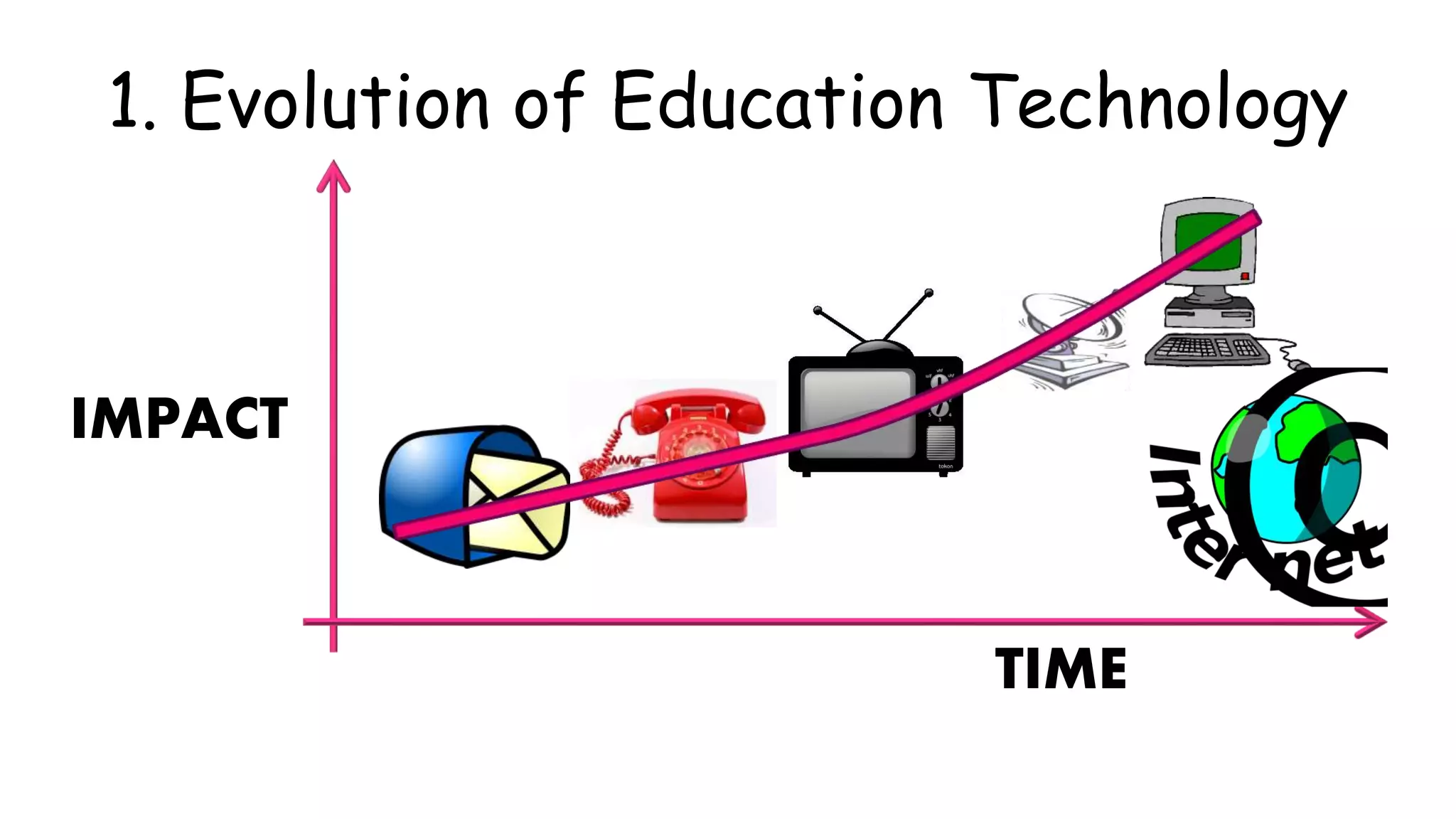
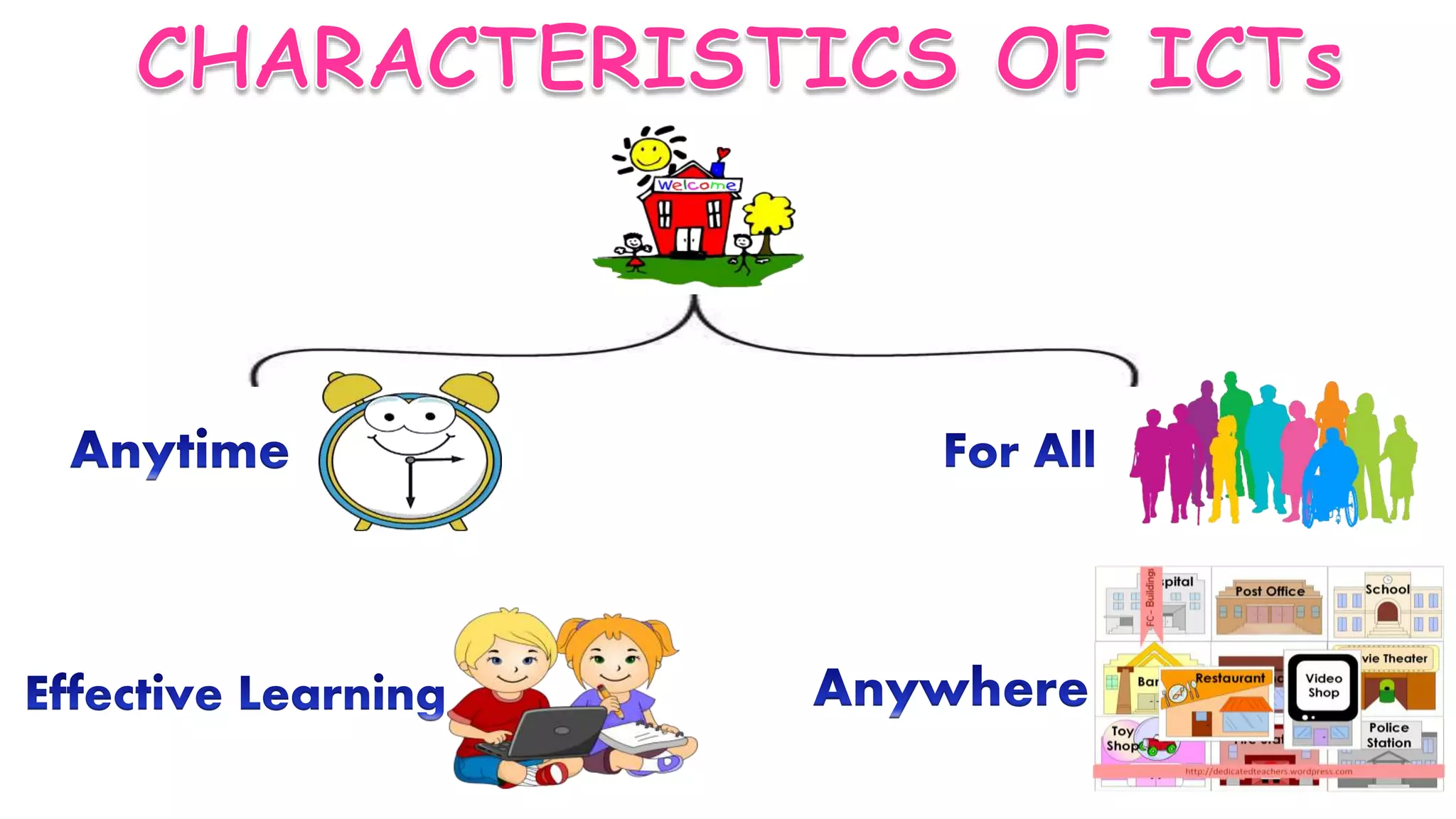
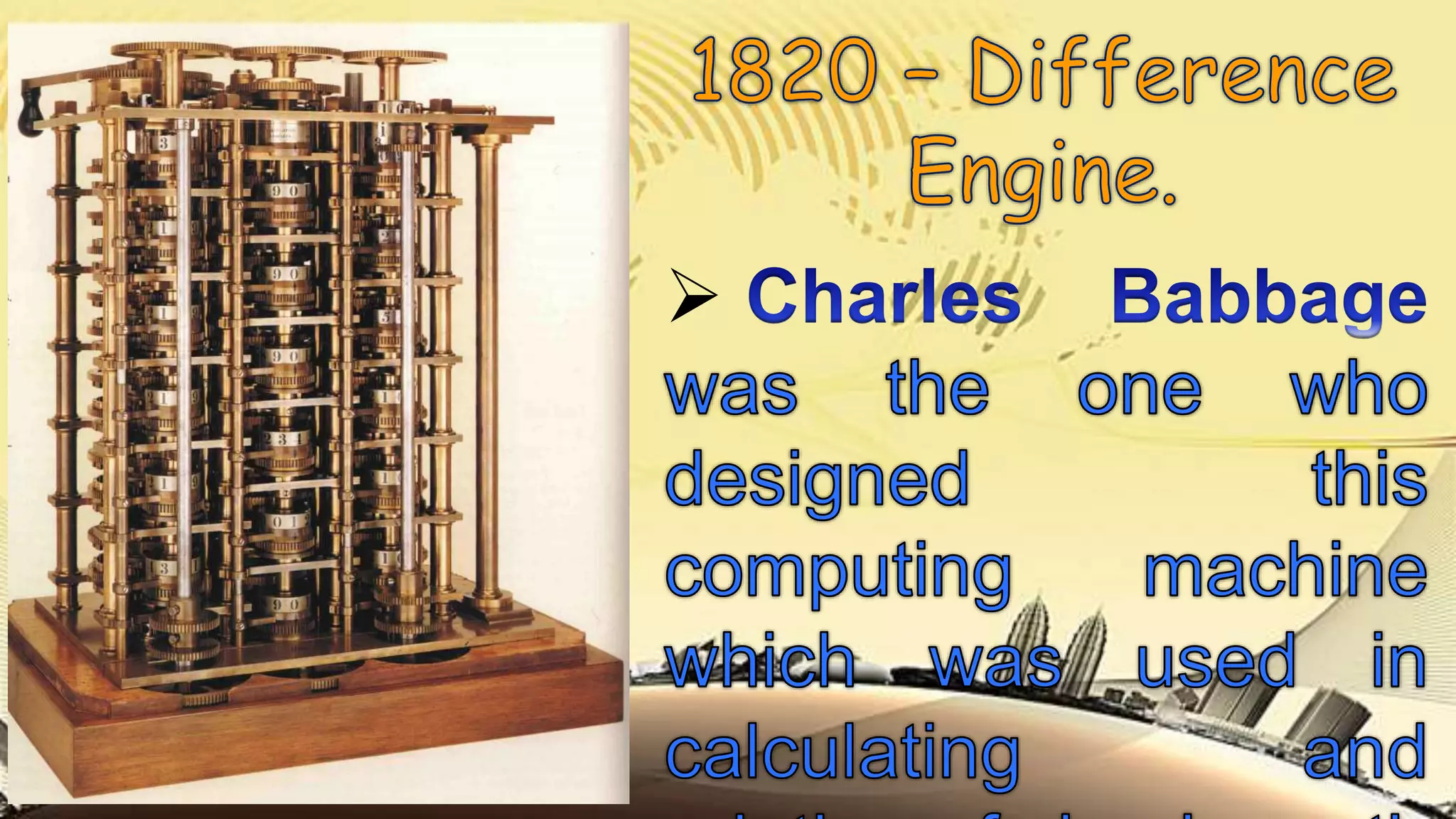
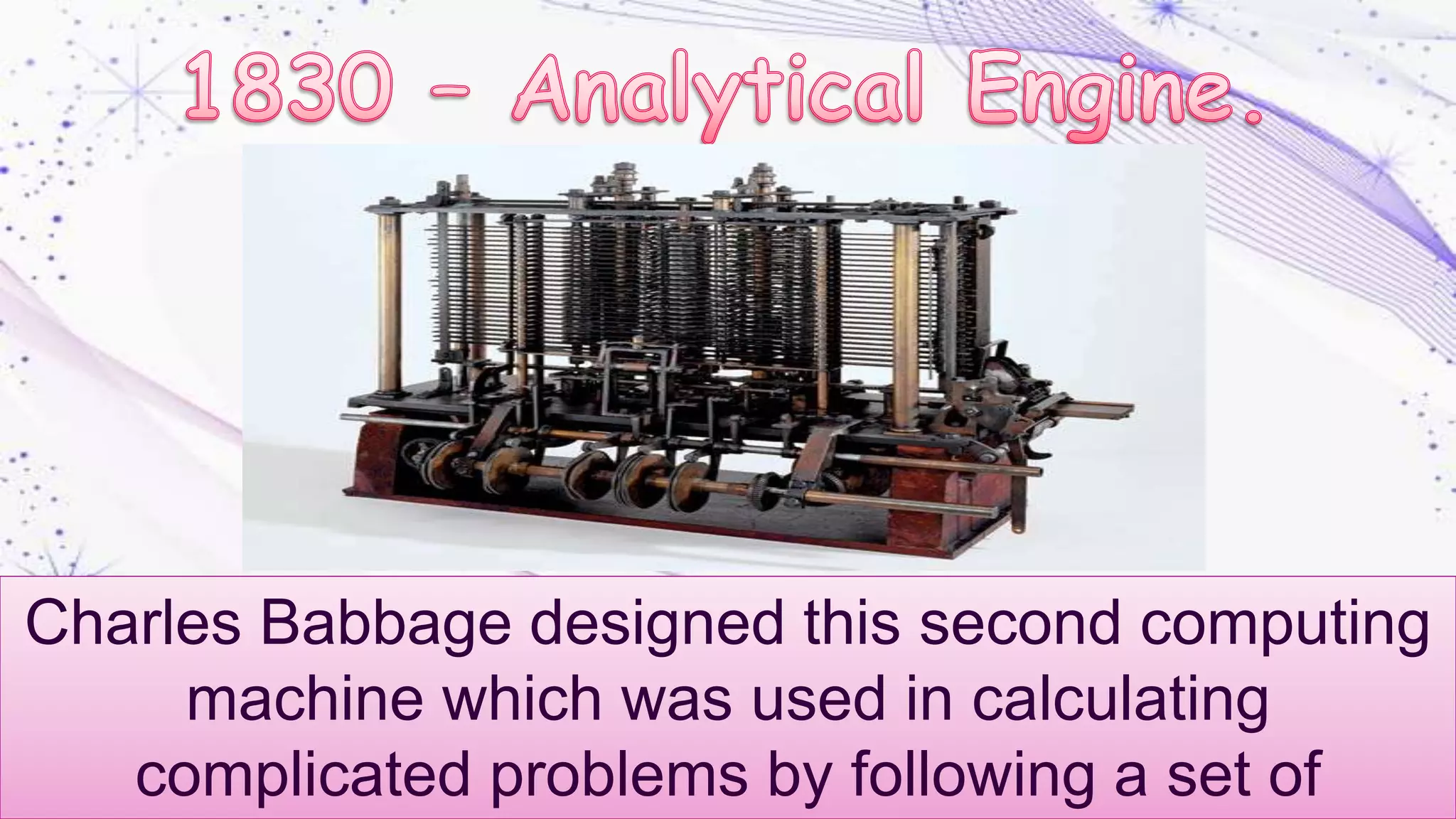
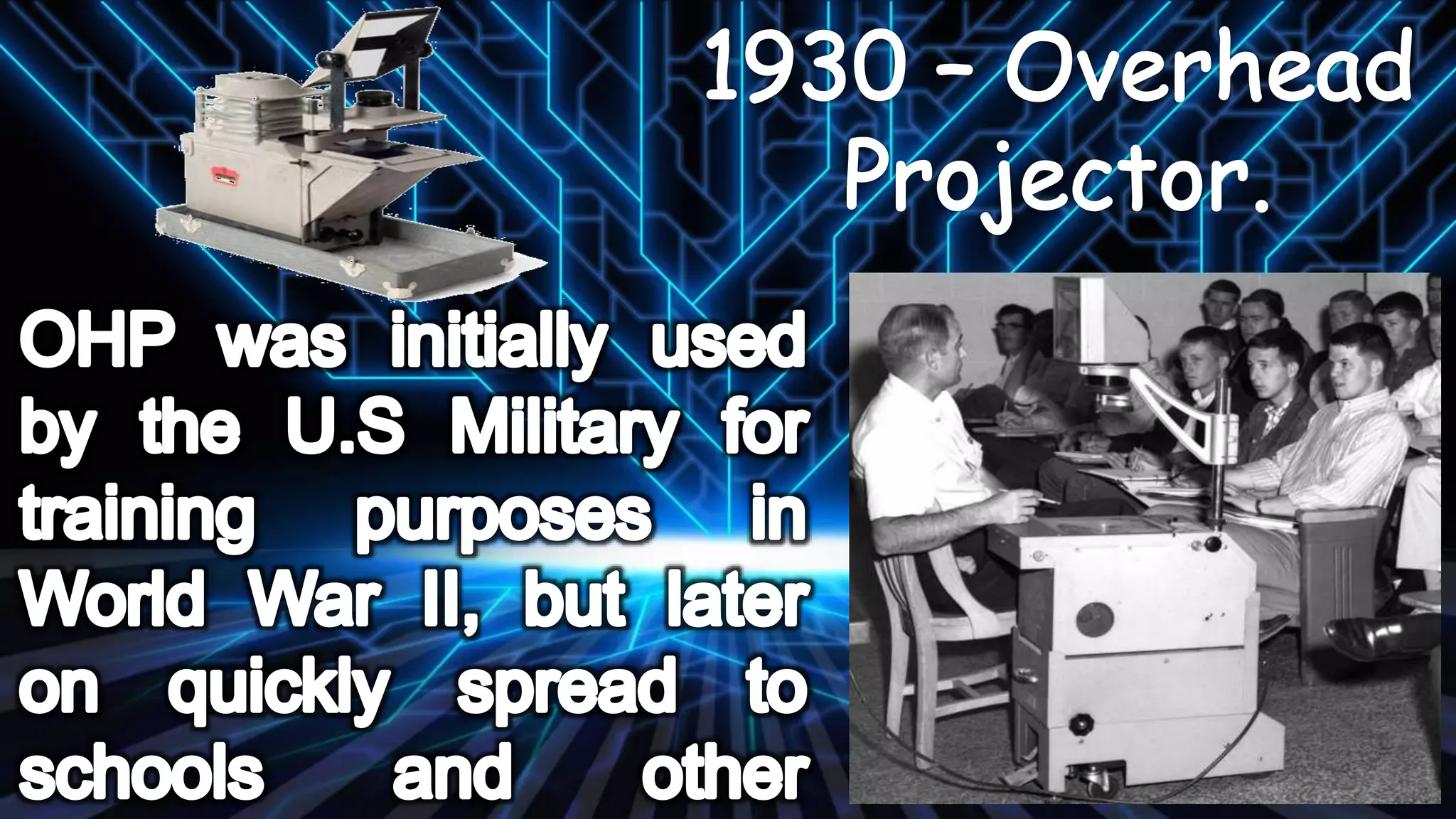
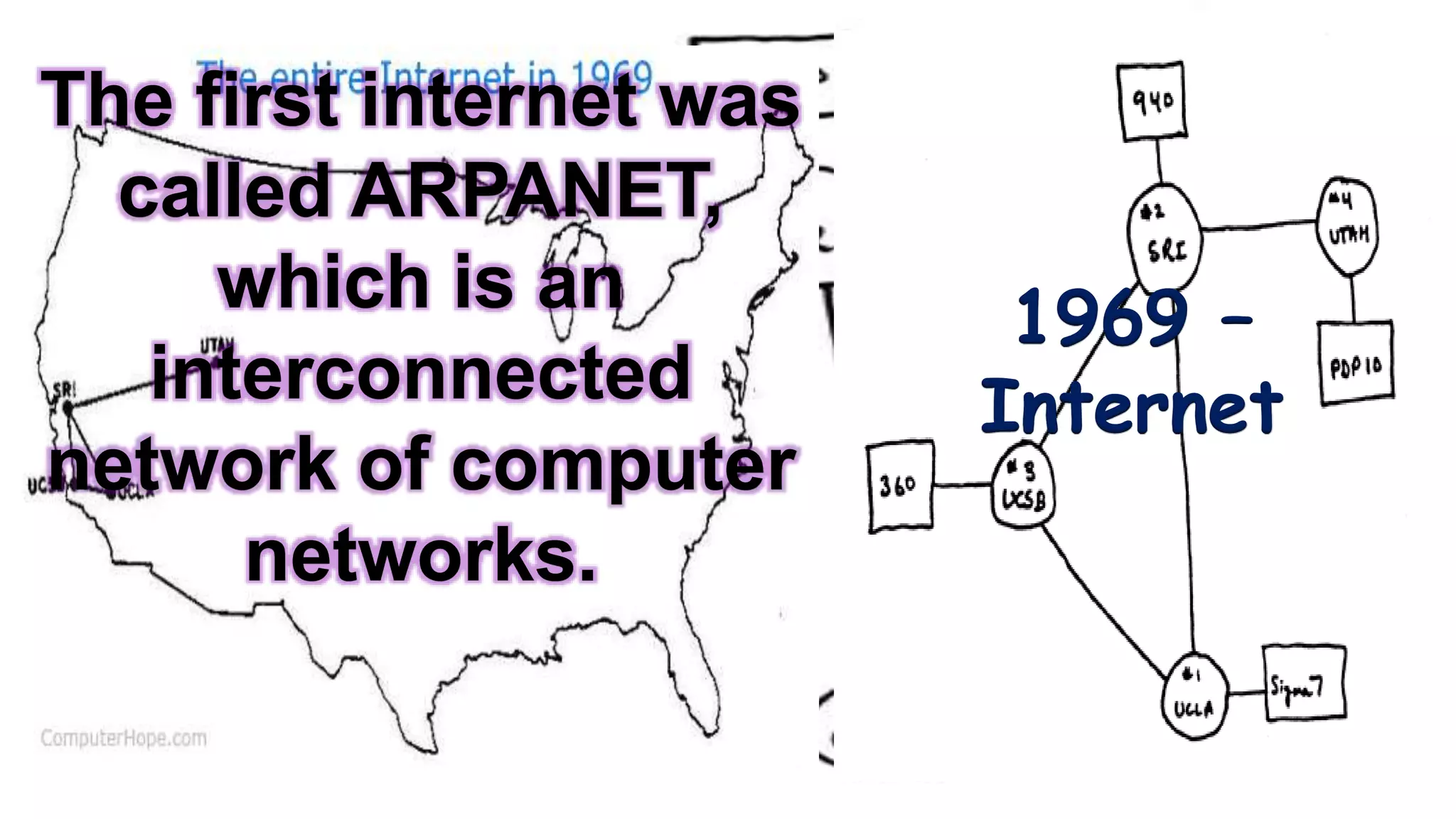
The document discusses the evolution of educational technology from traditional methods to modern digital media, highlighting tools such as radio, television, and computers. It emphasizes the importance of ICT in enhancing educational accessibility and personalized learning experiences. Additionally, it provides historical examples of educational devices and innovations that have shaped teaching and learning over time.