The document discusses various aspects of negotiation including:
1) Negotiation involves acting to make things change and evolve through exchange, rather than remaining inert.
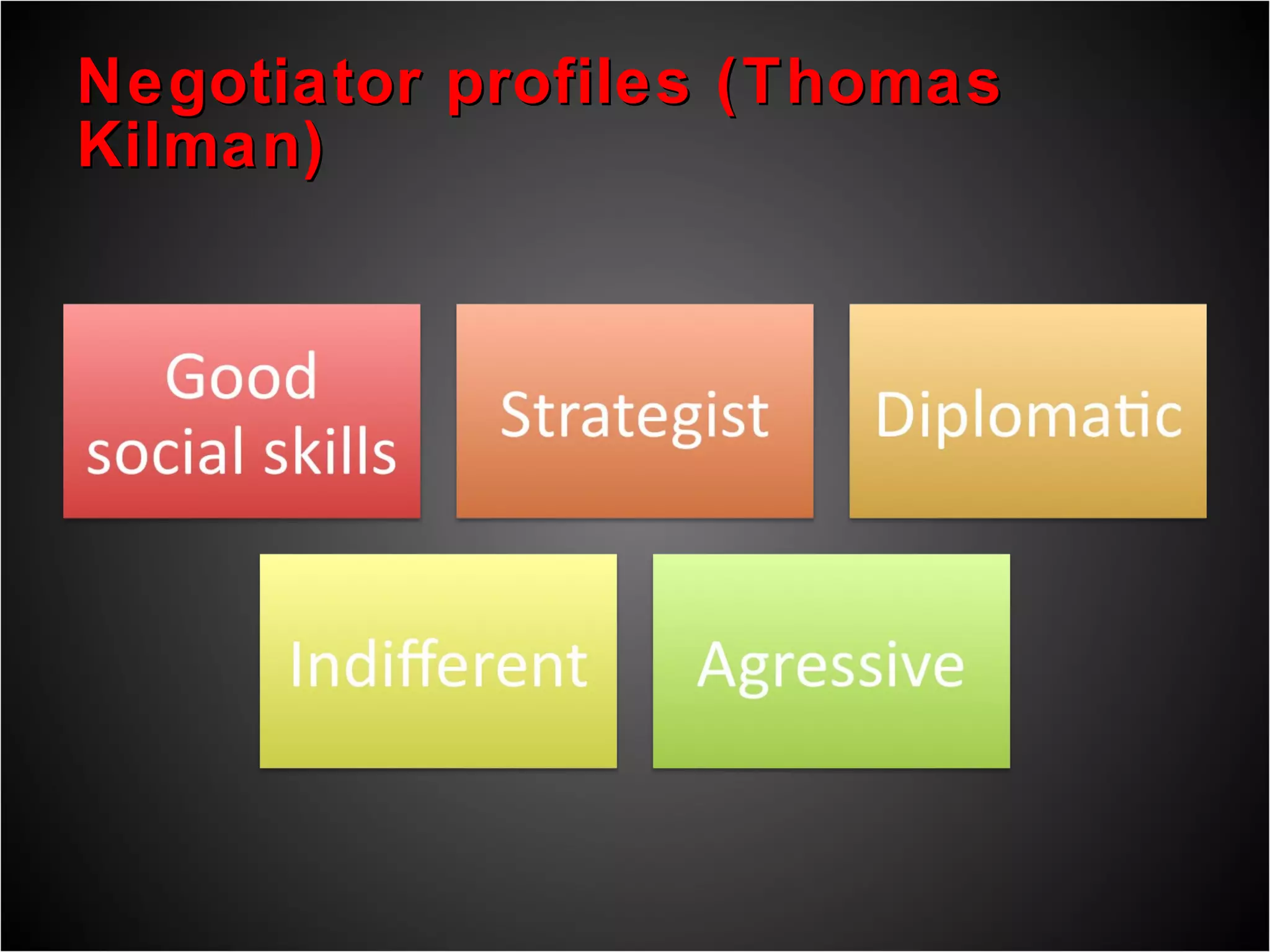
2) There are different approaches to negotiation such as advocating for one's own interests, finding win-win solutions, and collaborating creatively.
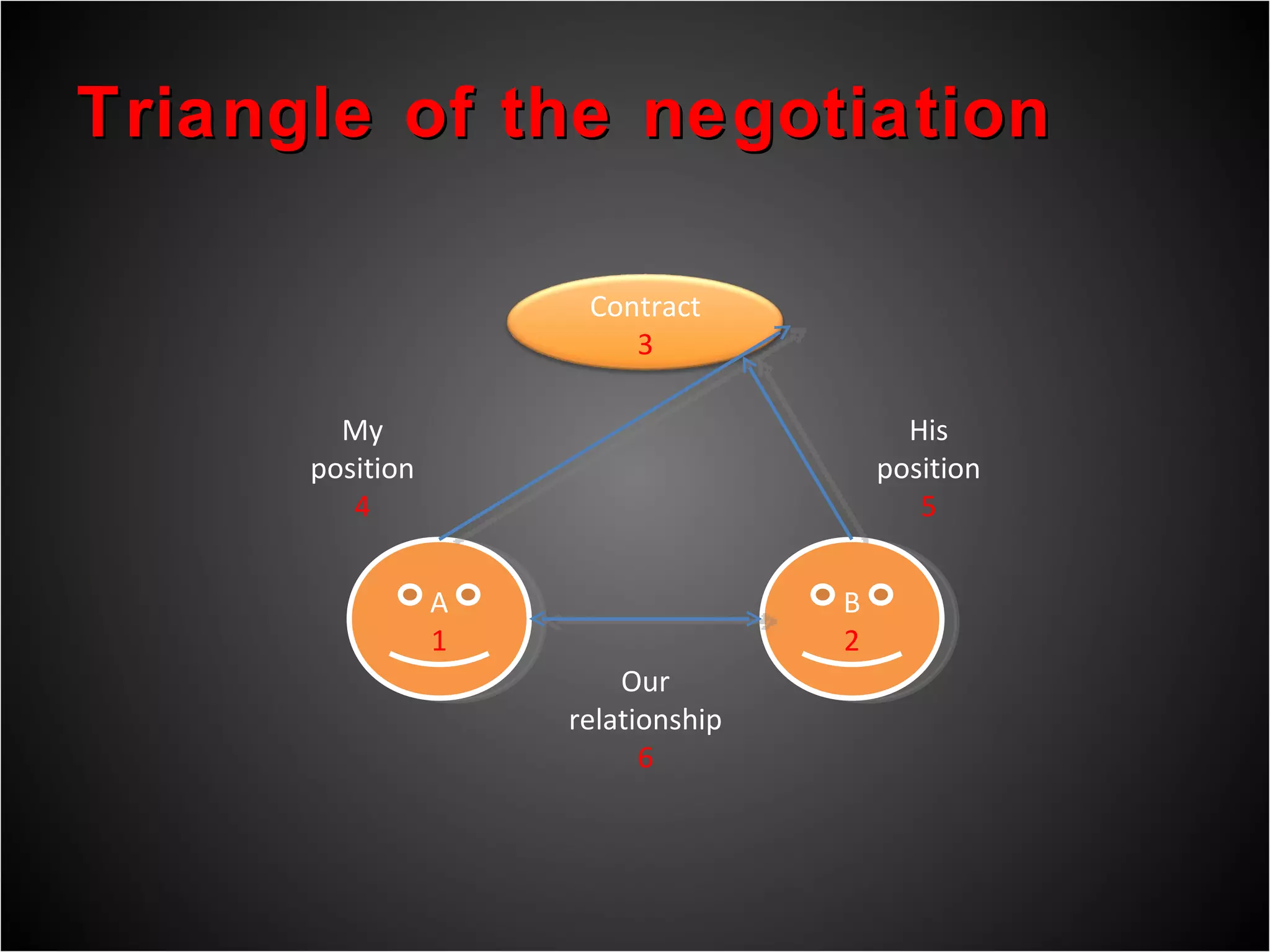
3) Proper preparation, understanding interests rather than positions, and developing solutions through open discussion and compromise are keys to successful negotiations.