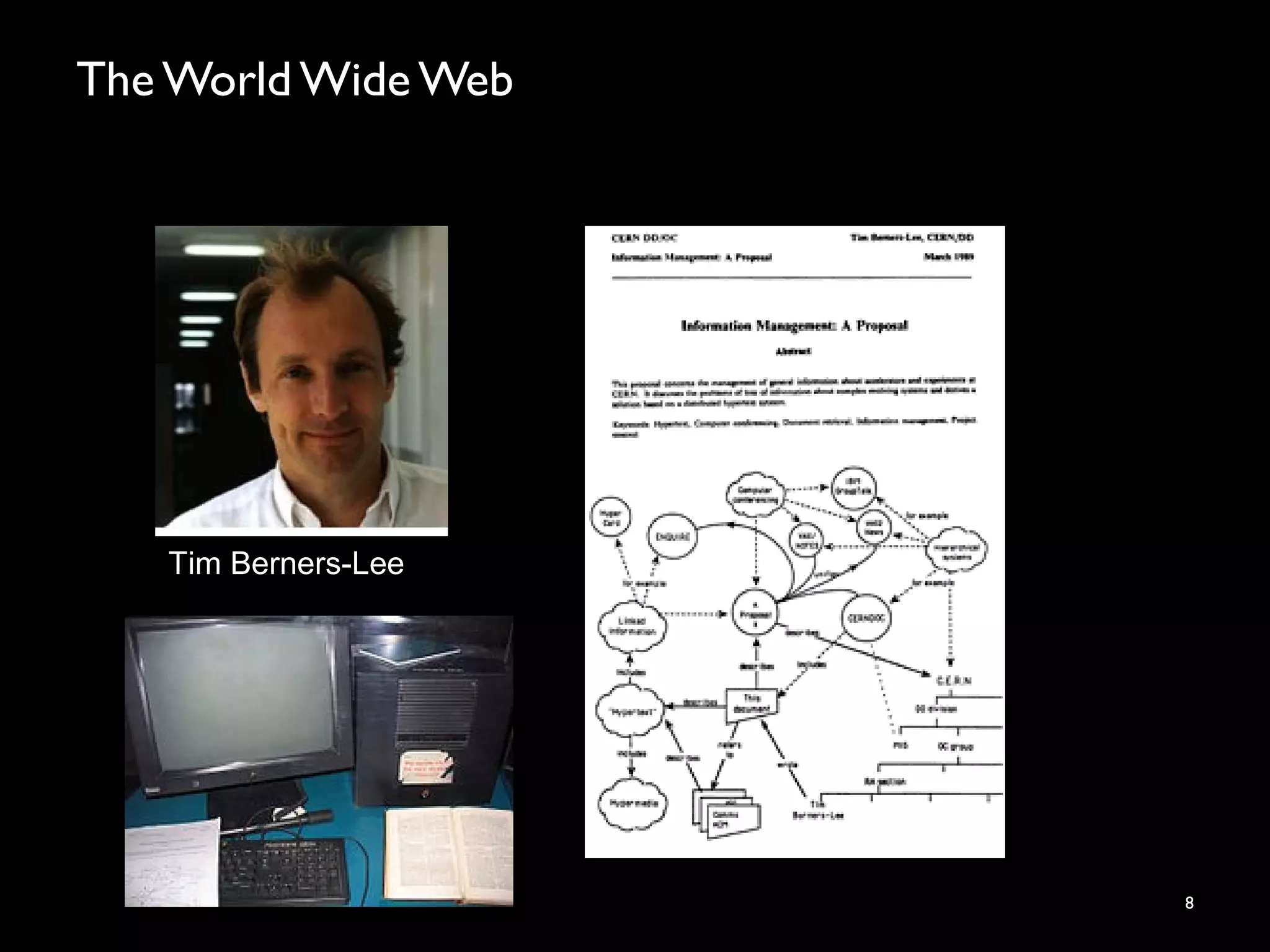
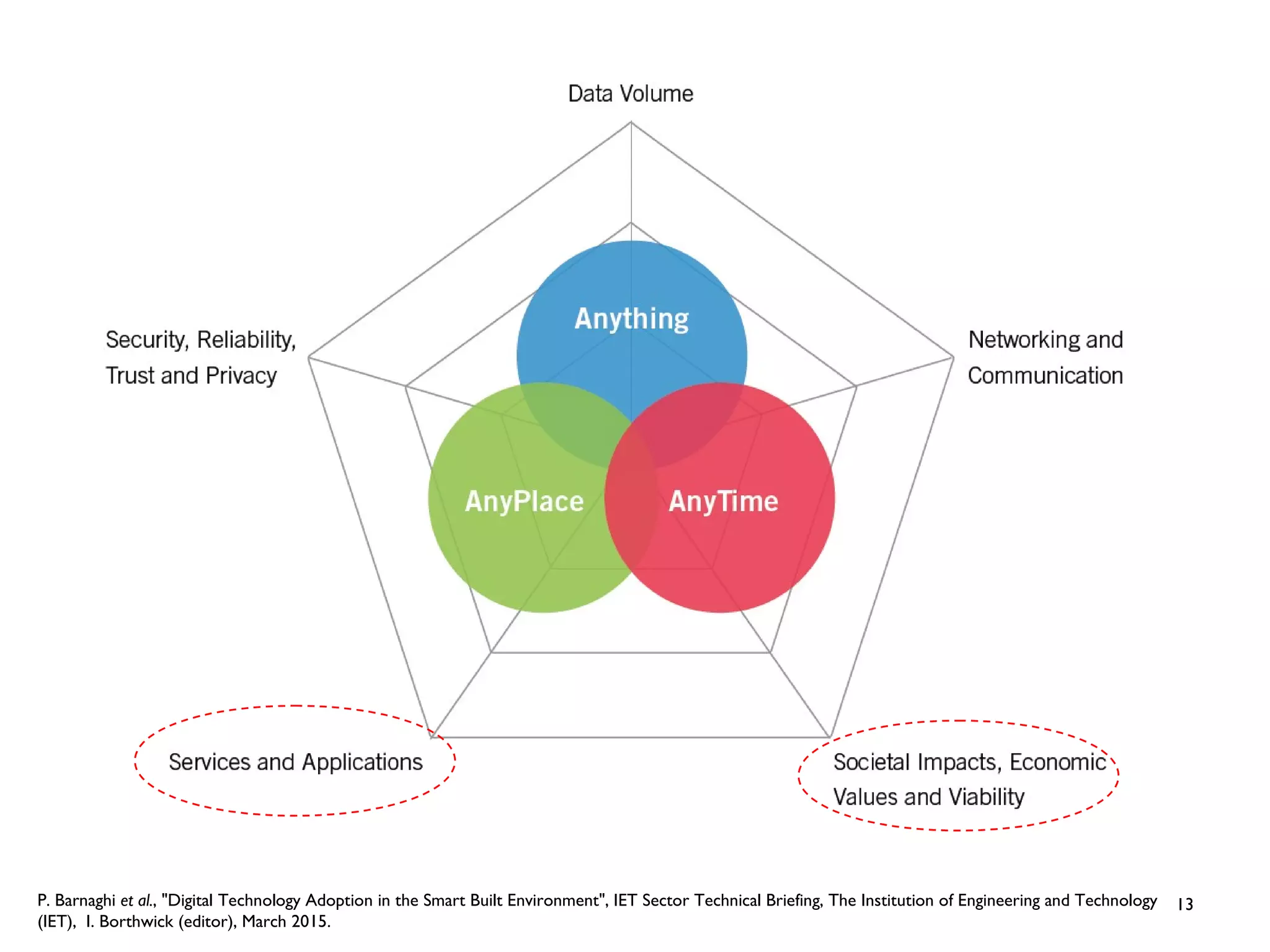
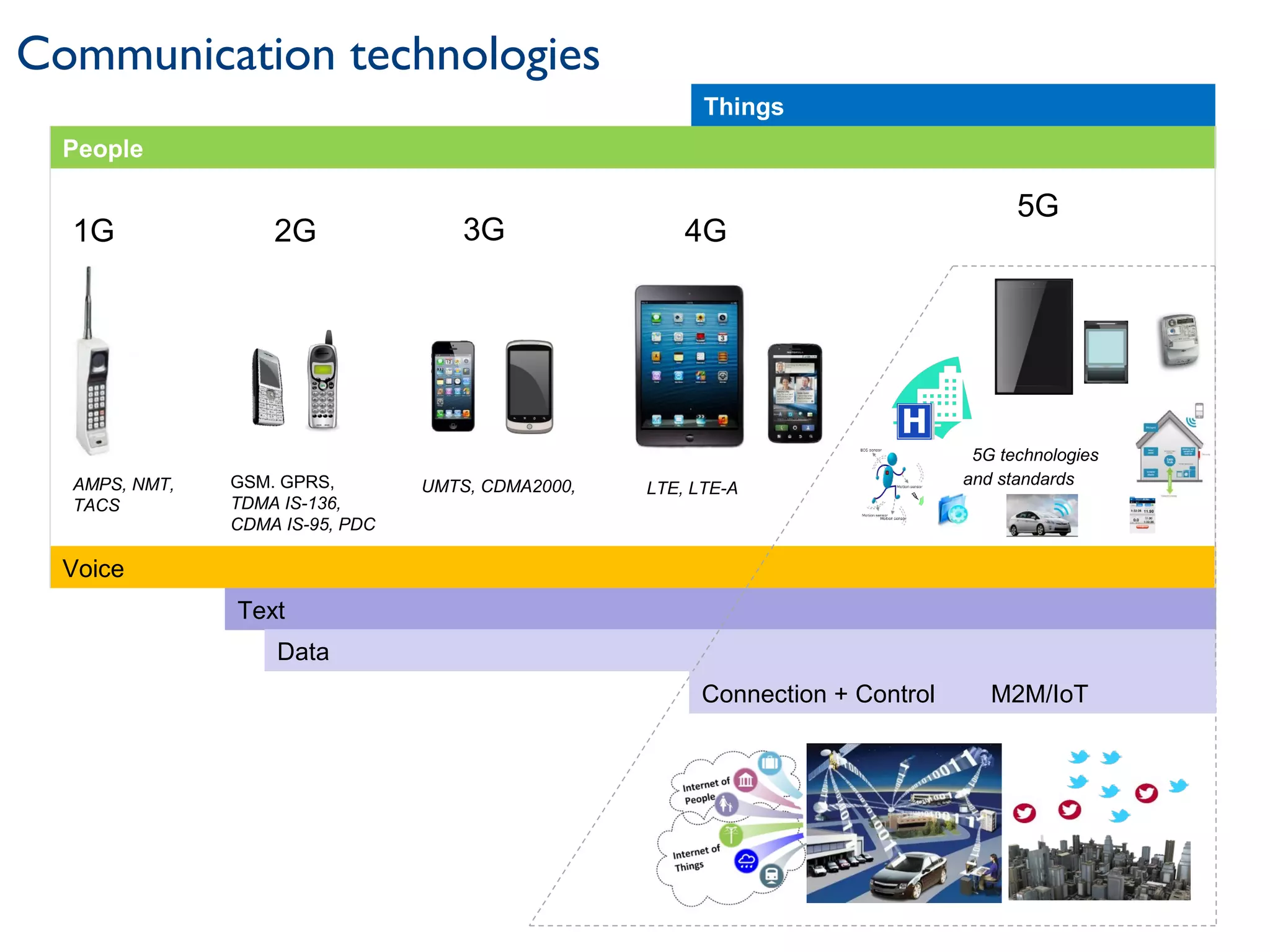
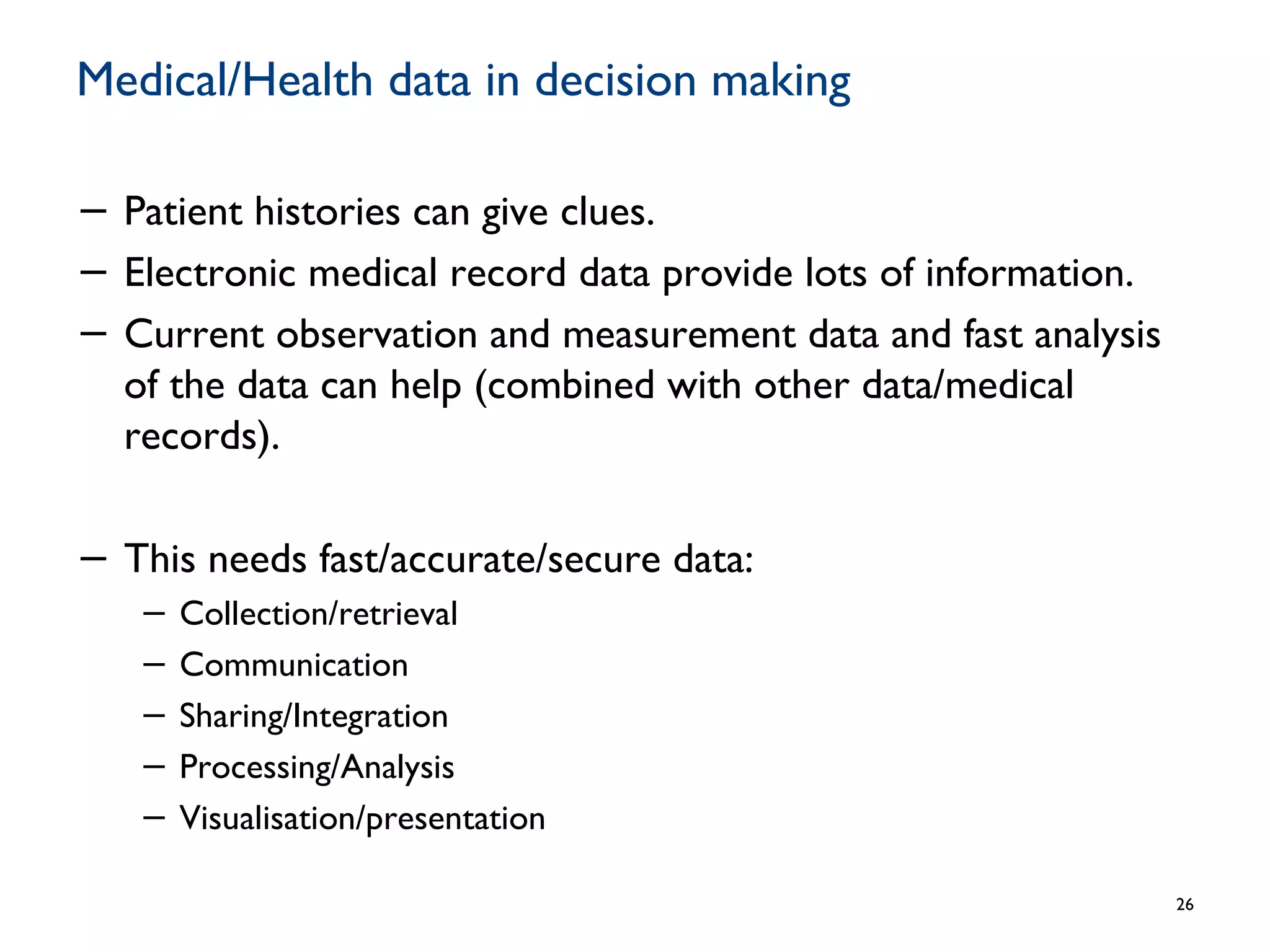
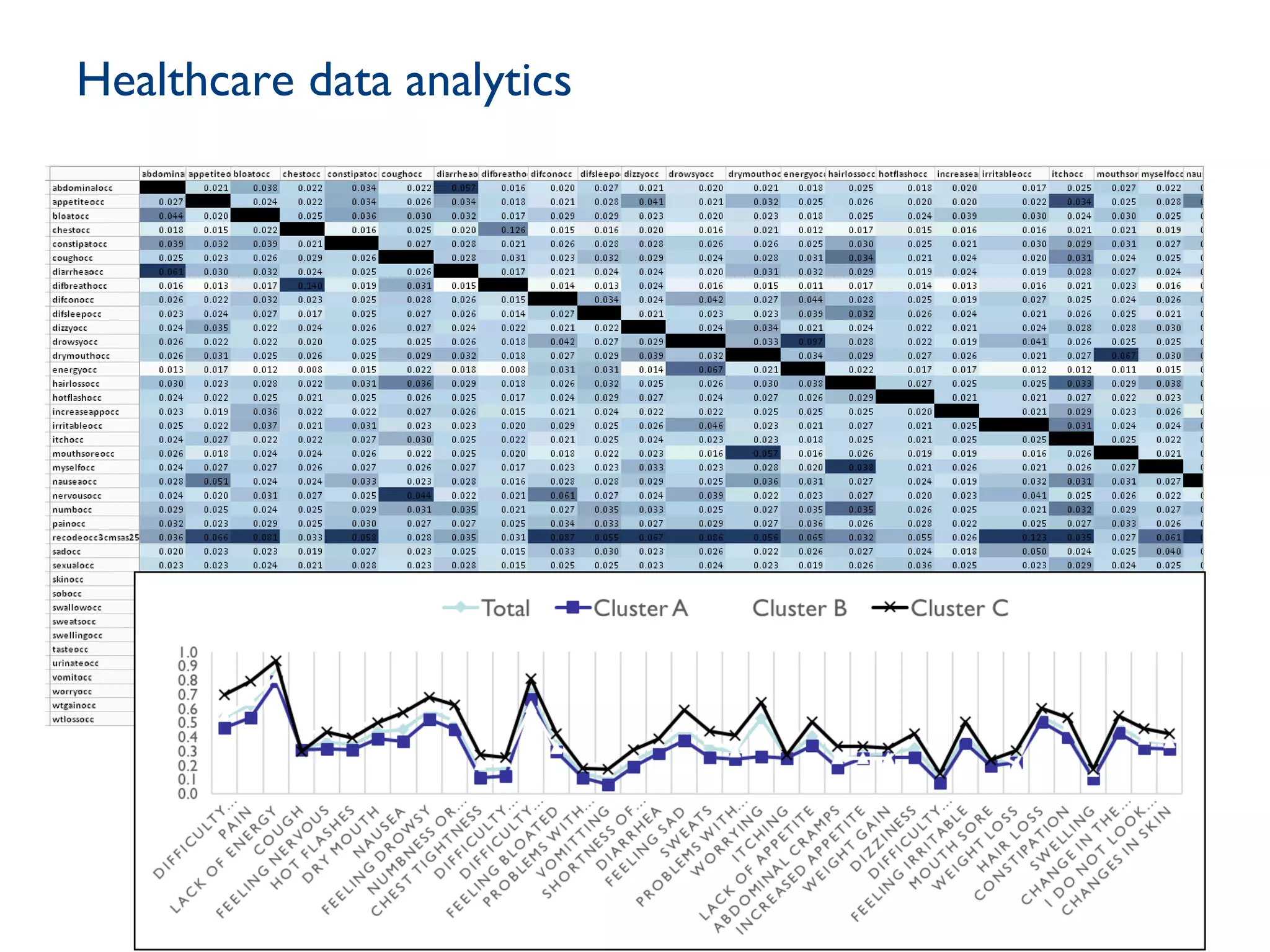
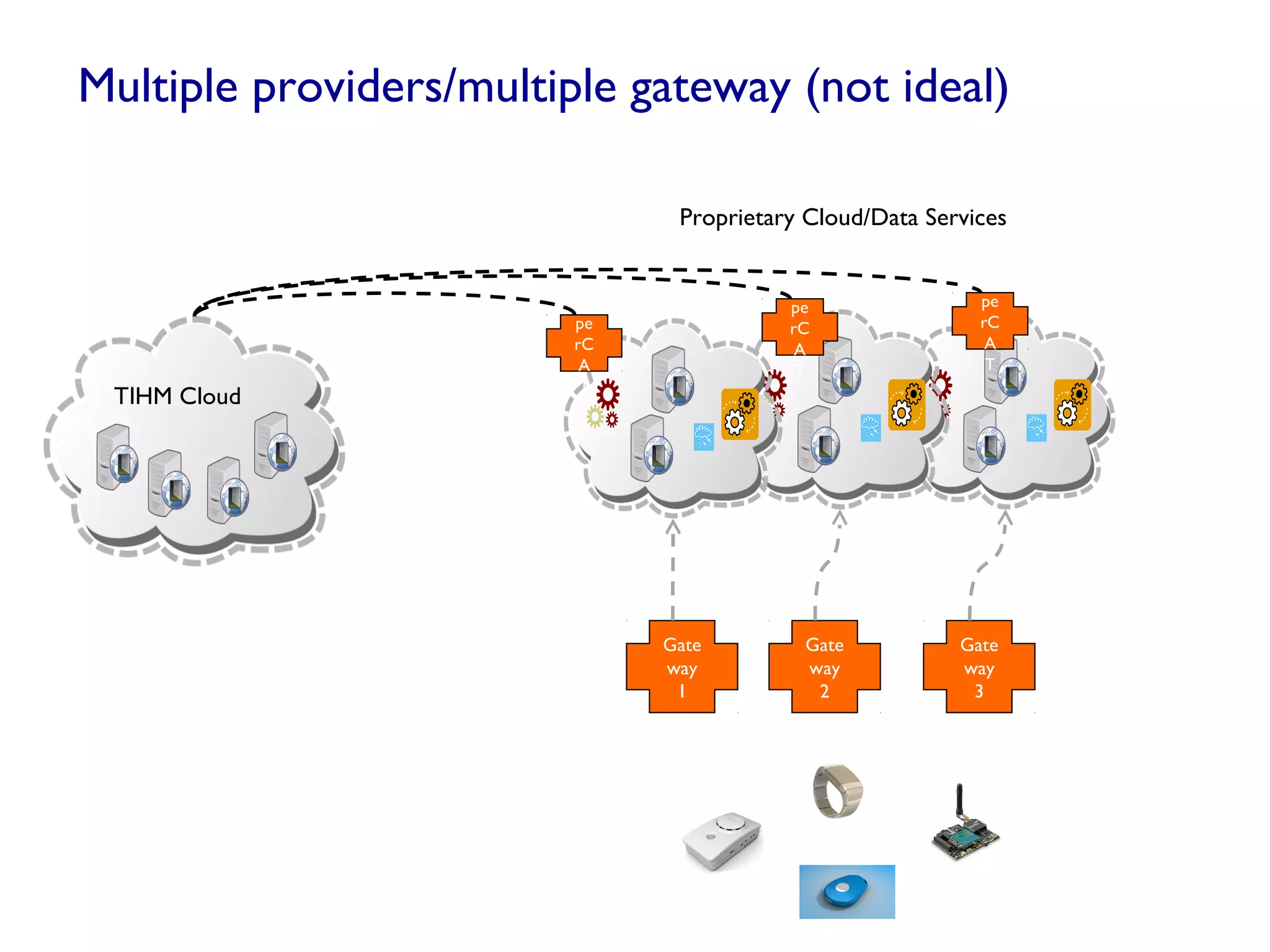
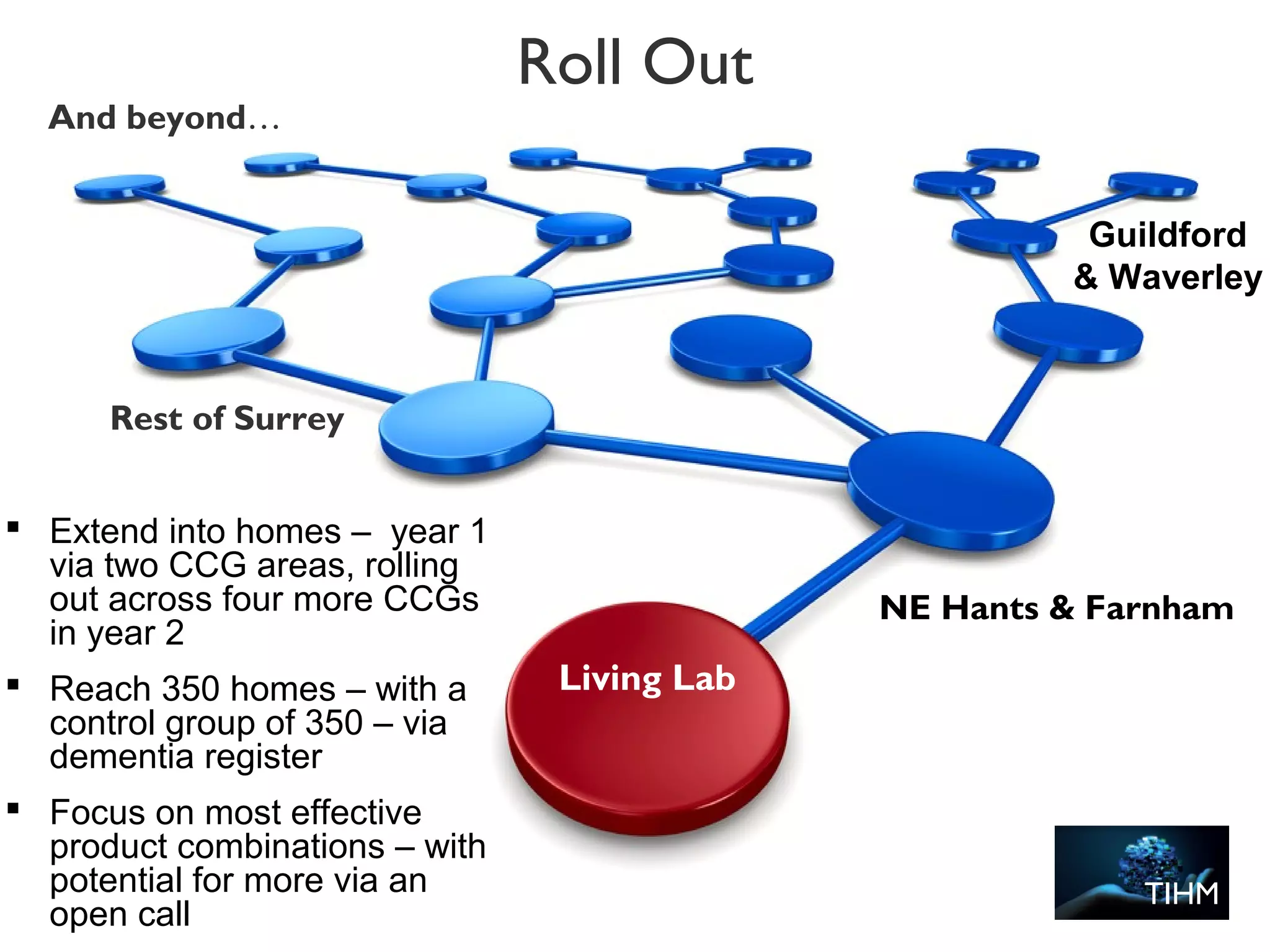
The document discusses the evolution and future prospects of cyber-healthcare, emphasizing the significant increase in computing power and data generation, particularly in the health sector. It highlights the challenges of managing massive amounts of unstructured health data, emphasizes the need for interoperability and machine-interpretable solutions, and outlines potential applications of IoT devices in addressing healthcare issues such as dementia and falls. Overall, it presents a vision of a more connected and data-driven healthcare system that enhances patient care while addressing privacy, security, and reliability concerns.