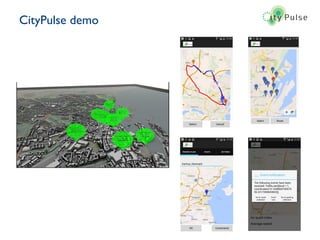
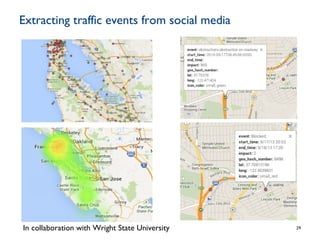
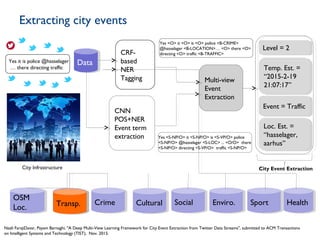
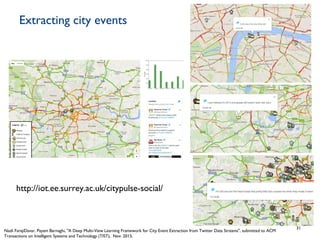
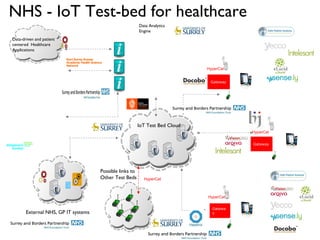
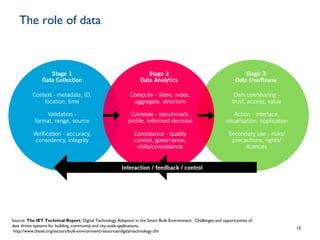
Dr. Payam Barnaghi discusses how cities can become smarter through the use of digital technologies and data. He defines a smart city as one that uses information and communication technologies to improve services, reduce costs and engage citizens. Barnaghi explains that smart cities are made possible by collecting data from sensors, integrating and analyzing that data, and using the insights to provide real-time information and automated services. He provides examples of applications including traffic management, power usage prediction, and healthcare monitoring. Barnaghi emphasizes that technology alone does not make a city smart and that open data, interoperability, and informed citizen participation are also important.



![Smart City
“A smart city uses digital technologies or information and
communication technologies (ICT) to enhance quality and
performance of urban services, to reduce costs and resource
consumption, and to engage more effectively and actively with
its citizens.” [Wikipedia]
5
Is this a good definition?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartcitiesukti-160309212905/85/How-to-make-cities-smarter-5-320.jpg)

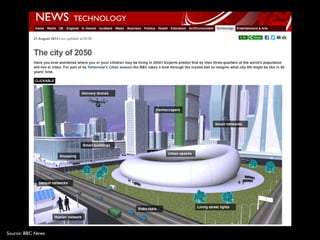









![19
Source: http://robertluisrabello.com/denial/traffic-in-la/#gallery[default]/0/
Source: wikipedia
Back to the Future: 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartcitiesukti-160309212905/85/How-to-make-cities-smarter-19-320.jpg)