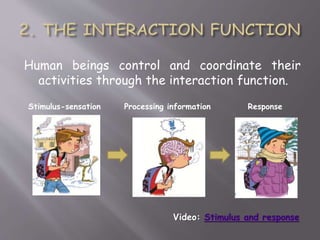
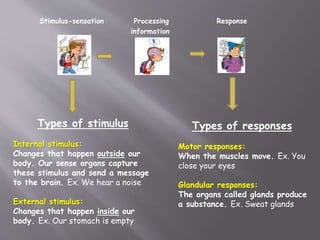
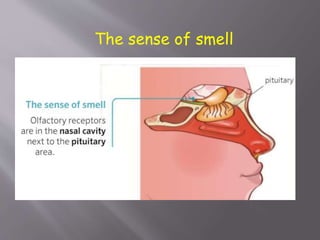
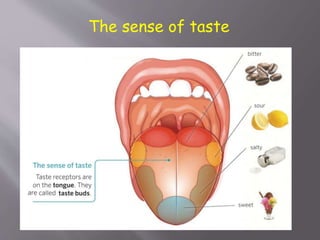
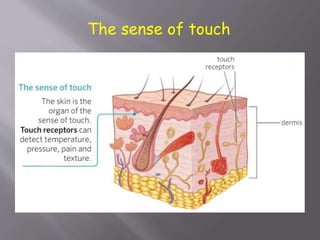
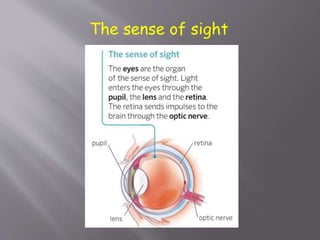
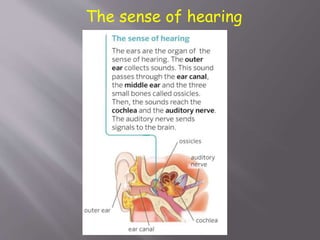
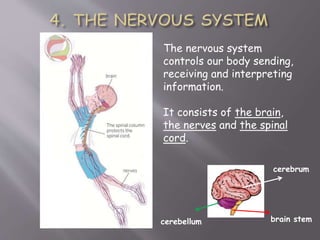
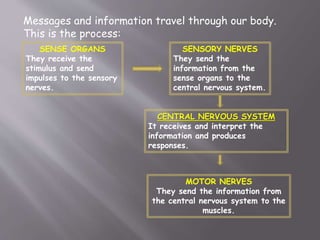
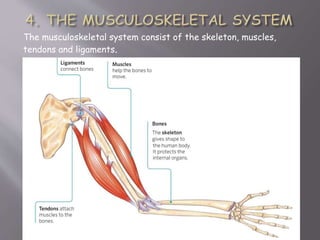
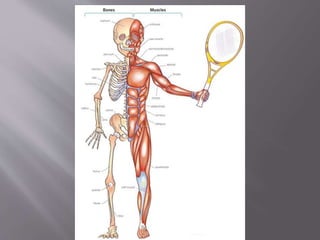
The document discusses the human body and interaction. It explains that humans have three vital functions: nutrition, interaction, and reproduction. For interaction, humans receive stimuli through their five senses of smell, taste, touch, sight, and hearing. The nervous system then controls the body by sending, receiving, and interpreting this sensory information to produce responses. It consists of the brain, nerves, and spinal cord working with sense organs, sensory nerves, and motor nerves to transmit messages and information throughout the body.