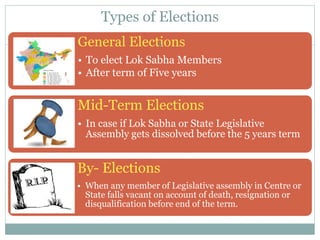
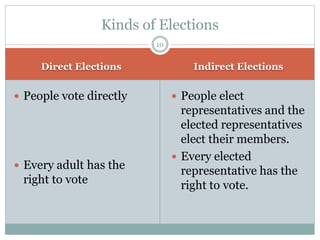
Elections are a process where citizens vote to choose representatives to govern. They allow for indirect participation in democracy. Elections in India include general elections every 5 years to elect members of Lok Sabha, and mid-term or by-elections if seats become vacant. Elections can be direct, with citizens voting directly for representatives, or indirect, with representatives selecting other representatives. The Election Commission of India oversees all elections and ensures they are free and fair. It is an independent body headed by the Chief Election Commissioner.