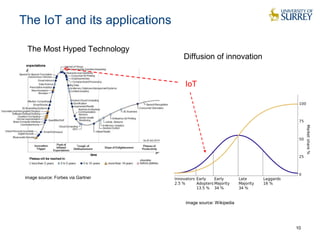
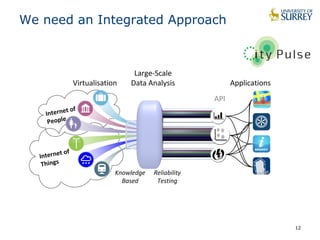
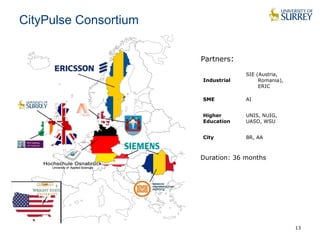
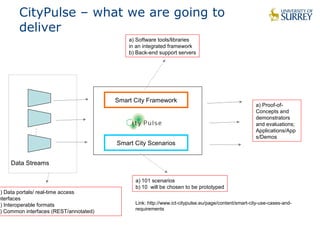
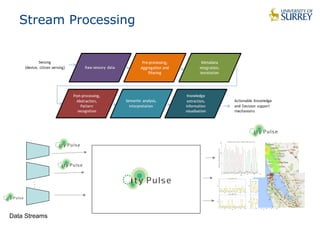
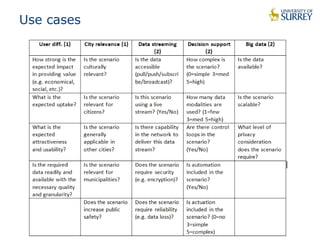
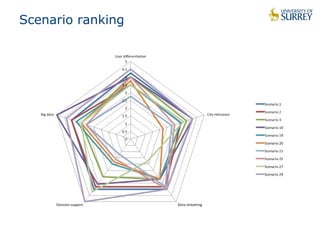
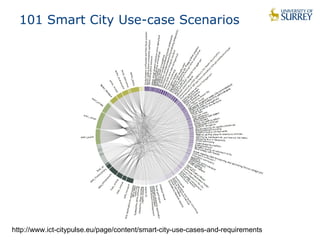
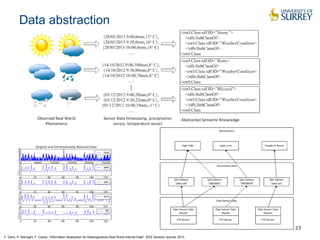
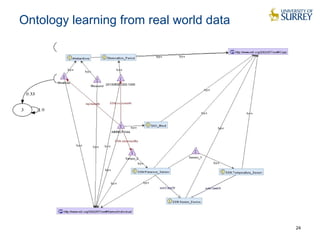
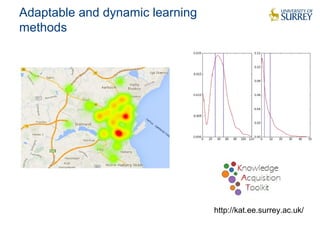
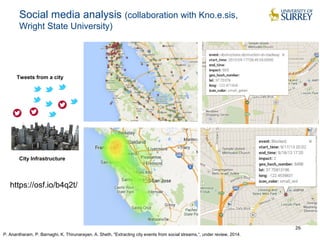
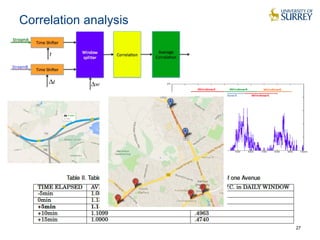
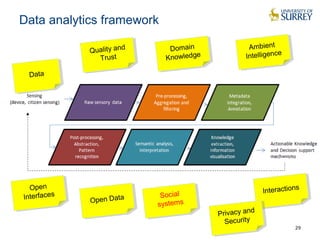
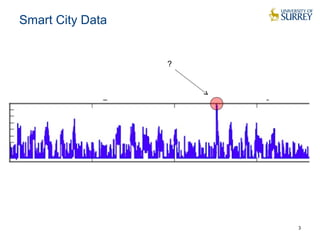
This document discusses the CityPulse project, which aims to develop large-scale data analytics solutions for smart cities. It notes that smart city data is multi-modal, heterogeneous, noisy, incomplete and dynamic. The CityPulse project brings together industry and academic partners to deliver an integrated framework and data processing tools to analyze diverse smart city data streams. It will prototype scenarios like infrastructure monitoring and social media analysis to extract events from cities. The goals are to develop adaptable learning methods and an integrated approach that handles real-world data challenges to provide insights for smart cities.






![Source: http://robertluisrabello.com/denial/traffic-in-la/#gallery[default]/0/ 8
Source: wikipedia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataanalyticstaipeipb-140930080215-phpapp01/85/CityPulse-Large-scale-data-analytics-for-smart-cities-8-320.jpg)